NE101 Lec 13: Vision I
1/64
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Focuses on eye anatomy, light transduction, and visual processing.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
65 Terms
sensory transduction
convert external modality into electrical charges
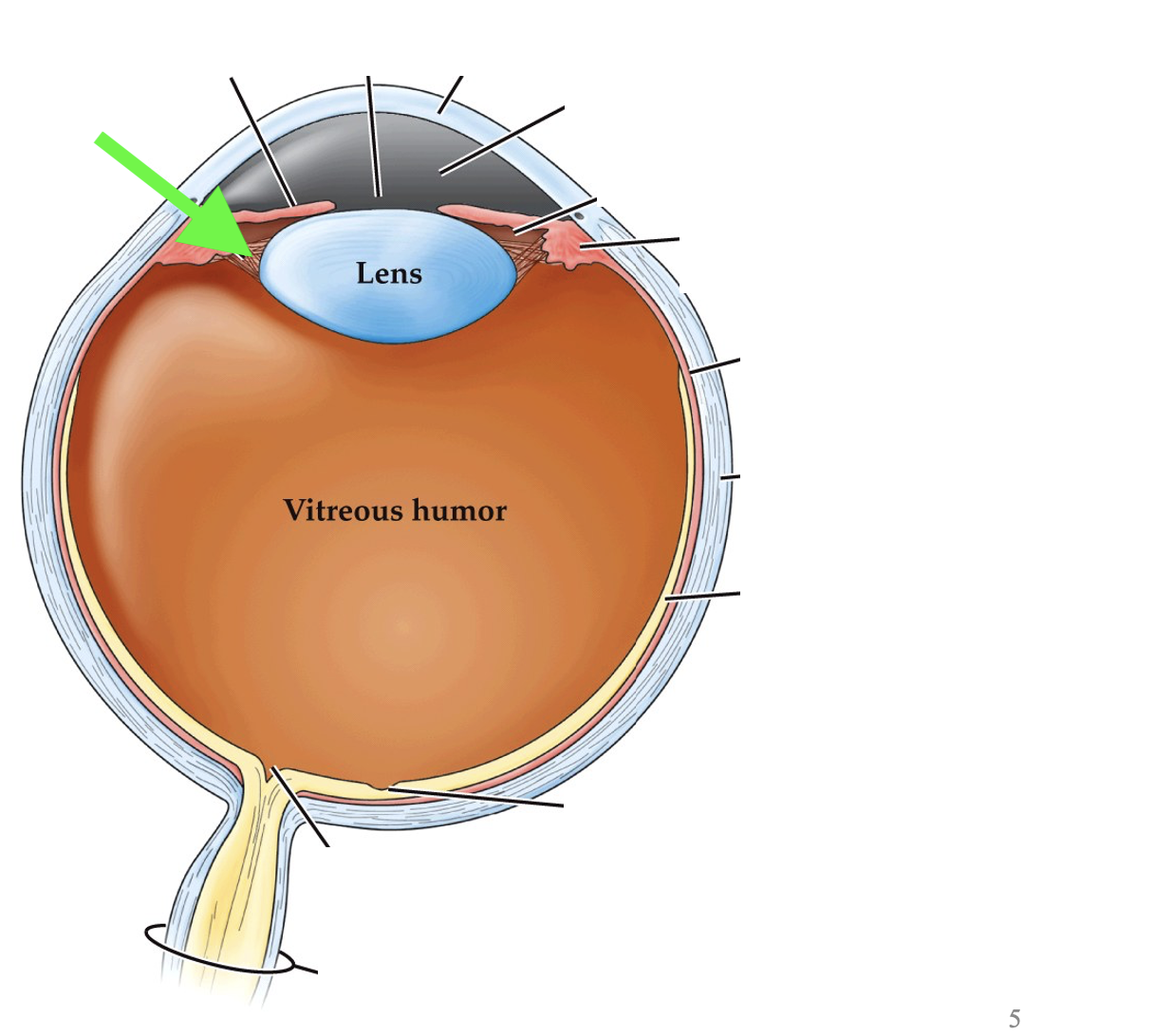
what part of the eye is this?
zonule fibers
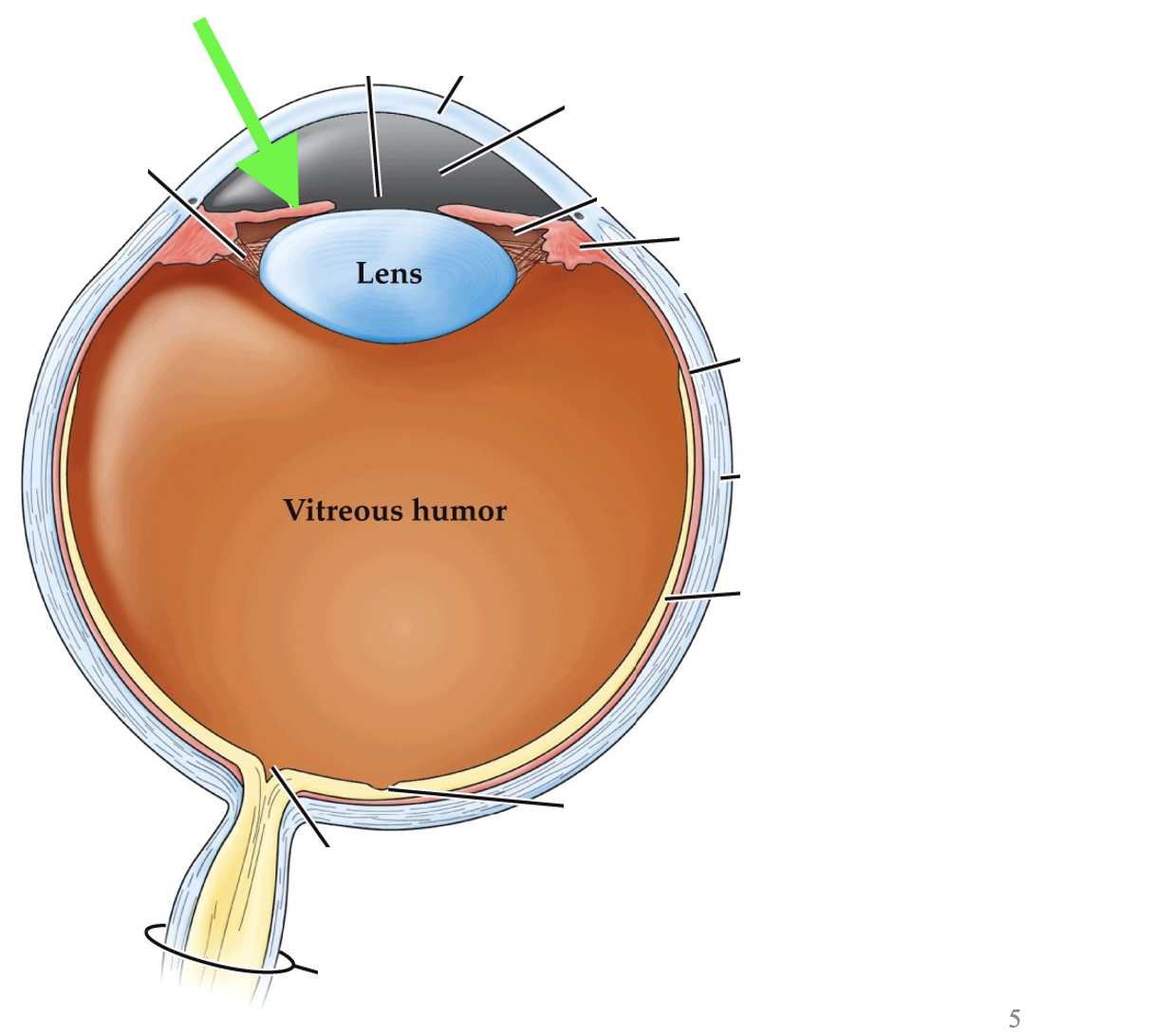
what part of the eye is this?
iris
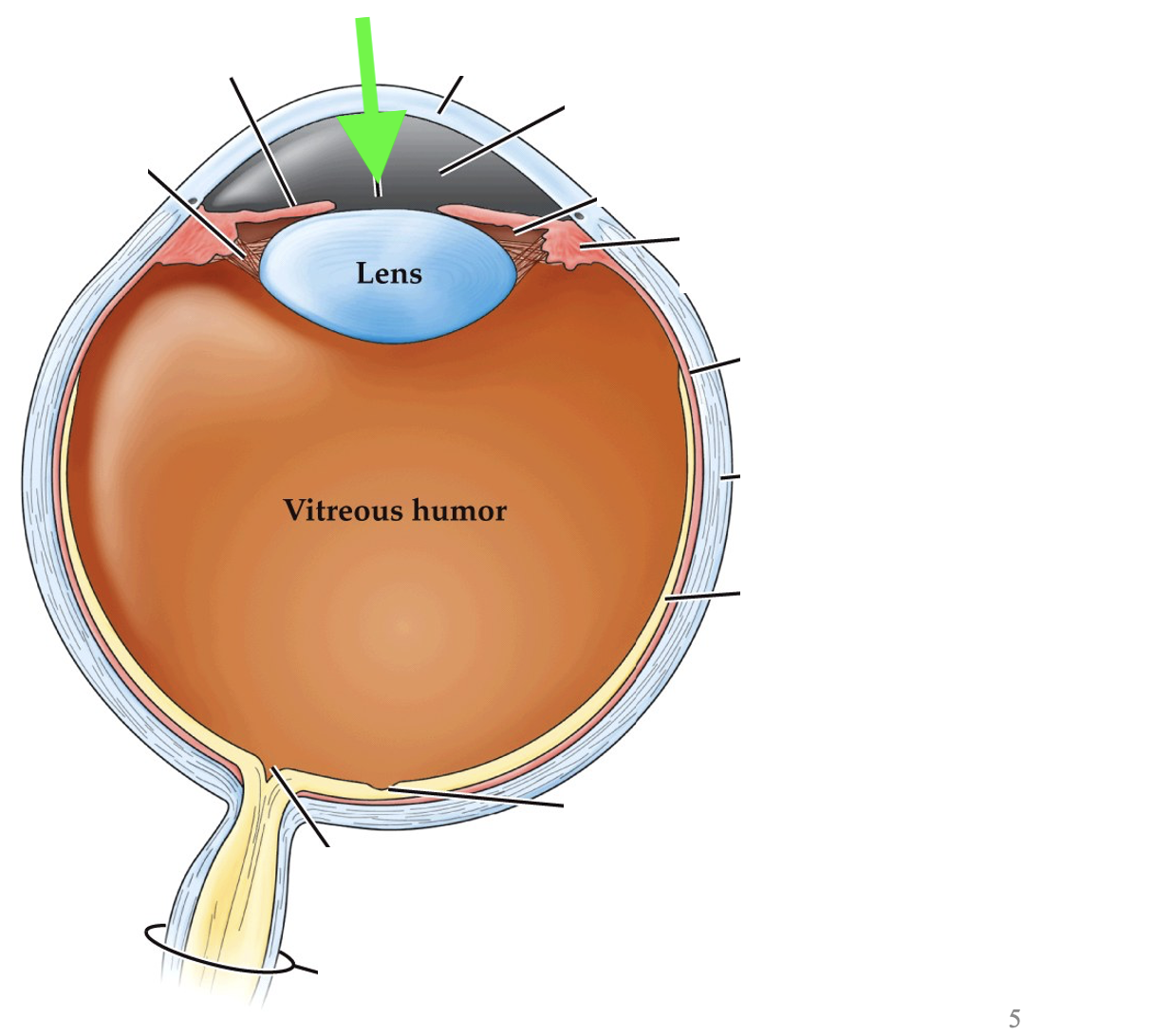
what part of the eye is this?
pupil
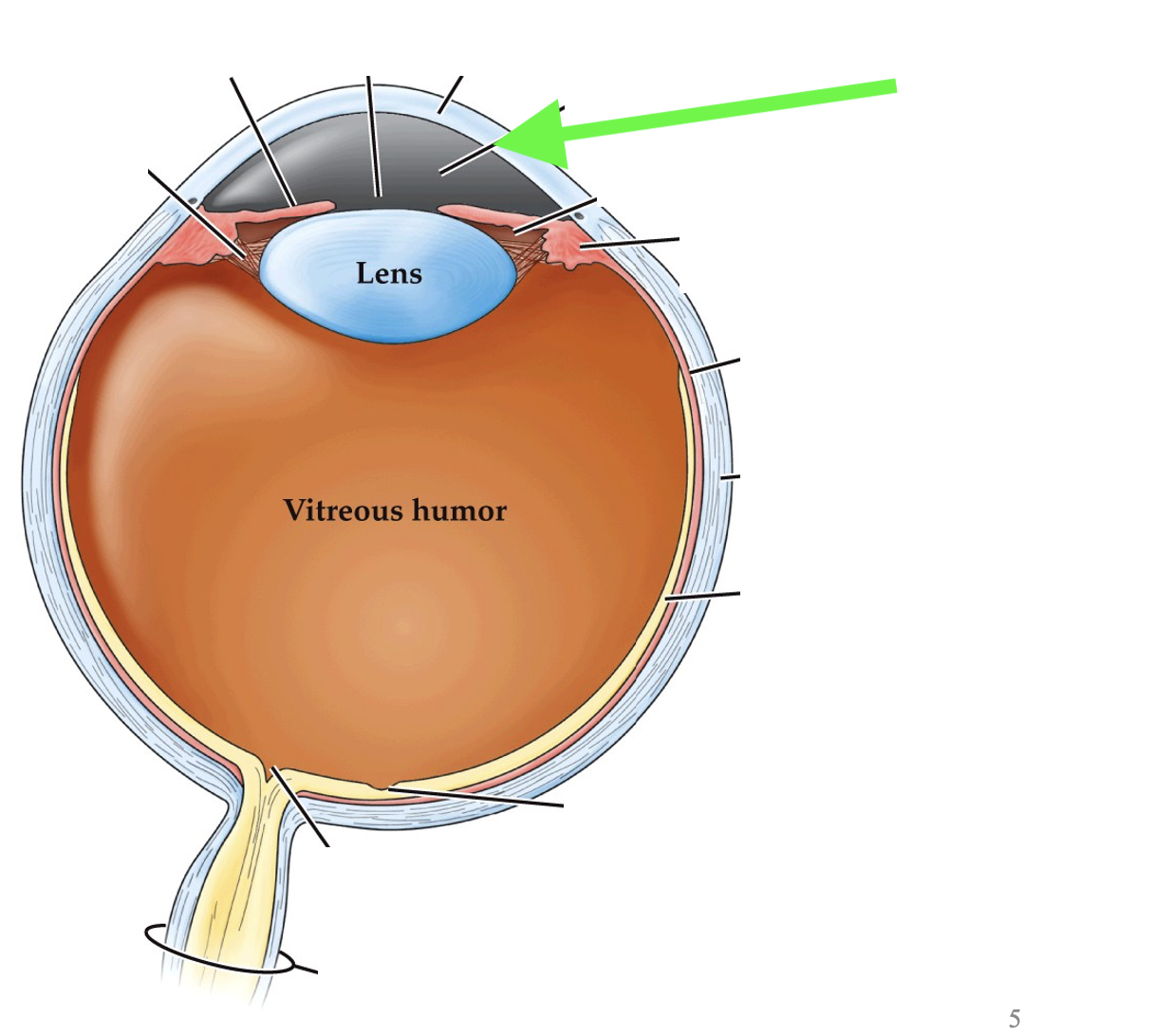
what part of the eye is this?
cornea
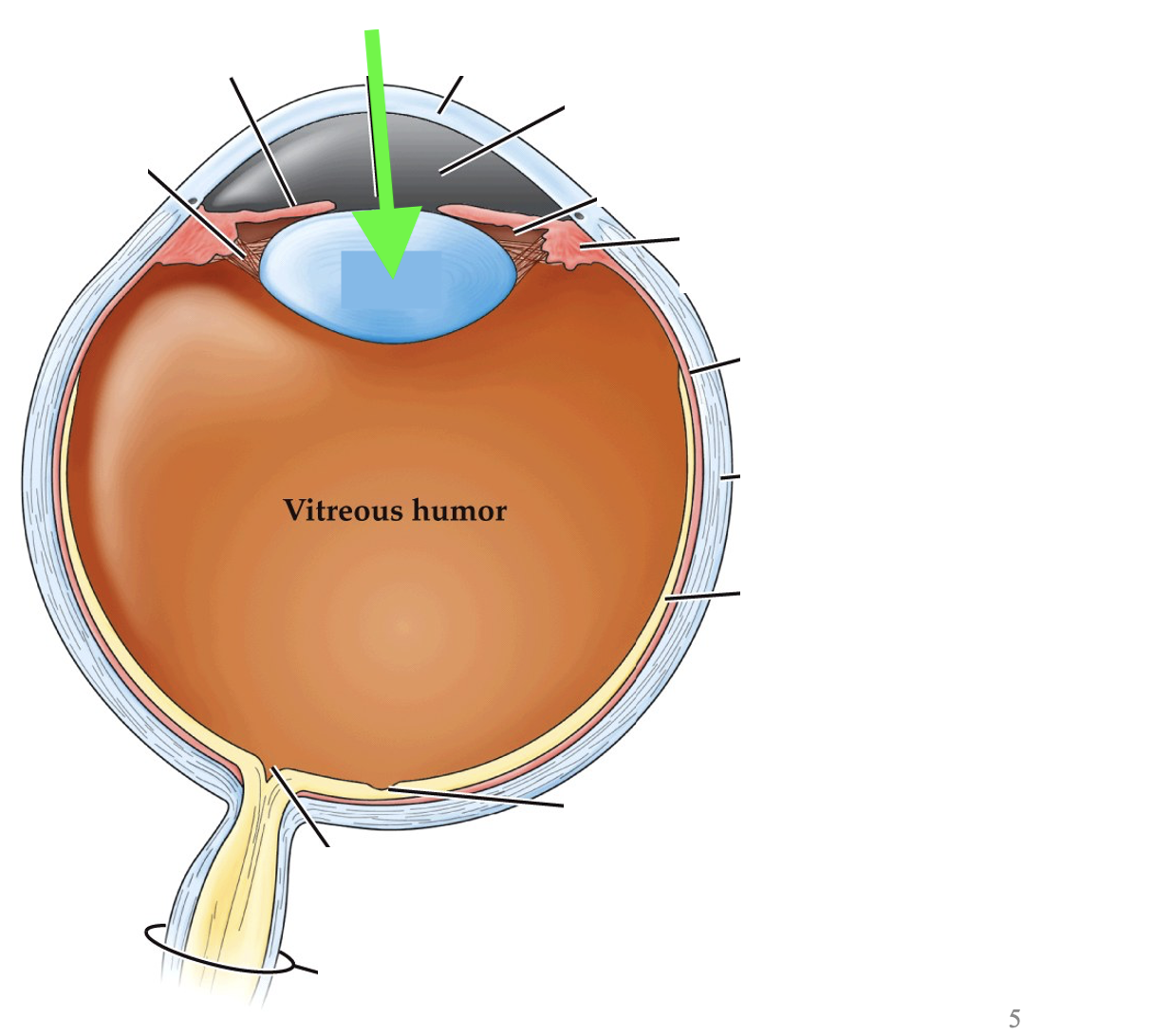
what part of the eye is this?
lens
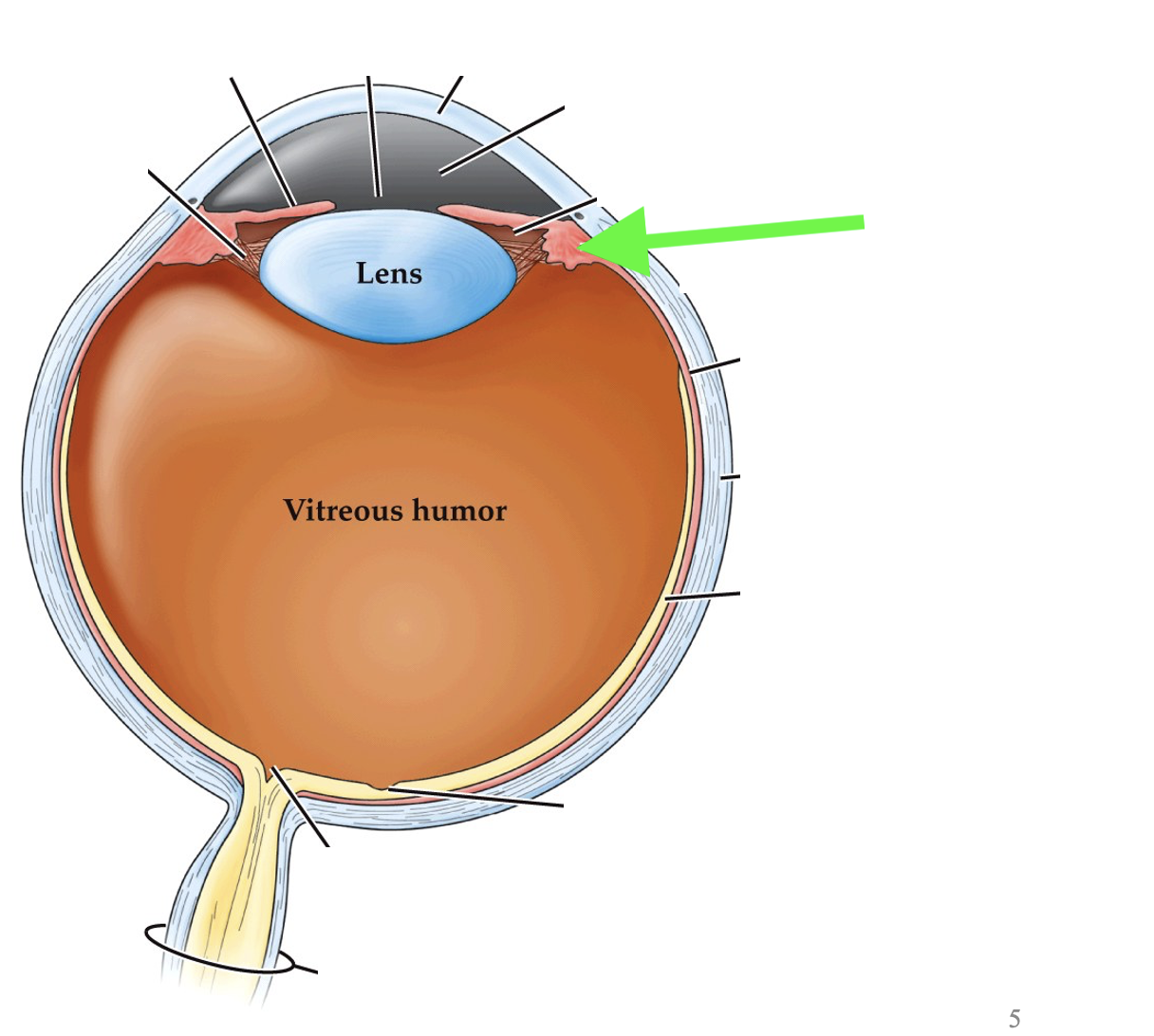
what part of the eye is this?
ciliary muscle
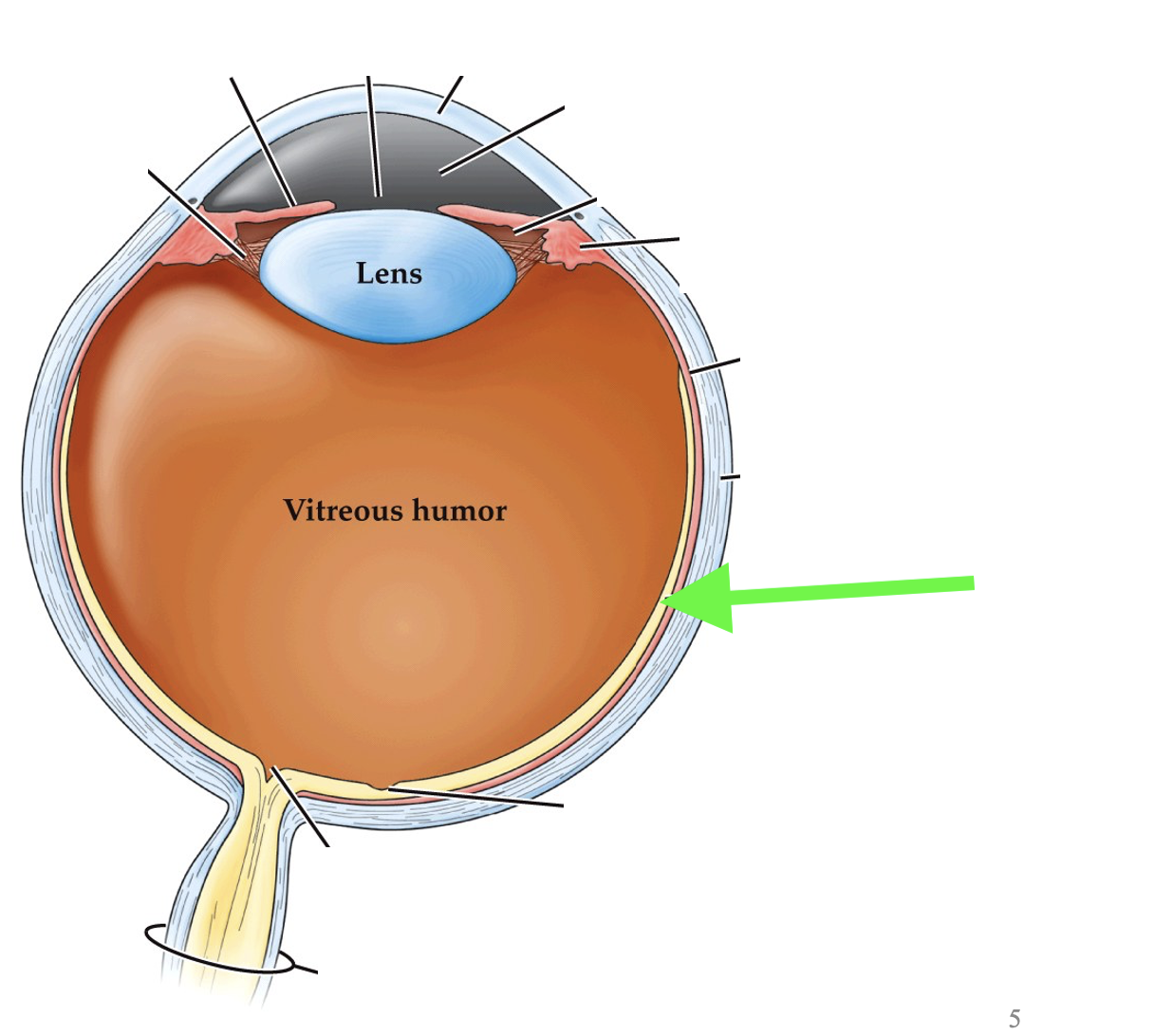
what part of the eye is this?
retina
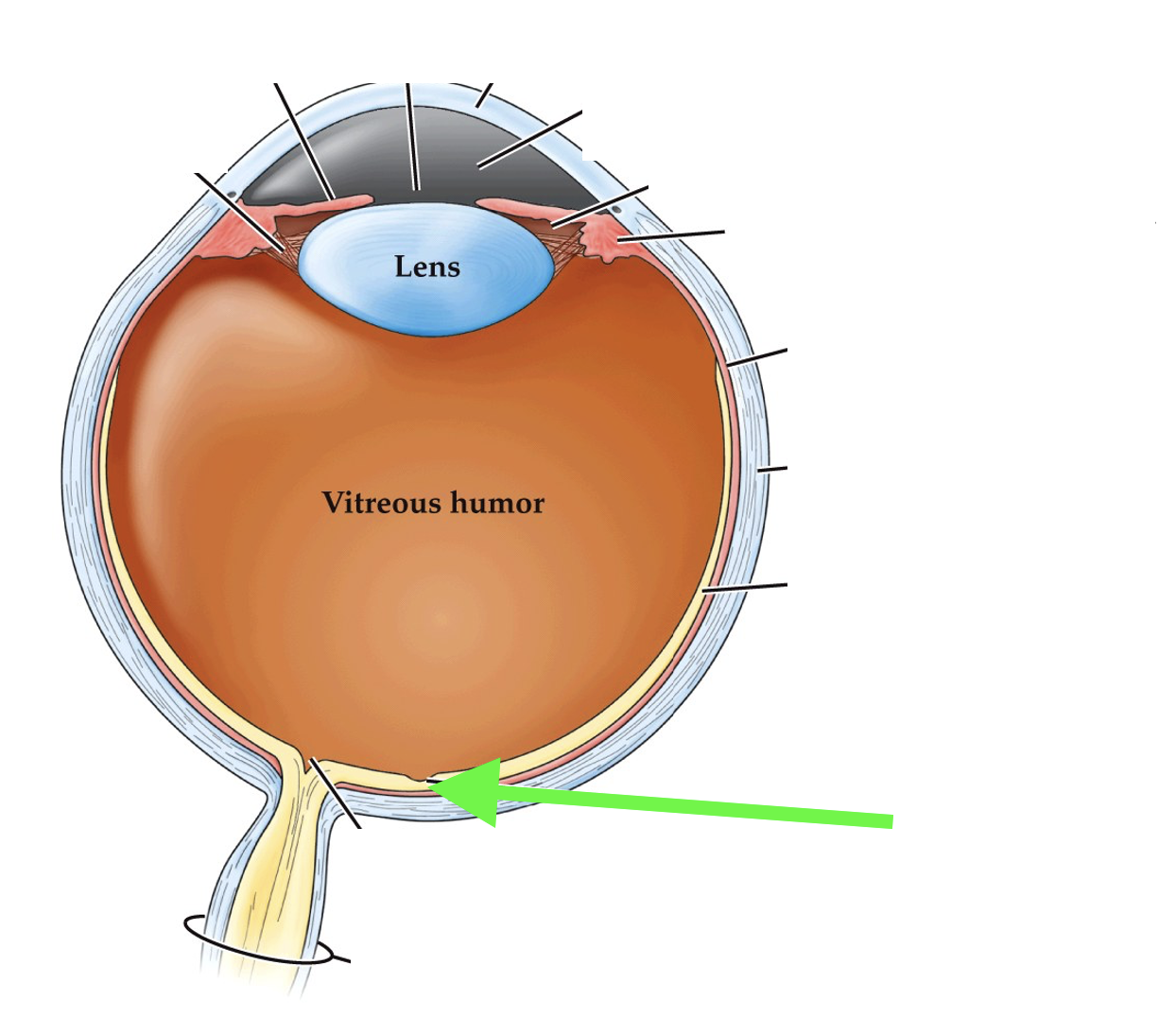
what part of the eye is this?
fovea
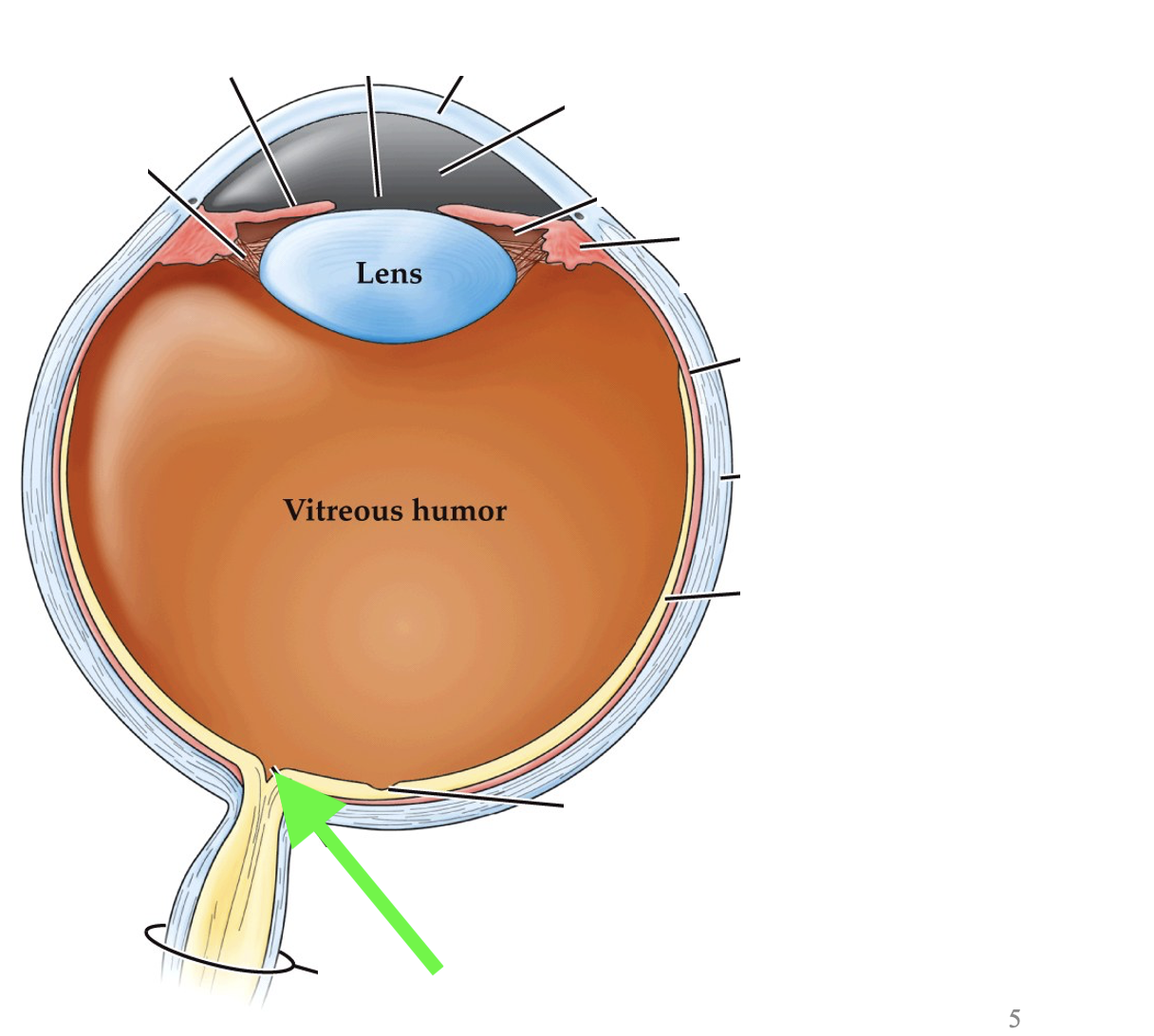
what part of the eye is this?
optic disk
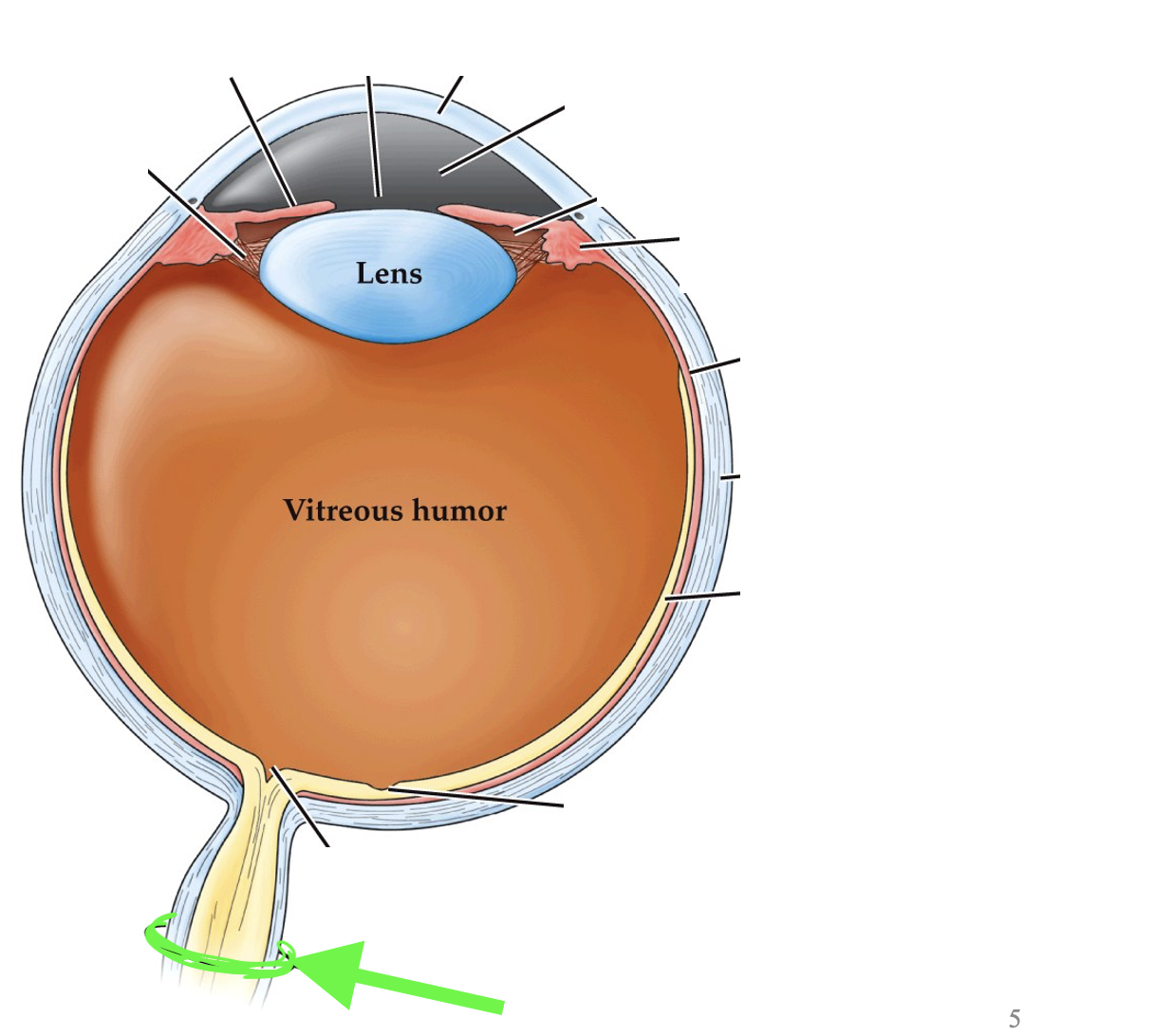
what part of the eye is this?
optic nerve
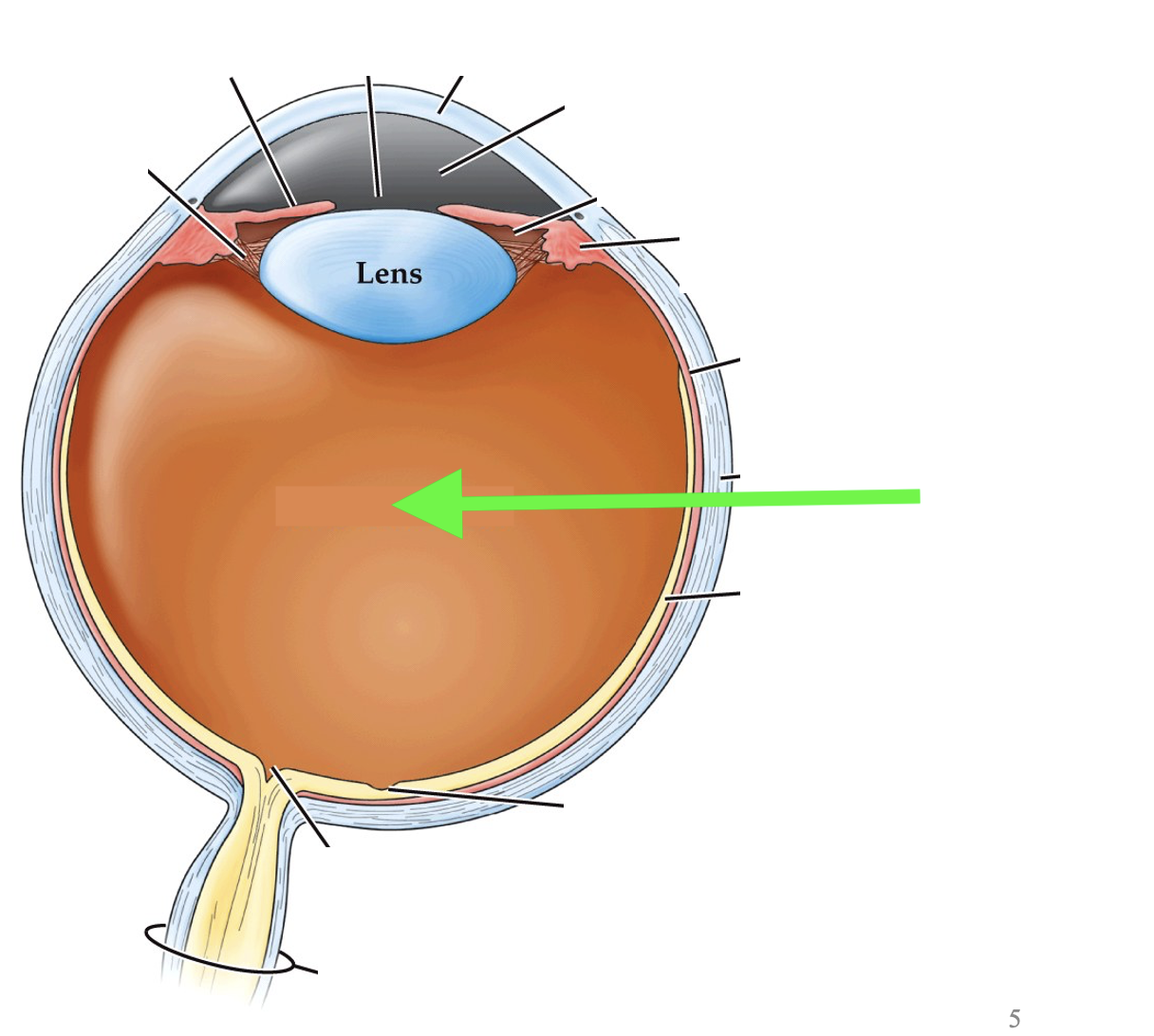
what part of the eye is this?
vitreous humor
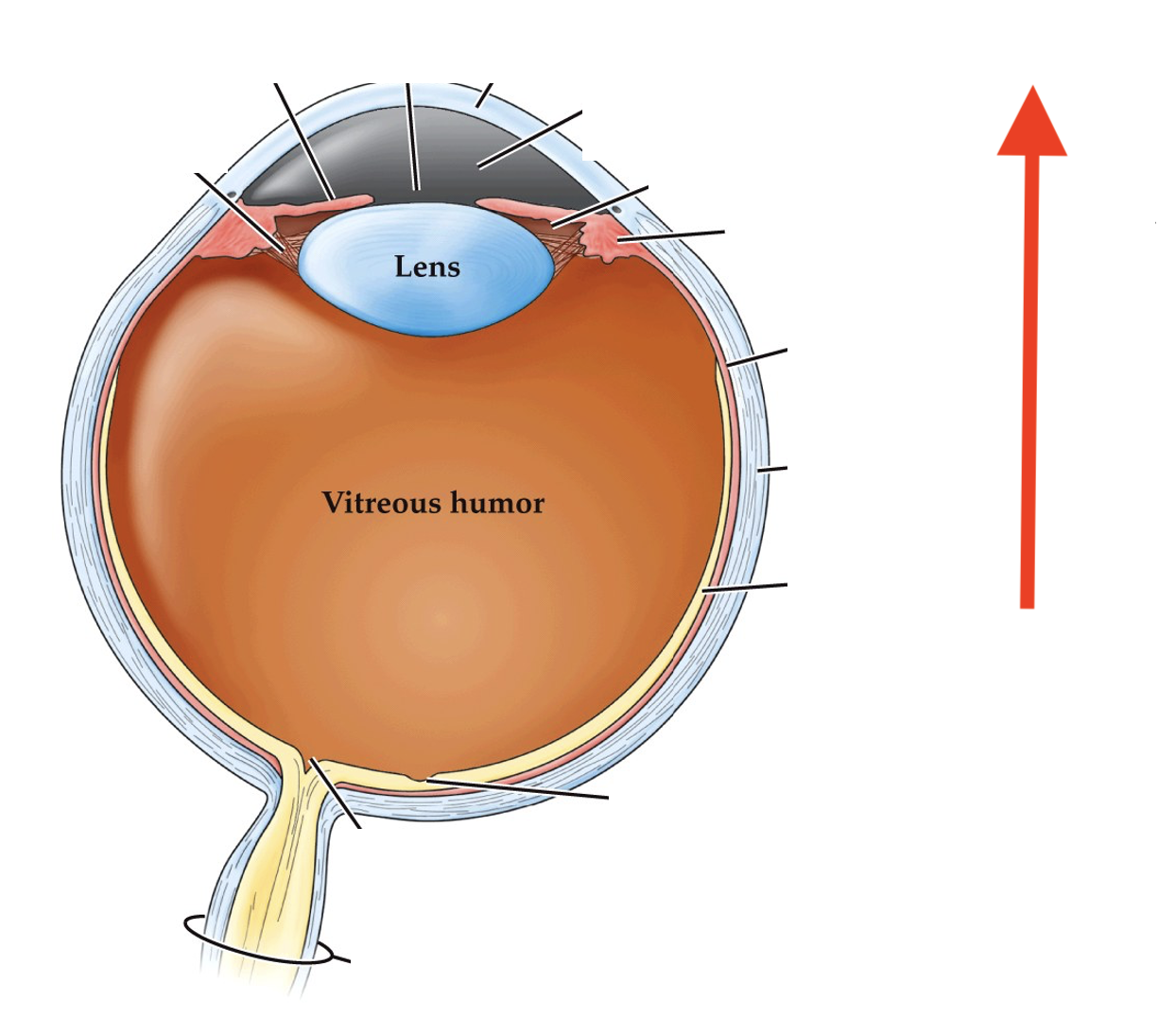
what direction of the eye is this?
anterior
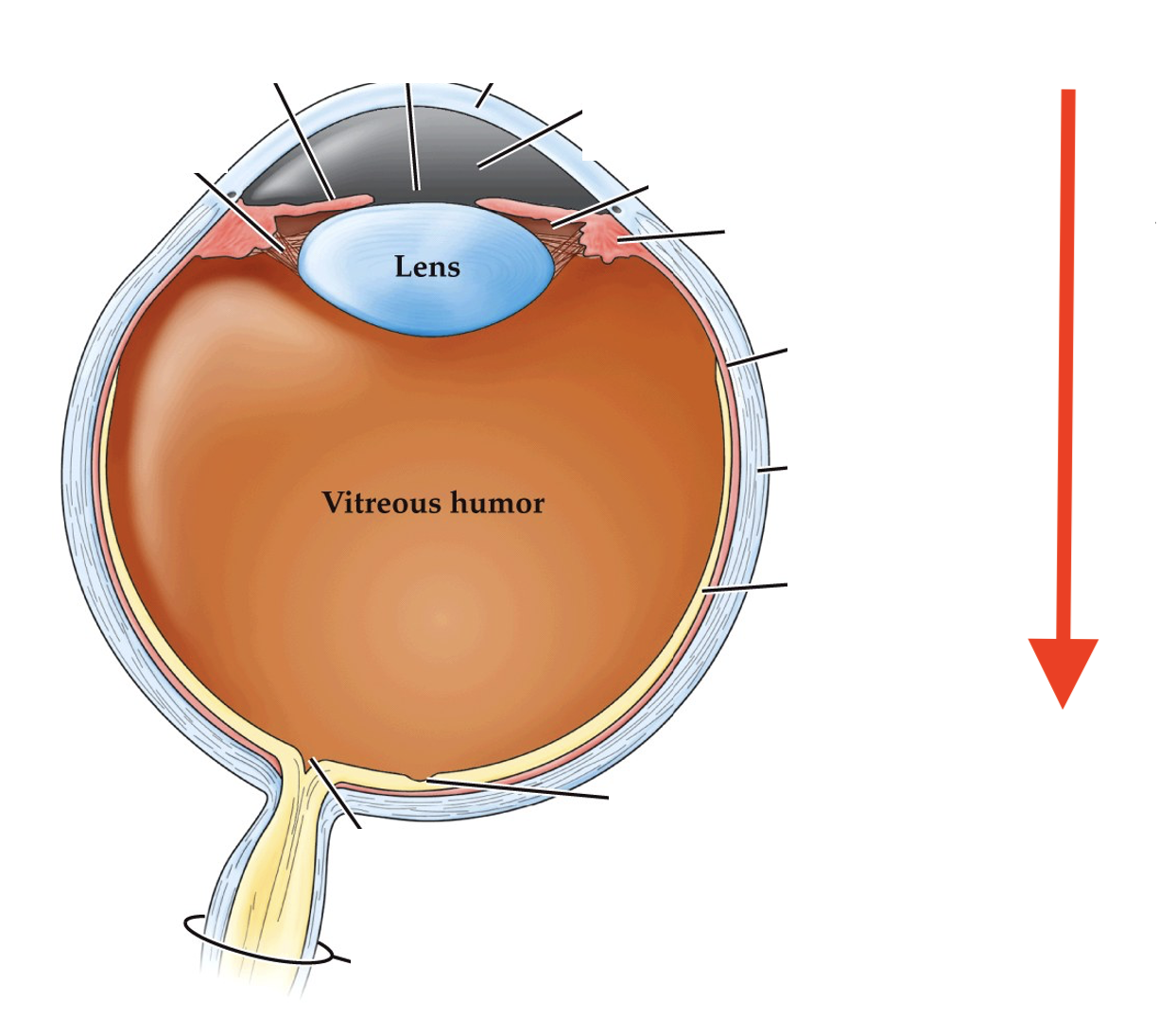
what direction of the eye is this?
posterior
refraction
bending of light from one medium (air) to another (water/glass/tissue)
focal distance
distance between the cornea and the retina at which light rays converge
ciliary muscle function
controls lens shape
_____ determines how light is bent
lens thickness
what is accomodation?
the process of changing the lens to focus on things closer or farther away
Humans can see wavelengths from about ________ to ________ nm.
400 to 750
The ________ and ________ focus light on the retina.
cornea, lens
The retina contains ________ that transduce photons into neuronal activity.
photoreceptors
The retina sends signals through the ________ nerve (CN II).
optic
The ________ is the region of the retina with the highest visual acuity.
fovea
A long, thin lens bends light ________ and focuses on ________ objects.
less, far
A short, thick lens bends light ________ and focuses on ________ objects.
more, near
When ciliary muscles are relaxed, the lens becomes ________.
thin
When ciliary muscles contract, the lens returns to its ________/normal shape.
thick
Hyperopia (farsightedness) occurs when the eyeball is too ________.
short
Hyperopia requires a ________ lens to converge light.
convex
Myopia (nearsightedness) occurs when the eyeball is too ________.
long
Myopia requires a ________ lens to diverge light.
concave
Pupil constriction occurs in ________ light and is controlled by the ________ nervous system.
bright, parasympathetic
Pupil dilation occurs in ________ light and is controlled by the ________ nervous system.
dim, sympathetic
Constriction allows ________ light in and ______ depth of focus.
less, increases
Dilation allows ________ light in but ______ depth of focus.
more, decreases
The retina is part of the ________ nervous system.
central
The ________ is the center of the visual field on the retina.
fovea
The ________ spot contains no photoreceptors.
blind
The blind spot doesn’t affect vision much because of ________ vision.
binocular
The outer segment of photoreceptors is where ________ occurs.
transduction
_____ are more sensitive to light but do not detect color.
rods
______ are less sensitive to light but detect color.
cones
Near the fovea, there are more ________, giving high color and spatial resolution.
cones
Away from the fovea, there are more ________, giving better low-light sensitivity.
rods
Photoreceptors have a resting potential around ________ mV.
-30
Sodium channels in photoreceptors are activated by ________.
cGMP
Light exposure ________ cGMP, closing sodium channels and ________ the cell.
reduces, hyperpolarizes
Photoreceptors release ________ in the dark and less of it in the light.
glutamate
______ is a g-coupled receptor that acts as a photosensor.
rhodopsin
When light hits rhodopsin, it activates the G-protein ________.
transducin
Light → retinal change → transducin activation → ↓cGMP → ________ close → membrane hyperpolarizes.
sodium channels
Short cones detect ________ light, medium cones detect ________ light, and long cones detect ________ light.
blue, green, red
Color vision results from activation of different ________ of cones.
proportions
Each cone type has a distinct ________ protein.
photosensor
Color blindness results from dysfunction or absence of specific ________ receptors.
cone
About ________% of the population is affected by color blindness.
5
Photoreceptors and bipolar cells fire ________ potentials.
graded
Only ________ cells in the retina fire action potentials.
retinal ganglion
On-center bipolar cells are ________ when light hits the center of their receptive field.
depolarized
Off-center bipolar cells are ________ when light hits the center.
hyperpolarized
The receptive field is the region of visual space that a cell ________ to.
responds
On-center retinal ganglion cells increase firing when light hits the ________ of their receptive field.
center
Off-center retinal ganglion cells increase firing when light hits the ________.
surround
On-center and off-center organization helps detect ________ in light intensity and contrast.
changes