Cardiovascular System Spaced Repetition
Due: Nov 7, 2025, 9:00 PM
1/121
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Access this daily for extra credit on your test.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|

122 Terms
pericardium
Membrane surrounding the heart
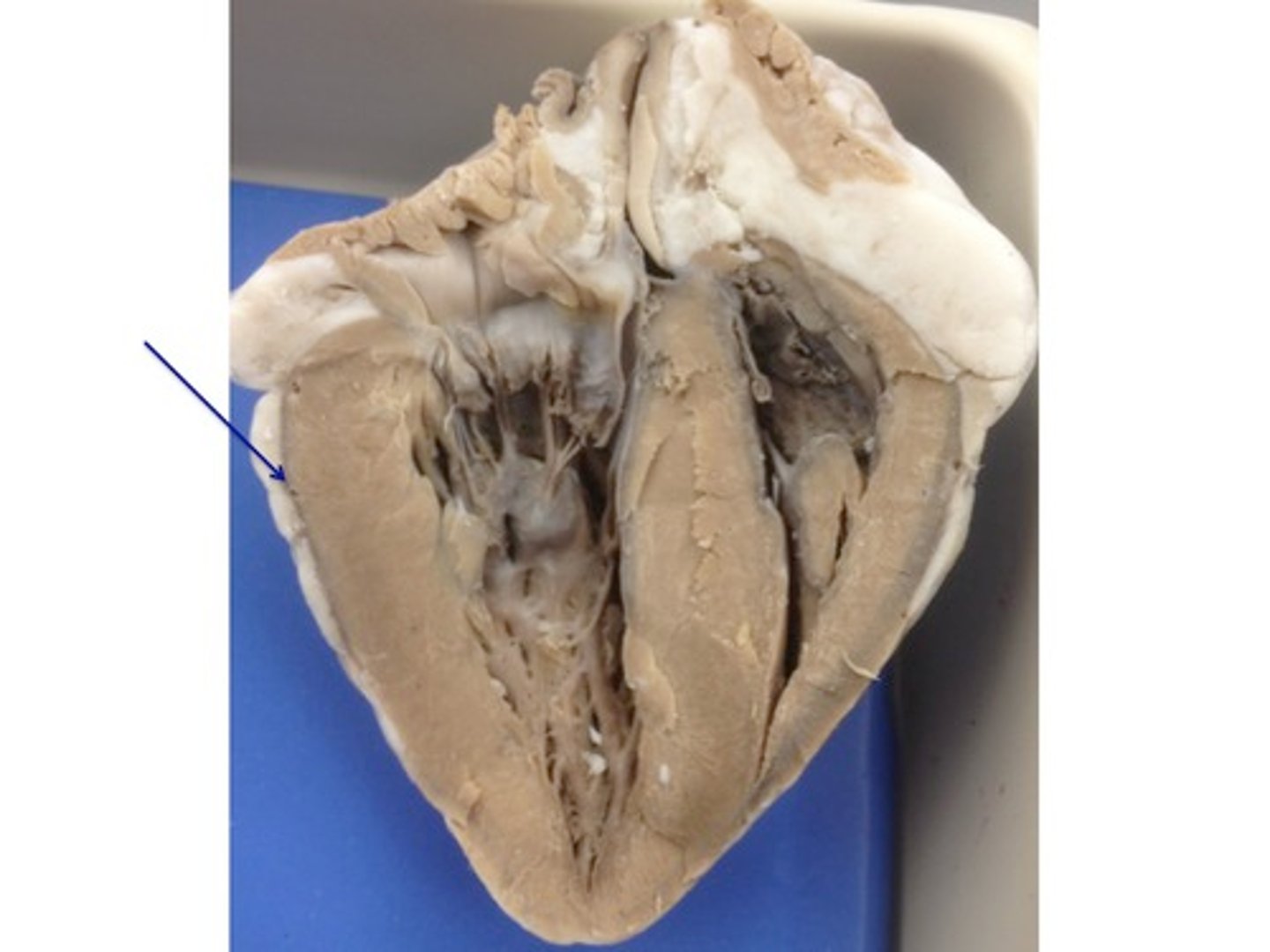
apex
bottom, pointed part of the heart
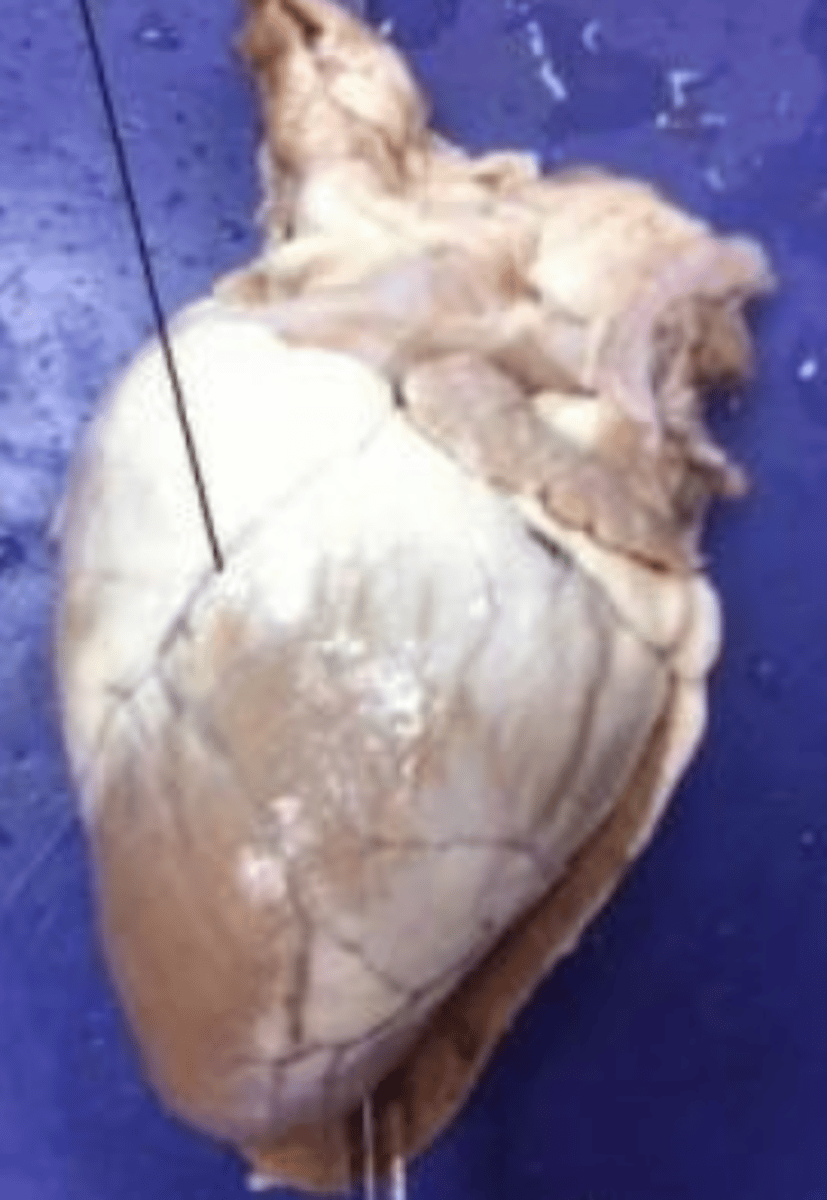
base
top region of the heart
coronary artery
the artery that supplies heart tissue with blood
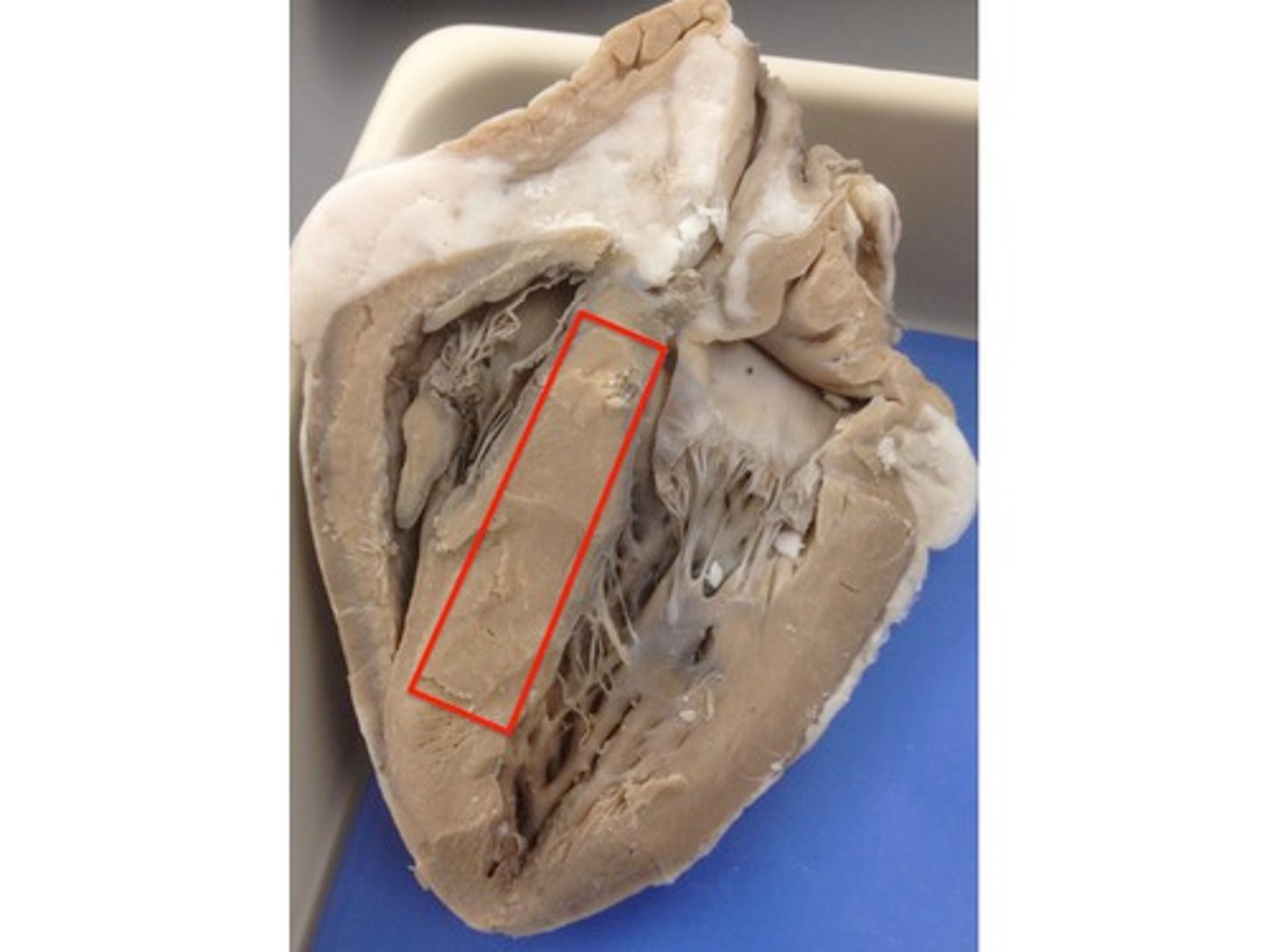
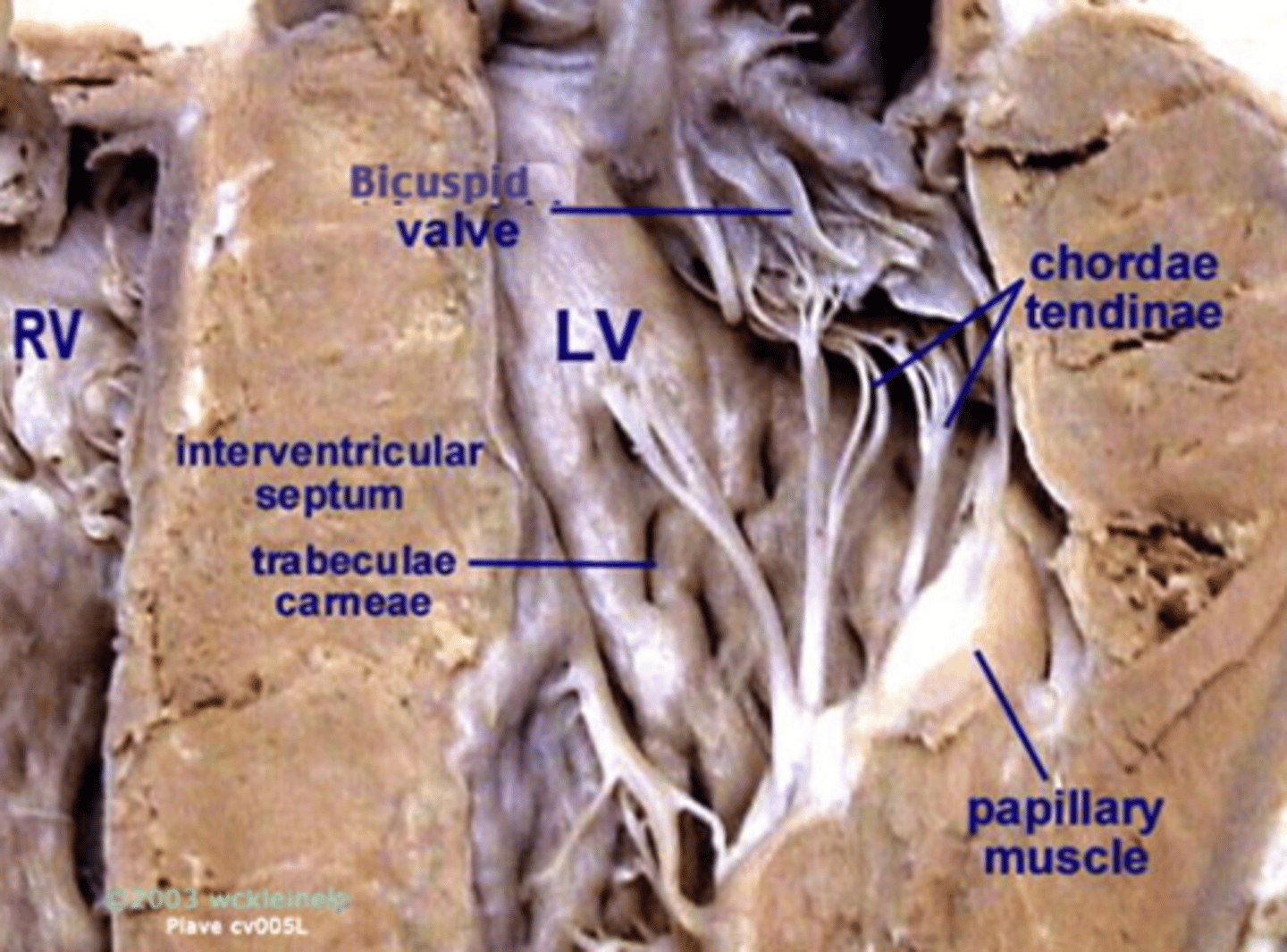
interventricular septum
prevents oxygenated and deoxygenated blood within the ventricles from mixing
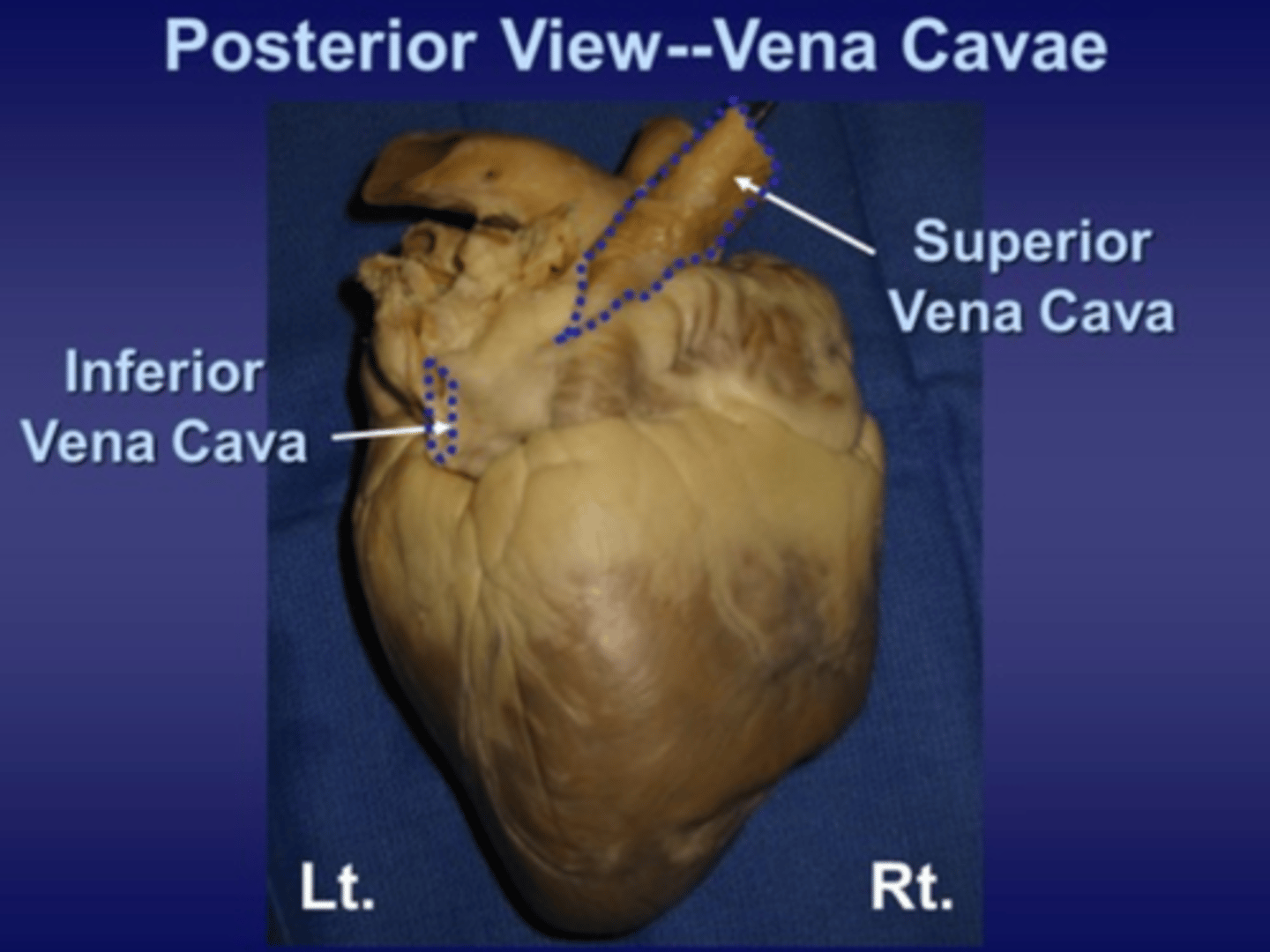
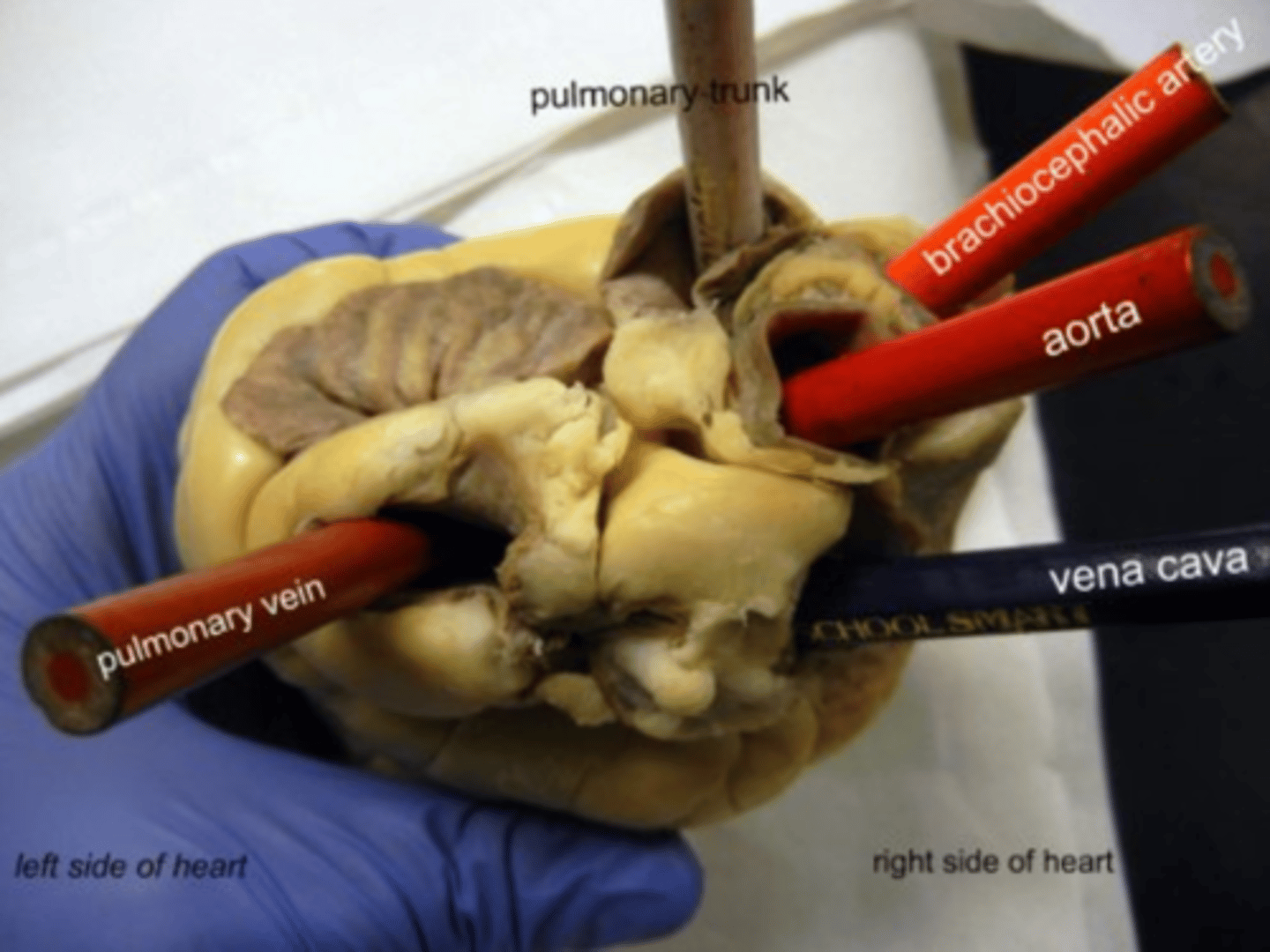
superior vena cava
blood vessel that returns blood from above the heart back to the heart
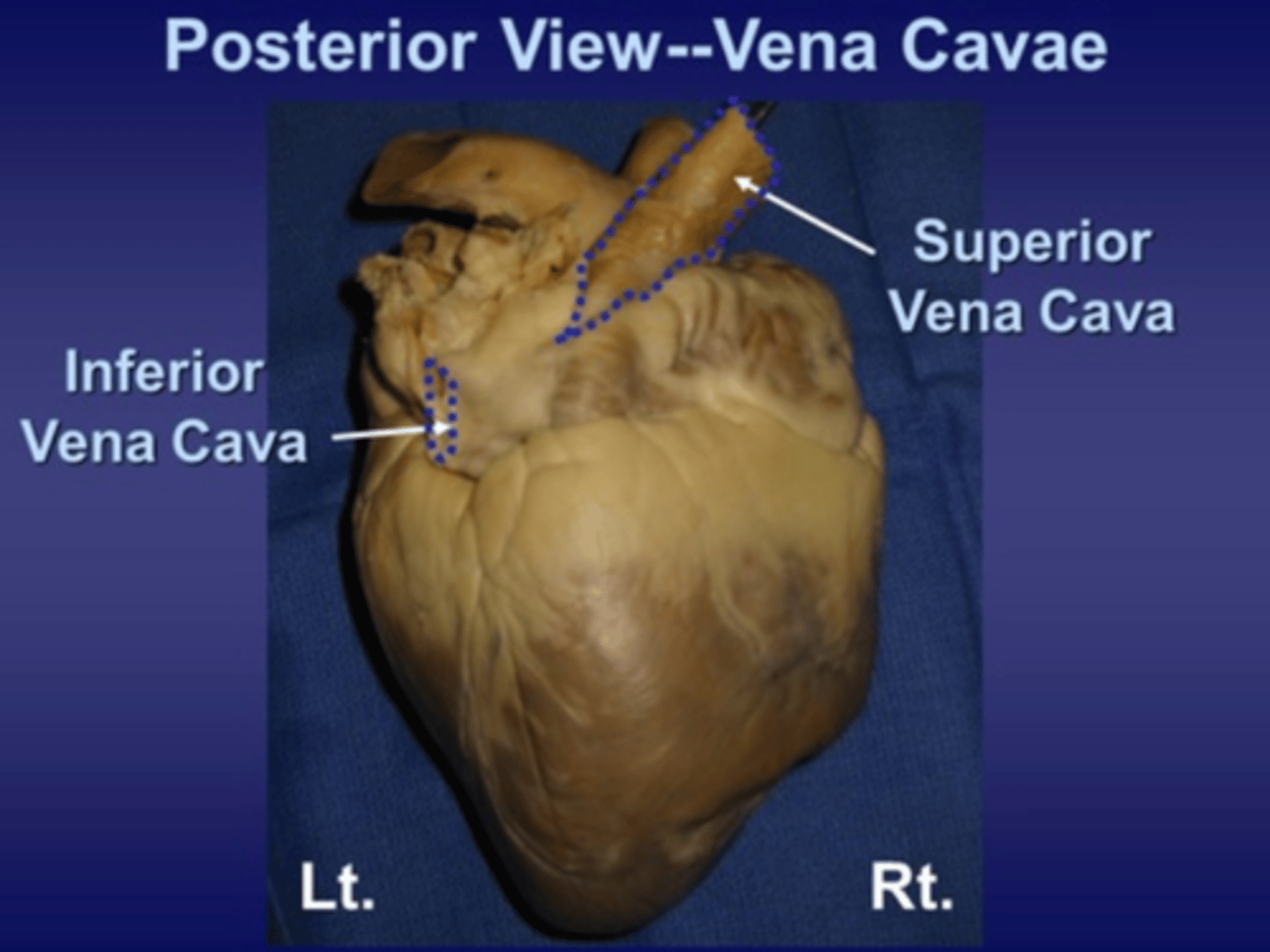
inferior vena cava
blood vessel that returns blood from below the heart back to the heart
right atrium
receives deoxygenated blood from the body
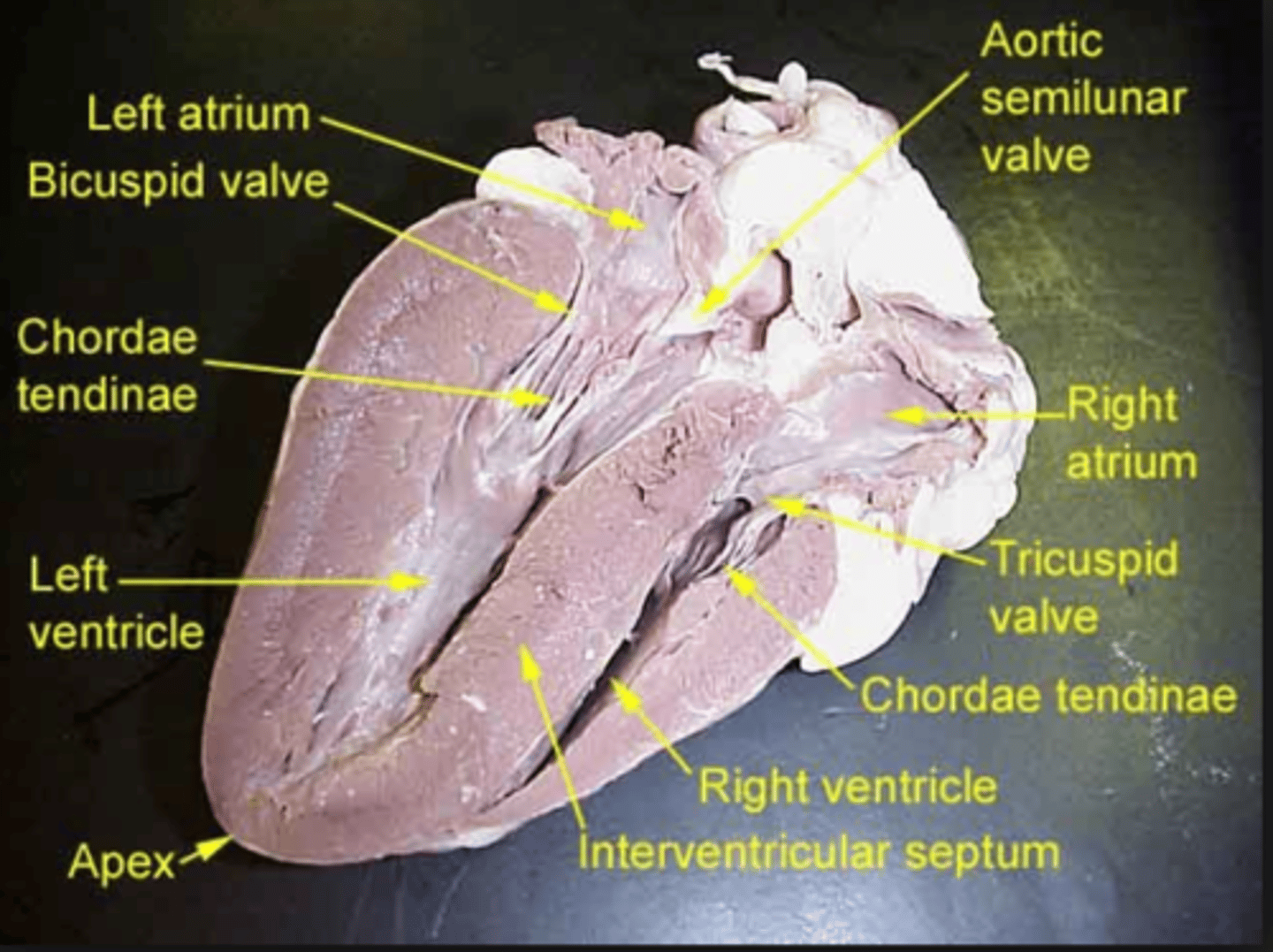
tricuspid valve/right AV valve
prevents blood from flowing back into the right atrium after it has entered the right ventricle
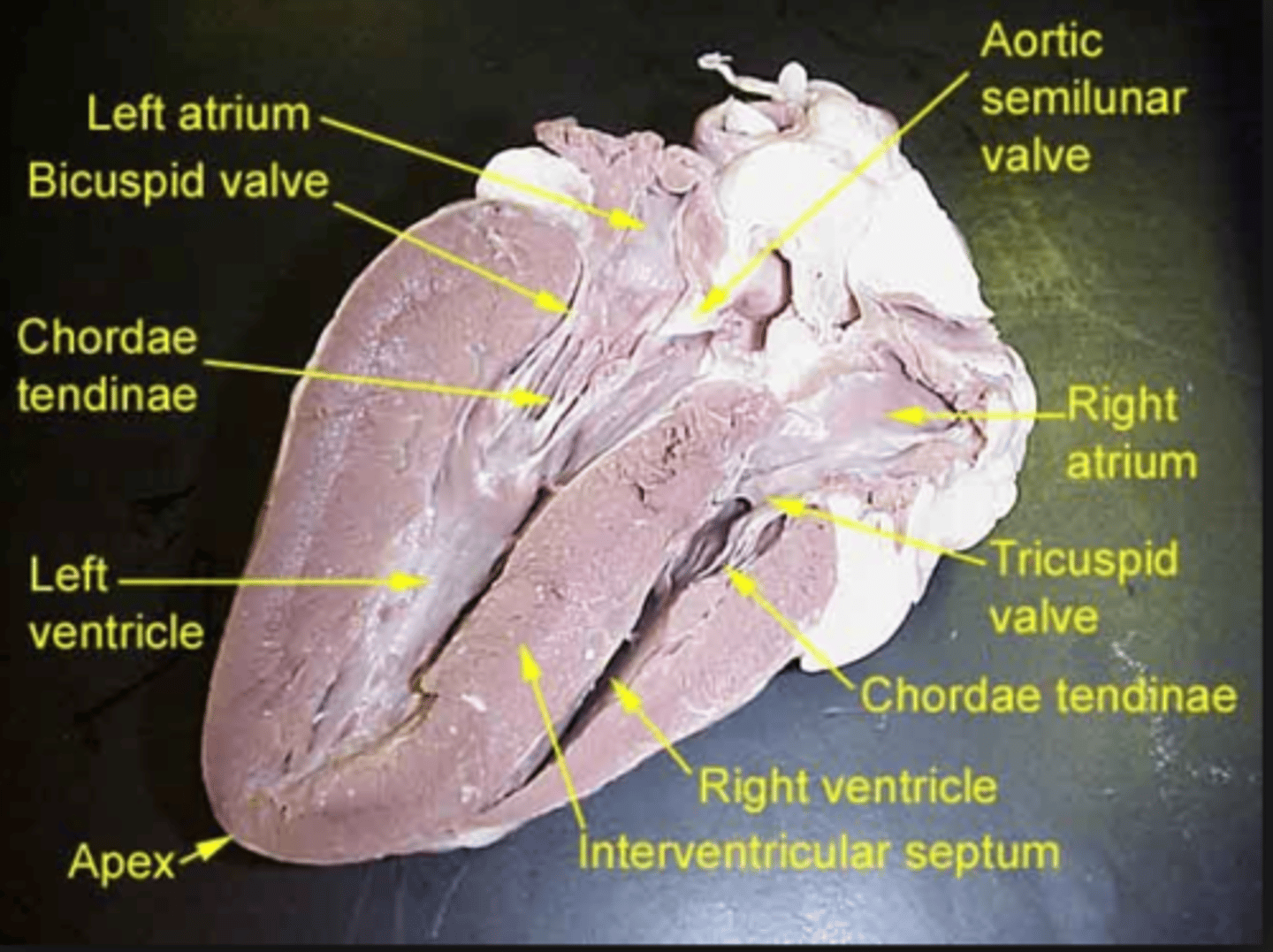
chordae tendinea
holds AV valves in place while the heart is pumping blood
papillary muscles
prevents inversion or prolapse of AV valves during heart contraction
right ventricle
chamber of the heart responsible for pumping deoxygenated blood away from the heart
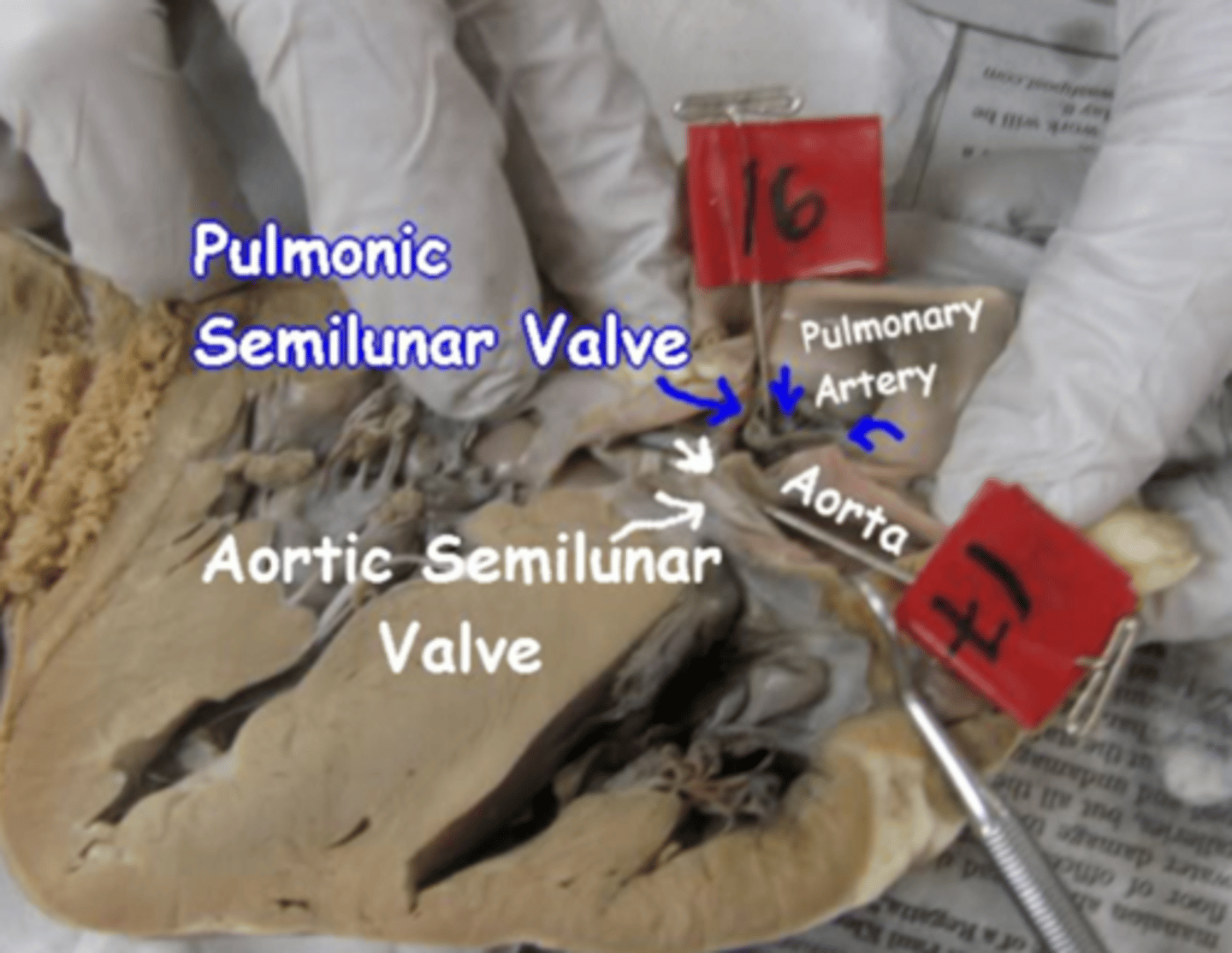
pulmonary semilunar valve
prevents blood from flowing back into the right ventricle
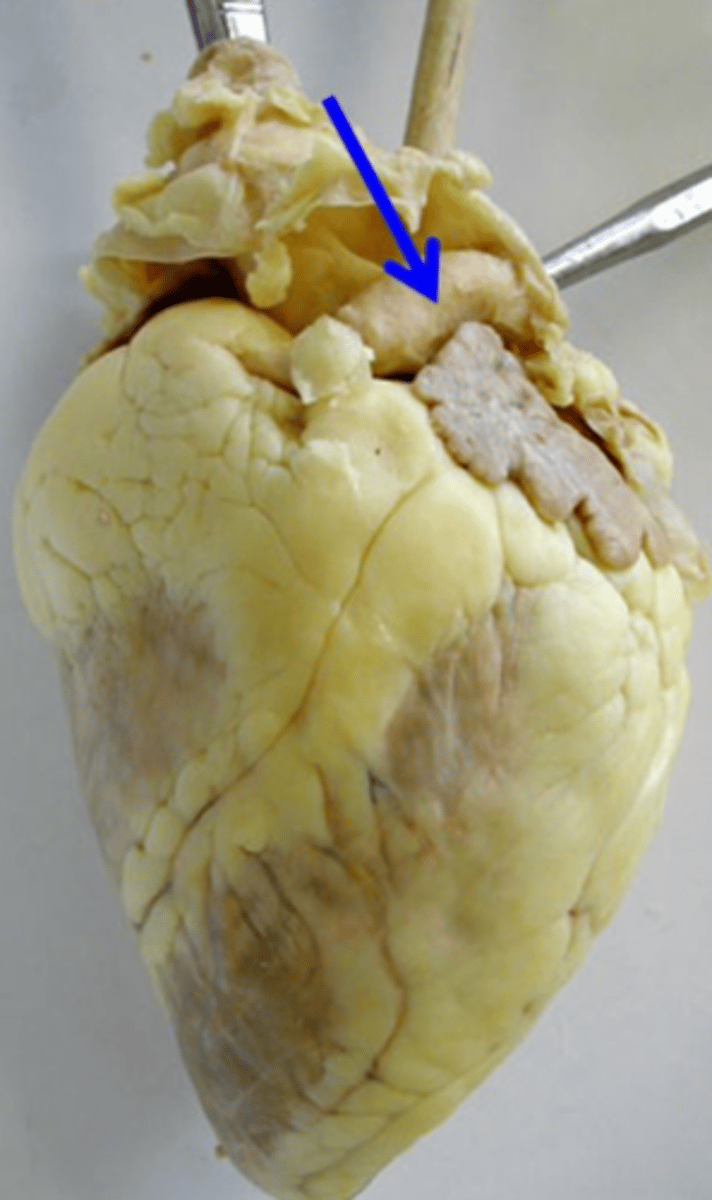
pulmonary trunk/artery
blood vessel that transports blood away from the heart to the lungs
pulmonary veins
blood vessel that transports blood from the lungs back to the heart
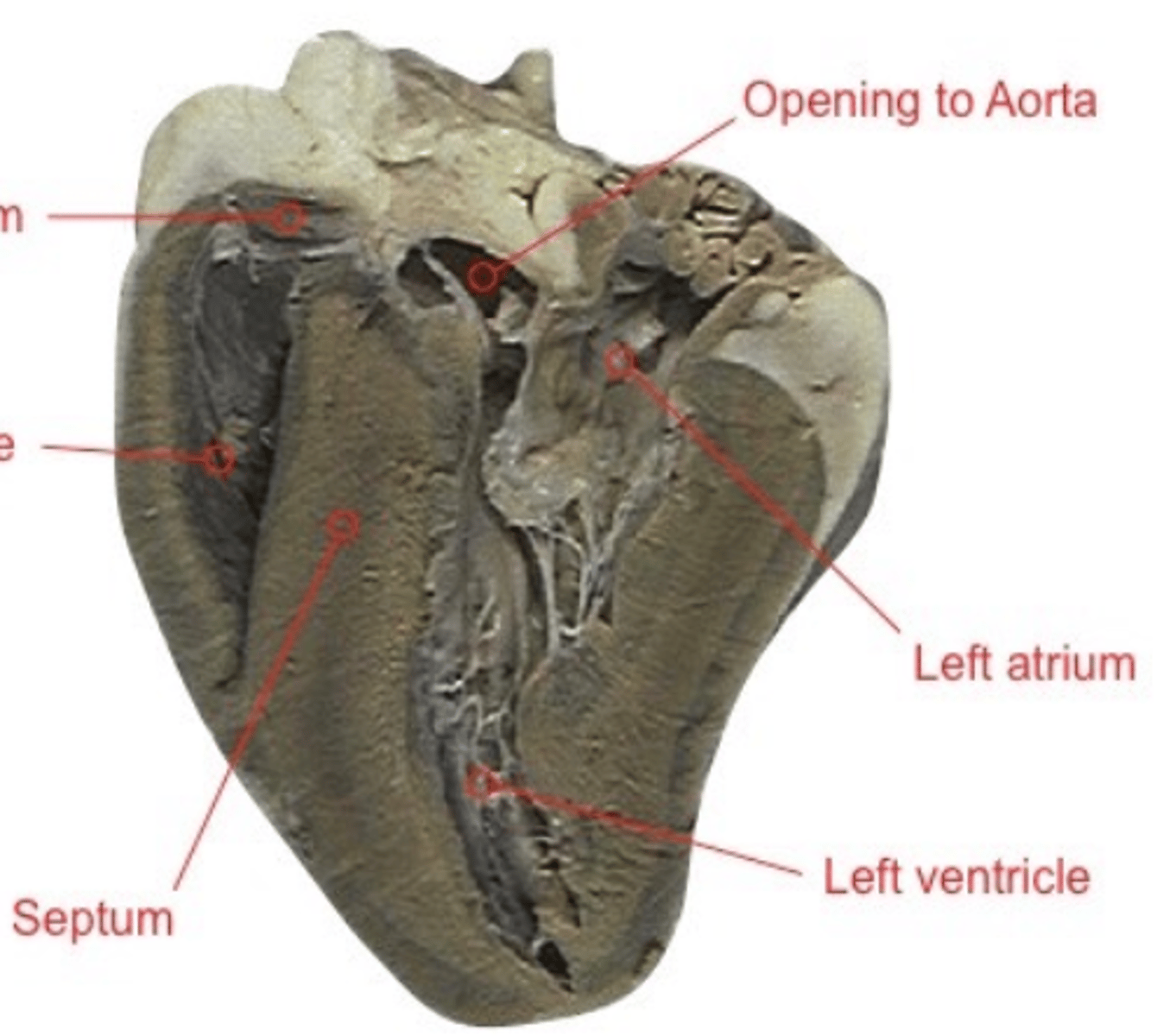
left atrium
chamber of the heart that receives oxygenated blood
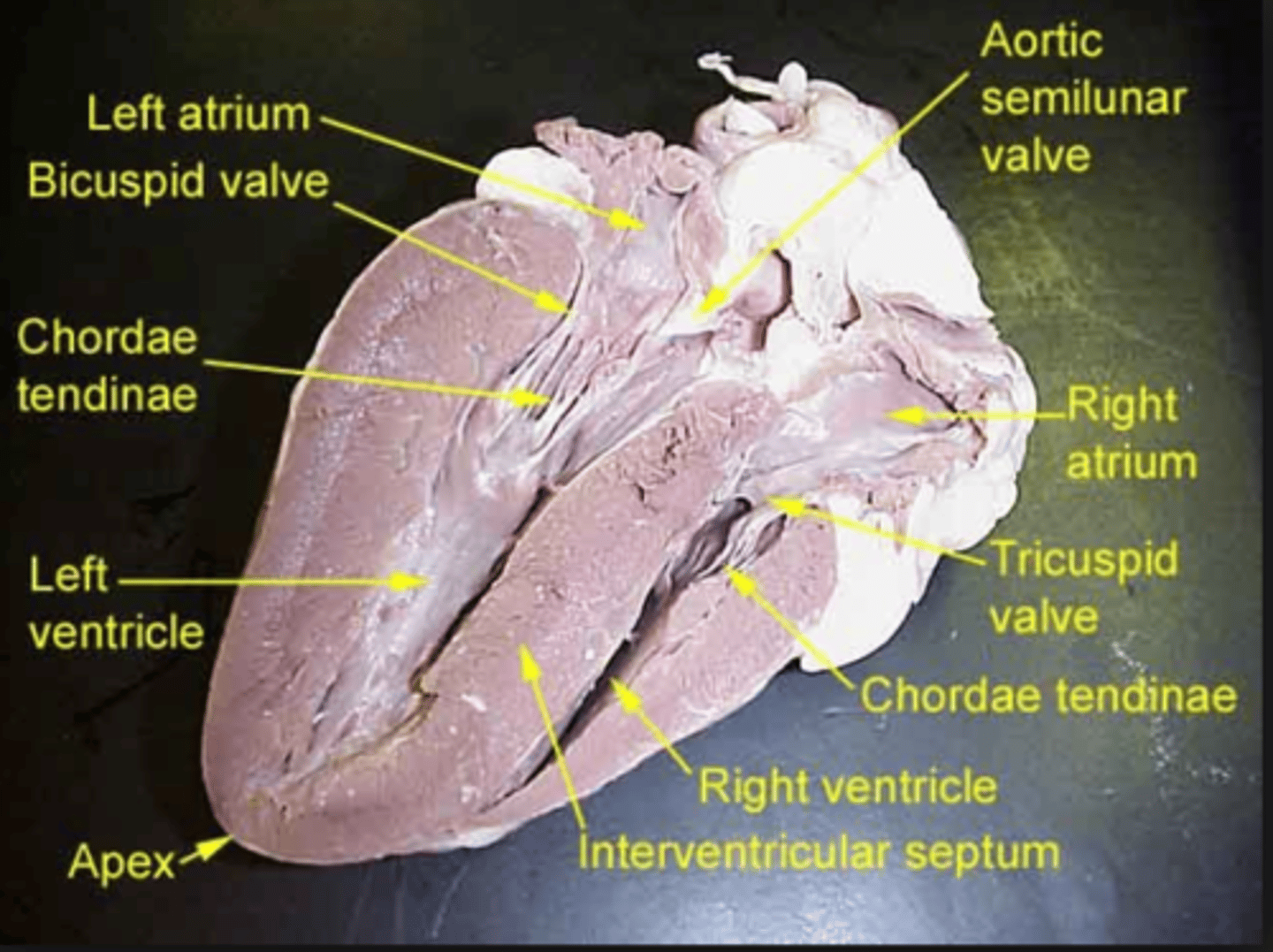
biscuspid/mitral/left AV valve
prevents blood flow from flowing backward into the left atrium
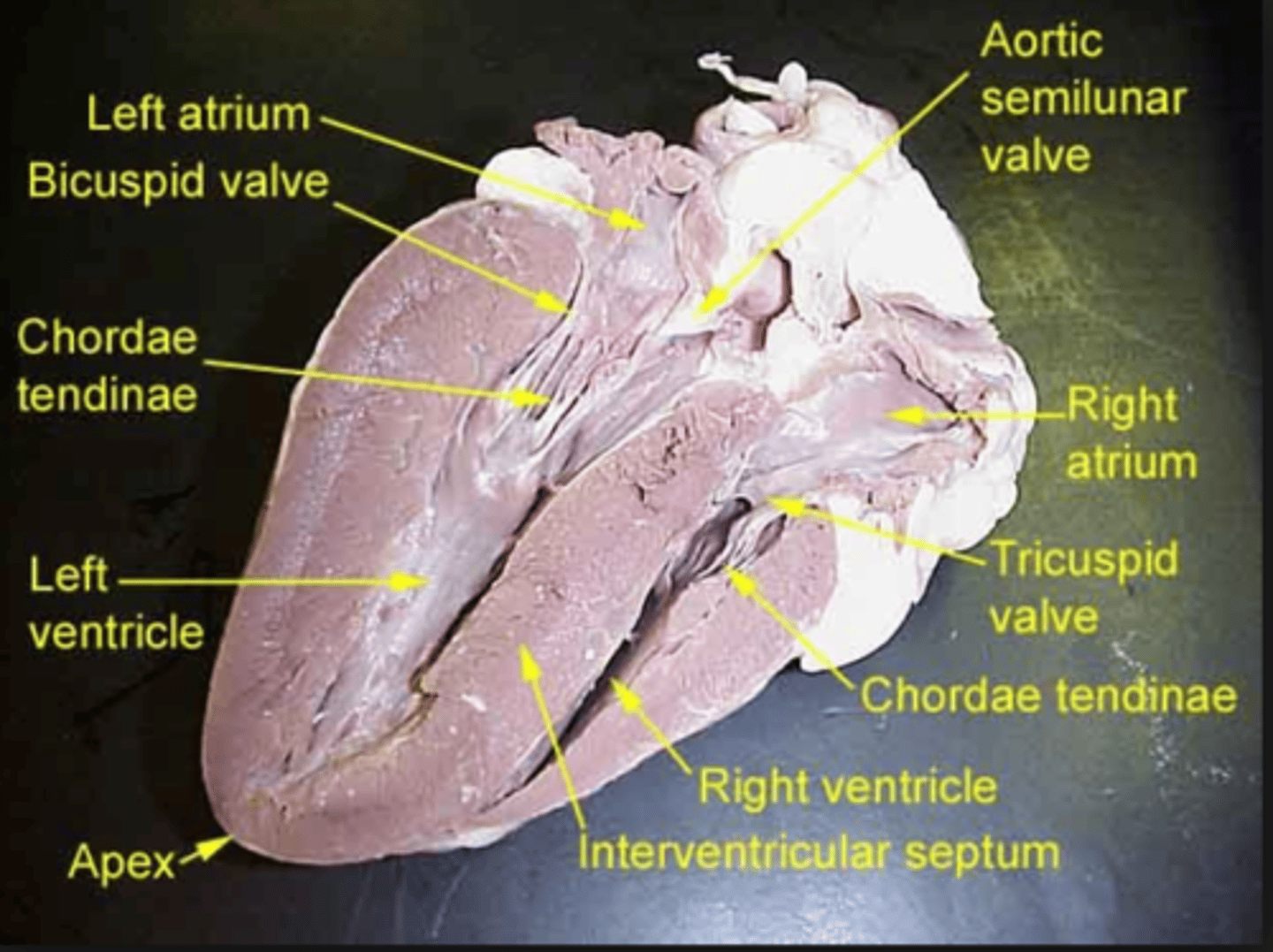
left ventricle
chamber of the heart responsible for pumping oxygenated blood away from the heart
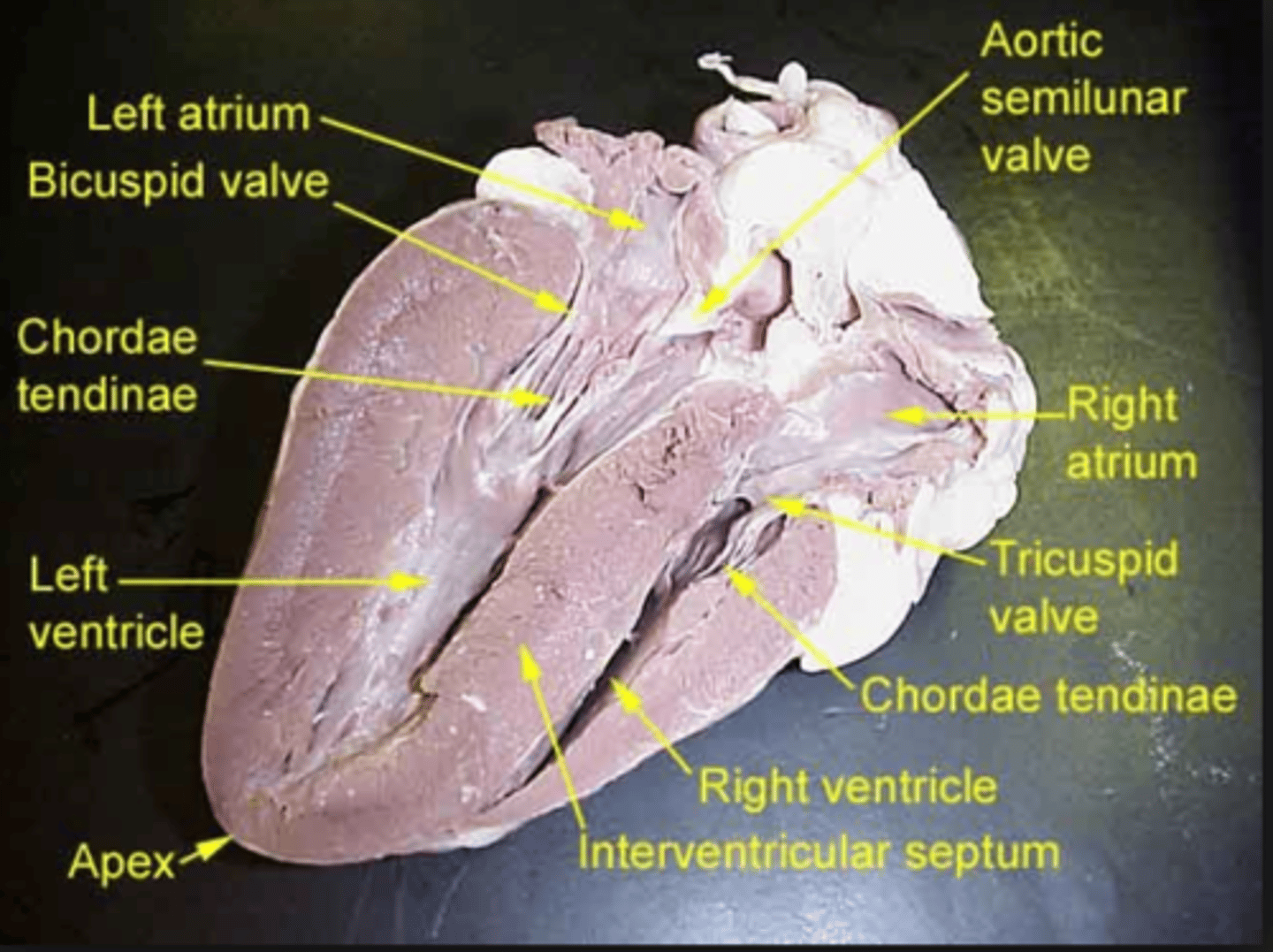
aortic semilunar valve
prevents blood from flowing back into the left ventricle
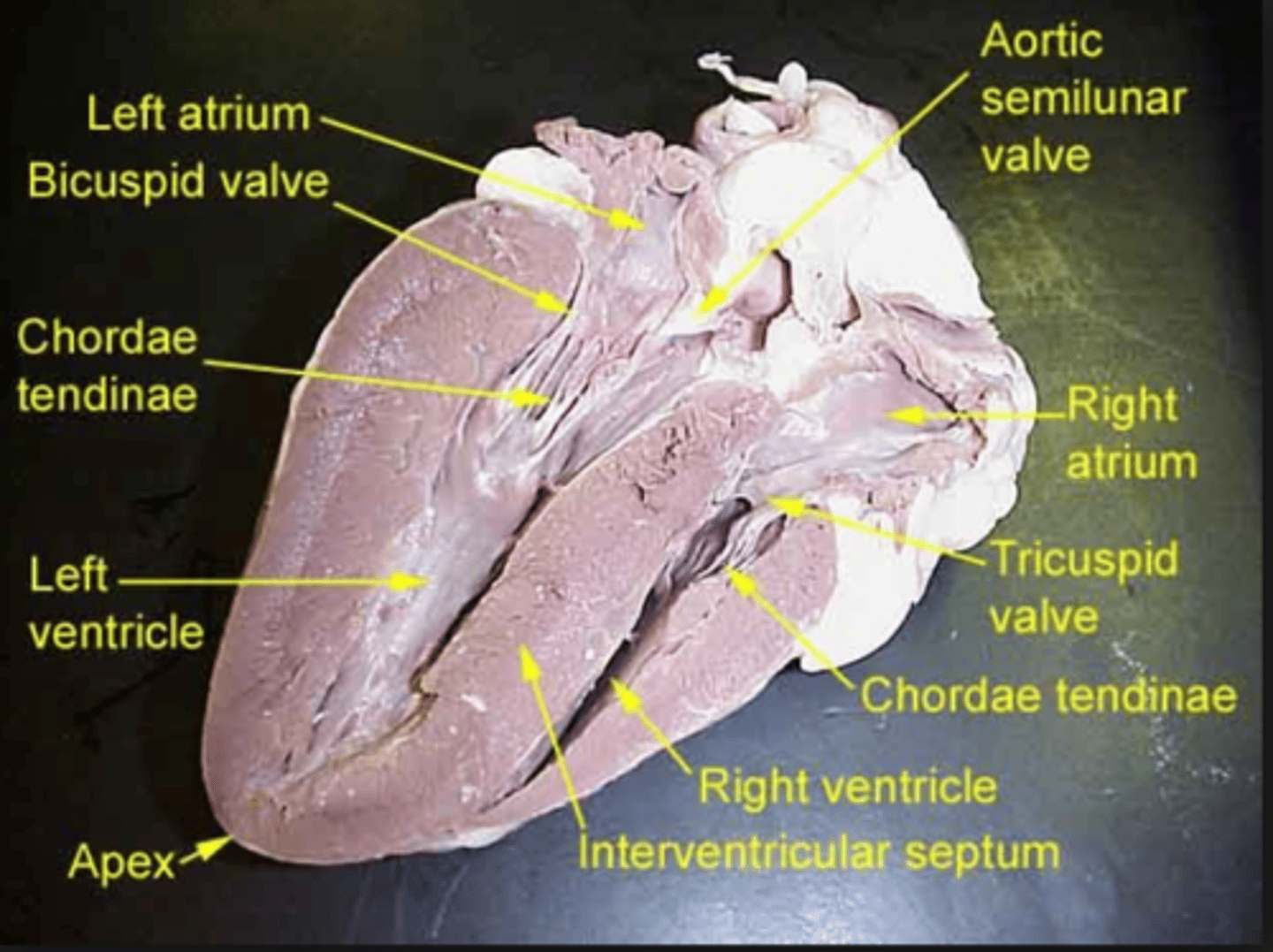
aorta
blood vessel that transports oxygenated blood to the brain and other organs and tissues
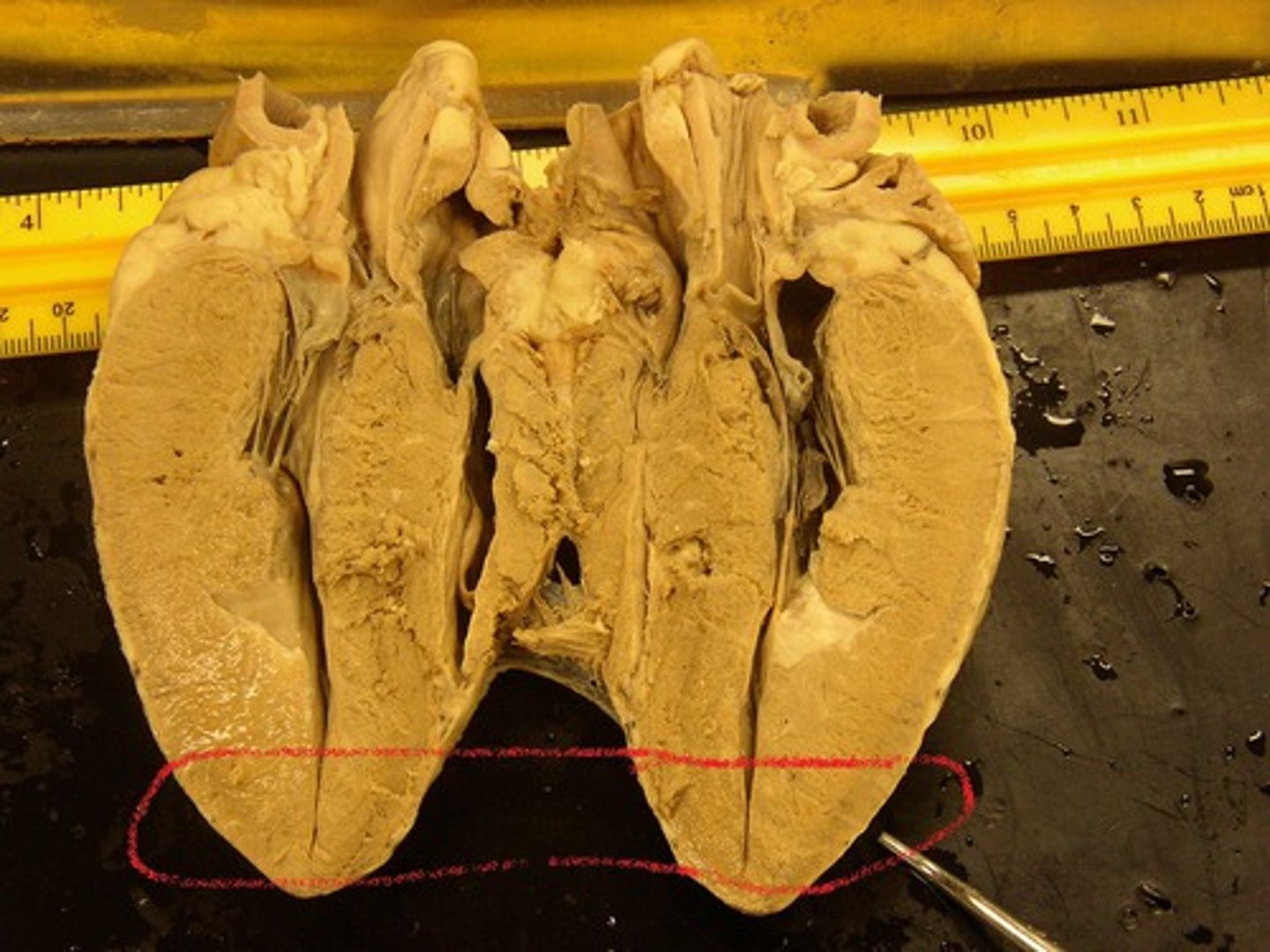
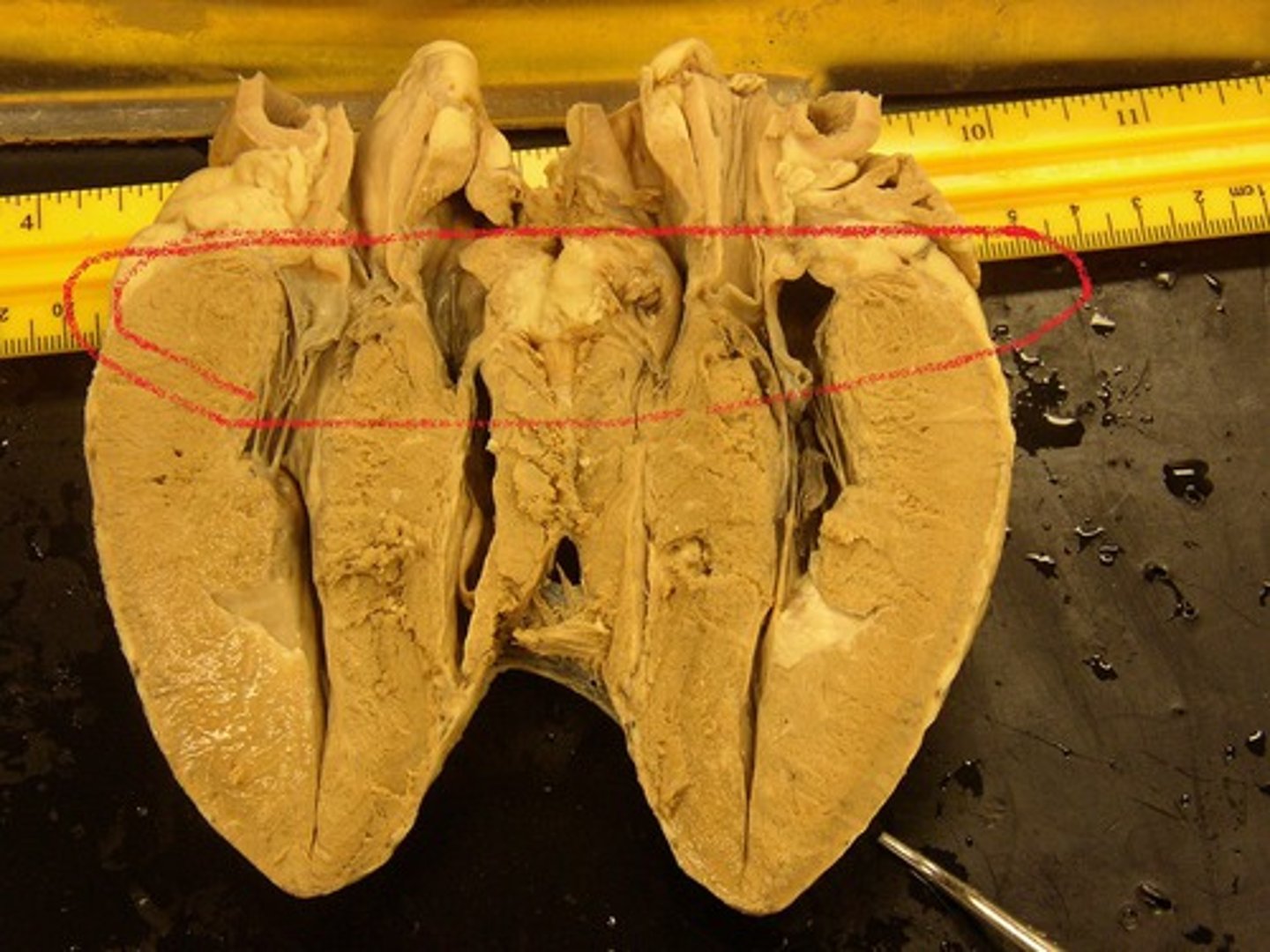
interventricular sulcus
large groove on the outside of the heart between the ventricles where the coronary artery and coronary vein lie
Asystole
absence of contractions of the heart
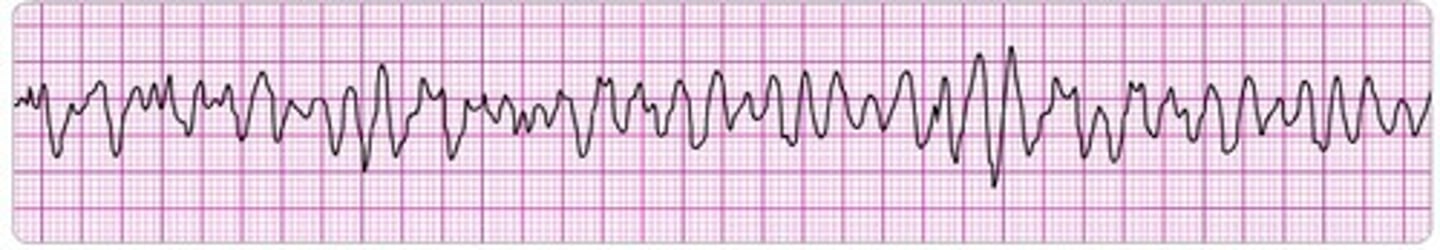
Ventricular fibrillation (V-Fib)
Disorganized, ineffective twitching of the ventricles, resulting in no blood flow and a state of cardiac arrest.
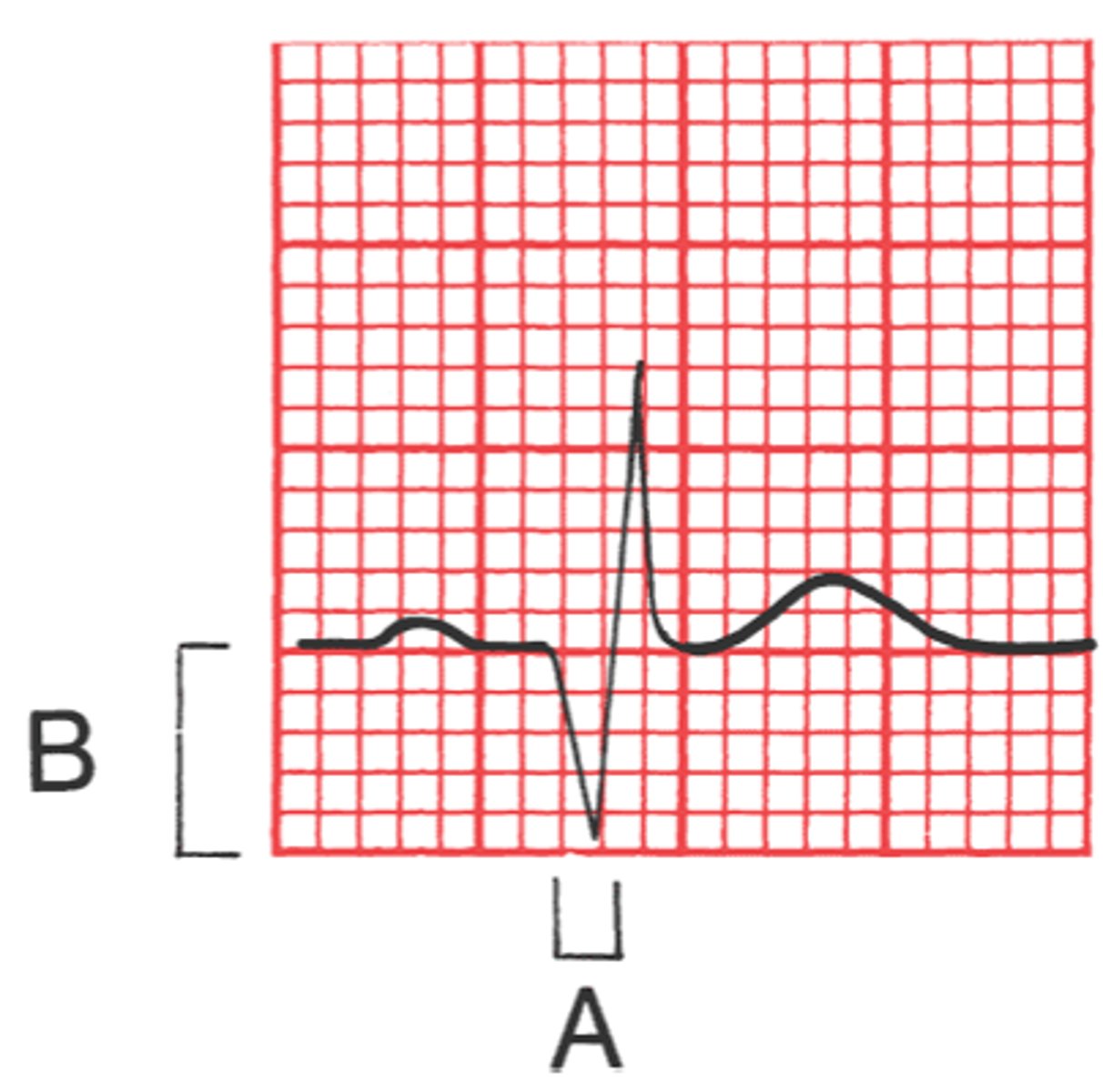
Normal EKG waves
normal sinus rhythm
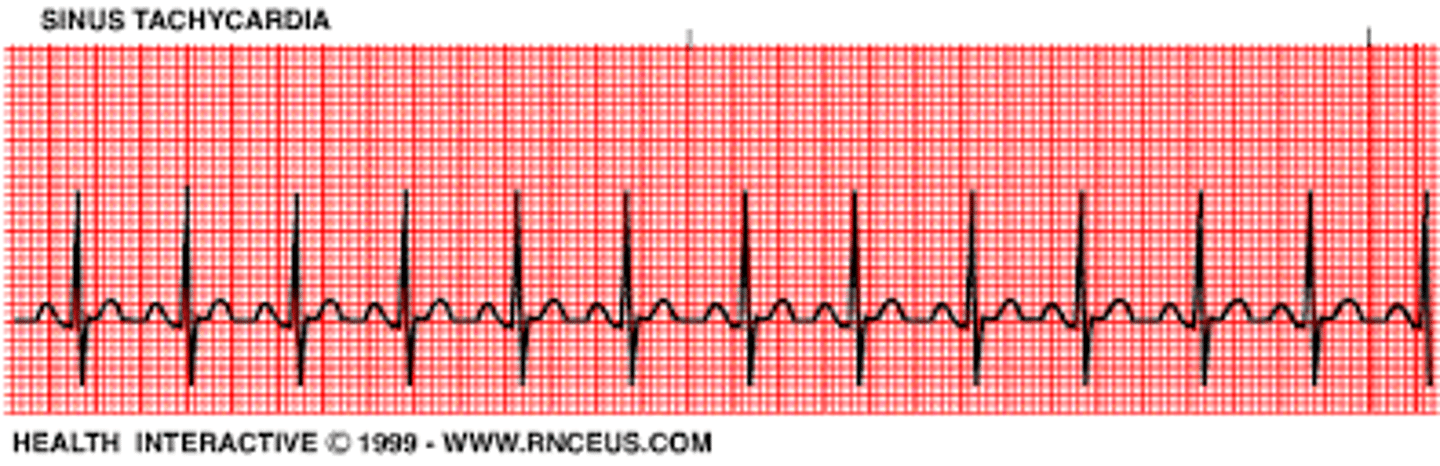
Tachycardia
Abnormally rapid heartbeat
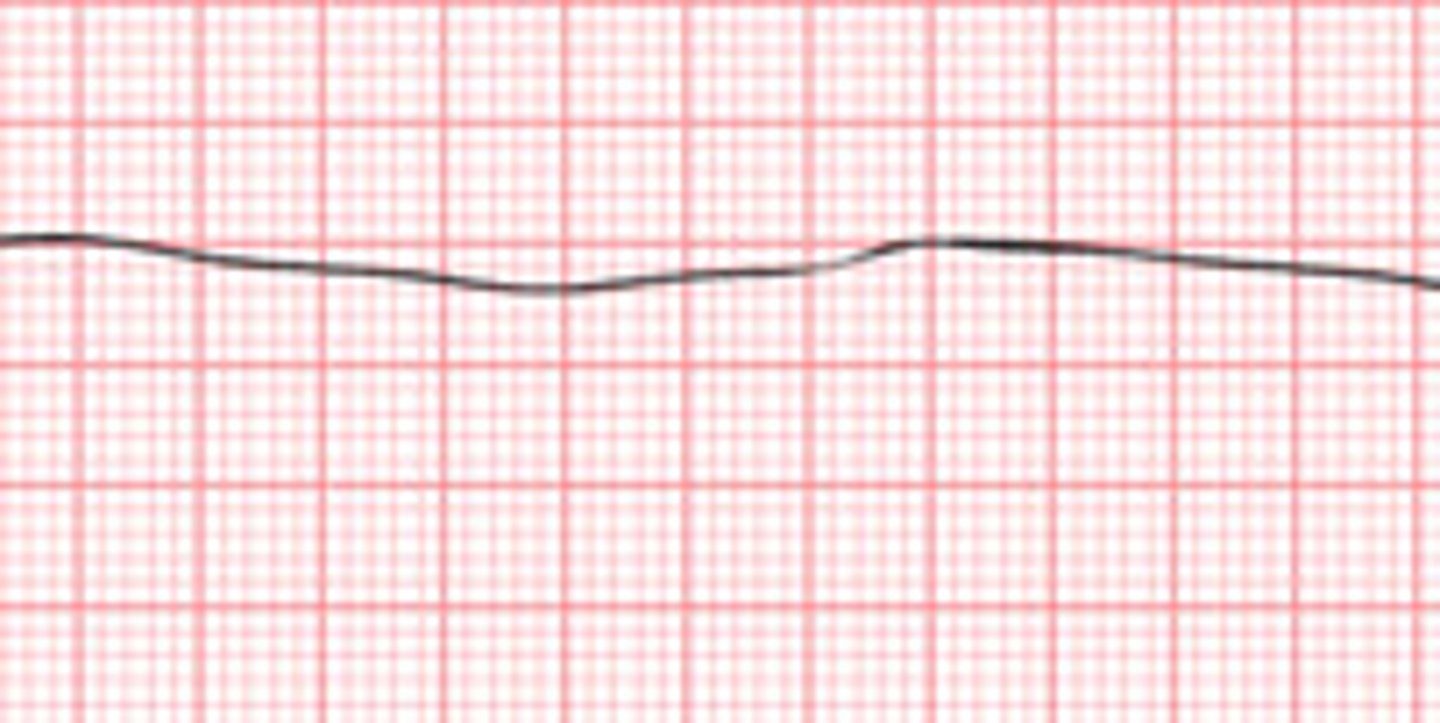
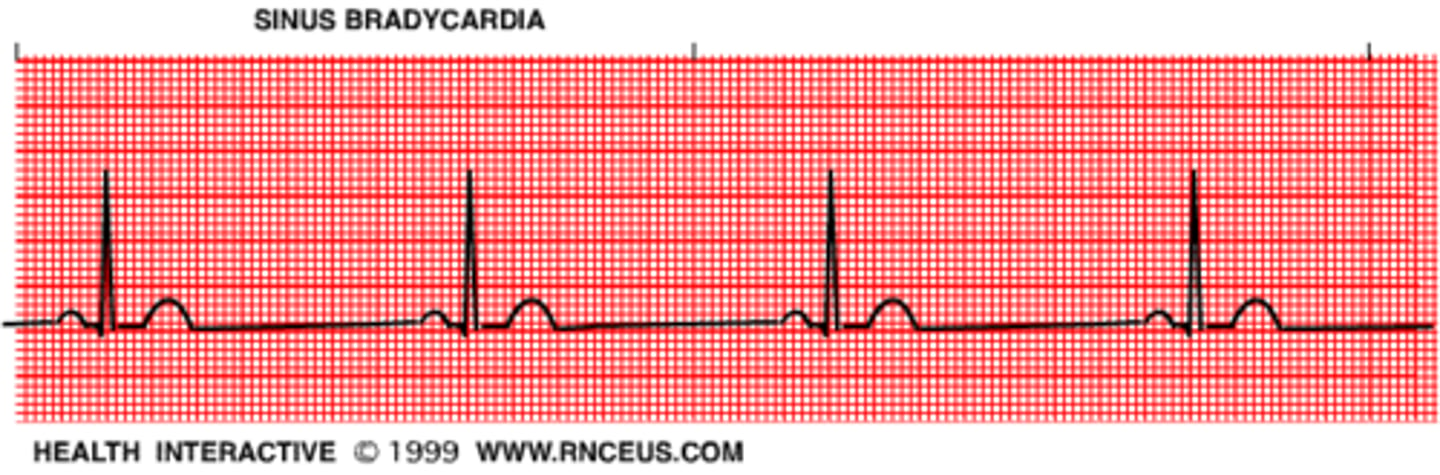
Bradycardia
abnormally slow heartbeat
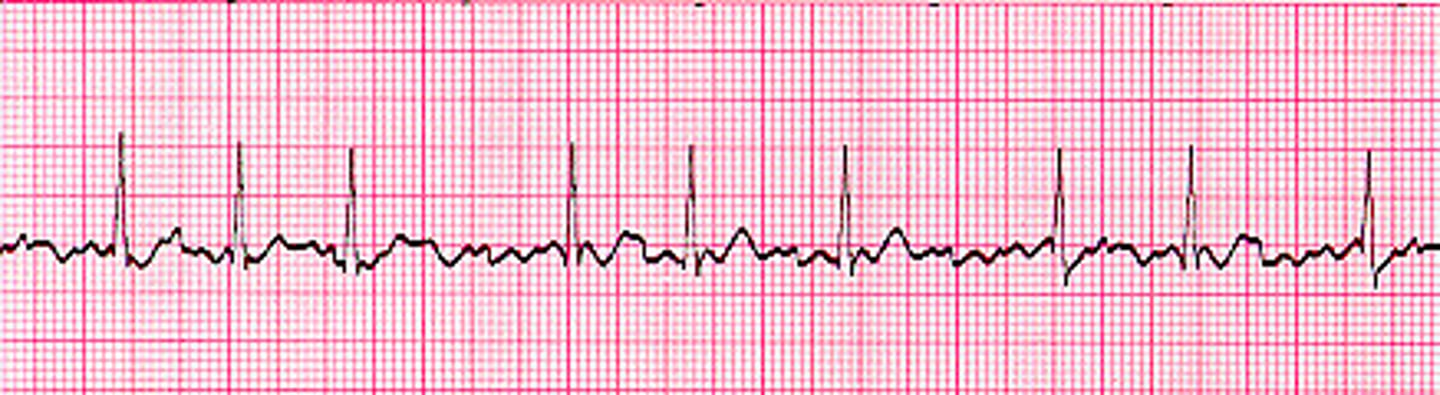
Atrial Fibrillation (A-Fib)
rapid, random, ineffective contractions of the atrium
diastolic pressure
the pressure in the arteries when the heart is at rest between beats. It is the lower number in a blood pressure reading.
systolic pressure
the pressure in the arteries when the heart beats. It is the higher number in a blood pressure reading.
lub
sound of heart’s AV valves closing
dub
sound of heart’s semilunar valves closing
hypertension
a condition of consistently elevated blood pressure levels, which can lead to serious health issues if left untreated.
normal blood pressure
is defined as a measurement typically around 120/80 mmHg, which is considered healthy for adults.
pulse
the rhythmic expansion and contraction of an artery as blood is pumped through it by the heart.
Arteries
Blood vessels that carry oxygenated blood away from the heart to the tissues.
Arterial System
The network of arteries that transport blood away from the heart.
subclavian artery
A major artery that supplies blood to the arms and some parts of the head and neck, branching from the aorta.
axillary artery
The artery that continues from the subclavian artery and supplies blood to the upper limb.
brachial artery
The major artery of the upper arm, supplying blood to the arm and forearm.
radial artery
The major artery of the forearm, supplying blood to the lateral aspect of the forearm and wrist.
ulnar artery
The major artery of the forearm, supplying blood to the medial aspect of the forearm and hand.
common carotid artery
The major artery supplying blood to the head and neck, branching into the internal and external carotid arteries.
celaic trunk
The major artery that supplies blood to the stomach, spleen, and liver, branching into three main arteries: the left gastric, splenic, and common hepatic arteries.
renal artery
The artery that supplies blood to the kidneys, branching from the abdominal aorta.
superior mesenteric artery
The artery that supplies blood to the small intestine and part of the large intestine, branching from the abdominal aorta.
inferior mesenteric artery
The artery that supplies blood to the distal part of the colon and rectum, branching from the abdominal aorta.
gonadal artery
The artery that supplies blood to the gonads (ovaries in females, testes in males), branching from the abdominal aorta.
common iliac artery
The artery formed by the branching of the abdominal aorta, which supplies blood to the pelvis and lower limbs.
internal iliac artery
The artery that branches from the common iliac artery to supply blood to the pelvic region and its organs, including the bladder, reproductive organs, and gluteal muscles.
external iliac artery
The artery that branches from the common iliac artery to supply blood to the lower limb, becoming the femoral artery as it passes under the inguinal ligament.
femoral artery
The major artery of the thigh that supplies blood to the lower limb, continuing from the external iliac artery as it passes beneath the inguinal ligament.
popliteal artery
The artery located at the back of the knee that continues from the femoral artery and supplies blood to the lower leg and foot.
anterior tibial artery
The artery that branches from the popliteal artery to supply blood to the anterior compartment of the leg and continues into the foot.
arcuate artery
A branch of the dorsalis pedis artery, the arcuate artery supplies blood to the foot's dorsal side and helps form the arterial arch.
external jugular vein
A major vein that drains blood from the face and neck and returns it to the subclavian vein.
internal jugular vein
A major vein that collects blood from the brain, face, and neck, draining into the subclavian vein.
subclavian vein
A major vein that carries blood from the arms and some neck structures back to the heart, merging with the internal jugular vein to form the brachiocephalic vein.
axillary vein
A vein that receives blood from the upper limb and drains into the subclavian vein.
brachial vein
A major vein that carries blood from the arm and forearm, merging into the axillary vein.
axillary vein
A vein located in the armpit area that collects blood from the upper limb and drains into the subclavian vein.
brachial vein
The major vein responsible for draining deoxygenated blood from the arm and forearm, it merges with the axillary vein.
hepatic portal vein
A major vein that carries blood from the gastrointestinal tract and spleen to the liver, allowing for nutrient processing.
renal vein
A vein that carries blood away from the kidneys to the inferior vena cava.
hepatic portal vein
Vein that transports blood from the intestines and spleen to the liver for detoxification and nutrient absorption.
renal vein
A major vein that drains blood from the kidneys and transports it to the inferior vena cava.
superior mesenteric vein
A vein that drains blood from the small intestine and parts of the large intestine to the hepatic portal vein.
inferior mesenteric vein
A vein that drains blood from the distal part of the large intestine and rectum into the hepatic portal vein.
common iliac vein
A vein that drains blood from the pelvis and lower limbs into the inferior vena cava, formed by the union of the internal and external iliac veins.
femoral vein
A major vein that drains blood from the thigh and continues as the external iliac vein.
great saphenous vein
The longest vein in the body, it runs along the length of the leg, draining blood from the superficial structures of the lower limb into the femoral vein.
aneurysm
A localized abnormal dilation of a blood vessel, usually an artery, caused by weakness of the vessel wall; may eventually burst
angina pectoris
A feeling of constriction around the heart or pain thatmay radiate to the left arm or shoulder, usually brought on by exertion; caused by insufficient bloodsupply to the heart
arrhythmia
Any abnormality in the rate or rhythm of the
heartbeat); also called dysrhythmia
arteriosclerosis
Hardening of the arteries, with loss of capacity
and loss of elasticity, as from fatty deposits,
deposit of calcium salts, or scar tissue formation
atherosclerosis
The development of fatty, fibrous patches in the lining of arteries, causing narrowing of the lumen and hardening of the vessel wall the most common form of arteriosclerosis
bradycardia
A slow heart rate of less than 60 bpm
cerebrovascular accident (CVA)
Sudden damage to the brain resulting from
reduction of blood flow
causes include atherosclerosis, embolism,
thrombosis, or hemorrhage from a ruptured
aneurysm; commonly called stroke
cyanosis
Bluish discoloration of the skin caused by lack of oxygen in the blood
embolism
Obstruction of a blood vessel by a blood clot or other matter carried in the circulation
fibrillation
Spontaneous, quivering, and ineffective contraction of muscle fibers in the atria or the ventricles
heart block
An interference in the electrical conduction system of the heart, resulting in arrhythmia
hypertension
A condition of higher-than-normal blood pressure
infarct
An area of localized tissue necrosis (death) resulting from a blockage or a narrowing of the artery that supplies the area
ischemia
Local deficiency of blood supply caused circulatory obstruction
murmur
An abnormal heart sound
heart failure
A condition caused by the inability of the heart to maintain adequate blood circulation
myocardial infarction (MI)
Localized necrosis (death) of cardiac muscle tissue resulting from a blockage or narrowing of the coronary artery that supplies that area.
occlusion
A closing off or obstruction, as of a vessel
plaque
A deposit of fatty material and other substances on a vessel wall that impedes blood flow and blocks the vessel
rheumatic heart disease
Damage to heart valves after infection
septal defect
An opening in the septum between the atria or ventricles; a common cause is persistence of the foramen ovale, an opening between the atria that bypasses the lungs in fetal circulation
tachycardia
An abnormally rapid heart rate, usually over 100
bpm
thrombosis
Development of a blood clot within a vessel
varicose vein
A twisted and swollen vein resulting from the breakdown of the valves, pooling of blood, and chronic dilatation of the vessel
atrial fibrillation (afib)
A medical condition characterized by rapid and irregular heartbeat due to chaotic electrical activity in the heart's atria.
ventricular fibrillation (vfib)
A life-threatening heart rhythm that results in the heart being unable to pump blood effectively, leading to loss of consciousness and cardiac arrest.
anemia
A condition characterized by a deficiency in the number or quality of red blood cells, leading to reduced oxygen transport in the body.
polycythemia
A condition characterized by an increased number of red blood cells in the bloodstream, which can lead to increased blood viscosity and potential complications such as thrombosis.
sickle cell anemia
A genetic blood disorder characterized by the production of abnormal hemoglobin, leading to misshapen red blood cells that can cause blockages in blood vessels and result in pain and organ damage.
pace maker
A medical device that provides electrical stimulation to regulate heartbeats in patients with arrhythmias or irregular heart rhythms.