Gregor Mendel Principles unit 4
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms

Monophonic crossing experiments
Gregor Mendel’s ____ ____ ____ produces the results that turned the principles of genetic science
He Developed The ____ ____ ____ To Investigate The Rules That Govern The Transmission Of One Trait From Parent To Offspring
He Replicated Each Monohybrid
Crossing Experiments Many Times
• This Increased The Probability Of Detecting Significant Patterns In The Results
Monohybrid crossing experiment
Parents With One Different Trait Are Mated (Crossed)
• Each Parent Breeds True For The Trait Of Interest
The Ratio Of The Two Traits In The F1 Offspring Is Determined
The F1 Offspring Are Mated
With Each Other
The Ratio Of The Two Traits
In The F2 Offspring Is Determined
Mix
The Two Different Traits Inherited From Each Parent Do Not ___ In Offspring
each parent transmits one unit of heredity (allele) to their offspring
2 alleles
A diploid (2N) individual has ___ _____ for the gene that regulates the flower color trait
Offspring Inherit One Allele From Each Parent
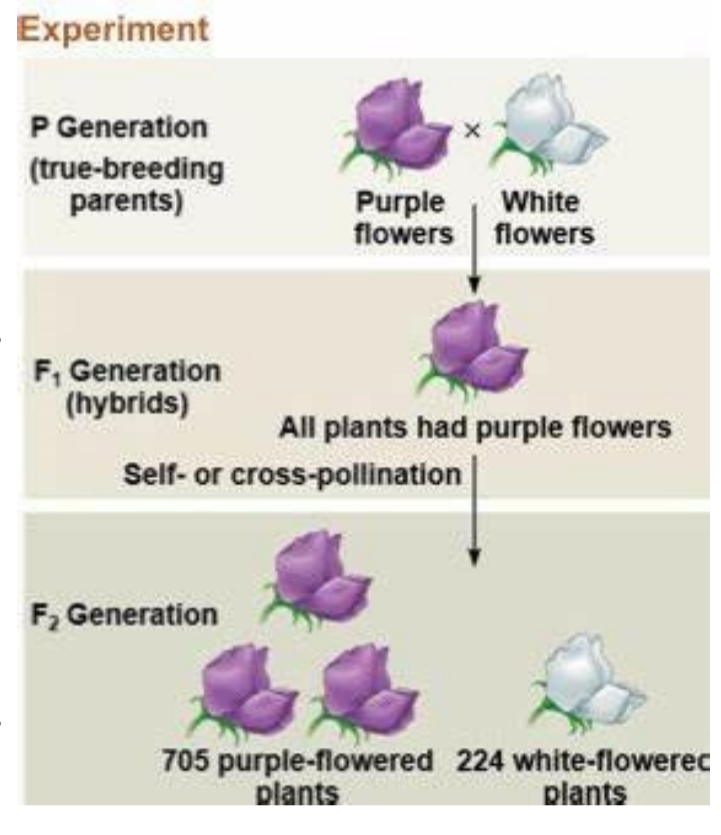
This Explanation Accounts For The 3:1 Ratio Of Purple Flowers To White Flowers Mendel Observed In The F2 Generation Of Offspring
One
Each parent transmits ____ of the 2 alleles for each gene to their offspring
Meiotic Cell Division Enables Diploid (2N) Individuals To Produce Haploid (1N) Gametes
• Each Haploid Gamete (1N) Has One Copy Of Each Chromosome And Consequently One Allele For Each Gene
Law of segregation
Gregor Mendel’s ____ ____ _____ :
The 2 alleles that control a train separate during meiosis and each allele enters a different gamete
Gregor Mendel Documented The Existence Of Dominant Phenotypes & Recessive Phenotypes
In Some Heterozygotes, Only One Of
The Two Alleles For A Gene Is
Expressed In The Phenotype
• The Expressed Allele Causes A
Dominant Phenotype (Dominant Trait)
• The Unexpressed (Hidden) Allele
Causes A Recessive Phenotype
(Recessive Trait)
This Conclusion Is Based On The
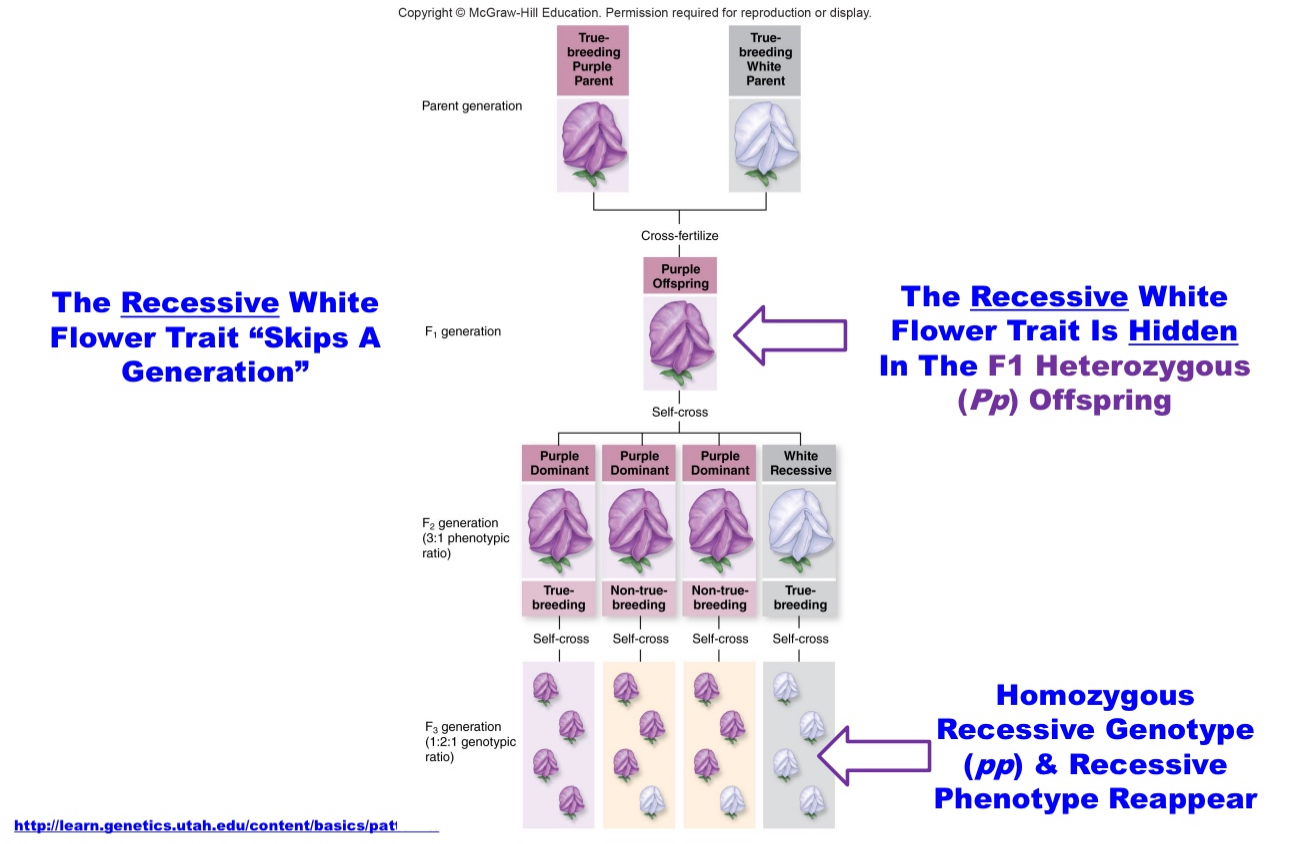
Observation That All Heterozygotes In The F1 Monohybrid (Pp) Generation Always Expressed The Purple Flower Phenotype
Recessive trait (read the pic)
A ____ ___ That Remains Hidden In The F1
Generation Can Reappear In The F2 Generation
Test cross experiment
Determines the genotype of individuals with a dominant phenotype
The ____ ____ mates the individual expressing the dominant phenotype with an individual expressing the recessive phenotype
The parent with the homozygous recessive genotype (pp) always produces gametes with the recessive allele (p)
Achondroplasia
The genetics of _______: The “a” allele causes the recessive wild-type phenotype the mutated “A” allele causes it he dominant reduced height phenotype
Achondroplasia
______ is due to a mutation in the fibroblast growth factor receptor 3 gene that reduces bone growth
Homozygous lethal genotype
If there is a homozygous dominant genotype it will self destruct because that cannot exist in human populations
More on achondroplasia
Some parents with The Homozygous Recessive Genotype (aa) Have A Child With Achondroplasia (Aa)
This is caused from a mutation in the recessive genotype that turns it into a Heterozygous dominant genotype