Colligative Properties
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
11 Terms
What are Colligative Properties
Properties that depend on the number of particles (ions) present rather than on the size, mass, or other characteristics
Depend on the concentration of the solute
DOES NOT depend on identity of the solute (What the Solute is)
The effect the # of Ions/particles on Colligative Properties
The more ions or particles, the greater the impact it will have on colligative properties
The Three Colligative Properties
Vapor Pressure Lowering
Boiling Point Elevation
Freezing Point Depression
Vapor Pressure Lowering
Vapor pressure is a measure of how easily molecules can go from liquid to gas (vapor)
Electrolytes can significantly affect vapor pressure
An aqueous solution with ions is an electrolyte and can conduct electricity
Strong electrolytes contain many ions
Weak electrolytes contain few ions
Ionic compounds and Acids will form electrolytes.
Electrolytes will form __ when dissolved
Electrolytes will form ions when dissolved
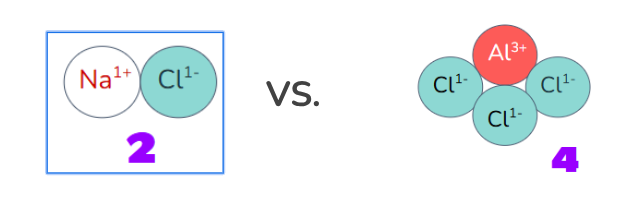
NaCl → Na+ + Cl-
This results in 2 “particles” in the solution instead of only 1.
Water molecules are “______” and ___ ___ to escape as gases
Water molecules are “occupy” and less free to escape as gases
Solute between molecules in a liquid keeps particles from escaping. This results in lower vapor pressure.
More particles dissolved in solution result in a larger effect
Example of Vapor Pressure Lowering (Not a Flashcard):
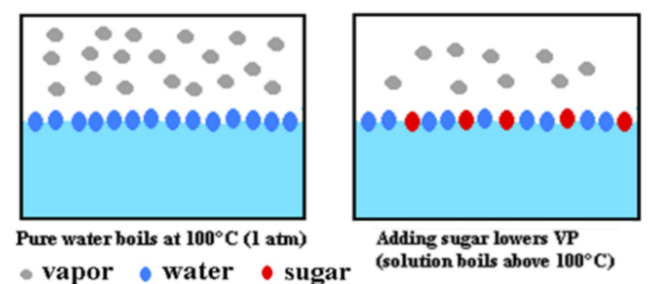
Adding more sugar means that less water molecules can escape from the surface so it will have a lower vapor pressure.
Boiling Point Elevation
Boiling point is determined by vapor pressure.
Lower vapor pressures require higher boiling points.
More solute = lower VP → higher BP
The boiling point of water is 100 oC.
The boiling point of salt water is above 100 oC.
Salt dissolved in water, resulting in a lower vapor pressure.
The Affect of adding Solute on a boiling point (Not a Flashcard):
The solute causes a lower vapor pressure which means the solution must be brought to a higher temperature in order for it to boil.
Freezing Point Depression
Solids form when molecules slow their movement and form an orderly pattern.
Dissolved solute particles break up the orderly pattern which results in a lower freezing point.
Water freezes at 0 oC.
Salt water freezes below 0 oC.
The degree of depression depends on how much solute is dissolved.
Example of Freezing Point Depression
Adding solute disrupts the attraction between the water particles and prevents them from freezing until the solute moves out of the way.