Rat Anatomy and Physiology
1/63
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
64 Terms
cranial region - head
cervical region - neck
pectoral region - area where front legs attach
thoracic region - chest area
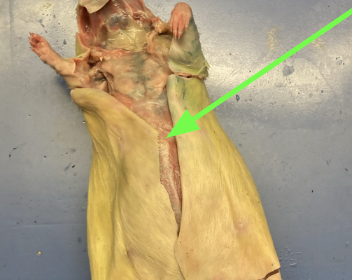
abdomen - belly
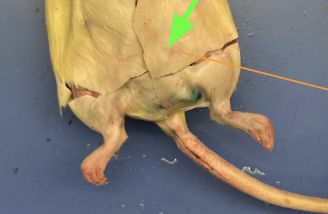
pelvic region - area where back legs attach
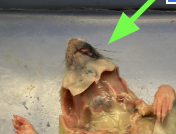
vibrissae - whiskers, external anatomy
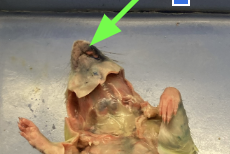
incisors - teeth, external anatomy
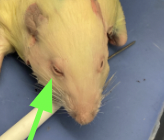
pupil - dark opening of the eye, external anatomy
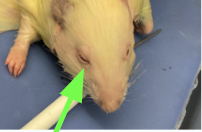
nictitating membrane - inner corner of eye, can be drawn across eye to protect it, external anatomy
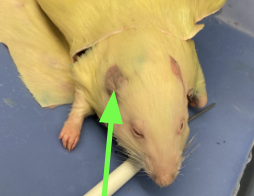
pinna - ear, external anatomy
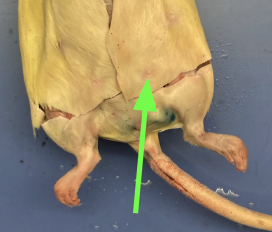
teats - nipples (only females), external anatomy
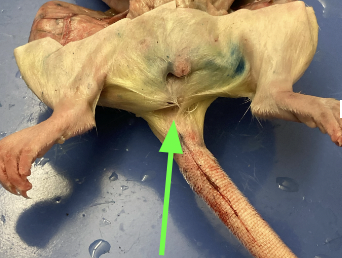
anus - booty hole at base of tail, external anatomy
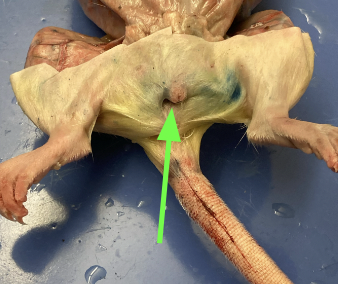
vaginal opening - opening above anus, external anatomy
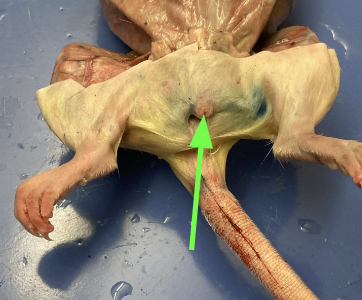
uretha - opening above vaginal opening, carries urine from bladder to urethral orifice, external anatomy and urogential system
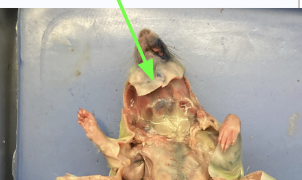
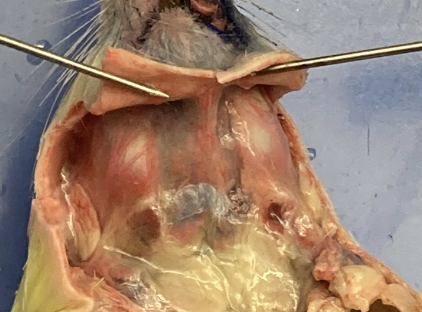
gastric - V shaped muscle below jaw, opens mouth, muscular system
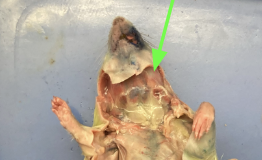
masseter - cheek muscle, chewing, muscular system
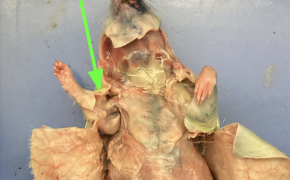
biceps brachii - anterior surface of upper arm, muscular system
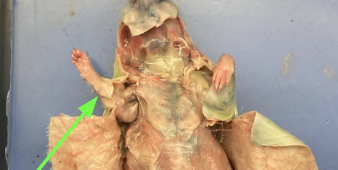
triceps brachii - sides and back of upper arm, muscular system
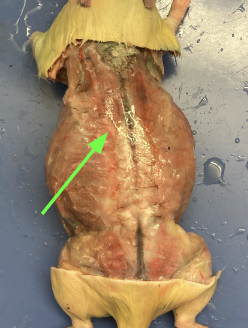
spinotrapezius - on dorsal thoracic region (back of chest), muscular system
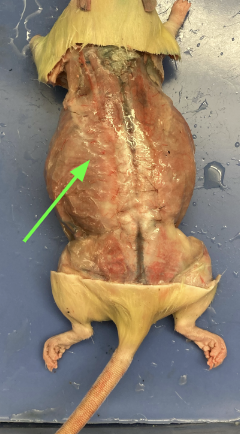
latissimus dorsi - posterior to spinotrapezius (behind and out), muscular system
biceps femoris - side of thigh, muscular system
tibialis anterior - front of leg, muscular system
gastrocnemius - lower leg calf muscle, muscular system
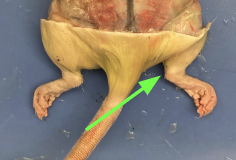
achilles tendon - connects gastrocnemius to heel, muscular system
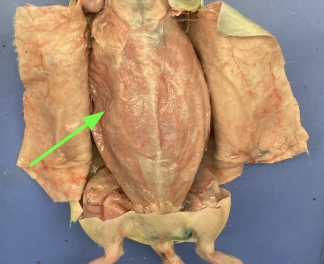
external oblique - side of abdomen, muscular system
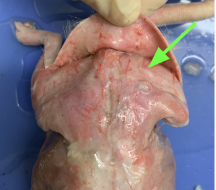
gluteus maximus - lower back and rear (butt), muscular system
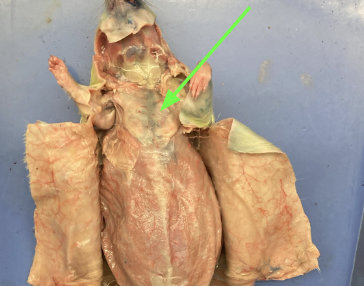
(muscle)
pectoralis major/minor - located in chest, muscular system
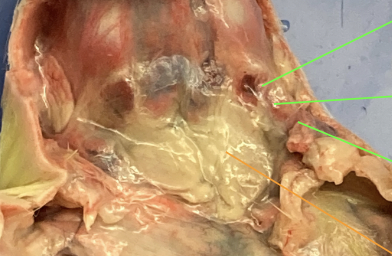
three salivary glands (picture unsure?)
sublingual, submaxillary, parotid, head and neck
lymph glands (picture unsure?)
anterior to salivary glands, circular, pressed against jaw muscles, head and neck
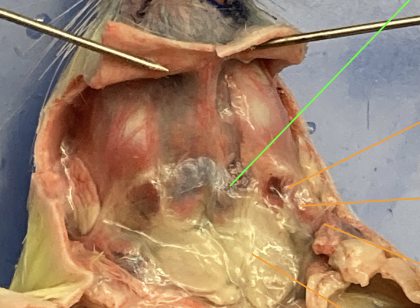
trachea - between the larynx and esophagus, characterized by the ringed cartilage, head and neck
esophagus - underneath trachea, head and neck
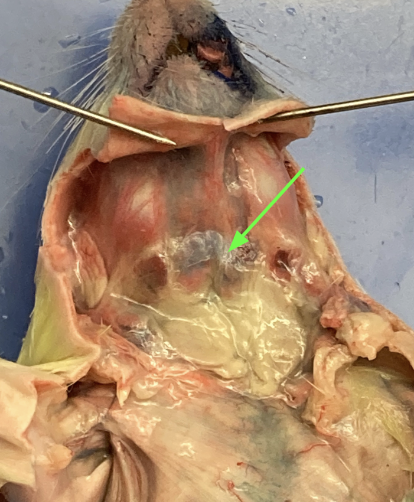
larynx (picture unsure?)
anterior to trachea, voice box, head and neck
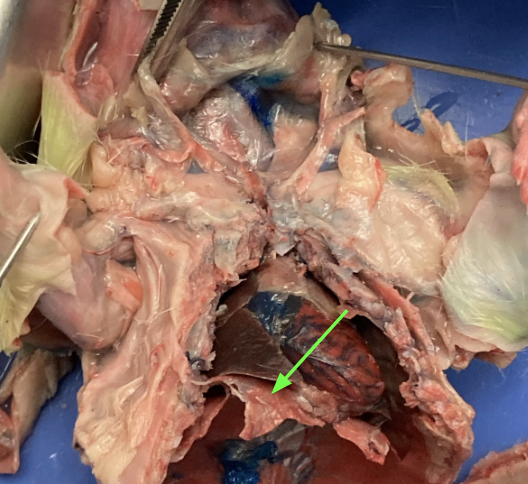
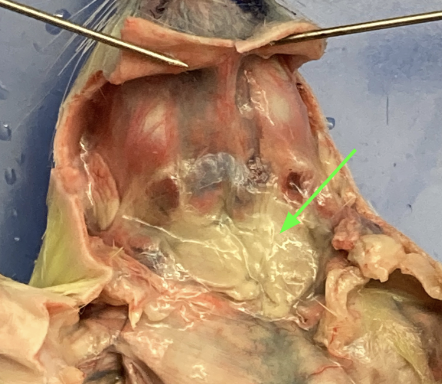
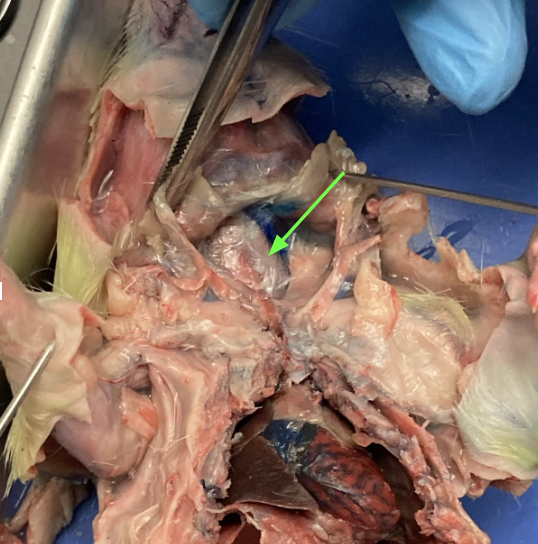
diaphragm - layer of muscle separating thoracic from abdominal region, thoracic
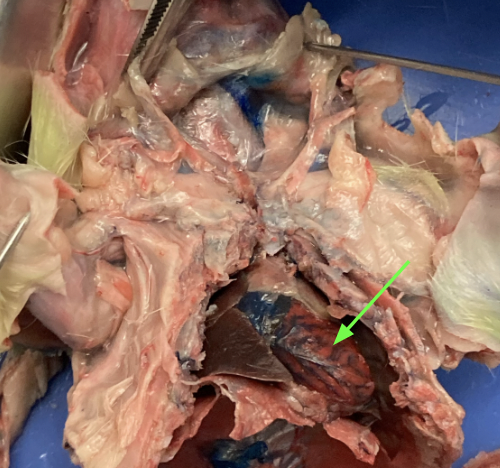
identify the organ and the membrane covering it
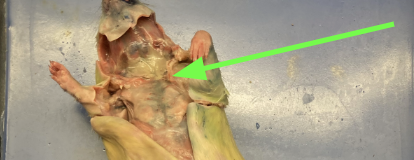
heart - centrally located in thoracic cavity, thoracic
pericardium - thin membrane encasing heart, thoracic
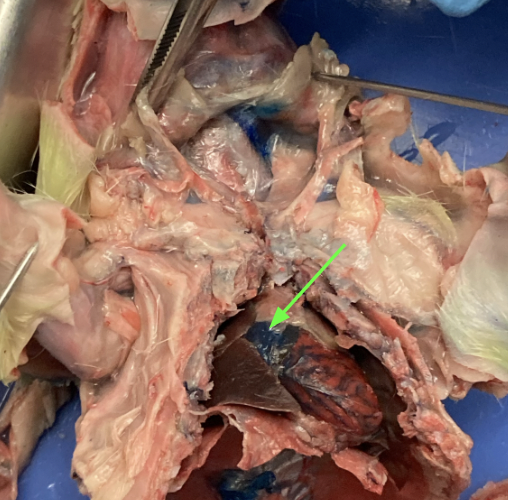
atria - dark colored chamber at top of heart, thoracic
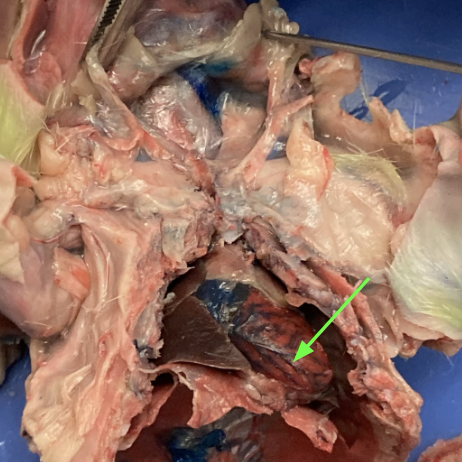
(bottom chamber)
ventricles - dark colored chambers at bottom of heart, thoracic
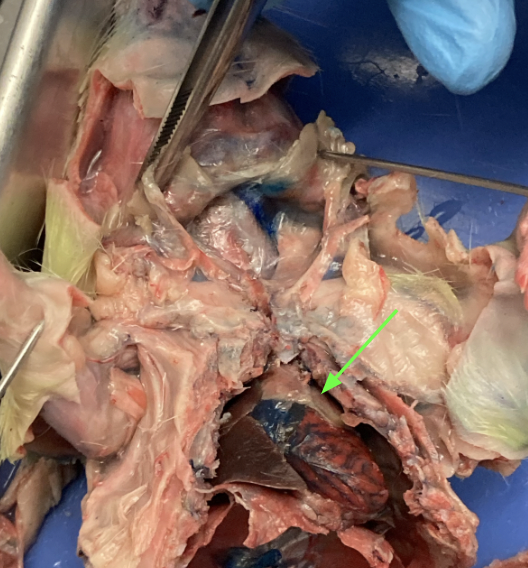
thymus gland - directly above heart, helps with development of immune system, thoracic
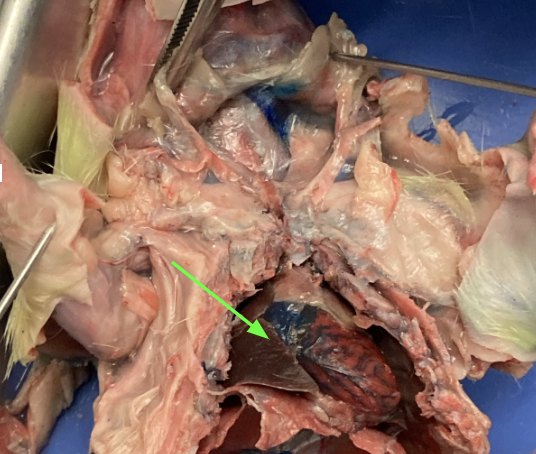
lungs - on either side of heart, thoracic
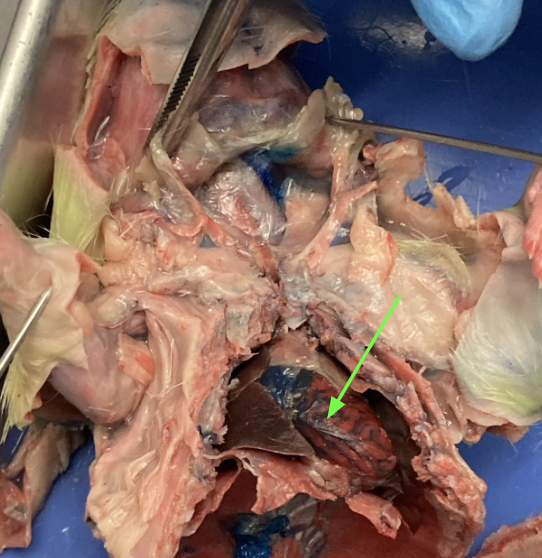
(artery)
coronary arteries - on top of heart, helps supply blood to the heart, circulatory system
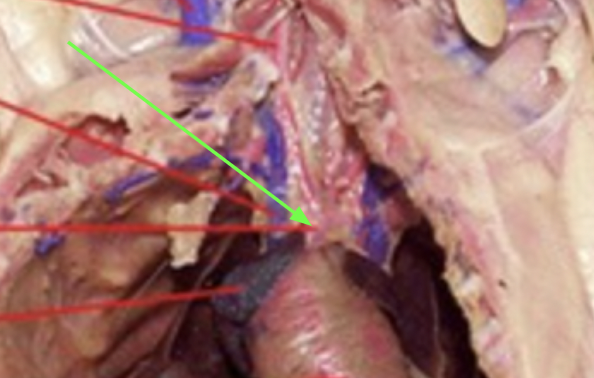
(branching from heart)
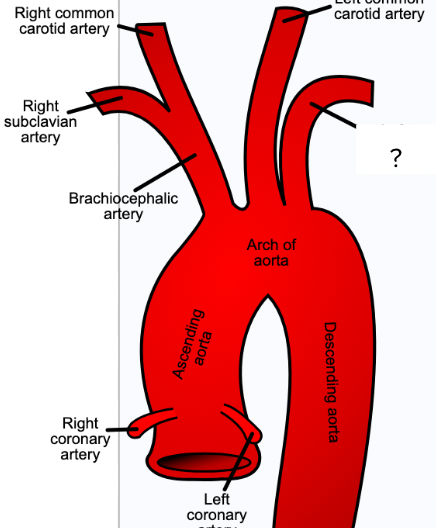
aorta - begins at left ventricle of heart, circulatory system
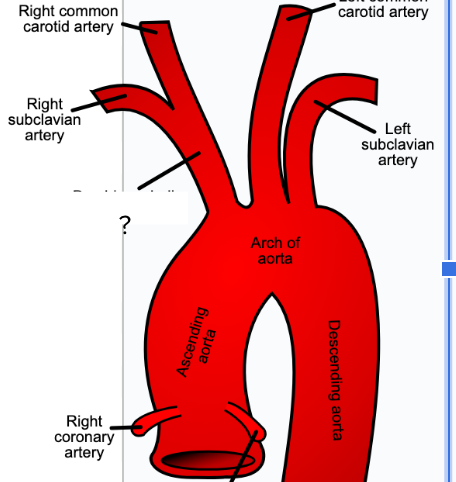
brachiocephalic artery - first visible branch from the aorta, circulatory system
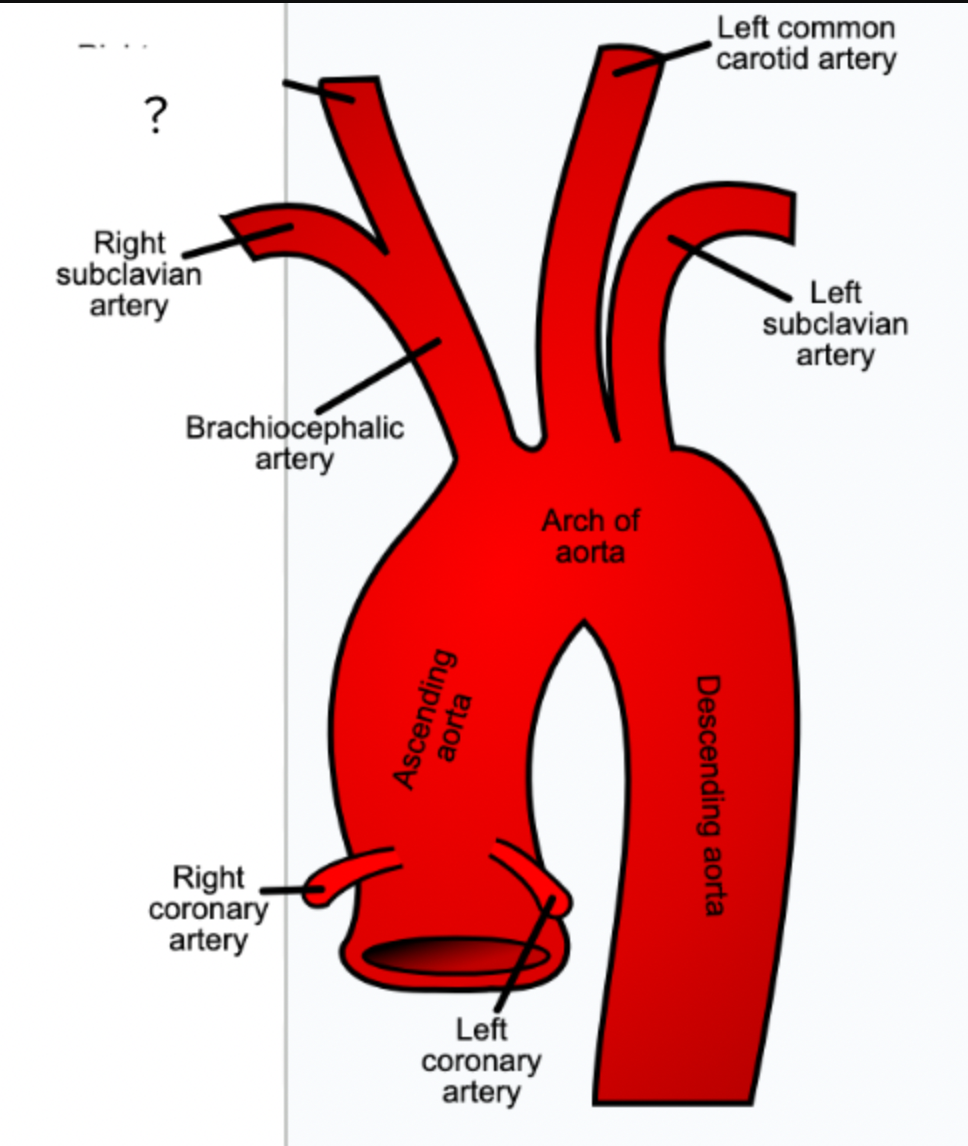
right common carotid artery - supplies the right side of neck, circulatory system
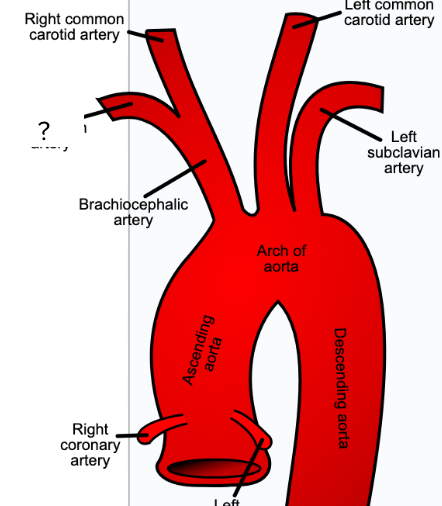
right subclavian artery - supplies right shoulder and arm, circulatory system
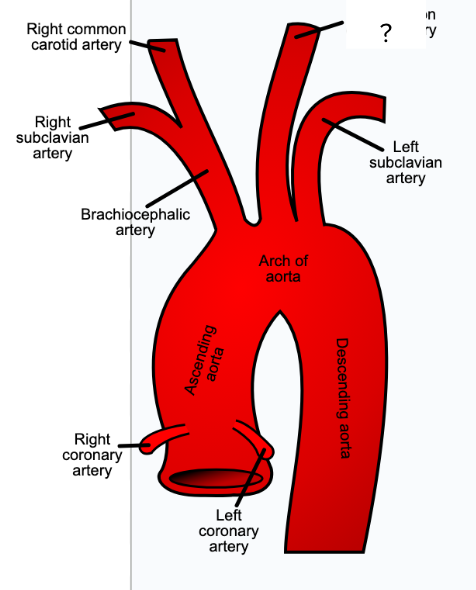
left common carotid artery - supplies blood to left side of neck, circulatory system
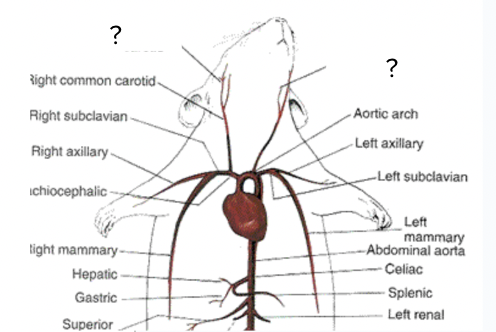
internal and external carotid, circulatory system
left subclavian artery - supplies blood to left shoulder and arm, circulatory system
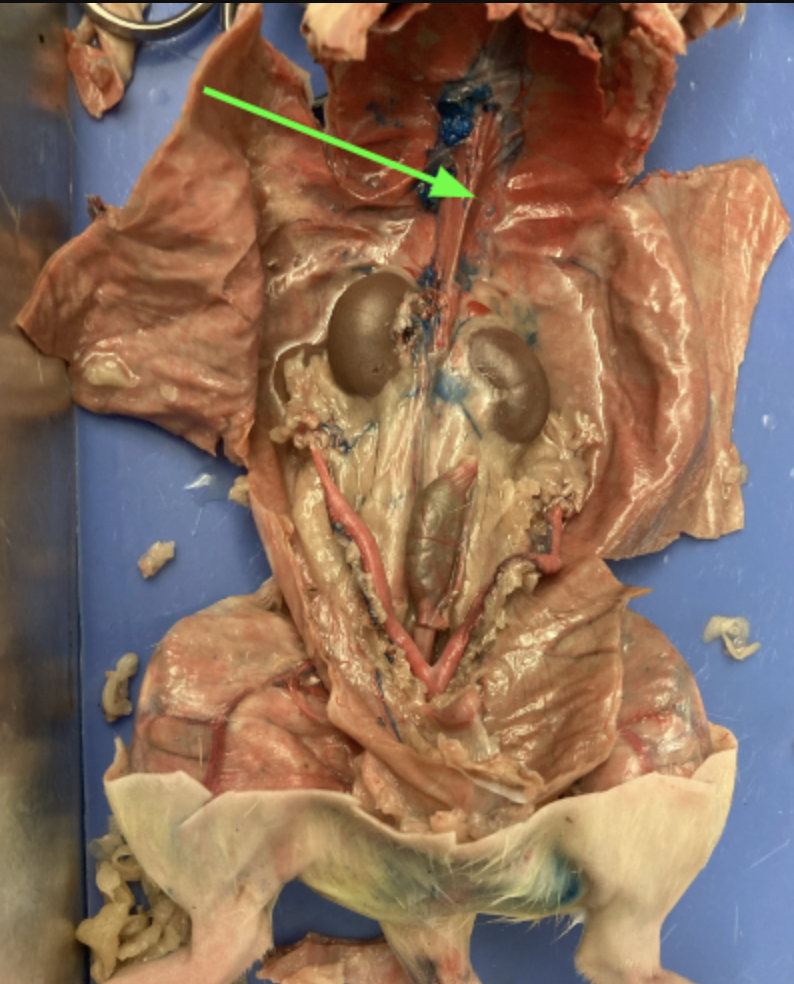
abdominal aorta, circulatory system
renal arteries - lead to kidneys, circulatory system
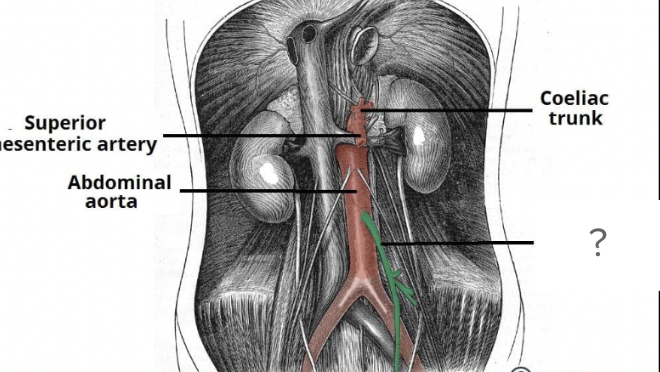
inferior mesenteric artery - connects to intestinal mesenteries, circulatory system
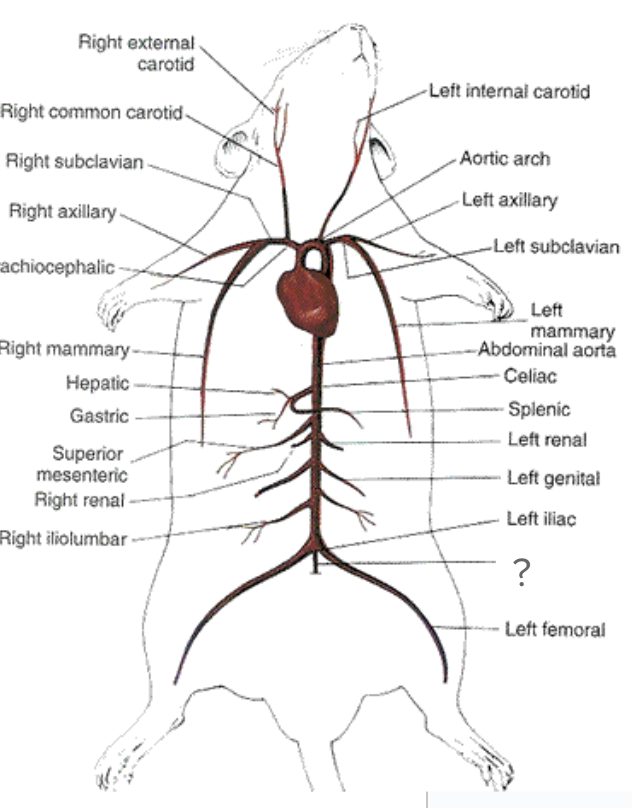
caudal artery - posterior to abdominal aorta, goes into tail, circulatory system
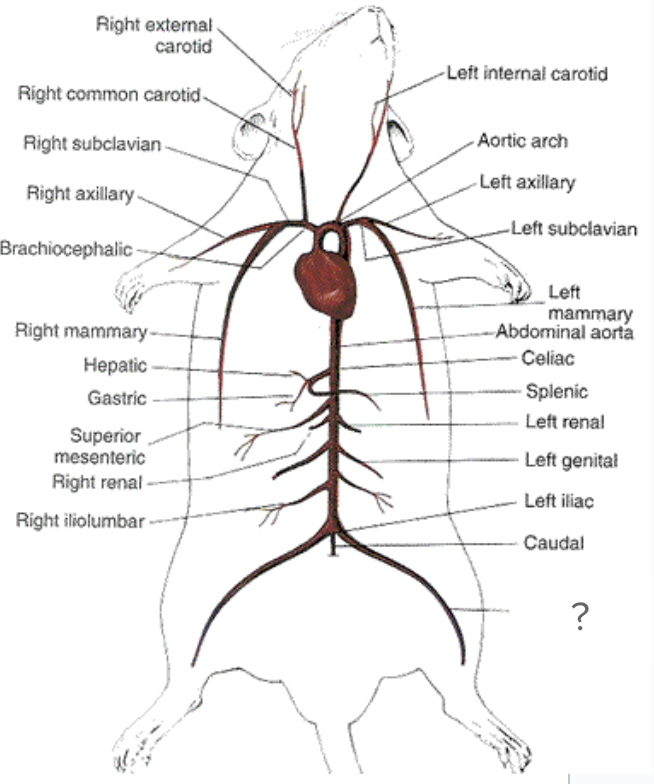
femoral arteries - in leg, circulatory system
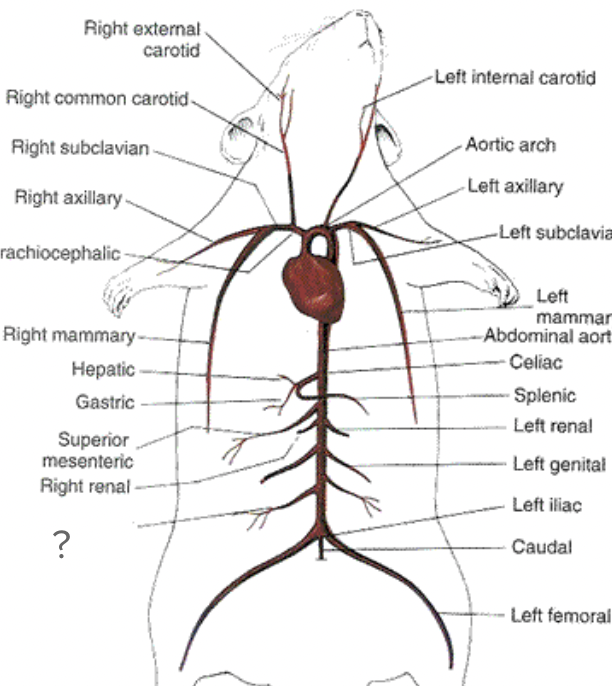
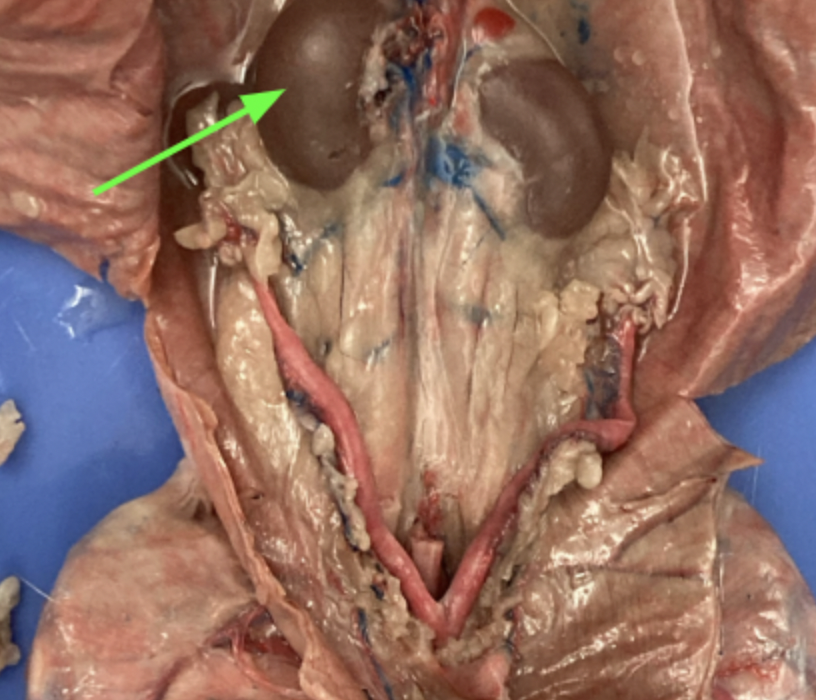
illiolombar arteries, circulatory system
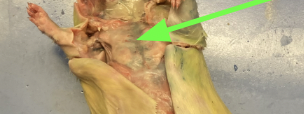
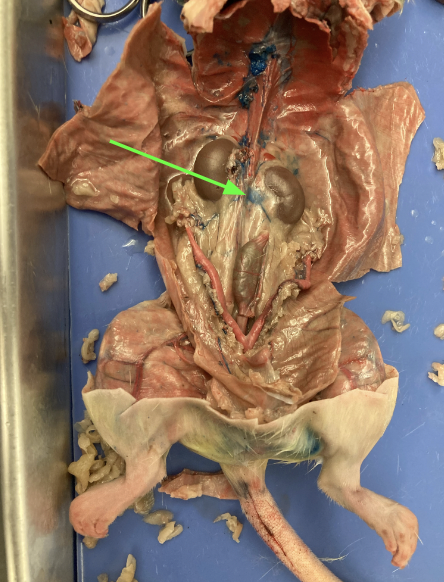
kidneys - large bean shaped structure, primary organs of the excretory system, urogenital system
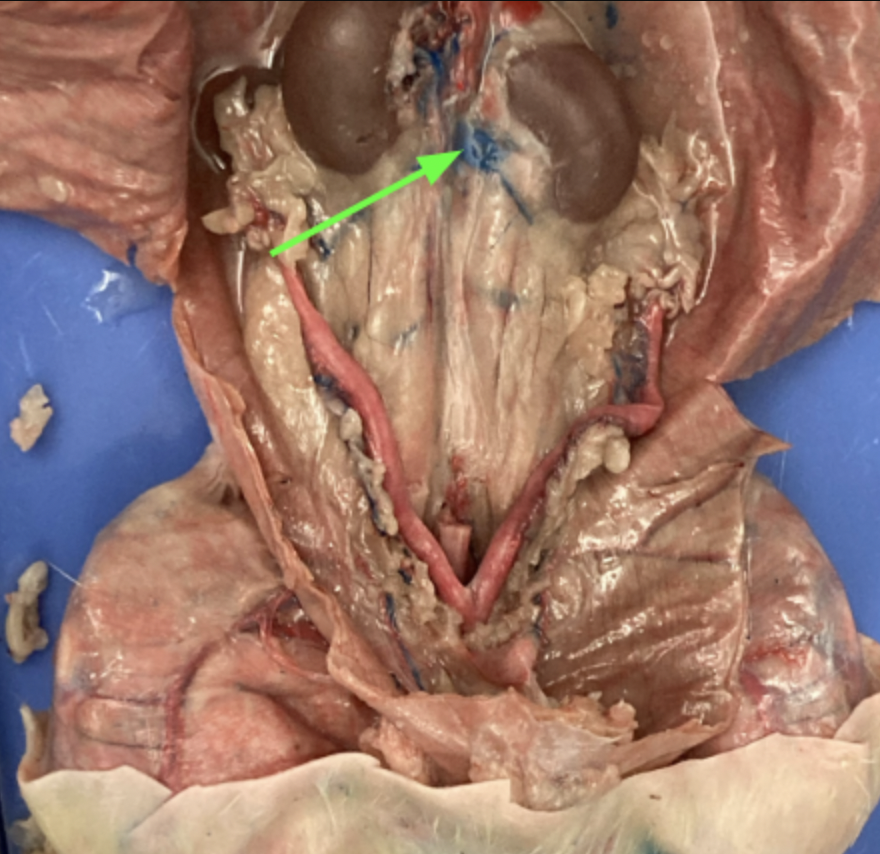
renal arteries and veins - supply kidney with blood, urogenital system
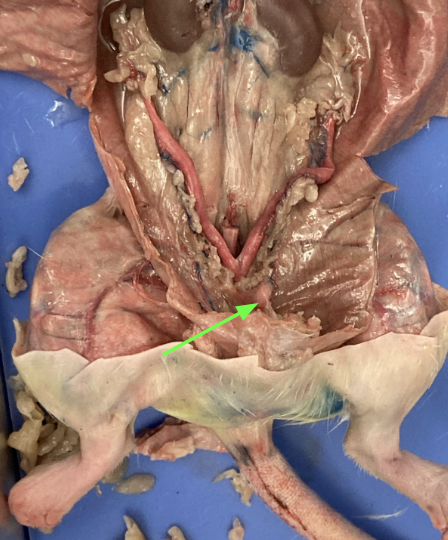
bladder, urogenital system
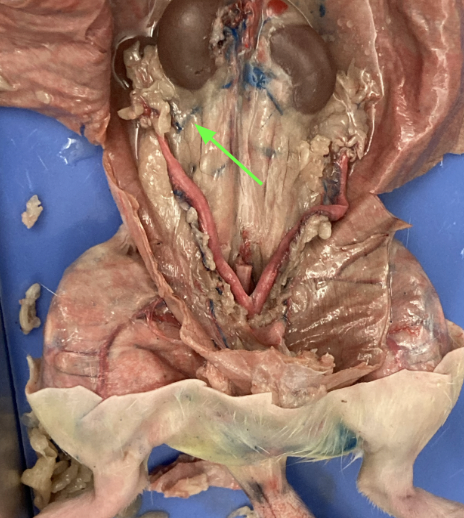
(picture unsure?)
ureters - attach to kidneys and lead to bladder, urogenital system
cortex and medulla (kidney)
cortex - outer area
medulla - inner area
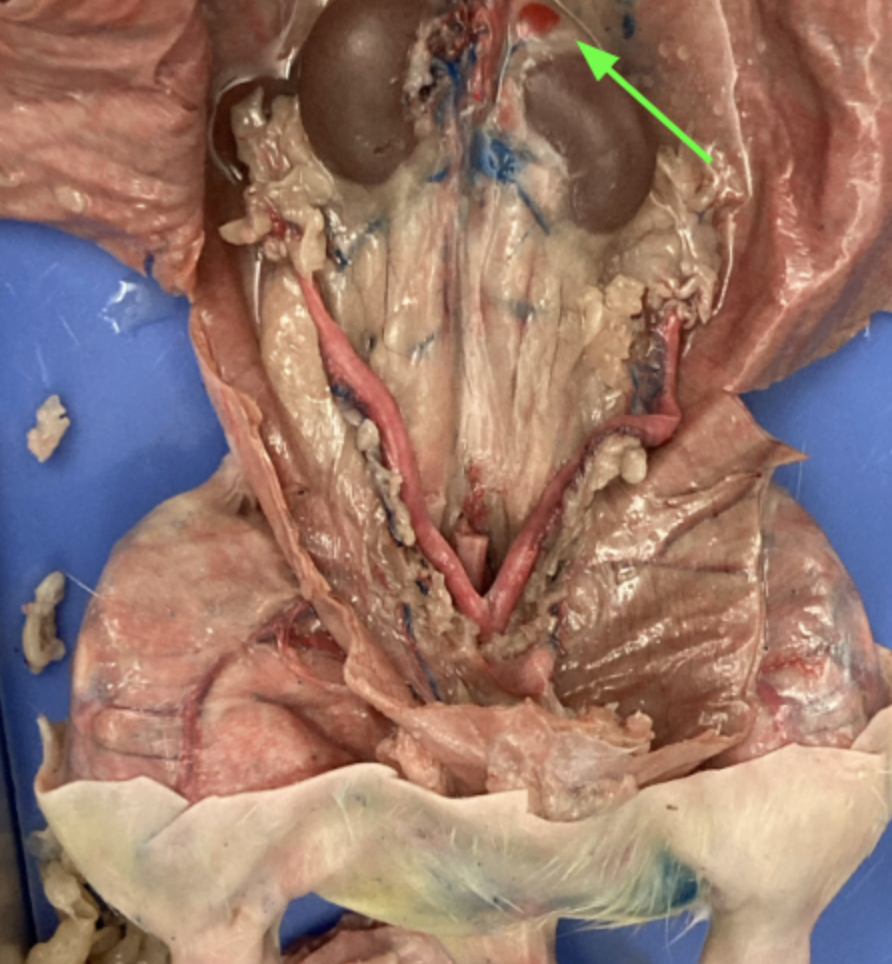
adrenal glands - yellowish glands above the kidneys, urogenital system
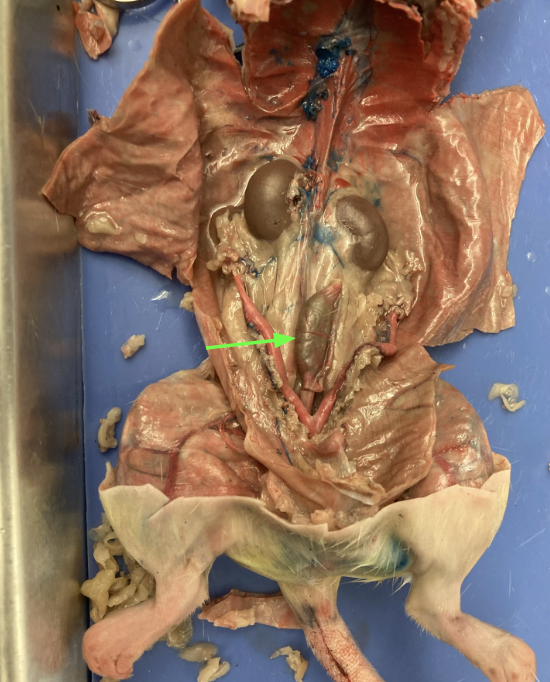
vagina - dorsal to urinary bladder, reproductive system
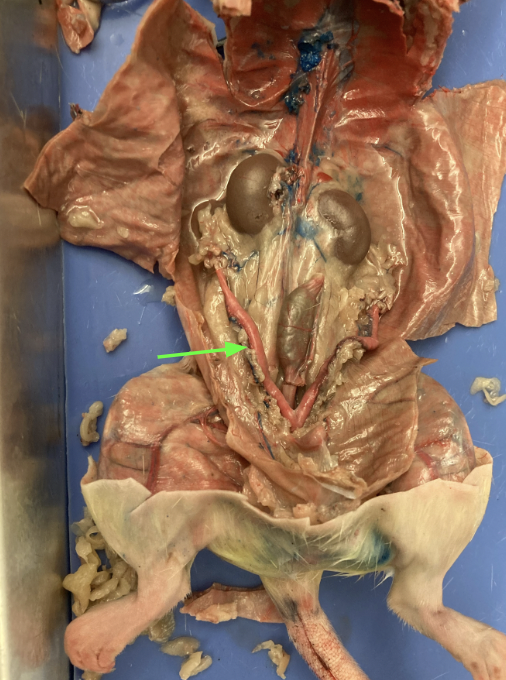
uterine horns, reproductive system
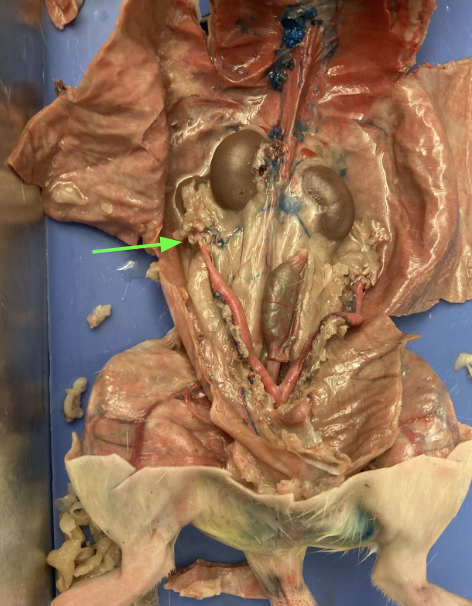
ovaries - tops of uterine horns, reproductive system
purpose of the circulatory system
move blood through the body
purpose of urogenital system
excretory system - removes waste
reproductive system - create gametes