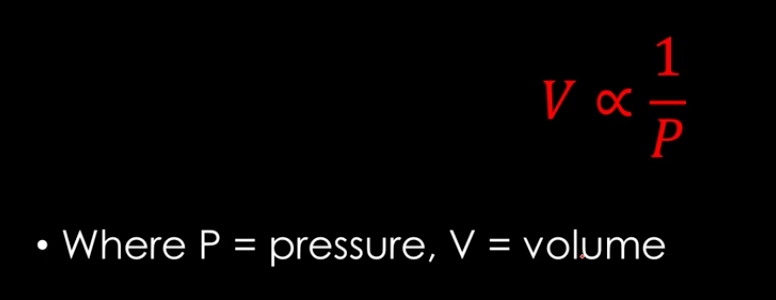chem - kinetic theory of gases
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
14 Terms
properties of gases
low density
spread to fill the available space
easily compressed
mix together rapidly
properties of liquids
high density
fixed volume; adopt shape of container
almost incompressible
mix slowly unless stirred
properties of solids
high density
fixed volume; generally rigid shape
almost incompressible
do not mix unless finely divided
what are all gases composed of?
atoms or molecules
kinetic theory of gases
gases are composed of atoms or molecules
the total volume of a gas is much greater than the volume of the particles and therefore most of the volume is empty space - LOW DENSITY
particles move randomly in straight lines and collide with other particles and the walls of the container
particles move around independently
the average kinetic energy of the particles increases as the temperature increases
all collisions are elastic
pressure definition
pressure is the force exerted on a unit area of surface
pressure formula

N (newtons) / metres squared (m^2) - directly relates to pascals but mostly used in physics
four common units for pressure
millimetres of mercury (mmHg)
atmospheres (atm)
pascals (Pa)
bars (bar)
converting between units of pressure

units for volume
litre (L)
millilitre (mL)
cubic metre (m^3)
cubic decimetre (dm^3), 1dm = 10 cm = 100mm
cubic centimetre (cm^3)
volume equivalents
1mL = 1cm^3
1L = 1dm^3
1L = 1x10^3mL = 1000mL
1m^3 = 1x10^3dm^3 = 1x10^6cm^3
1m^3 = 1x10^3L = 1x10^6mL
the gas laws
there are five laws which explain the behaviour of gases, the first of which is boyle’s law
boyle’s law
for a given amount of gas at constant temperature, the volume of gas is inversely proportional to its pressure
boyle’s law formula