8 - ABGs and A-Lines
1/38
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
39 Terms
arterial line (a-line) sites and selection (adults)
advantages of radial artery
easy access
good circulation
low infection risk
arterial line (a-line) sites and selection (adults)
disadvantages of radial artery
risk of radial artery occlusion
must pass Allen’s test
arterial line (a-line) sites and selection (adults)
advantages of femoral artery
large vessel
useful in emergencies
easy access
arterial line (a-line) sites and selection (adults)
disadvantages of femoral artery
high infection risk
risk of pseudo-aneurysm
difficult to monitor for ischemia
arterial line (a-line) sites and selection (adults)
advantages of brachial artery
larger vessel
good for high-flow monitoring
arterial line (a-line) sites and selection (adults)
disadvantages of brachial artery
poor collateral circulation
risk of limb ischemia
arterial line (a-line) sites and selection (adults)
advantages of dorsalis pedis artery
can be used on select patients
arterial line (a-line) sites and selection (adults)
disadvantages of dorsalis pedis artery
weak collateral circulation
hard to palpate
not ideal for critical patients
arterial line (a-line) sites and selection (neonates and pediatrics)
advantages of radial artery
common site for neonates
arterial line (a-line) sites and selection (neonates and pediatrics)
disadvantages of radial artery
Allen’s test must be performed
arterial line (a-line) sites and selection (neonates and pediatrics)
advantages of brachial artery
alternative site in infants
arterial line (a-line) sites and selection (neonates and pediatrics)
disadvantages of brachial artery
risk of poor collateral circulation
arterial line (a-line) sites and selection (neonates and pediatrics)
advantages of umbilical artery
used for NICU patients <7 days old
arterial line (a-line) sites and selection (neonates and pediatrics)
disadvantages of umbilical artery
requires sterile insertion
risk of thrombosis
arterial line (a-line) sites and selection (neonates and pediatrics)
advantages of dorsalis pedis / posterior tibial artery
alternative in older children
arterial line (a-line) sites and selection (neonates and pediatrics)
disadvantages of dorsalis pedis / posterior tibial artery
hard to palpate
special considerations for neonate a-line insertion
heel warmers
increases perfusion before puncture
small needles (25-27G)
reduces trauma and hematoma risk
minimal blood volume withdrawal
risk of vasospasm with frequent arterial sticks
Allen’s test
test that determines if ulnar artery can supply hand if radial artery becomes occluded
prevents hand ischemia and necrosis
must be performed before radial artery catheterization
steps of Allen’s test
occlude radial and ulnar arteries while patient makes a fist
have patient open hand; palm should be pale
release pressure on ulnar artery while still occluding radial artery
observe for hand color return within 5-15 seconds
test results:
positive: normal blood return → safe for cannulation
negative: delayed/absent return → avoid radial a-line
contraindications for arterial sticks
negative Allen’s test
severe coagulation / thrombocytopenia
skin infection / cellulitis
vasopressor-induced vasoconstriction
arterial occlusion / thrombosis
active Raynaud’s / severe peripheral artery disease (PAD)
relative contradictions for ABGs and a-lines
anticoagulation therapy
use small-gauge needle (22-25G) and apply pressure to site for at least 5 minutes post-puncture
severe hypotension/shock
femoral artery better in emergencies
history of vascular surgery/graft in affected limb
edematous extremity
previous failed attempt / multiple punctures in same artery
hazards and complications of ABGs and a-lines
pain
arteriospam
air/blood clot emboli
hematoma
anaphylaxis from anesthetic
hemmorhage
vessel trauma
arterial occlusion
vasovagal response
infection
needle stick (clinician)
capillary blood gas (CBG)
blood gas usually reserved for neonates/pediatrics when arterial access isn’t available or when frequent monitoring is required
limitations
doesn’t accurately reflect PaO2
best used for pH, PCO2, and HCO3- when arteries are unavailable
not reliable in patients with poor perfusion, hypotension, and vasoconstriction
steps for obtaining CBG sample
pre-warm site (heel warmer for 3-5 mins) to increase capillary perfusion
clean area with antiseptic solution
use lancet to make shallow puncture
wipe away first drop to avoid contamination with interstitial fluid
allow blood to flow freely into capillary tube; don’t squeeze too much
cap and mix sample to prevent clotting
apply pressure to puncture site and cover with bandage
indications for a-lines
frequent ABG sampling
continuous BP monitoring
hemodynamic instability
contraindications for a-lines
failed Allen’s test
infection at insertion site
coagulopathy
severe vasoconstriction
a-line insertion techniques
angiocath (over-the-needle catheter)
insert at 30-45° angle
reduce to 10-15° after blood return is seen
Seldinger (wire-guided insertion)
secure cath and connect to transducer
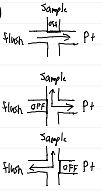
arterial waveform interpretation
normal waveform phases
anacrotic limb
ventricular systole
dicrotic notch
aortic valve closure

arterial waveform interpretation
abnormal waveforms
overdamped
underestimates BP
underdamped
overestimates BP

complications and troubleshooting for ABGs and a-lines
COMPLICATION | CAUSE | MANAGEMENT |
infection | poor sterile technique |
|
thrombosis | clot formation |
|
hematoma | poor pressure application | apply firm pressure for 5-10 minutes |
ischemia | poor collateral circulation | remove line if needed |
pre-analytical errors in ABG sampling
cause of air bubbles
incomplete syringe filling
pre-analytical errors in ABG sampling
air bubbles’ effect on ABG
↓CO2
↑pH
variable O2
pre-analytical errors in ABG sampling
cause of excess heparin
overdilution of sample
pre-analytical errors in ABG sampling
excess heparin’s effect on ABG
↓pH
altered CO2 & O2
pre-analytical errors in ABG sampling
cause of blood metabolism
delayed analysis
pre-analytical errors in ABG sampling
blood metabolism’s effect on ABG
↑CO2
↓pH
↓O2
pre-analytical errors in ABG sampling
cause of venous contamination
poor sampling technique
pre-analytical errors in ABG sampling
venous contamination’s effect on ABG
↓O2 (false hypoxia)
↑CO2
steps for obtaining ABG sample from a-line
verify waveform prior to sampling
turn stopcock off to flush bag, discard waste blood (~2-3 mL)
attach heparinized syringe, draw sample
flush line, ensure waveform normalizes