Organic Molecules
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
alkanes
saturated hydrocarbon chains
properties of alkanes
nonpolar, LDFs only
insoluble in water
low boiling point
low reactivity
formula is CnH(2n+2)
two types of alkanes
straight chain (stronger LDFs) and branched chain (weaker LDFs)
naming branched chain alkanes
parent molecule is the longest continuous strand of carbons
branches listed alphabetically, with -yl suffix
suffix -ane
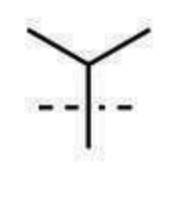
isopropyl substituent
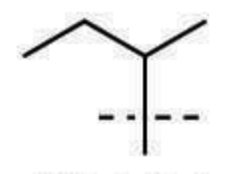
propyl substituent
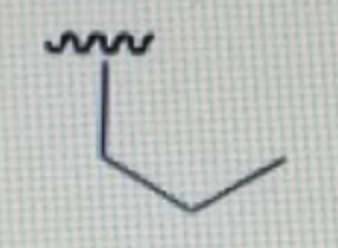
isobutyl substituent

sec-butyl substituent
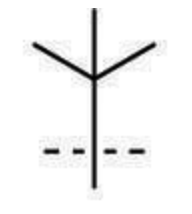
tert-butyl substituent
cycloalkane formula
CnH(2n)
cycloalkane reactivity
greater for larger cycloalkanes (less angle strain)
naming cycloalkanes
priority carbon goes to first ALPHABETICAL substituent
direction proceeds to the lowest point of difference
reactions of alkanes
combustion
halogenation
dehydrogenation
Combustion equations
amount of carbons in alkane(n) is the amount of CO2 produced, (3n + 1)/2 is the amount of O2 consumes, (n+1) H2O produced
halogenation reactions (substitution reactions)
UV light is used to knock a hydrogen off an alkane and replace it with a halogen (F, Cl, Br, I) to form a halogenated alkane and H(halogen)
dehydrogenation reactions
2 adjacent hydrogens are removed, consuming the halogen and releasing 2H
alkenes
hydrocarbons with double bonds between carbons
alkynes
hydrocarbons with triple bonds between carbons
naming alkenes
parent molecule is longest continuous carbon chain CONTAINING double bond
number location of double bond before parent molecule name
name substituents alphabetically
suffix -ene
if there are multiple double bonds, label both, and indicate number with prefix di-tri-tetra- -ene
naming alkynes
parent molecule is longest continuous carbon chain CONTAINING triple bond
number location of triple bond before parent molecule name
name substituents alphabetically
suffix -yne
if there are multiple triple bonds, label both, and indicate number with prefix di-tri-tetra- -yne
cis alkenes
both substituents are located on the same side of the double bond, allowing rotation
trans alkenes
substituents are located on opposite sides of the double bond, forcing rigidity
naming cycloalkenes
double bond gets priority
decrease numbers if there are multiple
indicate number of double bonds by prefix di-tri-tetra- -ene
alphabetize substituents
addition reactions of alkenes and alkynes
an alkene reacts with a hydrogen which is split by a catalyst and double/triple bond breaks replaced with hydrogen
reactions of alkenes and alkynes
addition and halogenation
halogenation reactions of alkenes and alkynes
an alkene reacts with a halogen which is split by a catalyst and double/triple bond breaks replaced with halogen atoms
aromatic hydrocarbons
have delocalized pi electrons creating extra stability ex) benzene
aromatic hydrocarbon reactions (substitution)
substituents replace hydrogens (C-C bonds are too strong)