Biology Topic 2: Organisation
1/26
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
What is a tissue?
A group of specialized cells with a similar structure and function.
Give an example of an organ system and its function.
The digestive system, which breaks down food into soluble molecules for absorption.
Explain the relationship between cells, tissues, organs, and organ systems. (3 marks)
Cells form tissues (specialized groups of cells).
Tissues form organs (combinations of tissues for specific functions).
Organs form organ systems (groups of organs working together).
What is the role of bile in digestion?
Neutralizes stomach acid and emulsifies fats to increase surface area for lipase action.
Describe the function of enzymes in digestion.
Enzymes act as biological catalysts, breaking down large, insoluble molecules into smaller, soluble ones for absorption.
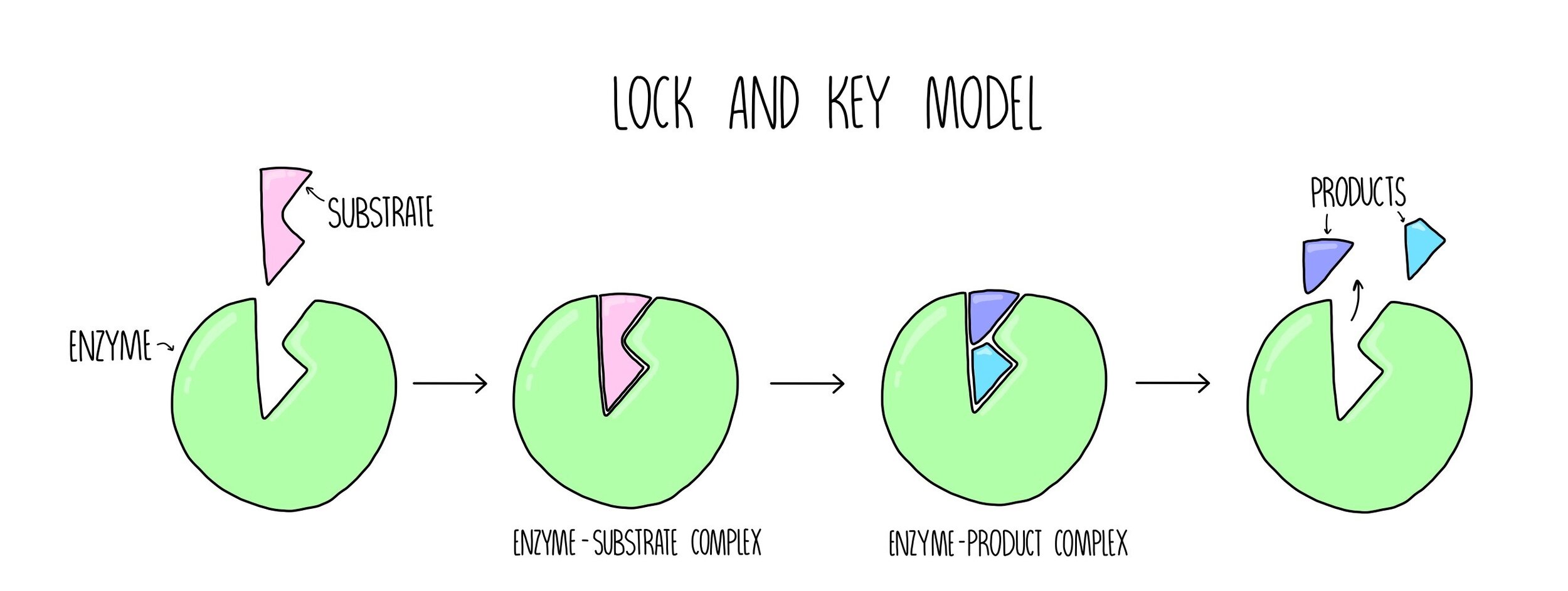
Explain the lock-and-key hypothesis for enzyme activity. (3 marks)
The substrate fits the enzyme's active site (like a key fits a lock).
This forms an enzyme-substrate complex.
The enzyme catalyzes the reaction, breaking down the substrate into products.
Why does the left ventricle have a thicker wall than the right?
It pumps blood around the entire body, requiring more force than the right, which pumps only to the lungs.
What is the role of the coronary arteries?
They supply the heart muscle with oxygenated blood.
Describe how the heart ensures blood flows in one direction. (4 marks)
Blood enters the atria and flows into the ventricles as valves open.
Ventricles contract, pushing blood into the arteries.
Valves close to prevent backflow.
The heart's structure ensures separation of oxygenated and deoxygenated blood.

What is the function of red blood cells?
Transport oxygen from the lungs to body tissues using haemoglobin.
Compare arteries, veins, and capillaries.
Arteries: Thick walls, narrow lumen, high pressure.
Veins: Thin walls, wide lumen, valves to prevent backflow.
Capillaries: One-cell-thick walls for diffusion.
Explain how the structure of red blood cells helps their function. (3 marks)
Biconcave shape increases surface area for oxygen diffusion.
No nucleus creates more space for haemoglobin.
Flexible to move through narrow capillaries.
What causes coronary heart disease?
Fatty deposits block coronary arteries, reducing oxygen supply to the heart.
List two treatments for coronary heart disease and a disadvantage of each.
Stents: Effective but risk of infection or thrombosis.
Statins: Reduce cholesterol but must be taken continuously and have side effects.
Evaluate the use of biological and mechanical valves for heart conditions. (6 marks)
Biological valves: Work well but last only 12–15 years.
Mechanical valves: Durable but require lifelong medication to prevent clotting.
Conclusion: Choose based on patient’s age and medical history.
What adaptations make alveoli efficient for gas exchange?
Large surface area.
Thin walls for a short diffusion pathway.
Rich blood supply to maintain a concentration gradient.
Explain what happens during inhalation.
The diaphragm contracts and flattens.
The ribcage moves up and out.
Thoracic volume increases, decreasing pressure, drawing air into the lungs.
How does smoking affect the lungs? (3 marks)
Damages alveoli walls, reducing surface area for gas exchange.
Leads to diseases like emphysema.
Irritates airways, causing mucus buildup and reducing airflow.
What is a non-communicable disease?
A disease that cannot be spread between people, such as coronary heart disease or type 2 diabetes.
Give two examples of how lifestyle choices can increase the risk of non-communicable diseases.
Poor diet can lead to obesity and type 2 diabetes.
Smoking increases the risk of lung cancer and cardiovascular disease.
Explain the link between obesity and type 2 diabetes. (3 marks)
Excess fat affects metabolism.
Fat molecules reduce the efficiency of insulin.
This leads to high blood sugar levels.
What is the difference between benign and malignant tumors?
Benign: Non-cancerous, do not spread.
Malignant: Cancerous, invade other tissues and form secondary tumors.
Name two lifestyle factors that increase cancer risk.
Smoking and exposure to UV radiation.
How does a malignant tumor spread? (2 marks)
Cancer cells break off the tumor, travel through the bloodstream or lymphatic system, and form secondary tumors in other organs.
What is the function of xylem?
Transports water and minerals from the roots to the leaves via the transpiration stream.
How are phloem and xylem different in their function?
Phloem: Transports food substances in both directions (translocation).
Xylem: Transports water/minerals upwards only.
Explain how guard cells control water loss in plants. (3 marks)
Guard cells swell when water is abundant, opening stomata for gas exchange.
When water is scarce, guard cells shrink, closing stomata to reduce water loss.
This helps maintain the plant’s water balance.