SEM2 The Ear Anatomy and Physiology
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
pharyngotympanic tube
connects middle ear to throat
opens when you yawn or swallow, which equalizes pressure in middle ear ( eardrum will only function if pressure inside/out is equal )
What are the smallest bones in the body?
malleus
incus
stapes
Inner ear
maze of body chambers called labyrinth
3 divisons
vestibule
cochlea
semicircular canals
labyrinth filled with perilymph ( fluid )
hearing
vibrating air particles
sound waves are directed into the auditory canal ( helped by pinna )
sound waves reach the eardrum, causing it to vibrate
vibrations are passed through the malleus, incus, then stapes
the stapes then presses on the oval window of the cochlea, which contains fluid
organ of corti
within the cochlea converts vibrations to a nerve impulse
fluid within cochlea starts to move
movement causes the tectorial membrane to move
membrane then causes the hair ( receptors ) on basilar membrane to move
the hairs then transmit a nerve impulse to the cochlear nerve
equilibrium ( balance )
involves vestibule and semicircular canals
one branch is responsible for static equilibrium, the other, dynamic equilibrium
static equilibrium
maculae receptors in the membrane of vestibule
each macula is a patch of receptor cells with “ hairs “ embedded in otolithic membrane
membrane contains otoliths ( calcium salts )
when head moves up+down, otoliths move
causes gel to move
gel moves hair
hair sends impulses along the vestibular nerve to the cerebellum
these receptors respond to gravity ( up+down )
dynamic equilibrium
receptors in semicircular canals
respond to angular, rotary head movements
receptor region called crista ampullaris
consists of tuft of hair cells and cupula ( gel cap )
when head moves, endolymph ( fluid ) lags behind
as cupula drags against, it bends
stimulates the hair cells which creates an impulse to send up the vestibular nerve to cerebellum
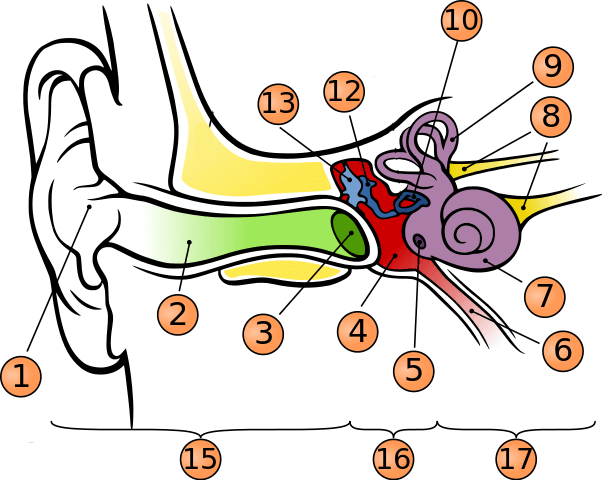
What is number 1?
pinna
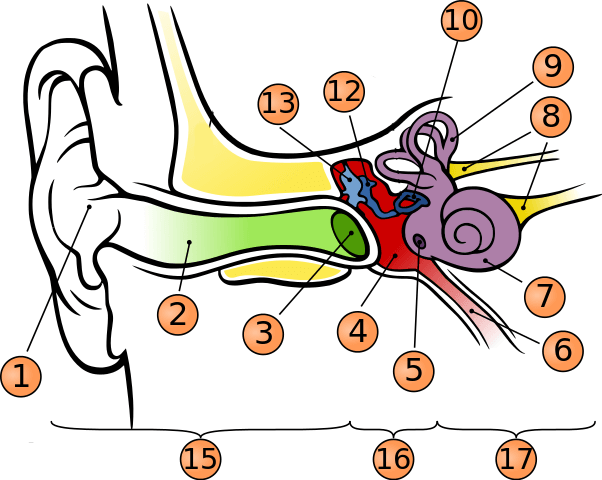
what is number 2?
auditory canal
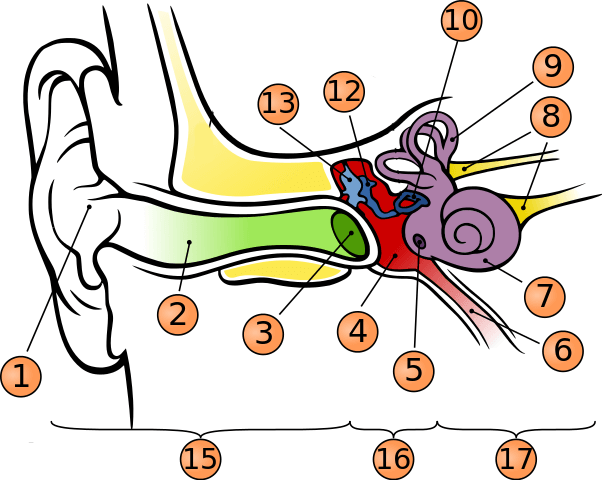
what is number 3?
tympanic membrane
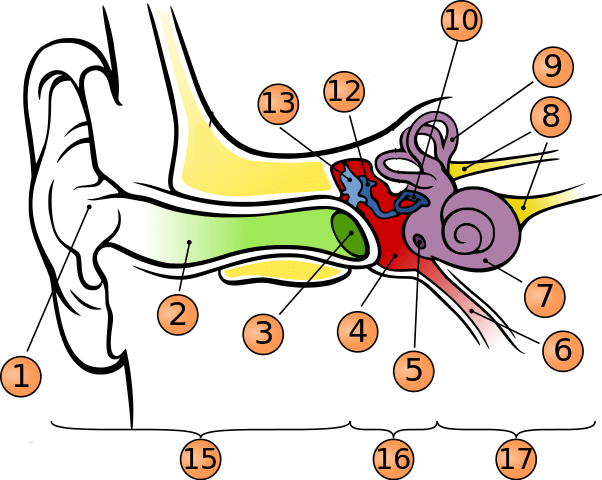
what is number 5?
round window
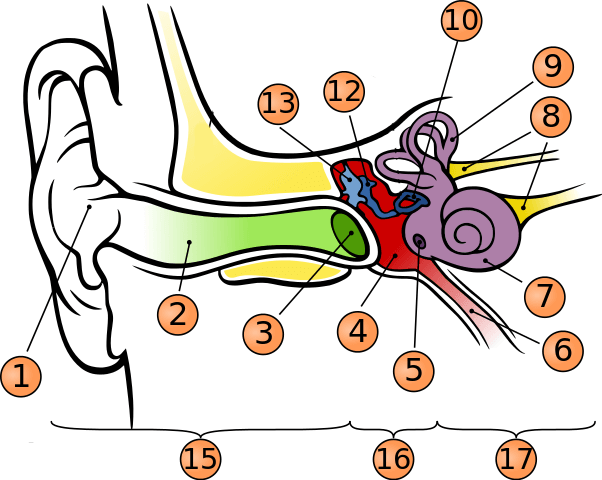
what is number 6?
phanymgotypanic tube
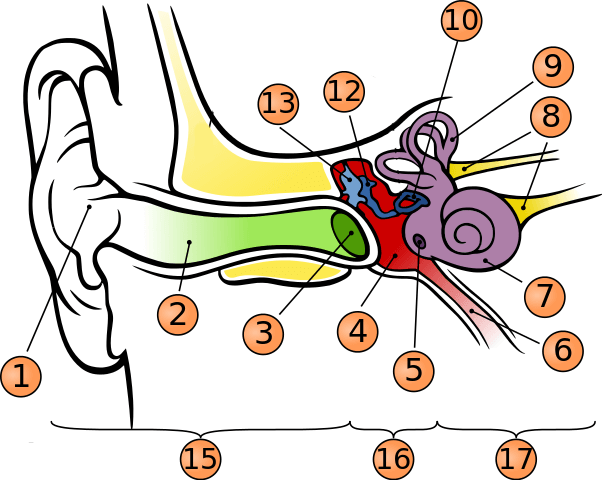
what is number 7?
cochlea
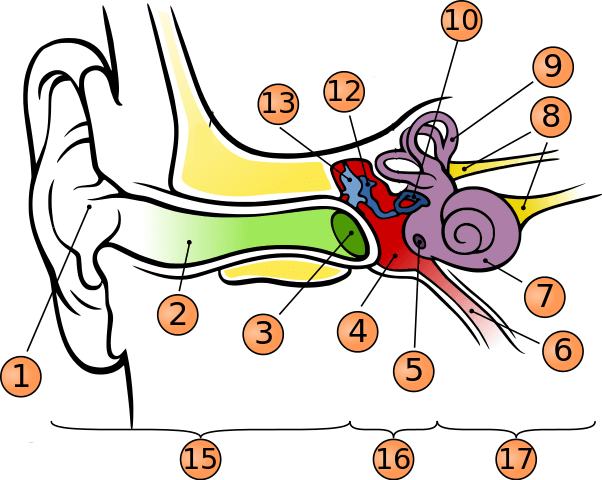
what is number 9?
semicircular canals
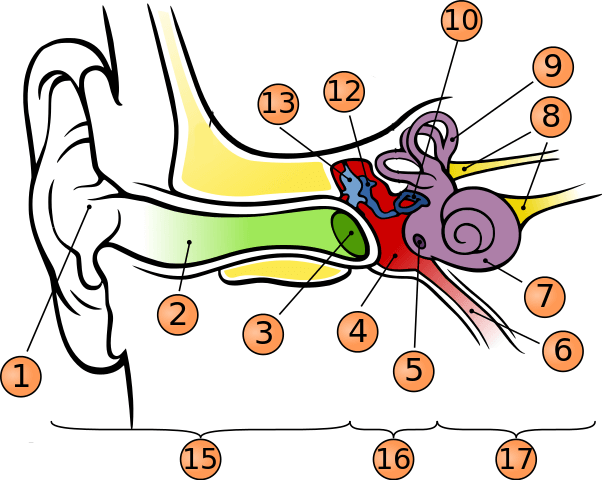
what is number 10?
stapes
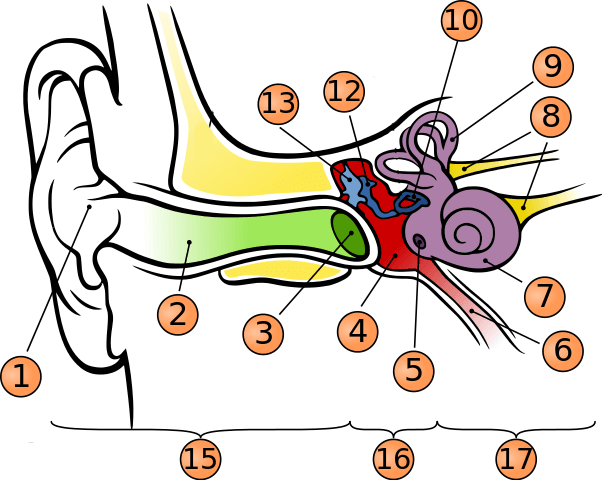
what is number 12?
incus
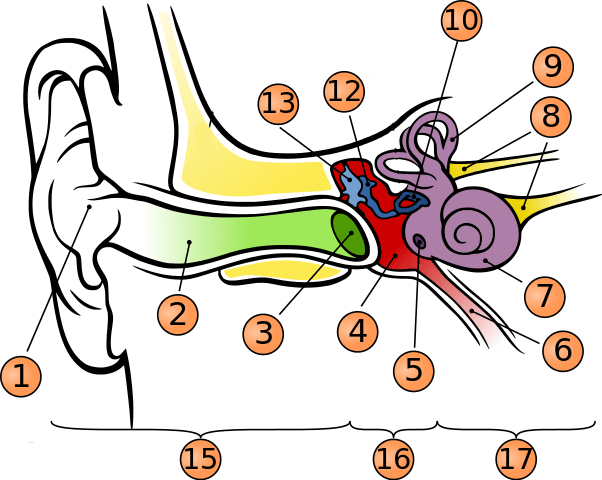
what is number 13?
malleus
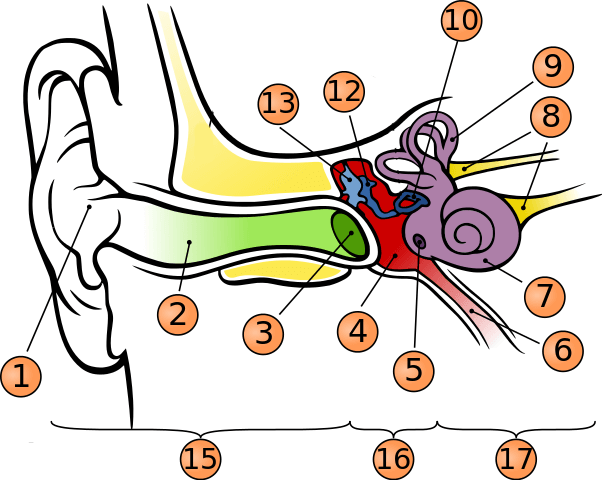
what is number 15?
outer ear
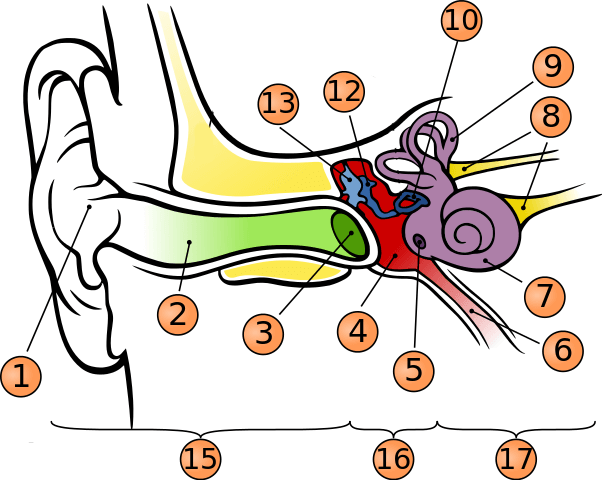
what is number 16?
middle ear
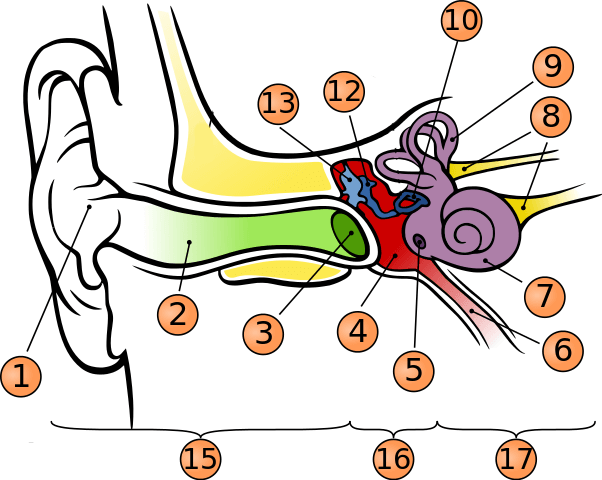
what is number 17?
inner ear
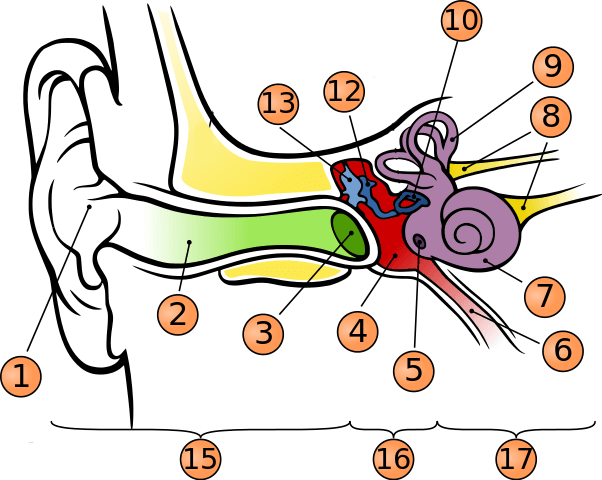
where is oval window?
in the middle of stapes
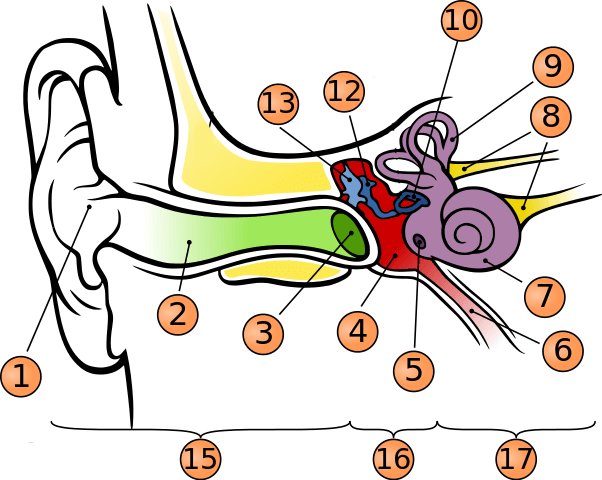
where is vestibule?
to the left of cochlea