week 2: the cell
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
32 Terms
cell/plasma membrane
outer boundary of the cell
selectively permeable
divides intracellular fluid from extracellular
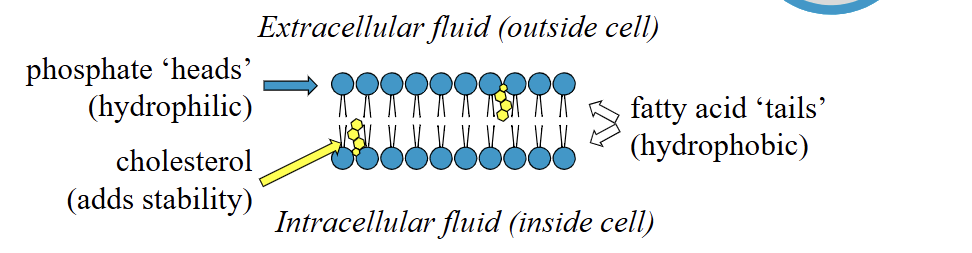
cell membrane: phospholipid bilayer
cell membrane: membrane proteins
function:
enzymes
form ion channels
transporters
hormone receptors
cell anchors
identity markers → for immune system
membrane proteins: integral vs peripheral proteins
integral: have hydrophobic and hydrophilic regions
transmembrane proteins: the ones that span the membrane completely
peripheral: attached to integral proteins on inner/outer surface of bilayer
cell membrane: membrane carbs
only on outer surface of cell
bound to proteins/glycoproteins or lipids/glycolipids
used to anchor cells together and for cell-to-cell recognition
ie: eggs, sperm
fluid-mosaic model of the cell membrane
cell surface is constantly changing as phospholipids and proteins are free to float around
cytoplasm
all cellular material between the cell membrane and nucleus
cytosol
gel-like ICF → mainly H2O
suspension of carbs, proteins, lipids, dissolved iron
site of many chemical reactions
higher K+ and lower Na- than ECF
may include inclusions → ie: melanin, glycogen
nuclear envelope
has 2 bilayer membranes → inner and outer
membrane is continuous with the ER
contains many pores
nucleolus (nucleoli)
non-membranous
dense, dark staining region of DNA, RNA, proteins within the nucleus
generally 1 or 2 per cell
site of ribosome production and assembly
chromosomes/chromatid
composed of DNA coiled around histone proteins
found in 2 states
chromatin
DNA strands not individually visible
most common state
present when cells aren’t dividing
chromosomes
condensed, individually visible bar-like bodies found only during the process of cell division
either:
single bars
pair of sister chromatids
somatic cells
all cells of the body except those undergoing/resulting from meiosis → gametes
nuclei is diploid → 2n = 46 chromosomes
autosomal chromosome pair
not identical but equivalent → 1 homologous chromosome from each parent
similar in length, centromere position, have genes for same traits at same locus
may have different alleles of genes
interphase
period of normal cell metabolism and growth
DNA and histone proteins present as chromatin
cells that no loner divide are in G0 phase
interphase: G1 phase
rapid cell growth
centrosome replication begins
interphase: S/synthetic phase
DNA replicates, new histone proteins are made
resulting chromatin pairs → each strand termed a chromatid
held together by centromeres
kinetochores (protein) form on each centromere
site of attachment of spindle microtubules
interphase: G2 phase
additional growth and protein synthesis
production of enzymes and proteins needed for cell division
centrosome replication is completed → is initiated in G1
cell division: M-phase
essential for growth, tissue repair, reproduction
involves:
mitosis: division of the nuclear material → chromosomes
cytokinesis: division of the cytoplasm
mitosis
production of 2 identical daughter cells → 1hr
occurs only in somatic cells
mitosis: prophase
chromatin condenses, coils → becomes individually visible
nuclear envelope disintegrates, nucleolus disappears
centrosomes move to opposite poles of the cell
microtubules grow + attach to kinetochore proteins = spindle apparatus
spindles begin moving chromosomes towards cell equator
mitosis: metaphase
all 46 double-stranded chromosomes line up along cell equator
mitosis: anaphase
spindle microtubules shorten causing centromeres to split → 92 single-stranded chromatids
spindle pulls 46 to each pole
cytokinesis beings
mitosis: telophase
spindle apparatus disassembles
chromatids uncoil and nucleolus reappears
a nuclear envelope forms around each chromatin mass
cytokinesis ends → the two cells split
meiosis
production of gametes
one diploid (2n) creates 4 genetically distinct haploid (1n) cells
meiosis: similarities to mitosis
prophase 1 and 2
anaphase 1 and 2
telophase 1 and 2
meiosis: unique processes
P1: homologous chromosomes pair and align gene-to-gene during synapsis = tetrad
crossing over between non-sister chromatids occurs here
M1: tetrad orientation during lining up is independent of others
A1: separation of homologous chromosomes → sister chromatids remain attached at the centromere
produces haploid cells
interkinesis
interphase like period
no DNA replication occurs during this phase
happens before meiosis 2
cell membrane composition
phospholipid bilayer + cholesterol (stability) + membrane protein (integral + peripheral) + membrane carbs
2 divisions of the cytoplasm
cytosol: gel-like fluid = H20 + ions + suspended molecules
organelles
3 types of cytoskeletons
microfilaments: made of actin
intermediate filaments: tissue specific → ie: keratin
microtubules: hollow tubes of tubulin