Lesson 2
1/3
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
4 Terms
VaR or value at risk
VaR(value at risk) - is a way to quantify the risk of potential losses for a firm or an investment.
Invented after crash of 1987
units of $ for a given probability or time horizon
1% one-year VaR of $10 million - 1% that a portfolio wil loose $10 million in a year
Stress Test
Stress Testing - method used to test resilienace of institutons and companies to possible financial crisis (banks)
used to determine portfolio risks
helps to asses the adequacy of assets
can use hypothetical scenarios
response to 2008 crisis, 2010 Dodd-Frank Act
as a firm you can demand info from other firms
S&P 500
Market Capitalization (or cap) - the total market value of a company’s outsanding shares of stock
Market Cap = Current Share Price * Total Number of Shares Outstanding
S&P 500 - market-capitalization-weighted index of 500 leading publicly traded companies in the US
Companies are from the US
at least 20$ billion dollars cap
public float of at leat 50 % shares
positive earnings
has been publicy traded for 12 months
Limitations of S&P 500 - when stocks in the index become overvalued the stock inflates the overall value or price of the index if it has heavy weighting
The larger the market weight of a compnay the more imact each 1% of change in a stcok’s price will have on the index
\frac{\text{market cap of one company}}{\text{total SnP cap}} *100
Apple compared to S&P 500
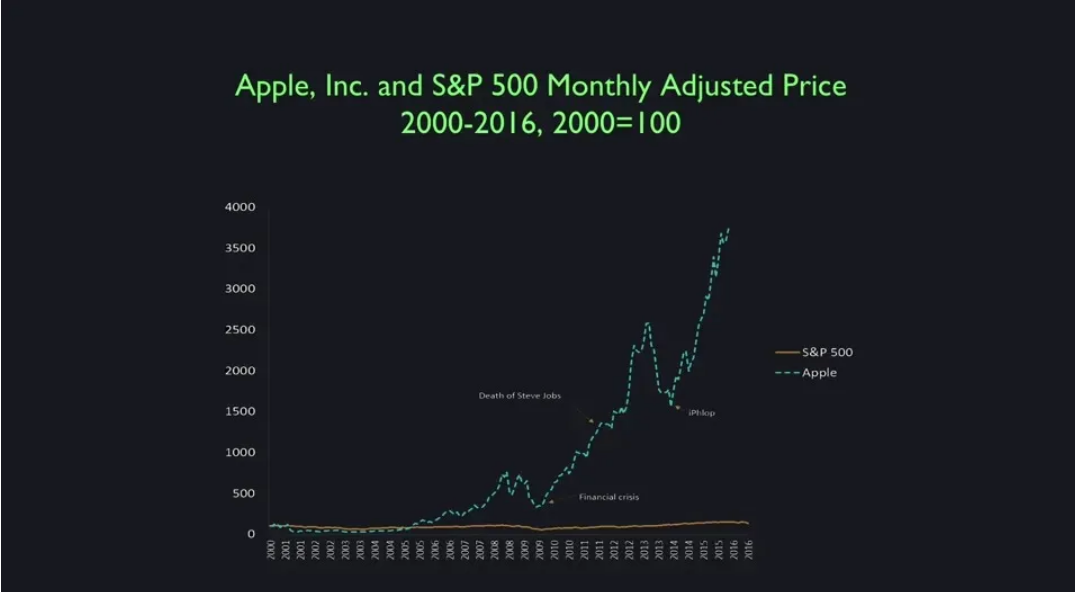
Beta
Is a measure of a stock’s volatility in relation to the overall market
Volatility - statistical measure of the dispersion of returns for a given security or market index over a specific period of time. The higher the riskier the security is
HOW GREATLY AN ASSET’S PRICE SWINGS AROUND THE MEAN PRICE
Volatility = σ\sqrt{T}
where:
σ = standard deviation of returns
T = number of periods in the time horizon
📏
1.0 - a stock that swings more than a market
like elasticity