Software II Exam 2 Concepts
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
33 Terms
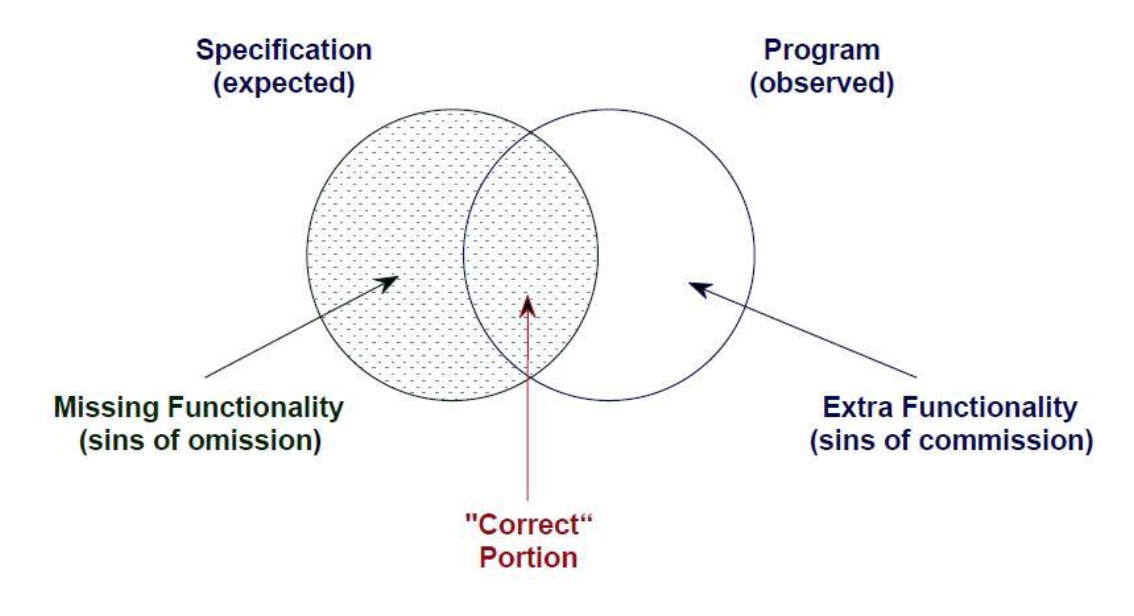
Sins of Omission
Missing functionality that is part of the theoretically correct program.
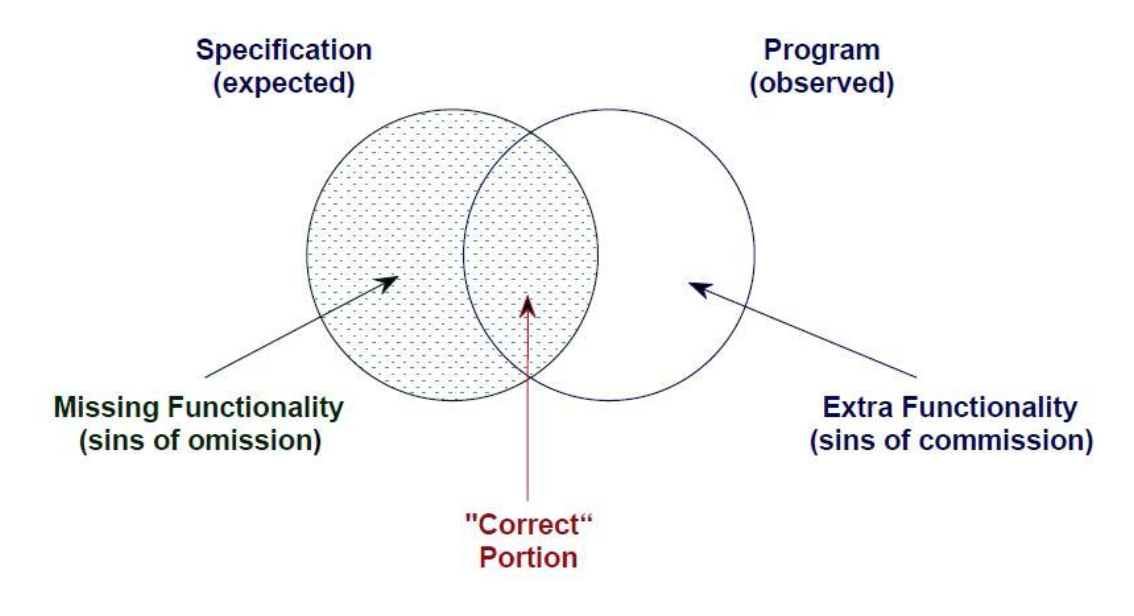
Sins of Comission
Extra functionality the actual program contains that is not part of the correct program.
First Law of Systems Engineering
No matter where you are in the system life cycle, the system will change, and the desire to change it will persist throughout the lifecycle.
Exhaustive Testing
Testing with every member of the input value space.
Static Testing
Testing a unit without executing the unit code. (Code Inspection/Code Walkthroughs)
Dynamic Testing
Testing a unit by executing a program unit using test data. (Black-box Testing, White-box Testing)
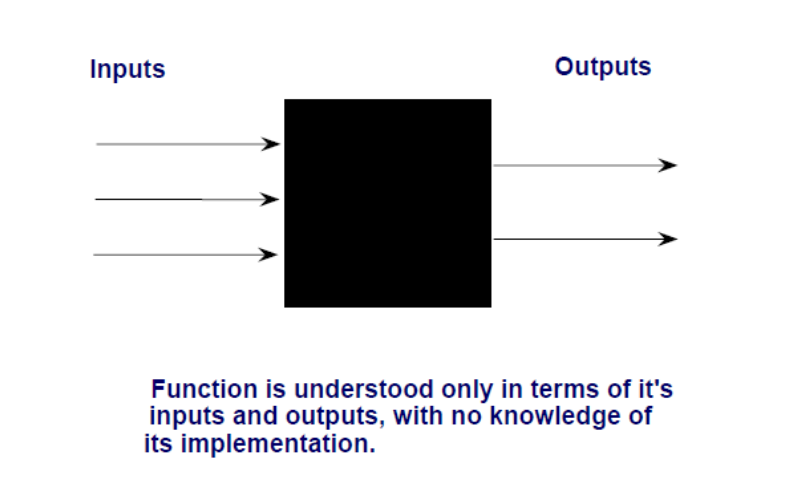
Functional (Black Box)
Function is understood only in terms of inputs and outputs, with no knowledge of its implementation.
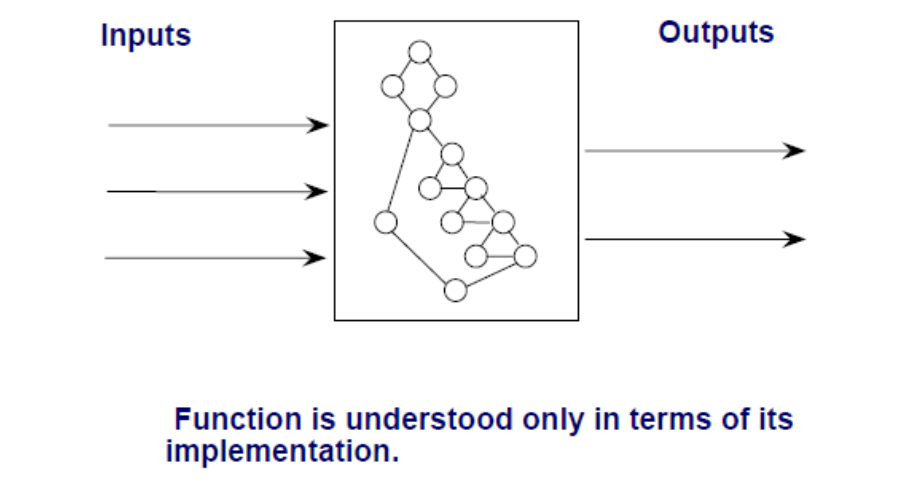
Structural (White Box)
Focuses on implemented program.
Test Case
Tuple pair of test data (input) and the expected output.
Test Suite
A collection of 0 or more test cases.
Test Oracle
Observer who compares the output with the expected output.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Black Box
+Directs tester to choose subsets to tests that are both efficient and effective in finding defects.
-Never sure of how much of the system under test (SUT) has been tested.
Equivalence Class Testing
Technique used to reduce the number of test cases to a tolerable level while still maintaining reasonable test coverage.
Any data value within an EC (set of data) is treated the same as the other data values.
Every possible input belongs to one of the classes.
(e.g. if (x>y) then S1 else S2 => there are 2 EC (x>y) and (x<=y)
Equivalence Classes Conventions
Combine as many valid EC’s into a test, have only one test for every invalid EC.
Boundary Value Testing
Must be able to partition input spaces into equivalence classes.
Identify boundaries of each EC, create 3 test cases: immediately below the boundary, exactly on the boundary, and immediately above the boundary.
Boundary Value Testing Example
EC:
Empty => Return False (1 test case) ((<{}, 2>, false)
EC:
Not Empty
EC:
Key in Array
On Boundary (1 test case)
First element in array (1 test case)
Last element in array (1 test case)
EC:
Key not in Array (1 test case)
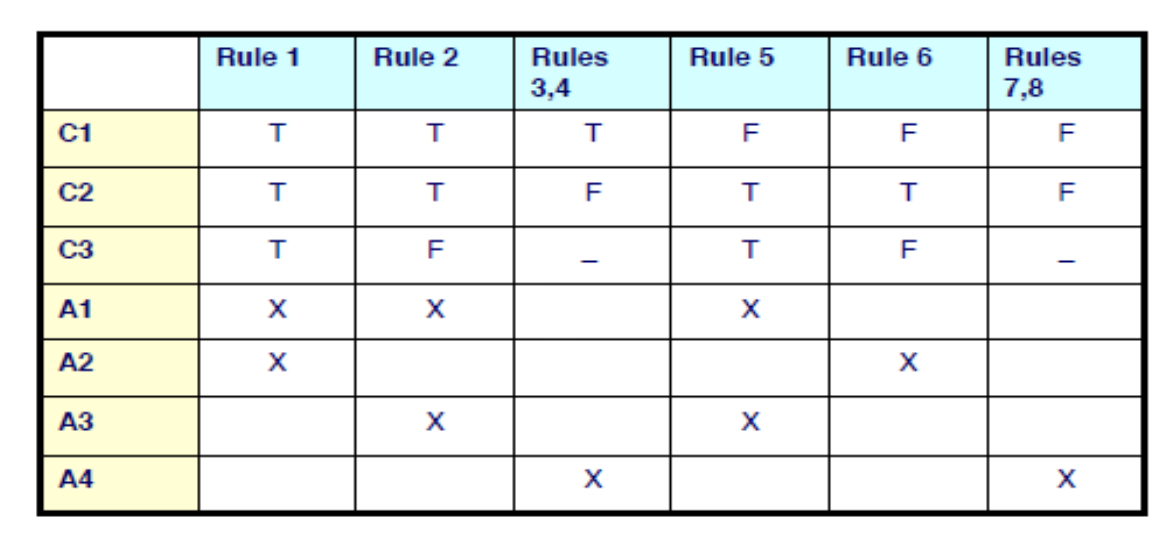
Decision Table Testing
Mechanism to define actions to be taken given certain conditions, where selected actions do not occur in any particular order.
If conditions are binary, then number of columns = 2^n , (n is number of conditions)
Number of rows: n + m where m is the number of actions
Pairwise Testing
Ensures every possible pair of input parameter values is covered by at least one test case.
Used when all combinations cannot be tested.
Single-Mode Defect → Caused by one parameter alone
Double-Mode Defect → Caused by interaction between two parameters
Orthogonal Array
Every
4 columns attributes, maximum value 3 (1-3)
L_9(3^4), 9=#ofrows,3=maximumvalue,4=#ofcolumns
Basic Block
Has a single entry and exit point.
Branch Coverage
Each edge of a program’s CFG is traversed at least once in some test. An independent path is a unique way to reach from source to dest. 1 test case for each path. If possible, do it in less paths.
Basis Set (Minimal Set of Test Cases)
Set that ensures every condition has been covered that covers both true and false.
A set of paths such that if test cases force execution of these set of paths, then every statement in the path and every condition will be executed (both true and false)
Cyclomatic Complexity
Software metric provides a quantitative measure of the logical complexity of a program. Provides upper bound to ensure all statements have been executed at least once.
E=edges,N=# of nodes,B=# of branches.
V(G) = E - N + 2
V(G) = B + 1
Path Coverage
Every distinct path through the code is executed at least once.
Def-Use Coverage
Every path from every definition of every variable to every use of that definition is exercised in some test.
Use → variable used in computation
Def → variable creation or introduced
Def and Use can be None.
Test cases that cover every definition and use of the corresponding variable.
X: (x=1,z=2) {1,2,3},{4,5} … but doesn’t matter as long as {1,2,3},{4,5} is traversed.
Z: (x=1,z=2) {1,2,3},{4,5} … but doesn’t matter as long as {1,2,3},{4,5} is traversed.
Y: (x=1,z=2) {1,2,3},{4,5},{J},{7},{8},{J} … covers every definition and use of variable Y.
Order of weakest to strongest Coverage Criteria
Statement, Branch, Condition, Path
Def Use is between branch and condition coverage.
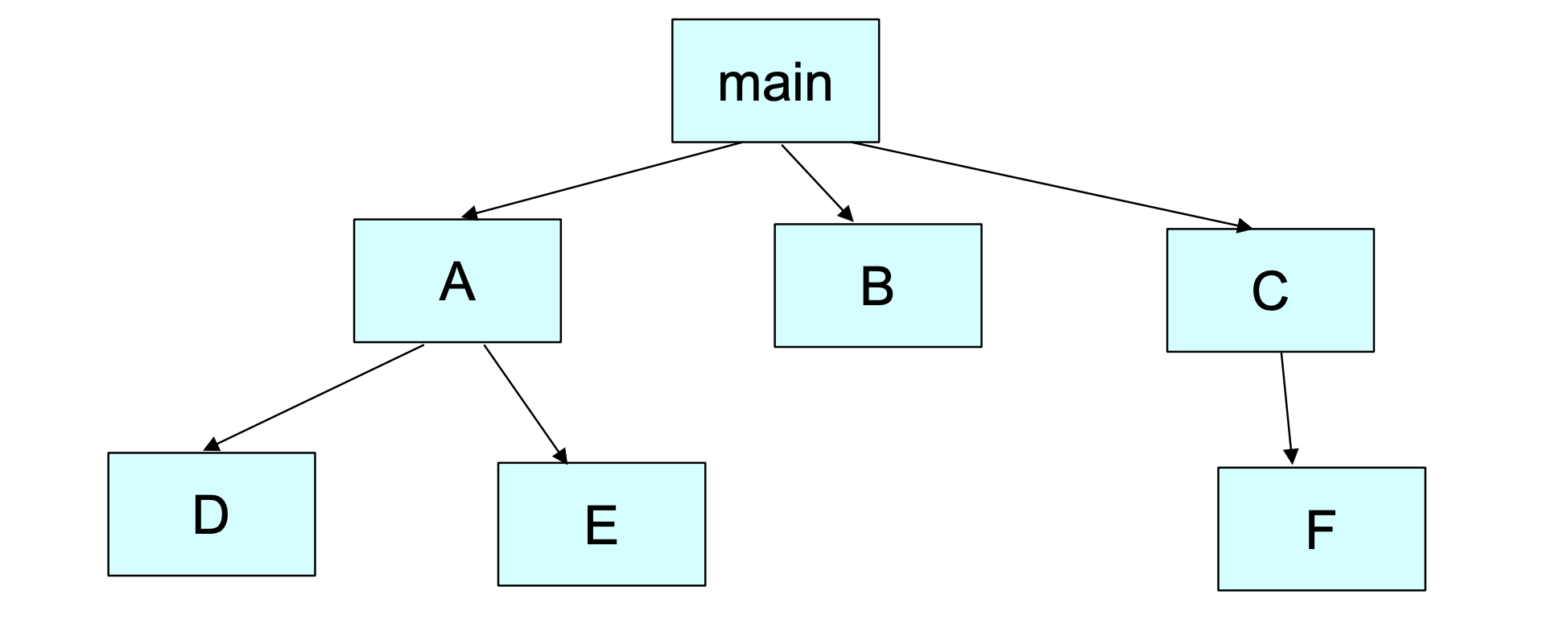
Integration Testing
Done between unit and system testing. Ensure assembled modules work fine in isolation, work well together. Often requires module call graph.
Stub vs Driver
Called program/module, Calling program/module
Big-Bang Integration
Non-incremental, unit test each module in isolation, integrate as a whole.
Pro: Convenient for small teams
Cons:
Integration testing can only begin when all modules are ready
Fault localization difficult
Easy to miss interface faults
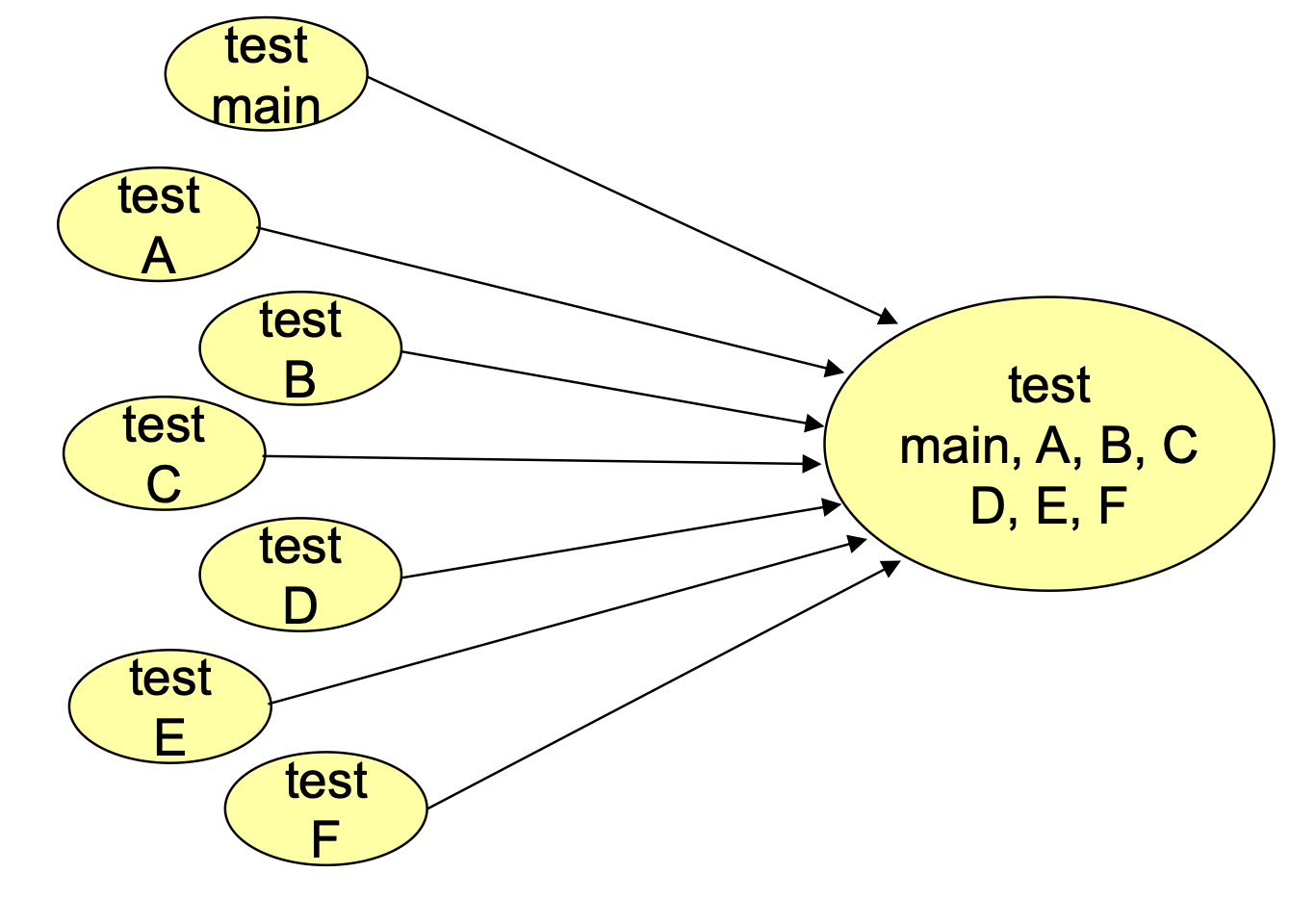
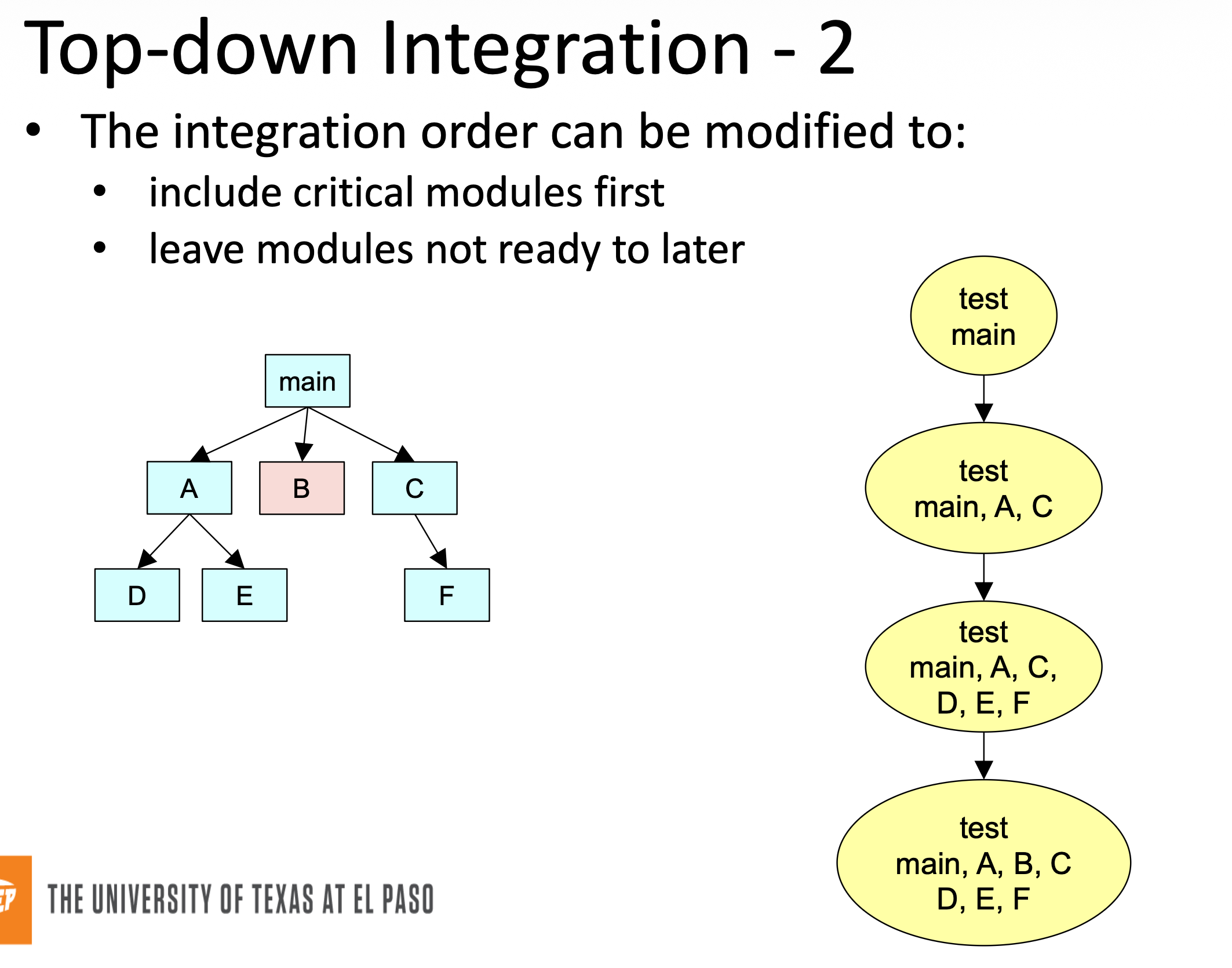
Top-Down Integration
Start with highest level of module call graph, going down until all layers have been tested.
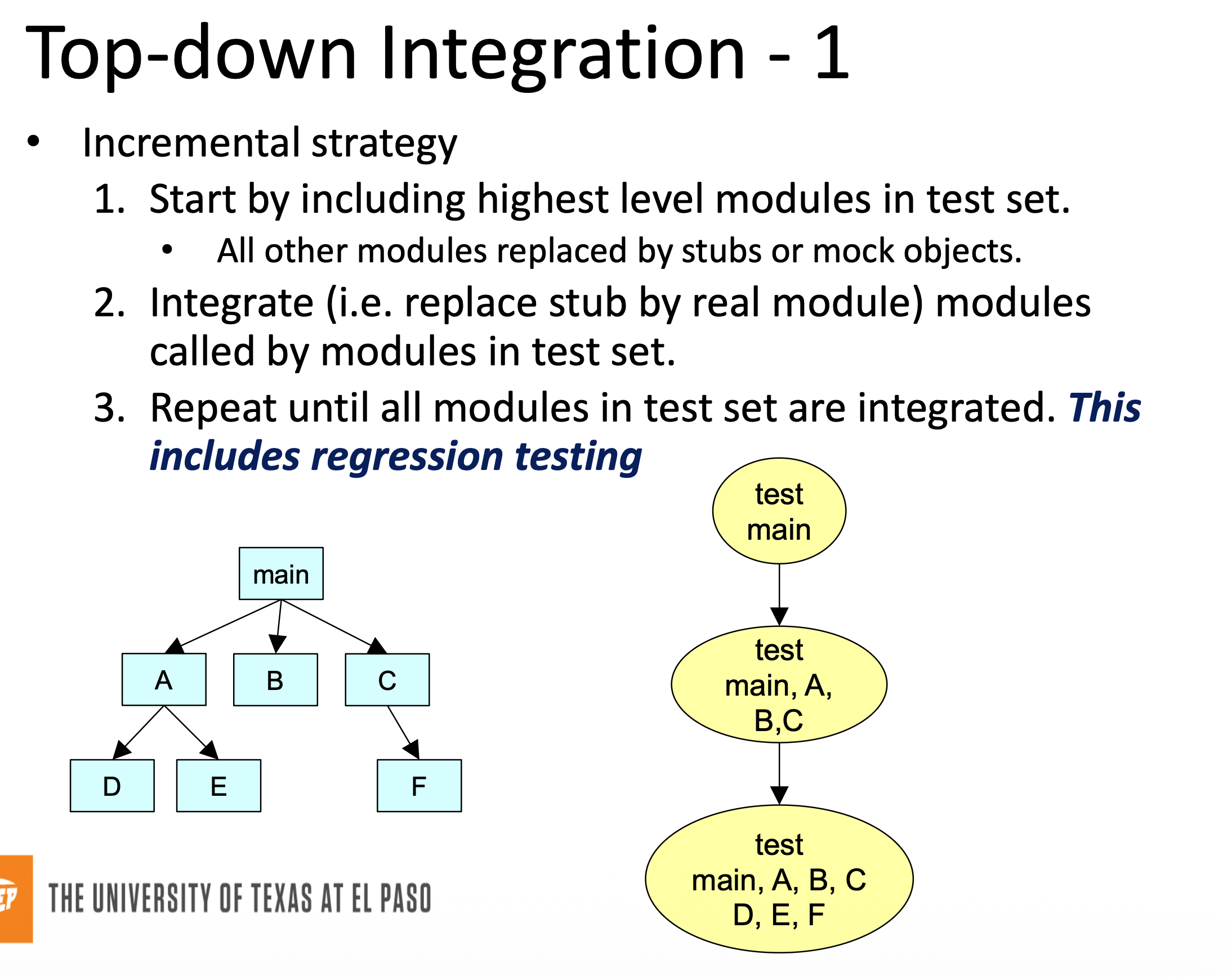
Top-Down Integration Variation
Pros:
Fault localization easier
Few or no drivers needed
Possibility to obtain an early prototype
Different order of testing/implementation possible
Major design flaws found first
Cons:
Need lots of stubs/mock objects
Potentially reusable modules (bottom) can be inadequately tested
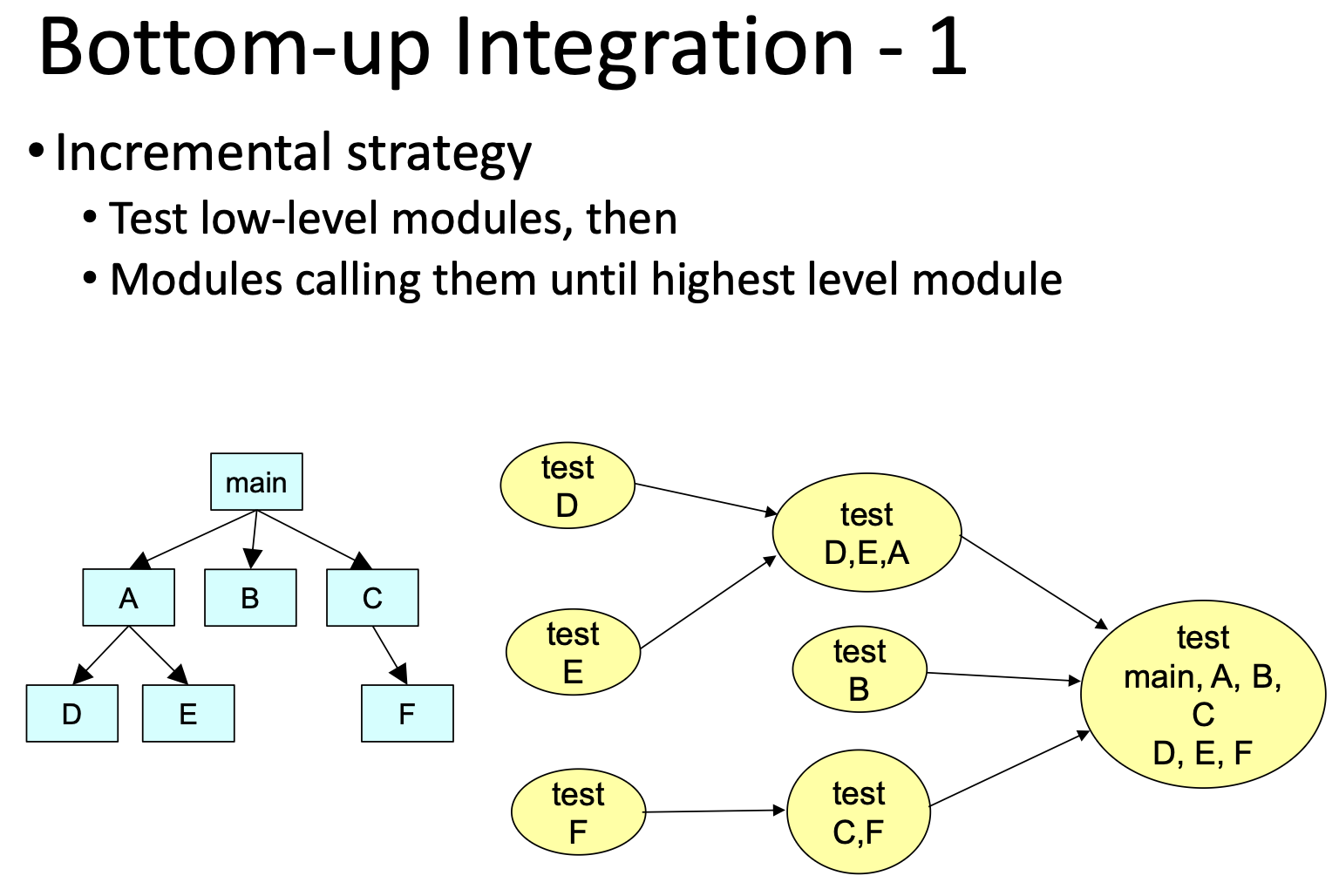
Bottom--up Integration
Pros:
Fault localization easier
No need for stubs
Operational modules tested thoroughly
Testing can be in parallel with implementation
Cons:
Need drivers
High-level modules tested last and least
Sandwich Method
?