Belted Galloway Management Lab Practical
1/143
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
144 Terms
Where did the Belted Galloway breed originate?
southwestern Scotland
The Belted Galloway breed likely resulted from crossing which two breeds?
Galloway cattle and Dutch cattle
Are belties polled?
yes
What does polled mean?
no horns
List the three colors for belties.
black
red
dun (brown)
(sub = silver dun)
In order to properly be registered, cattle must be "properly marked." What does "properly marked" mean for Belties?
Solid-colored with continuous, uninterrupted, white belt around/encircling mid section of body, but may have white feet below dewclaws or fetlocks
What are some types of mis-markings?
white elsewhere on body (M4)
white above dewclaw (M3)
incomplete belt (M1)
No belt (M2)
True or false: You should never work with the cattle alone or be in a pasture or a pen alone in South Deerfield.
True
True or false: Cattle are independent and prefer to spend time alone as individuals; cattle are content to be alone or in groups.
False
True or false: Cattle feel safe in dark, enclosed spaces.
False
Where is a cow's point of balance?
shoulder
How can you use flight zone and point of balance to move a cow?
move b/w POB and rear to move cow forward
move b/w POB and front to move cow backward
If you want to move cattle from one location to another, you should:
get boss cow moving in desired direction
shake a grain bucket as you walk in desired direction
make sure pathway b/w locations
walk in serpentine pattern behind cattle's POB, toward desired location
List 5 different types of restraint for cattle.
halter
head lock
chute (show/squeeze)
nose ring/twitch
tail jack
When leading a cow, where should you stand relative to the cow?
at its shoulder on its left side
In order to start a halter-training session, why do you need to work in small space with a calf?
impossible to catch babies w/ halter in pasture, able to restrain moms in headlocks + catch babies in catch pen + go from there, much easier to handle
Describe the pull and release method.
Apply pressure on the halter in a forward motion to get calf to walk. When calf takes a step, release pressure to provide reinforcement for cooperation.
After placing a halter on a calf, how far away from a post should the calf be tied with a quick-release knot?
1 foot
Why do we tie a calf's head up when it misbehaves?
post is stronger than us so they'll get used to being restrained by humans eventually
What can you do to settle a stressed calf?
back away and let baby settle down
List 3 safety concerns that you should be aware of when visiting a farm with a bull.
never enter a pen w/ a bull
never get in between mom & baby
always be aware of where cows are in pen/always keep them in sight
What are you looking for during a heat check?
standing when mounted by other cows
roughened tail head
clear, stringy mucus from vulva
attempts to mount other cows
At what ranges of weights and ages do beef cattle typically go to processing?
900-1450 pounds
18-24 months
Commercial beef heifers are usually bred for the first time at what age?
15 months (65% adult weight and height)
What is the length of pregnancy in days for cattle?
283 +/- 5 days
What is the length of pregnancy in months for cattle?
9 months
On average, which breeding method has a lower pregnancy rate?
artificial insemination
What are 2 advantages of artificial insemination?
can choose genetic traits
much safer
What are 2 advantages of natural or bull breeding?
much less work for us
can be cheaper
higher pregnancy rate
What is the length of a cow's estrous cycle?
21 +/- 3 days
What is the length of estrus (or heat) in cows?
18 hours
What are 3 sign of estrus in cows?
standing when mounted by other cows/bull
roughened tail head
clear, stringy mucus discharge from vulva
True or false: Blood-tinged discharge from the vulva is a sign of estrus in cows.
false, it's a sign of metestrous
How long after estrus ends do cows ovulate for?
10-14 hours
Cow-calf
goal output: weaned calves (produce + sell heaviest weaned feeder calves)
target weight: 400-750 lbs
target age: 6-10 months
Stocker/Backgrounding
goal output: stocker yearlings (grow + develop weaned feeder calves purchased from cow-calf operations)
target weight: 600-850 lbs
target age: 12-18 months
Feedlot/Finishing
goal output: market-weight cattle (finish cattle to market weight in final 4-6 months before slaughter)
target weight: 900-1400 lbs
target age: 18-24 months
How is the cattle ration on a stocker operation different than from a feedlot ration?
feedlot rations more high E with corn + silo trying to gain 3lbs a day. stocker rations are more roughage. all phases have roughage to keep microbes alive. most expensive feed is feedlot phase.
What is the difference between segmented production and vertical integration?
segmented industry- diff owners for diff phases of operation
vertical integration- 1 owner for multiple phases of operation
How is beef production classified in the United States?
segmented production
What is the formula for percent calf crop?
# calves born / # cows in breeding herd
What is desired percent calf crop?
95% or higher
What is the formula for weaning percent?
# calves weaned / # cows in breeding herd
What is the desired weaning percent?
85% or higher
What are the 6 regions of BCS?
brisket
back
ribs
hooks
pins
tail head
What is optimal BCS for rebreeding performance
5-6
Are beef cows re-bred before or after weaning their calves?
before
At what points of the reproductive cycle should we BCS cows?
beginning of breeding season
calving time
weaning time
45 days after weaning
90 days before calving
Some girls from the herd who were BCSed
whisper: 7 (spinous processes very fatty, no ribs visible)
wanda: 6/7 (some fat in brisket, can feel spinous processes, no ribs visible)
wren: 7/8 (no ribs visible, no hooks visible, round)
stella: 6 (last few ribs visible, hooks more visible)
What is the BCS range?
1-9 (1 = emaciated, 9 = severely obese)
List 2 reasons that it is necessary to vaccinate beef cattle.
raise level of resistance to pathogens
save money!
Which type of vaccine contains an inactivated bacteria or virus?
killed vaccine (KV)
Which type of vaccine elicits a faster immune response?
modified live vaccine (MLV)
Which type of vaccine elicits a stronger immune response?
modified live vaccine (MLV)
Which type of vaccine is always safe for both open and pregnant cows?
killed vaccine (KV)
Which type of vaccine is safe for a pregnant cow if she received initial vaccine and booster before breeding?
modified live vaccine (MLV)
What does IM stand for?
intramuscular vaccine
What does SQ stand for?
subcutaneous vaccine
What does IN stand for?
intranasal vaccine
Where should IM or SQ vaccines be administered on an animal?
triangle-shaped area on neck of animal above jugular
Where shouldn't IM or SQ vaccines be administered on an animal?
top of the neck
near jugular vein
on shoulder
anywhere on hind end b/c that's where the most expensive meat comes from
Explain the relationship between needles gauge number and diameter.
as the gauge # gets bigger, the diameter of the needle gets smaller
Which needle gauge numbers are typically used to administer IM and SQ vaccines to cattle?
16, 18, 20
(IM = longer ; SQ = shorter)
What 3 factors should a producer consider when selecting a needle gauge and length?
size of animal
route of administration
viscosity of liquid
List 2 times a beef producer might use an IN vaccine.
right off the truck to boost immunity against pathogens
when calf's too young to receive MLV or KV so they don't interfere w/ maternal antibodies (maternal interference)
How long do you have to wait after vaccinating to ship cattle to processing?
21 days
What is an RFID tag?
Radio Frequency Identification Device
emits radio frequency signal that can be detected by a special reader (cannot remove!!!)
How does hot branding work?
branding iron heated electrically or in a fire
difficult on long-haired animals
scars hide
How does freeze branding work?
branding iron cooled in dry ice or liquid nitrogen
does not scar hide, but damages pigment producing hair cells
What is the formula to determine dry matter demand?
BW x %DM = DM demand
amount dry matter needed per animal
What is the dry matter requirement for beef cattle?
2-3% of body weight each day
Describe the difference between vegetative growth and reproductive growth in terms of pasture forage.
vegetative growth: leafy, early to middle to grazing season, most nutritious
reproductive growth: seed-producing stage, late grazing season, less nutritious
Why does soil health matter?
if there are unhealthy plants, cattle will not be getting optimum nutrients --> bad for production animals (dairy). pasture serves as bulk of beef cattle's dietary needs in seasons it is available
Describe continuous grazing.
when cattle graze on the same pasture for extended periods of time w/o allowing plants to rest from grazing
Describe rotational grazing.
system where large pasture is divided into many small sub-pastures, livestock are moved from pasture to pasture every 4-7 days to allow regrowth of vegetation between grazings
Describe managed intensive grazing.
similar to rotational grazing, MIG is where large pasture is divided into many small sub-pastures, rotated every 1-3 days
Advantages and disadvantages continuous grazing.
adv: low labor and low fencing
dis: higher risk of parasites and grass has difficulty growing back
Advantages and disadvantages to rotational grazing.
adv: It improves plant performance, lowers wastage, longer grazing season, fertilizer is distributed
dis: It's more time and labor intensive than continuous and more fencing is need compared to continuous grazing
Advantages and disadvantages to managed intensive grazing.
adv: Allows grass to regrow quicker and lowest risk of parasites
dis: The most time and labor intensive and needs most amount of fencing
What are the 3 most common forages found in pastures in New England?
Kentucky Bluegrass
Tall Fescue
Orchardgrass
Describe the differences between first and second cut hay.
First cut - First cut of season, thick stems, more stem than leaf, high fiber, low protein and fat
Second cut - Second cut of season, crop is leafier, finer texture, lower fiber, higher in protein and fat, greener
What are the 5 steps, in order, involved in making hay?
Mowing
Tedding
Raking
Rolling
Bailing
What are 3 reasons hoof maintenance is vital for beef herds?
less likely to walk to locations of feed + water to maintain high BCS
less likely to display signs of estrus or cycle entirely, make repro difficult to detect
hoof care = cost-effective
Define gait.
the manner of movement
Define lameness.
abnormal gait
Label the parts of the cow hoof.
interdigital space
hoof wall
toe region
sole region
heel bulb
white line
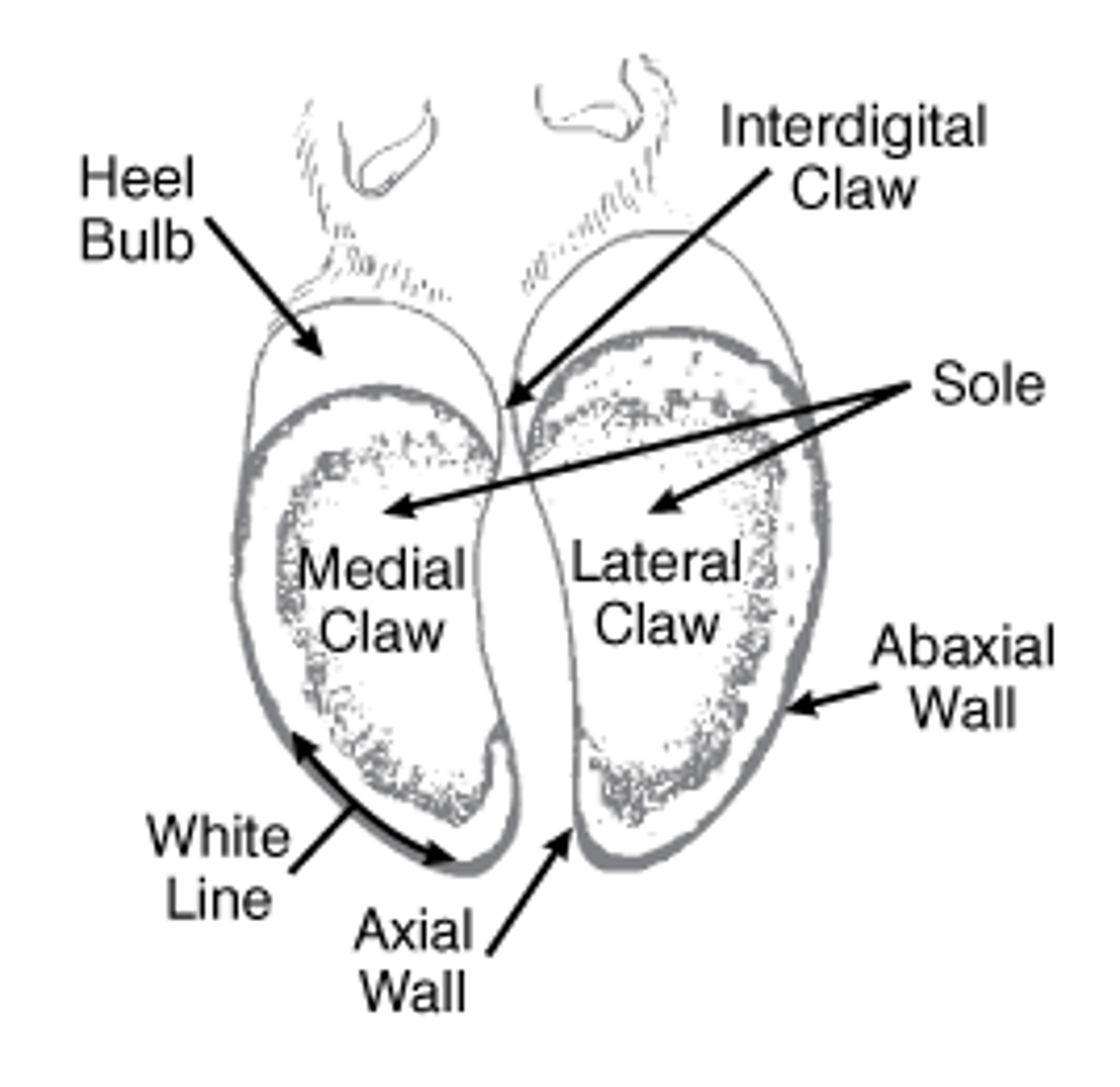
Where is the coronary band?
junction b/w hoof + skin
What is the range of locomotion for beef cattle?
range: 0-3
0 = no lameness
3 = extremely lame
What does locomotion score evaluate?
evaluates standing and walking, determines if cow is lame and to what degree
Describe bow legged conformation.
hocks bent out, hooves turned in
front or hind legs
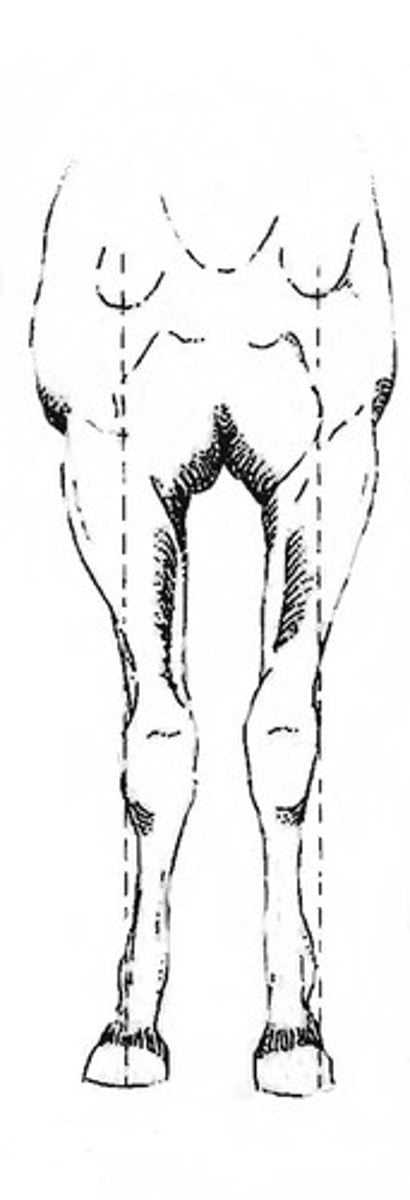
Describe knock-kneed conformation.
hocks bent in, hooves turned out
only front legs
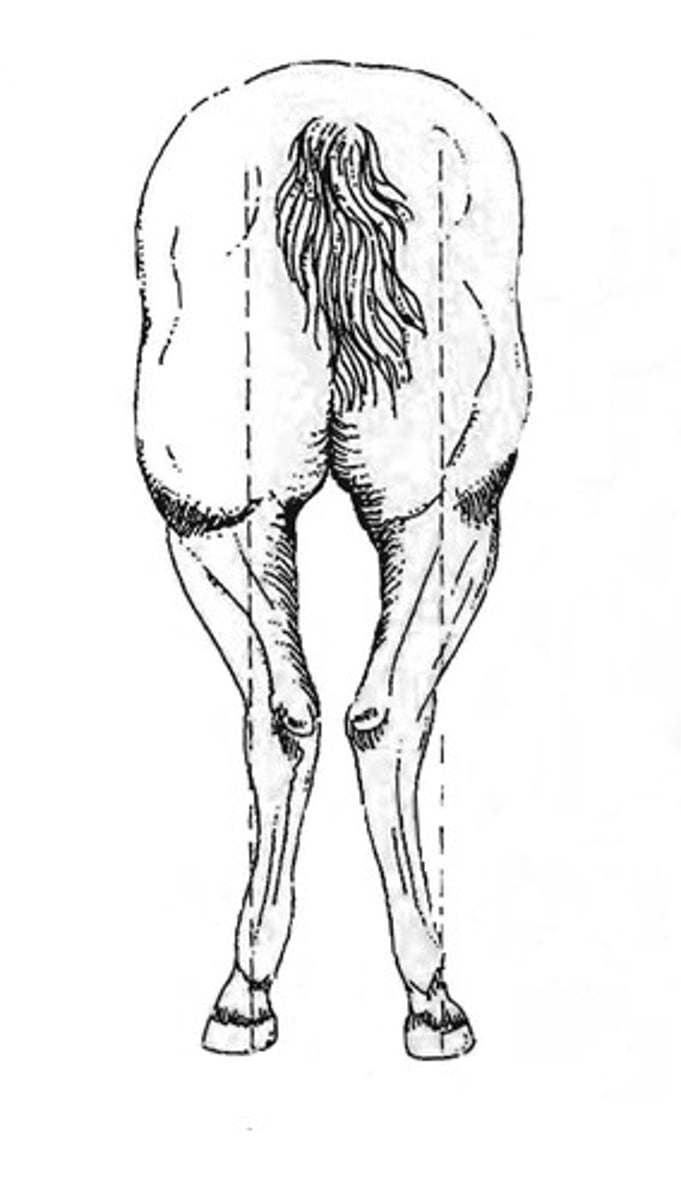
Describe cow hocked conformation.
hocks bent in, hooves turned out
only hind legs
What are the 4 tools used during hoof trimming?
hoof knife
grinder
nippers
hoof rasp
What's the function of a hoof knife?
clean sole, trim wall, dish out sole, keep blade sharp, if dull apply pressure to shape hoof, but could result in cutting too deep in claw
What's the function of a grinder?
grind excess horn from hoof, quick + efficient, need excellent restraint
What's the function of nippers?
cut toe + hoof wall to desired length
What's the function of a hoof rasp?
smoothes rough edges to create flat surface on hoof
What is the purpose of hoof testers?
to identify painful areas of a hoof
What are the natural weight-bearing surfaces of a cow's hoof?
hoof wall (hardest part) + heel (softest part)
Define conformation.
skeletal structure of an animal