B5 - Communicable Diseases
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
Factors in Illness
- diet
- stress
- life situation:
poverty
sanitation
health care accesses
gender
environment
nationality
Aseptic Techniques
techniques that prevent contamination by unwanted microorganisms - sterile environments
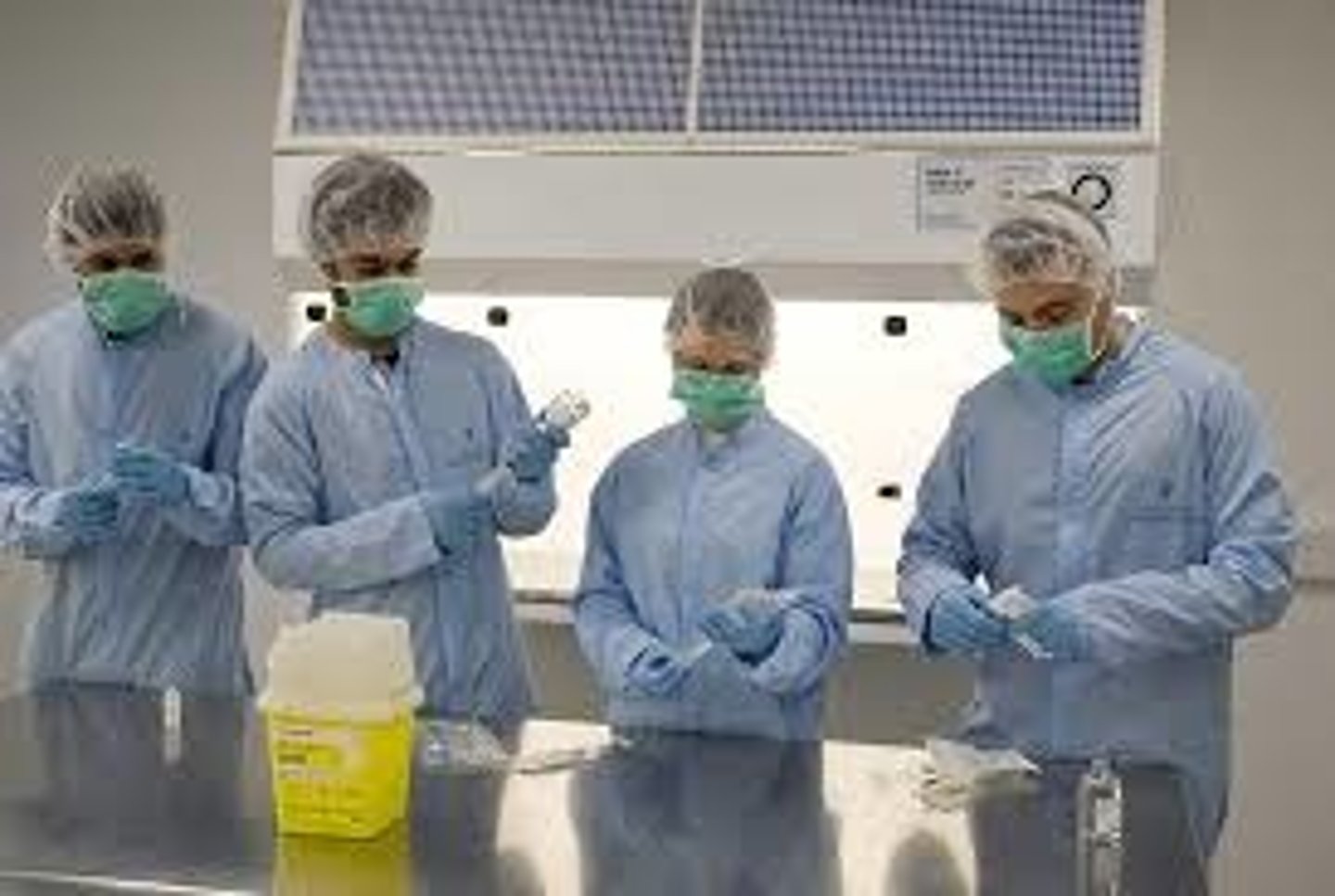

Bacteria Growth Required Practical
- sterilise petri dish by putting it in an autoclave: kills of any other unwanted bacteria
- fill dish with sterile agar: provides nutrients for bacteria to grow
- sterilise neck of culture bottle through blue bunsen flame: kills unwanted bacteria on neck
- use a disposable sterile cotton bud: keep unwanted bacteria away (if it touches another object dispose and use another)
- put cotton bud in culture bottle and spread through the semi open dish zig zag: keep unwanted bacteria & oxygen away and lets the culture spread evenly
- replace lid quickly, tape in 3 places , turn upside down: to keep unwanted oxygen away, keeps it from falling off and prevents condensation
- incubate dish for a few days at 25°c: lets bacteria grow but prevents creating pathogens instead
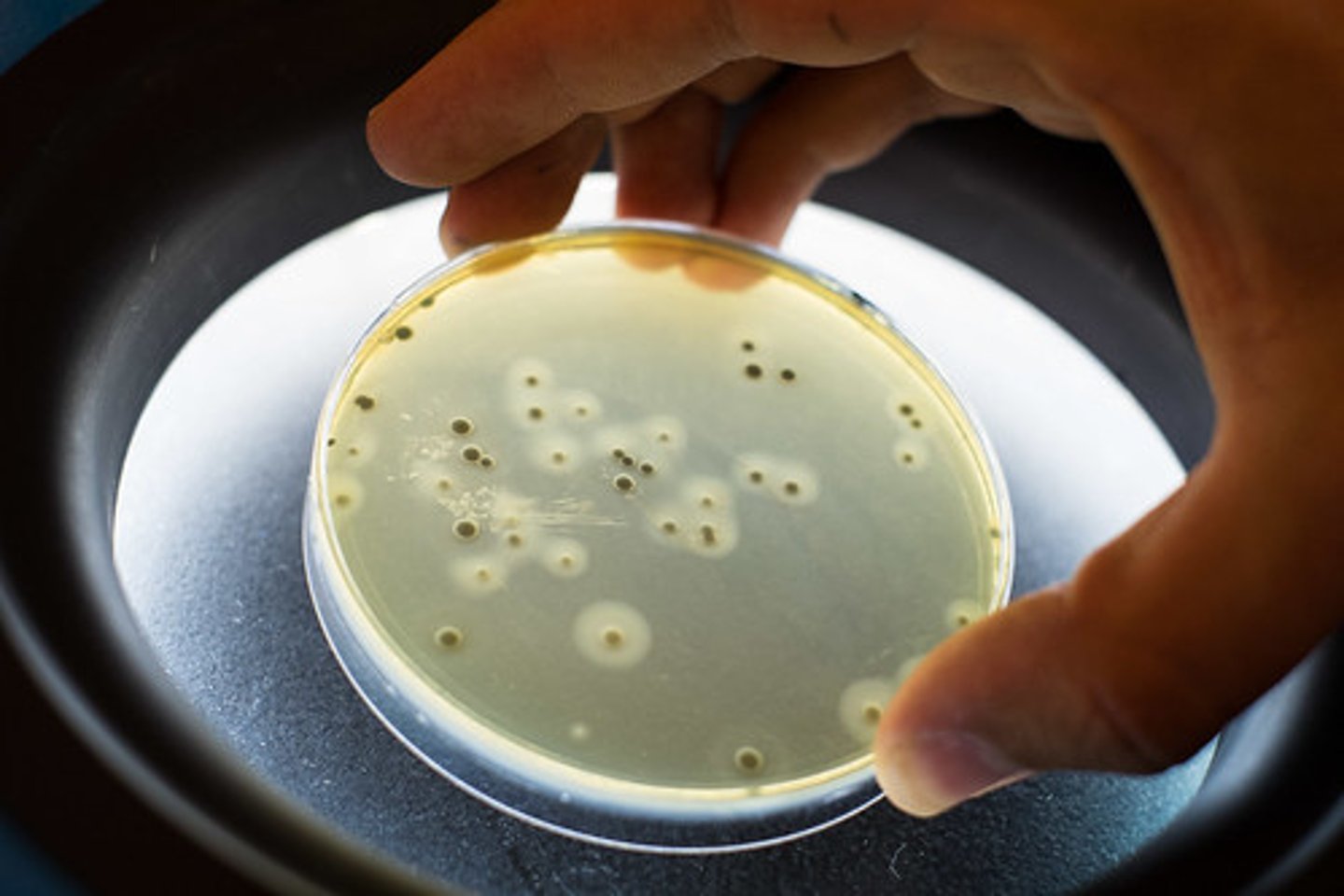
Comparing Bacteria Growth
- set up uncontaminated culture bacteria on agar
- add circles of filter paper which are soaked in different concentrations of disinfectants & antibiotics to kill bacteria
- have a circle with nothing as a control
- incubate several days to see results
- the biggest/widest circle the most effective: largest zone of inhibition
- the smallest circle is the least effective
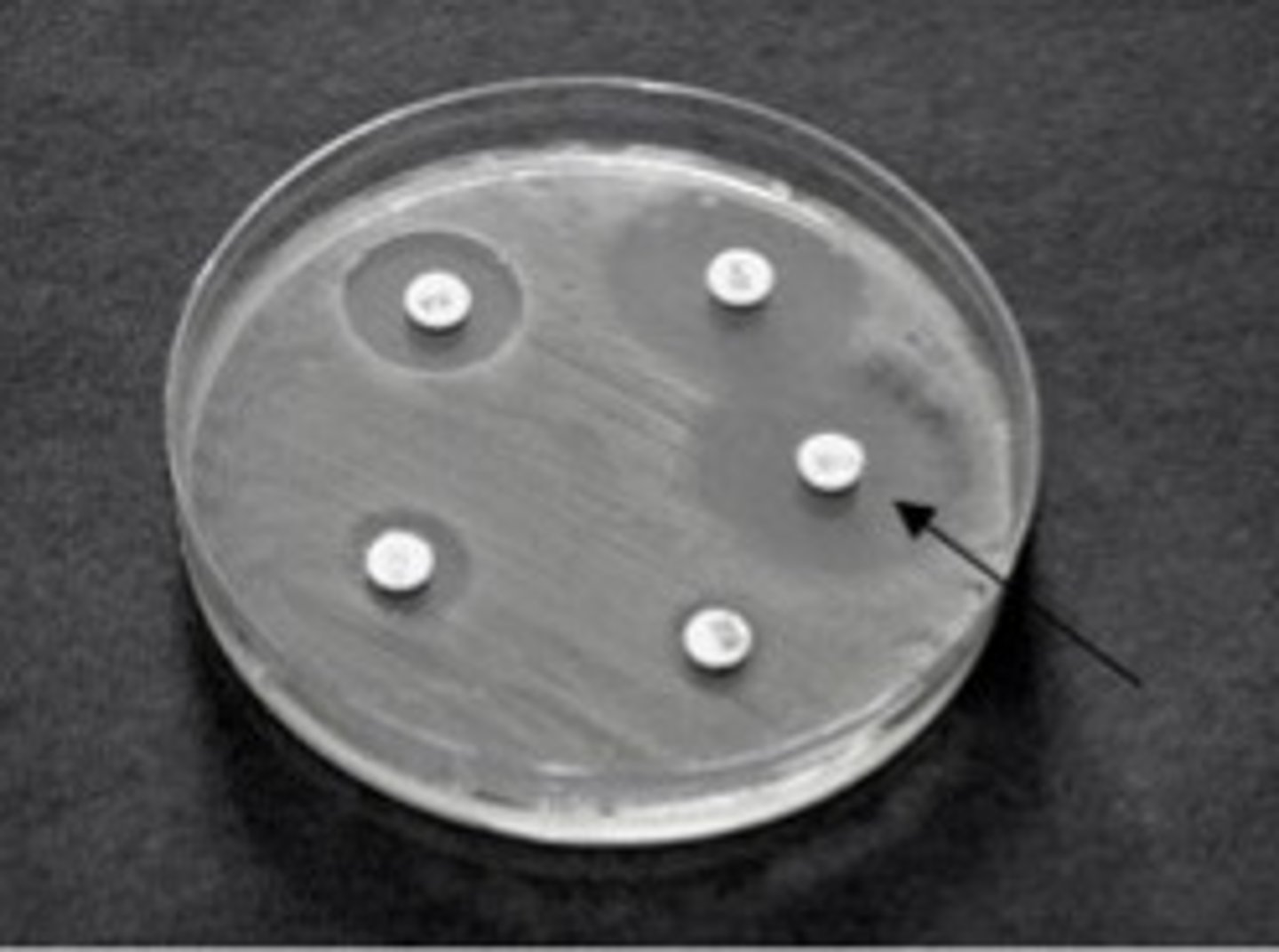
Zone of Inhibition
the clear region around a chemical saturated disc
- where bacteria are unable to grow due to adverse effects of the compound in the disc
Semmelweis
- a Hungarian maternity doctor
- advocated hand-washing to prevention disease transmission* from one patient to another
- was shunned by peers

How Diseases are Spread
- physical contact
- contaminated food/water
- infected animals
- droplets in the air
How to Prevent Infection
- skin hygiene
- nutrition
- protect skin,
- no sharing utensils
- cut raw meat separately
- disinfecting
- vaccines
- masks
- antiseptics

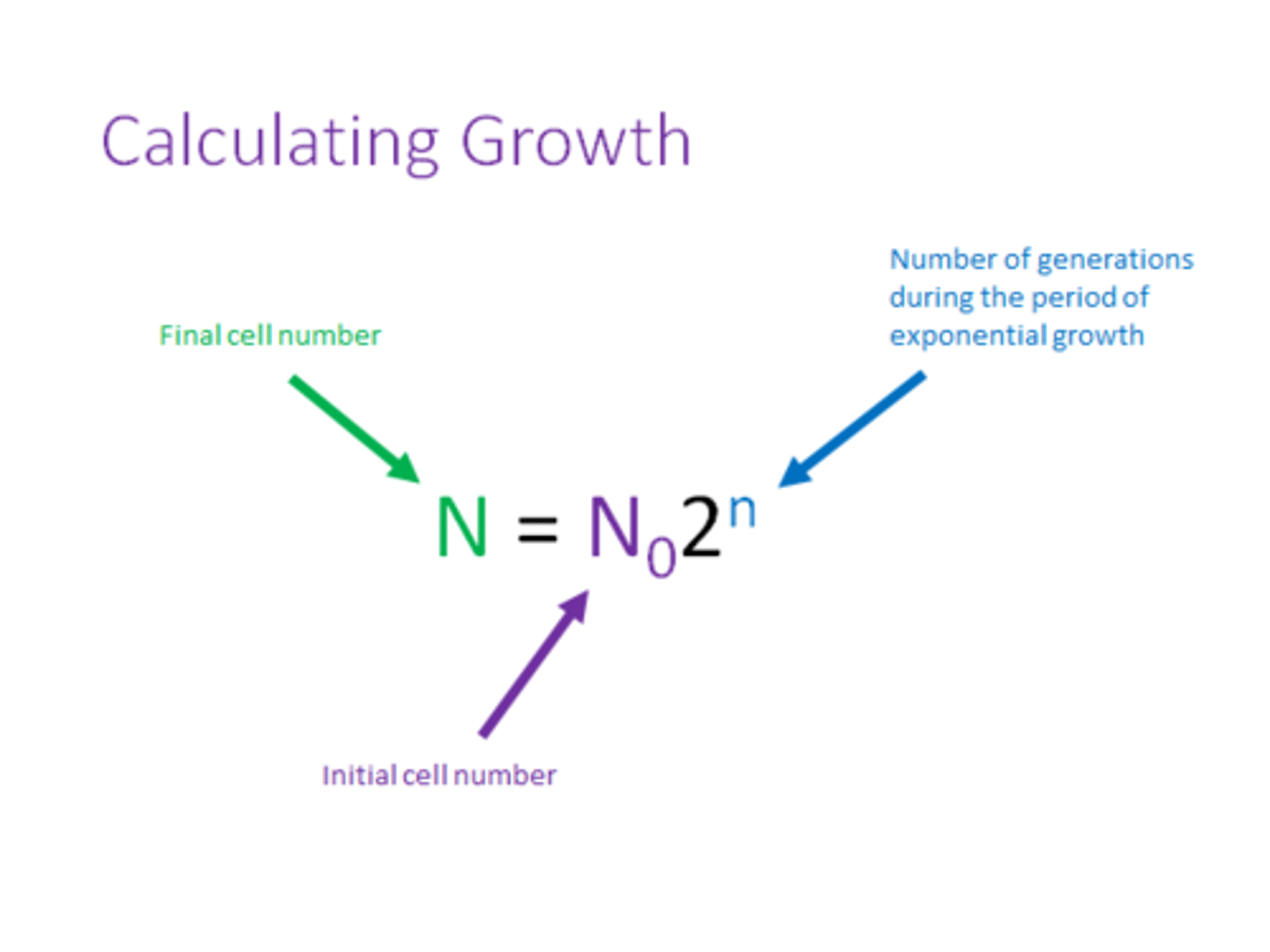
Final Number of Bacteria
start number x 2^number of divisions
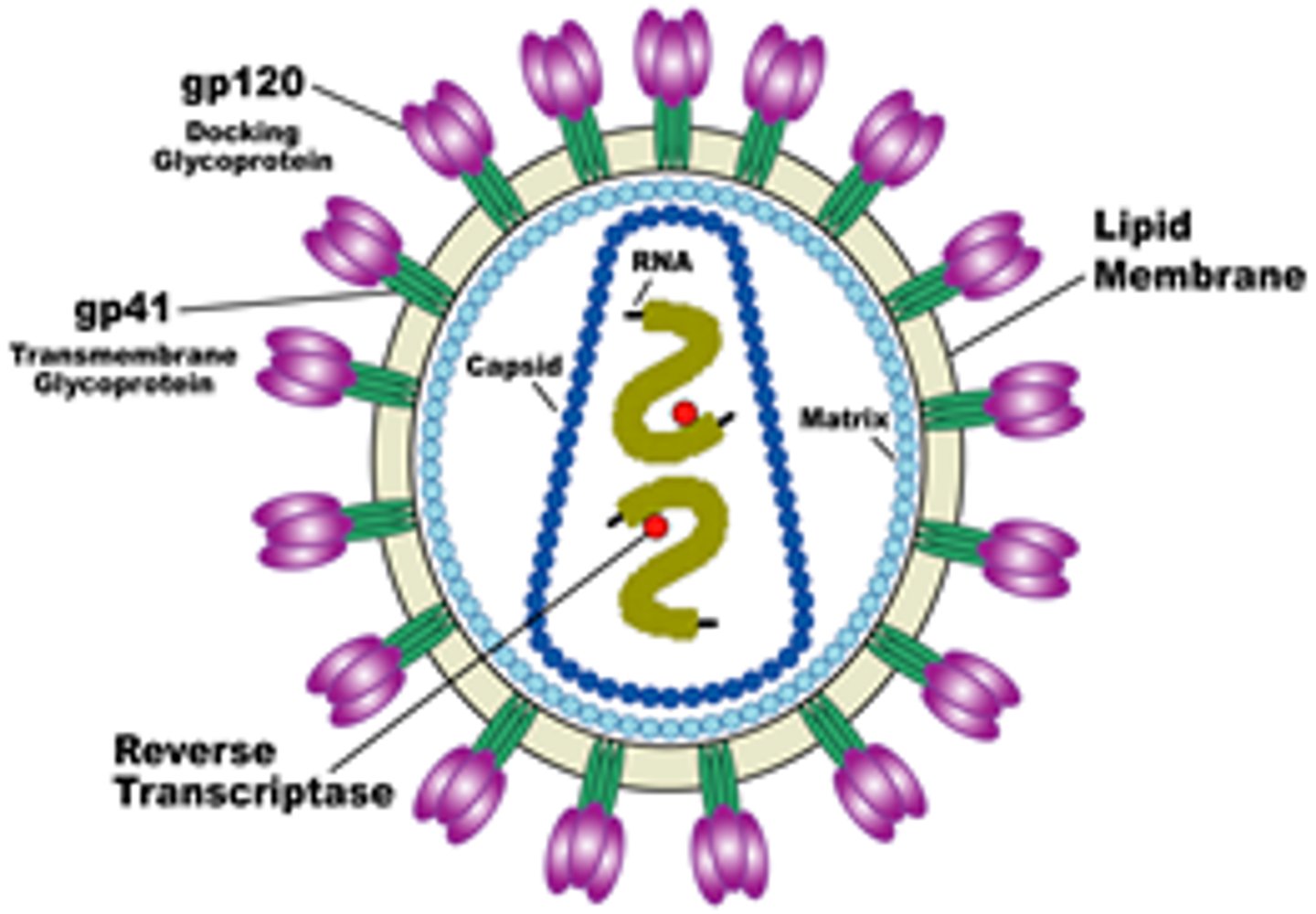
Illness - HIV/AIDS
virus that destroys the immune system that should protect the body from diseases
- passed from person to person through sexual acts, blood transfusions, used hypodermic needles, or from mother to child during birth
- experience a short flu-like illness 2 to 6 weeks laters
- can get a fever, sore throat, and body rash
- treated with antiretroviral medication to stop the virus replicating
Illness - Gonorrhea
a sexually transmitted bacterial disease caused by a gonococcus bacterium
- causes inflammation of the genital mucous membrane, burning pain when urinating, and a thick yellow discharge
- treated with antibiotics
- use barrier contraception
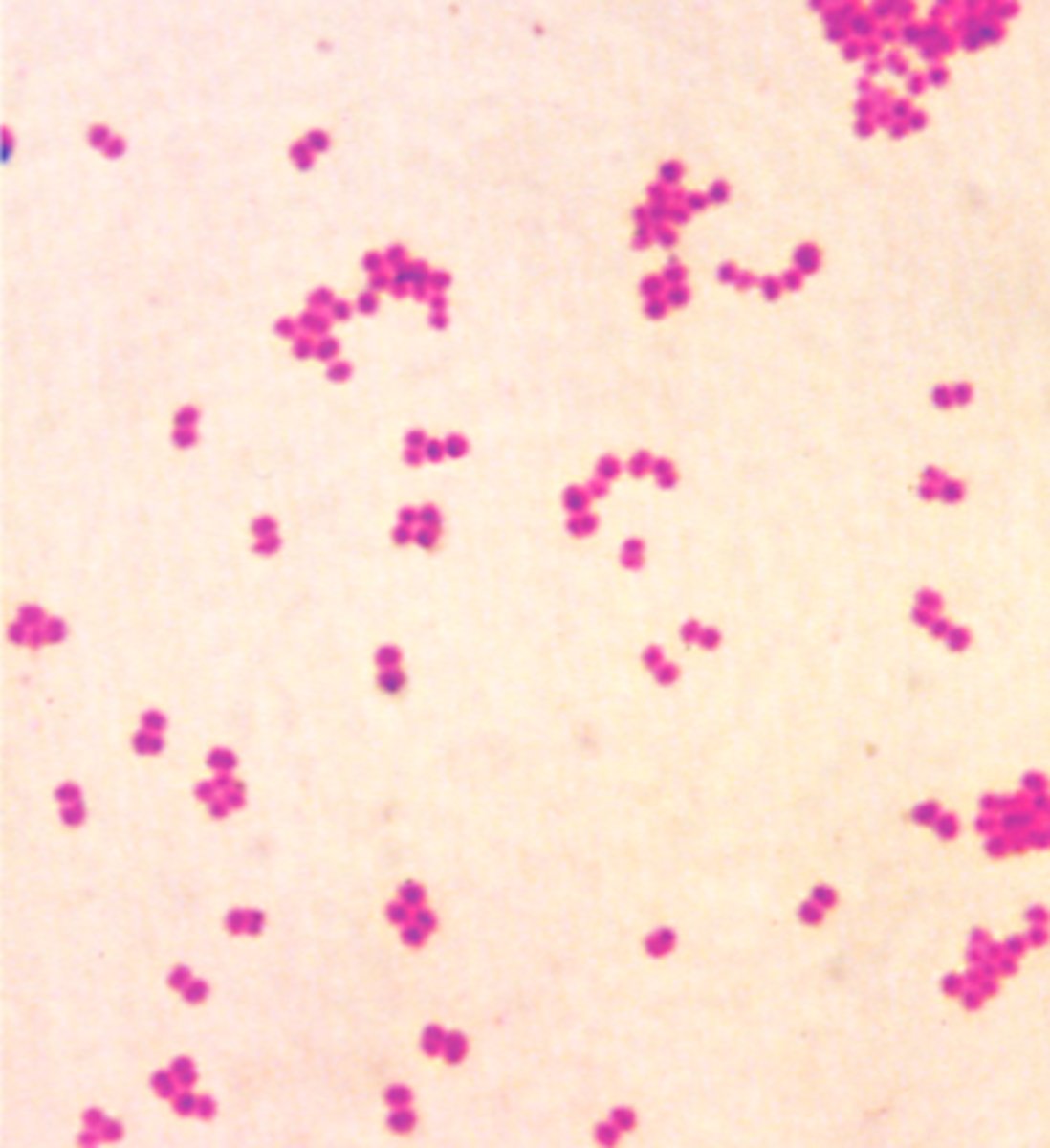
Illness - Measles
an infectious viral disease
- causing fever and a red rash on the skin
- cause aches and pains
- spread by inhalation of droplets
- typically occurring in childhood
- should avoid contact
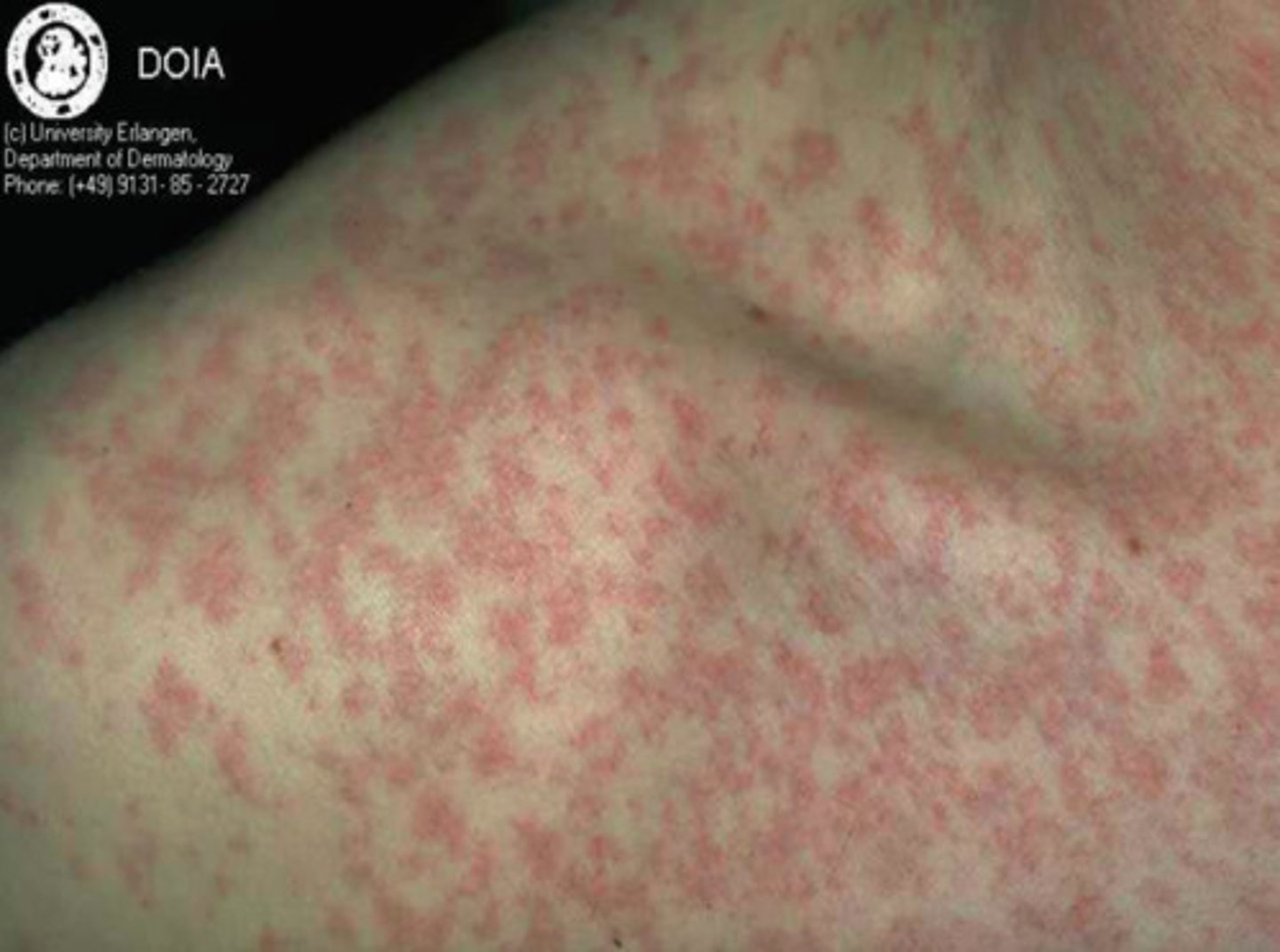
Illness - Tobacco Mosaic
a plant virus cause by contact with diseased plants
- causing mosaic patterns and reduced yields
- due to a lack of chlorophyll
- causing discolouration
- thus less photosynthesis
- unable to be cured with chemicals: no treatment
- need good field hygiene, pest control or using virus free seedlings

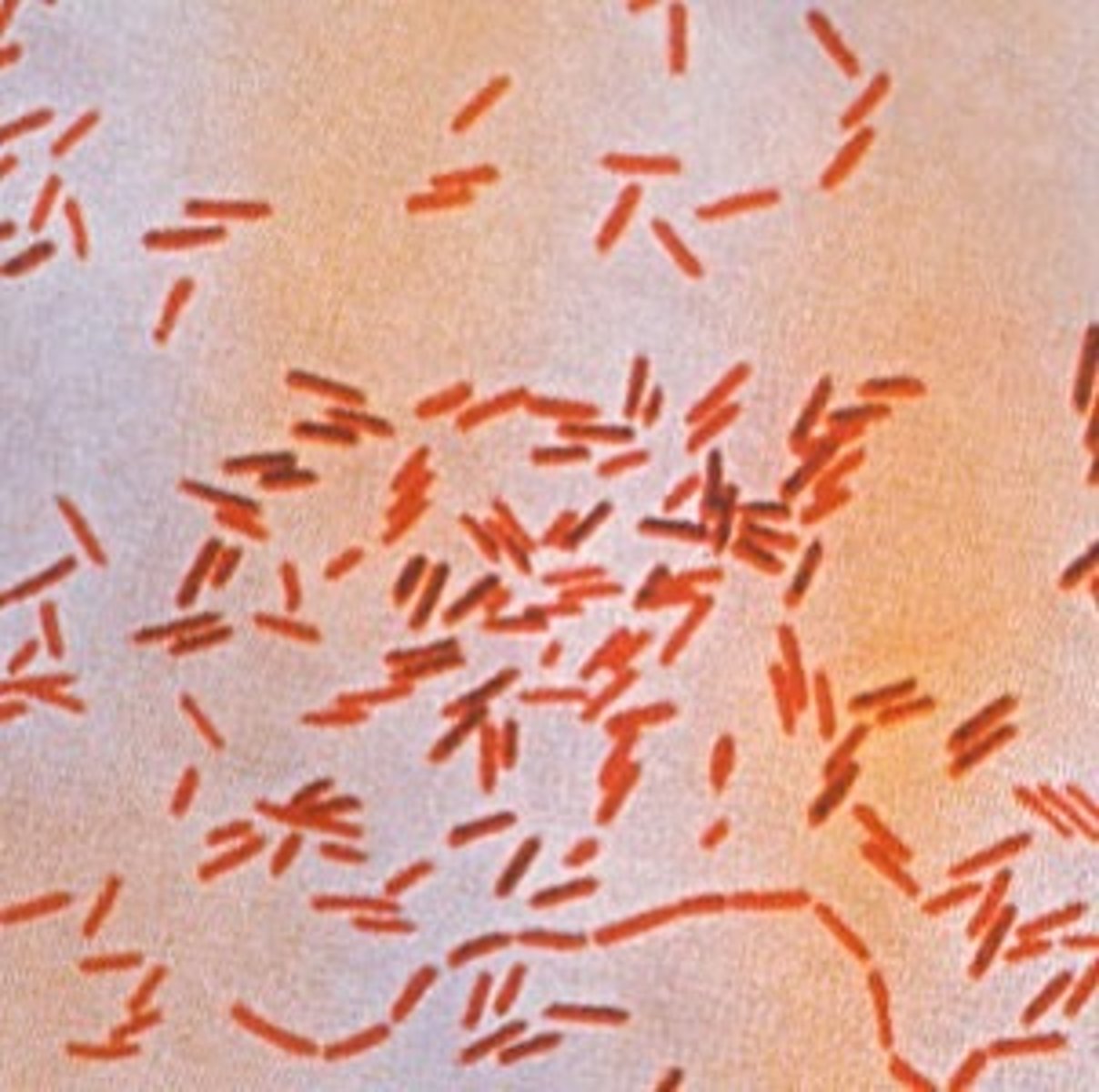
Illness - Salmonella
a bacterium
- occurs mainly in the intestine, especially a serotype
- causing food poisoning
- eating uncooked meat and eggs
- cause fevers, abdominal cramps, diarrhoea and vomiting
- no treatment: relies on immune system
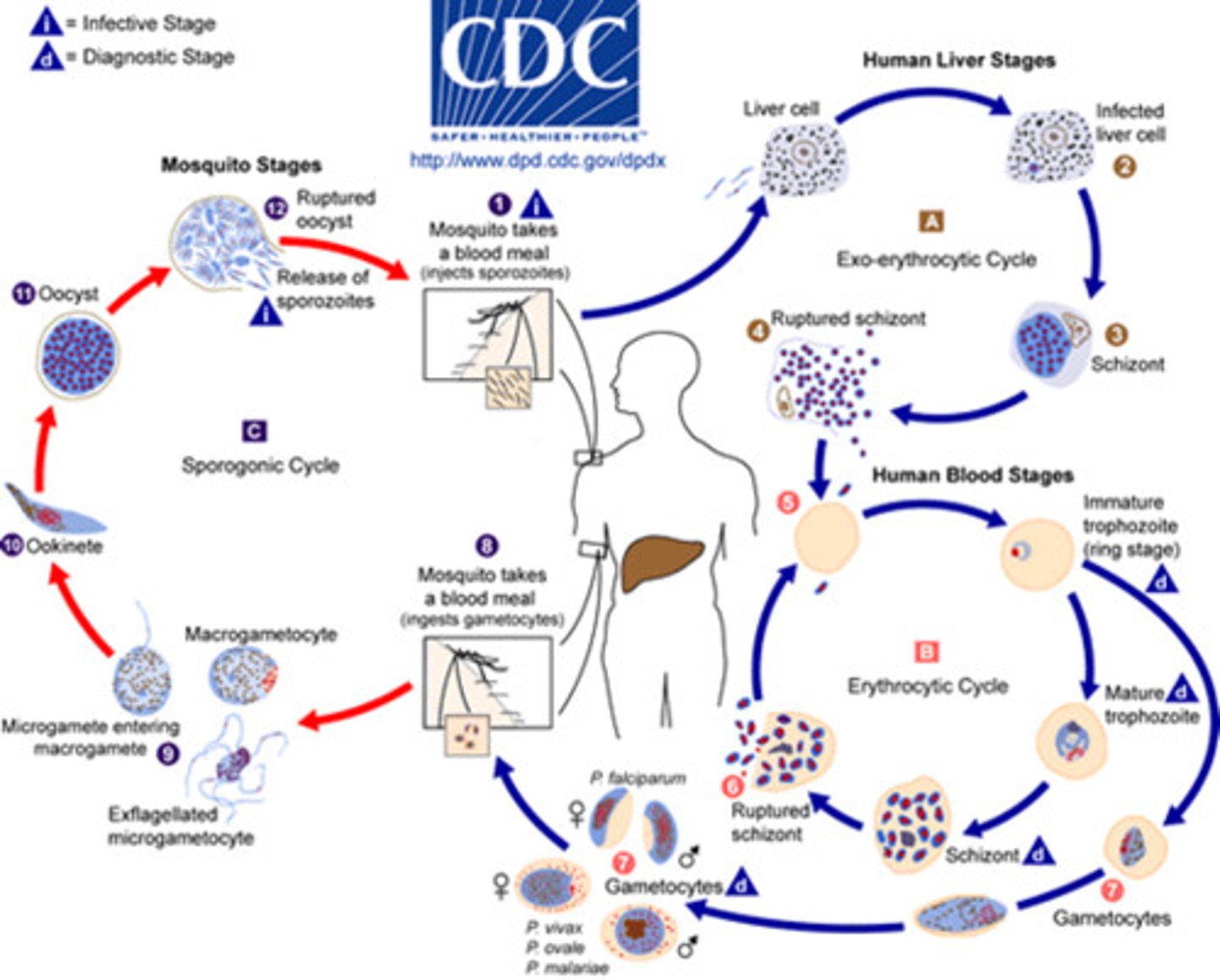
Illness - Malaria
- causes a recurrent fever, shaking, death and liver and RBC damage
- needs a combination of drugs or anti-malarial medication
- reduced by pesticides, repellents, nets and having less stagnant water
Illness - Rose Black Spot
- spread by spores in the air & water
- attack plant cells, reducing photosynthesis, black spots on leaves, chlorosis, leaves dropping off early
- needs chemical fungicide or to remove infected parts and burn
- reduced by selective breeding resistant roses
Protists
a eukaryotic organism that can not be classified as an animal, plant, or fungus.
- are living
- microscopic to large
- either unicellular or multicellular
- in a moist environment

Malaria Cycle
- pregnant female mosquito bites human
- malaria parasite reproduce asexually in the liver
- gets into the blood
- different mosquito feeds in the blood and gets infected
- grows sexually in its salivary gland: causes variation so is hard to vaccinate against
Unhealthy Person's Symptoms
- a temperature
- hair loss
- lethargic
- swelling
- bad teeth
- patchy skin
- paleness
- vomiting
- blood shot/tired eyes
Communicable Disease
disease that is transmitted from one individual to another
A Healthy Person
- free from disease
- balanced diet
- positive mental health

Health
complete physical, mental, and social well-being

Pathogens
micro-organisms that cause communicable disease
Bad Bacteria
- are living cells
- produce toxins inside your body
- can damage cells & tissues
- in & our body: everywhere and anywhere
- are very small
- can reproduce rapidly: in binary fission
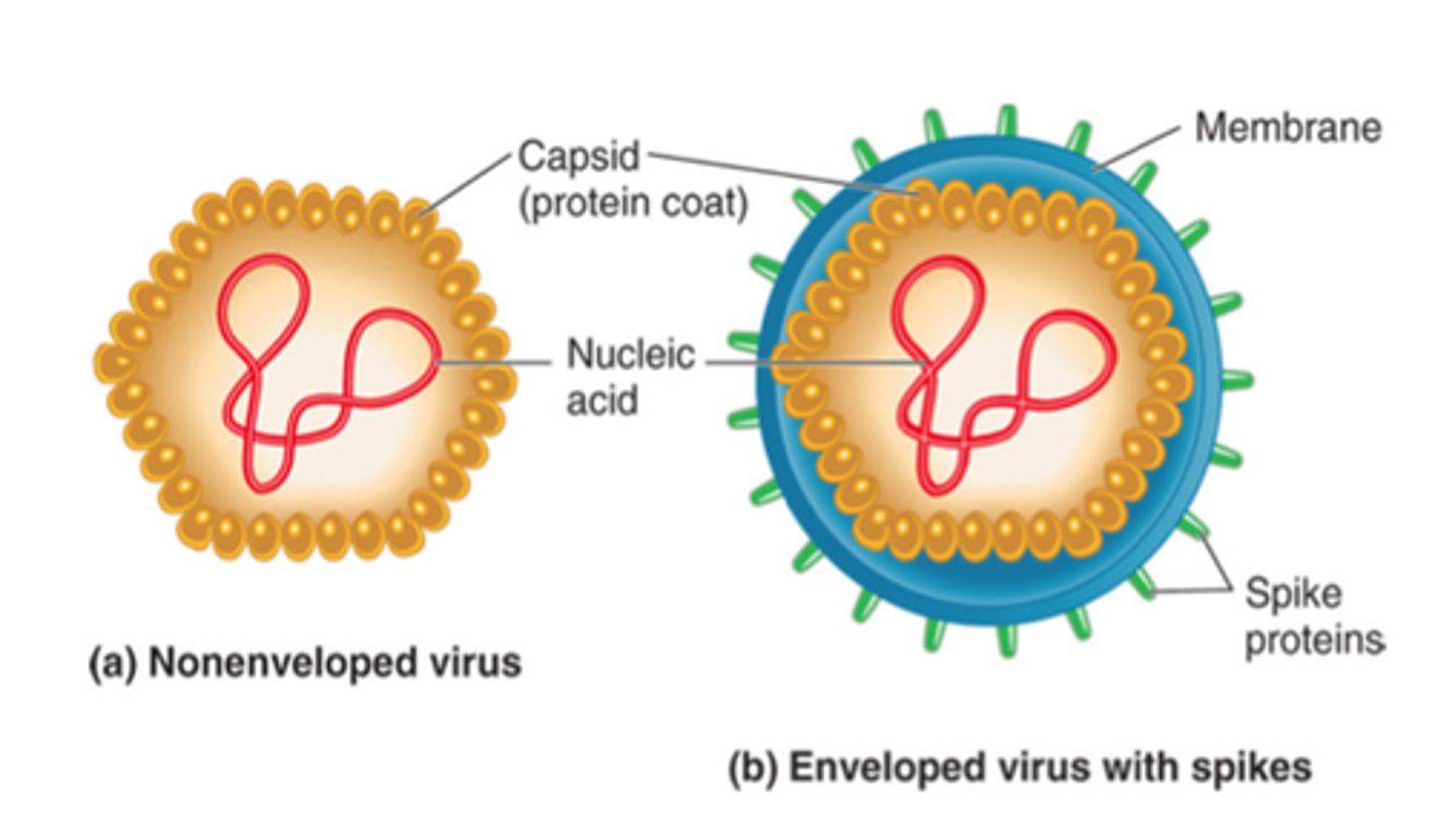
Viruses
- are not living
- can reproduce & replicates rapidly
- takes over / get in cells
- can make cells burst/ get damaged
- are 1/1000th of a bacteria cell
Human Defence Responses
- physical contact: ear wax / hair, tears, eyelashes, dead skin, body hair, scabs
- contaminated food/water: stomach acid, vomiting
- droplets in the air: nose hair, mucas, sneezing
- white blood cells engulfing pathogens/ creating anti toxins

Phagocytes
a type of white blood cell that ingests invading microbes
- attack anything foreign to the body
Lymphocytes
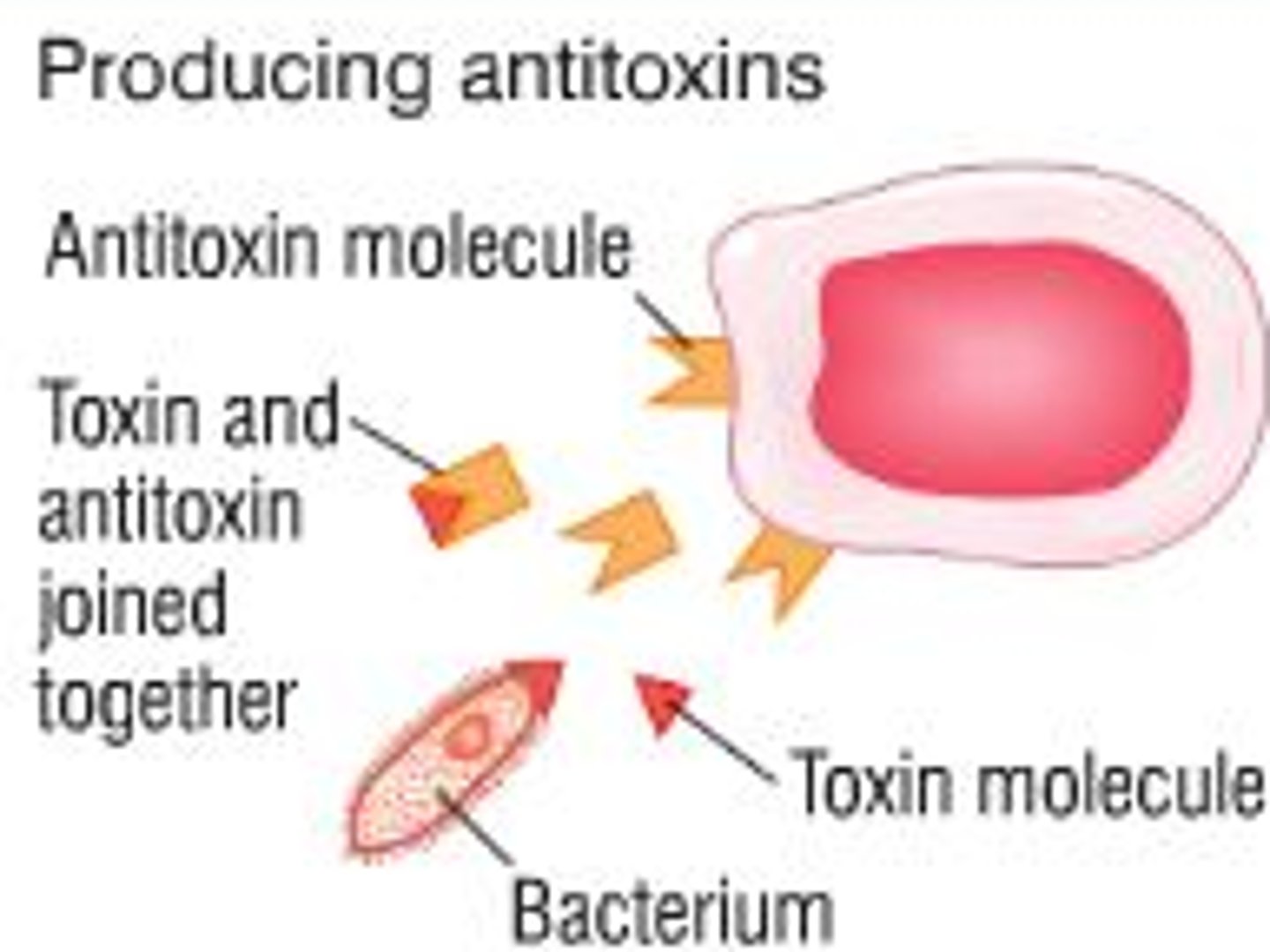
a type of white blood cell that make antibodies to fight off infections
- specific to the antigen
- produce antitoxins
Antitoxins
produced by the host body and neutralise toxins
Aphids
insects that penetrate the plant phloem and feed on the dissolved food
- act as plant pathogens
- vectors that carry pathogens: viruses, bacteria, and fungi into healthy plant tissue
- does not allow glucose to be received: less photosynthesis
- leaves holes that let other pathogens enter
- leaves hone due which becomes a fungal colony habitat and attracts other insects

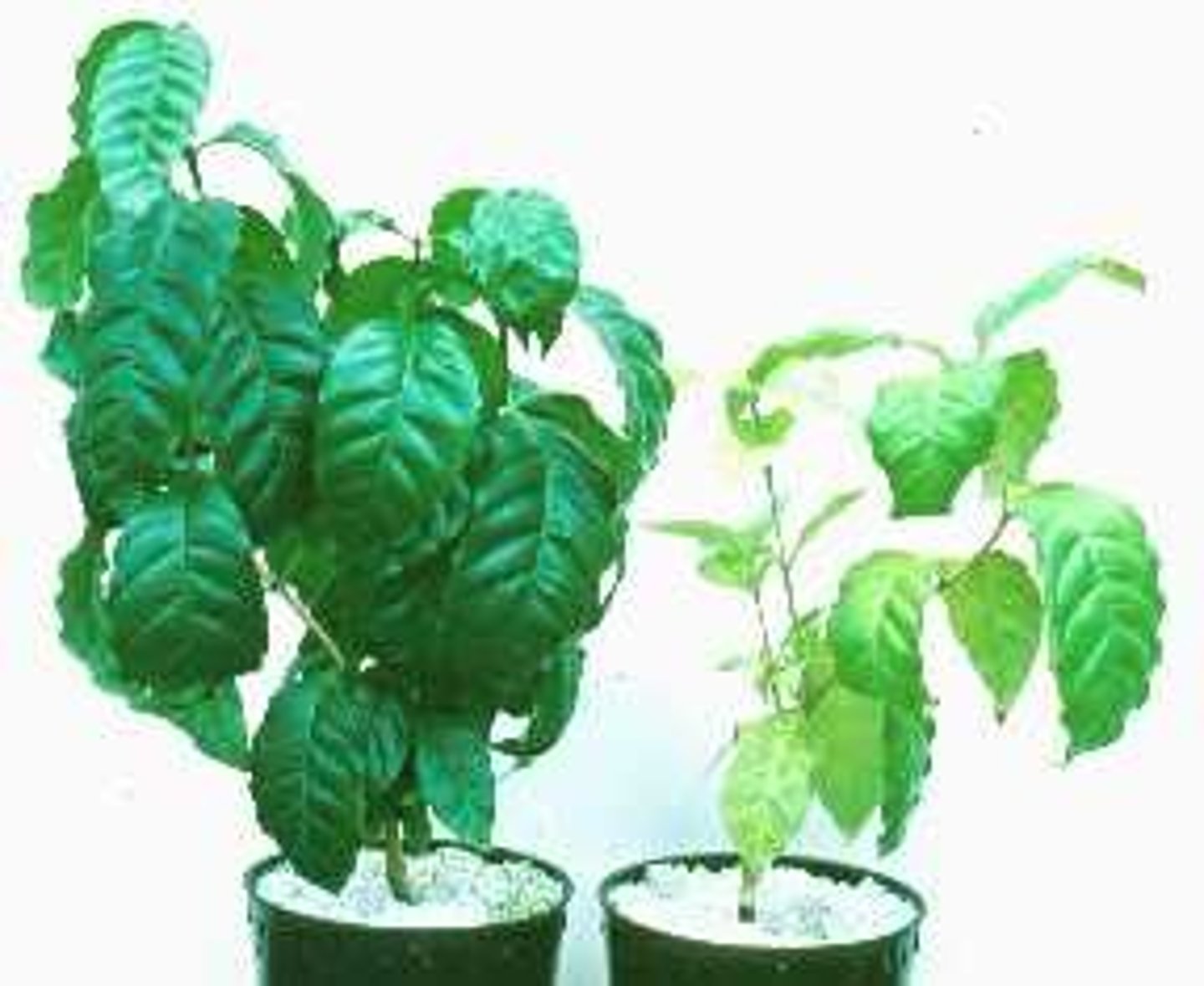
Lack of Nitrate in Plants
- lack of amino acids / proteins
- can stunt growth
- cause yellow leaves (chlorosis)

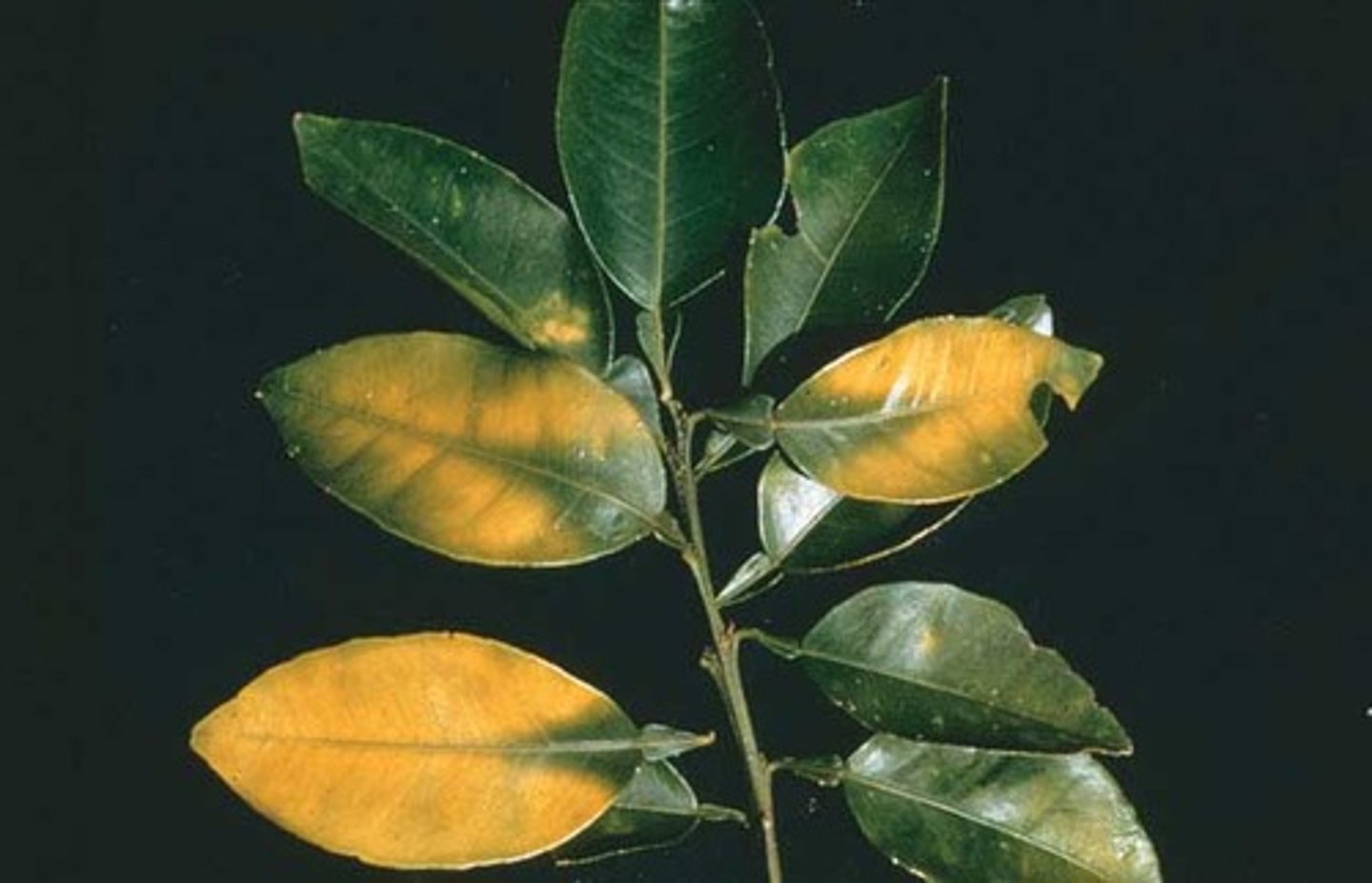
Lack of Magnesium in Plants
- lack of chlorophyll
- cause yellow leaves (chlorosis )

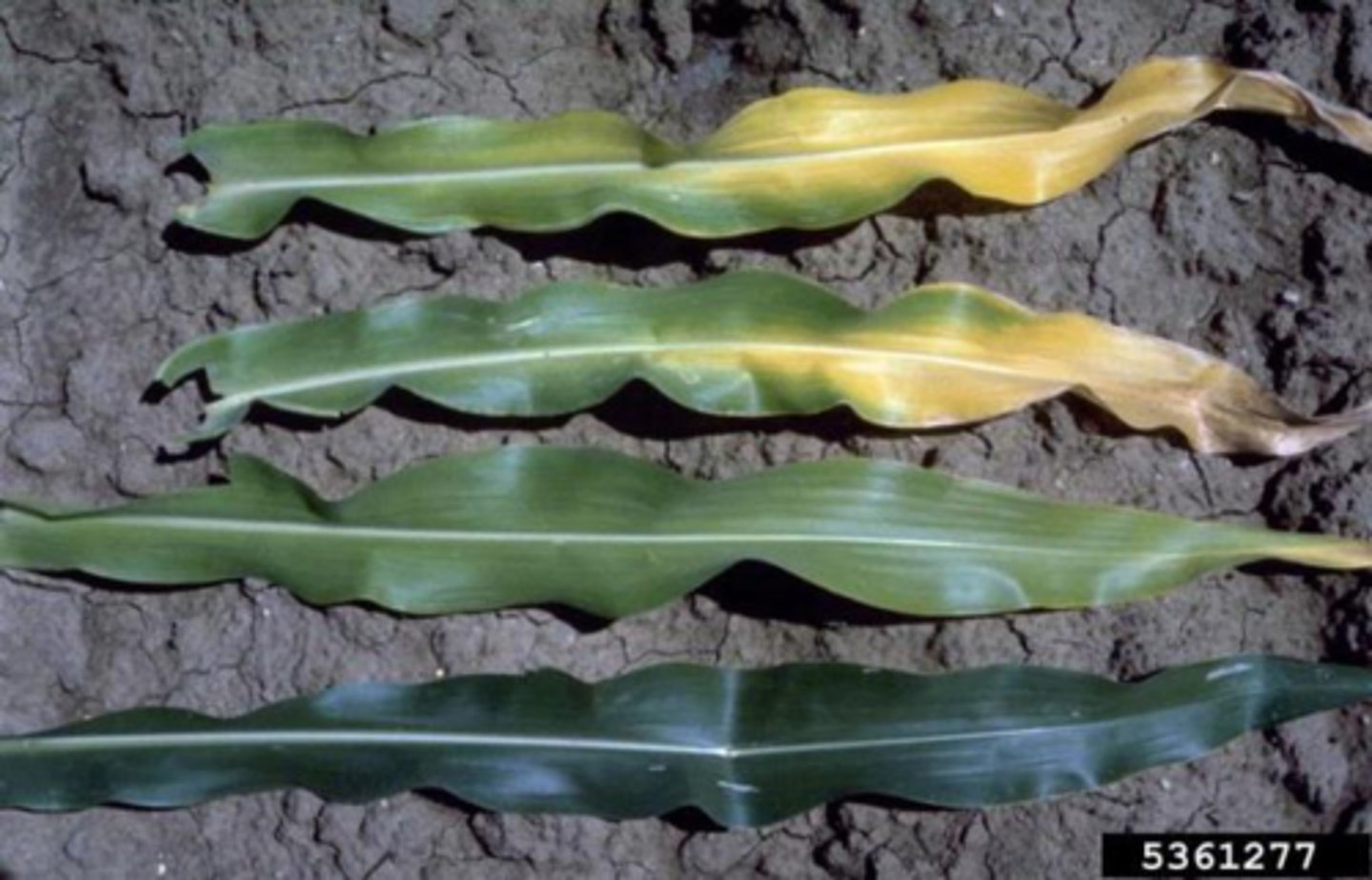
Lack of Phosphate in Plants
- lack of DNA/ cell membrane
- so there's reduced root growth
- causes discoloured leaves: lack of minerals and water available
Lack of Potassium in Plants
- lack of photosynthesis/ respiration
- cause poor growth
- discolour leaves

Plant Defence Response - Celluose Cell Walls
- strengthens plant cells
- resistantto pathogens invading
- physical
Plant Defence Response - Tough Waxy Cuticle
barrier to pathogens entry
- physical

Plant Defence Response - Layer of Dead Cells
protective layer against pathogens
- when it sheds, the pathogens fall as well
Plant Defence Response - Antibacterial Chemicals
attack against pathogens
- chemical
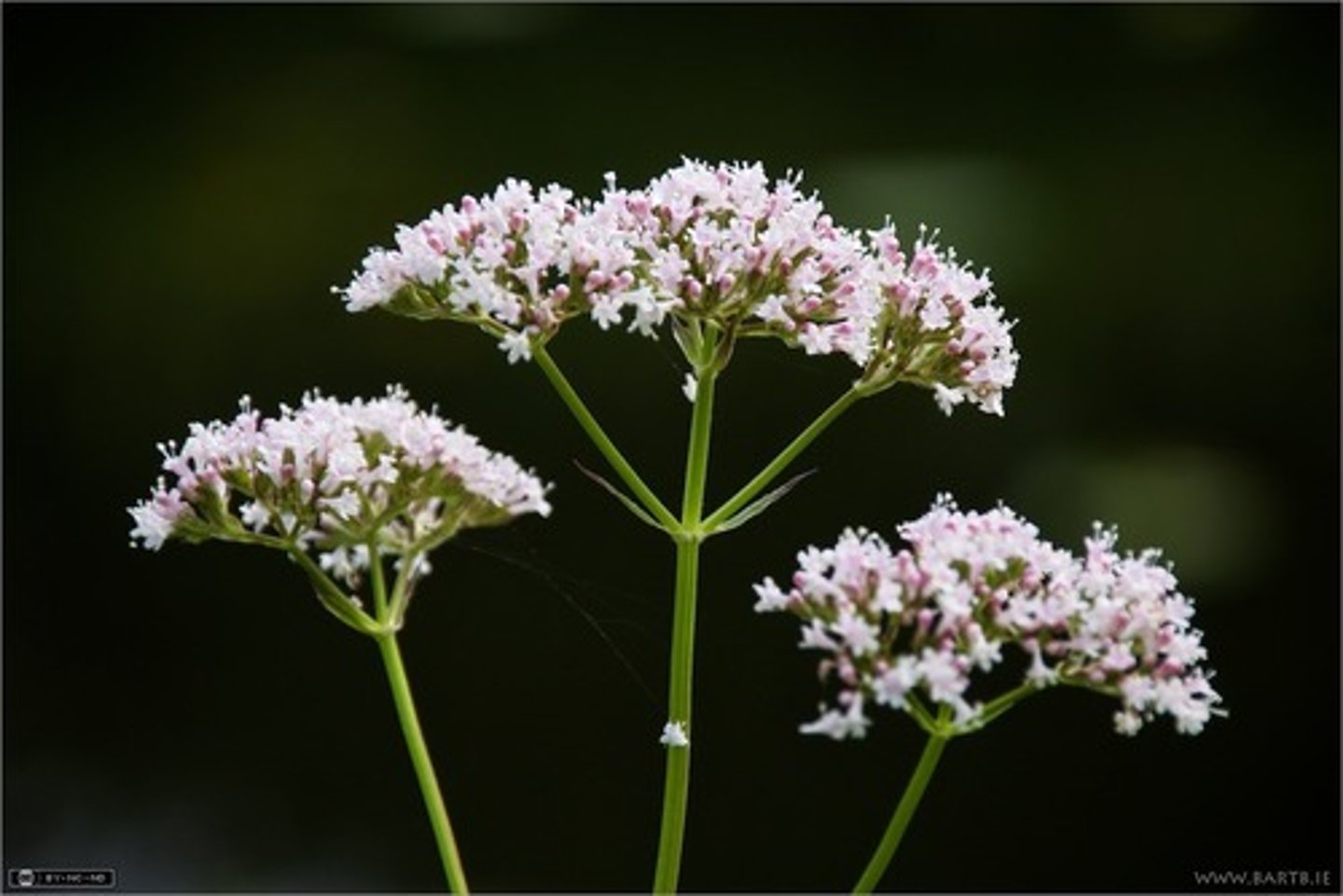

Plant Defence Response - Poison
deters animals away from eating
-less likely to be eaten
- chemical
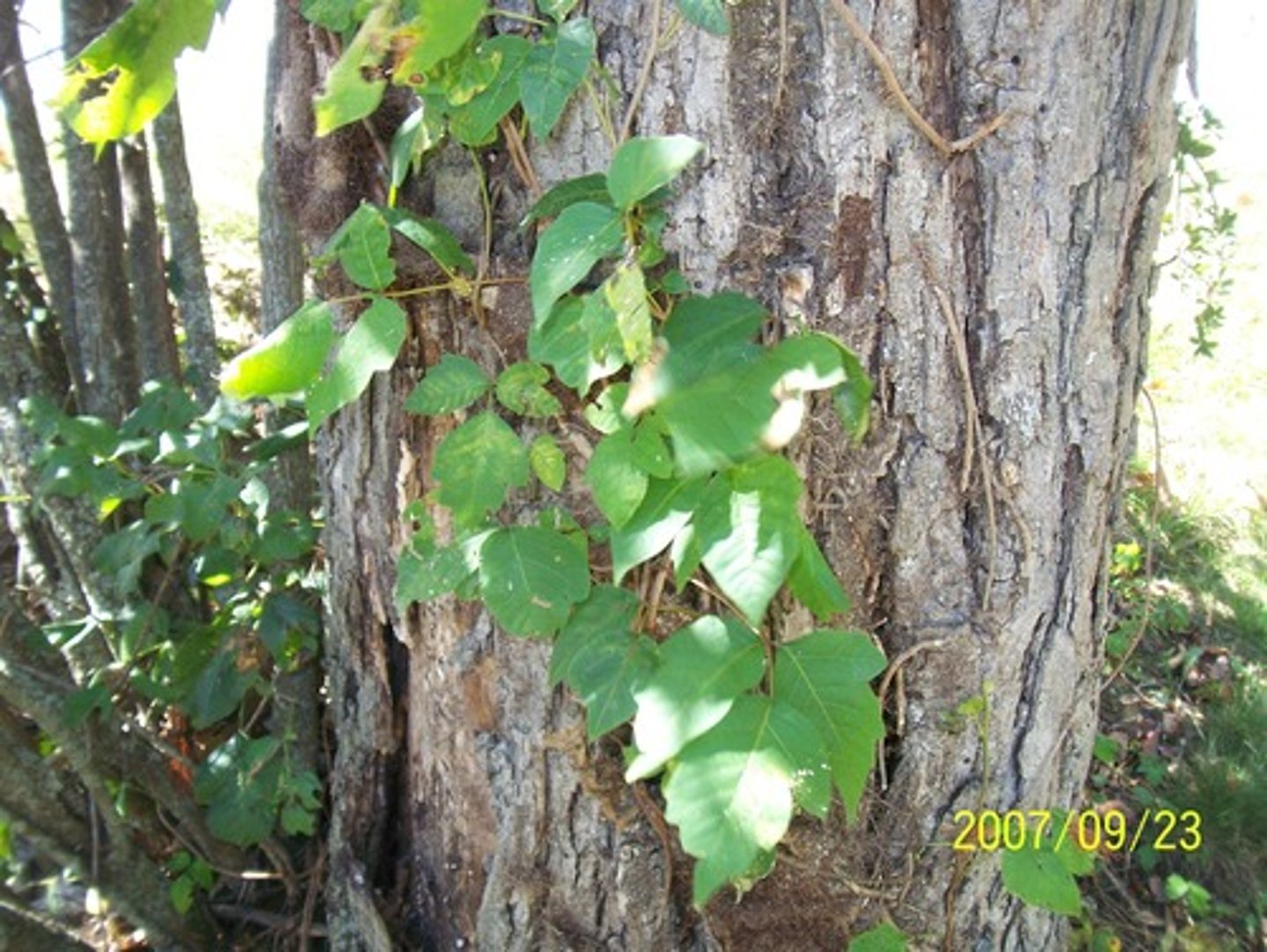

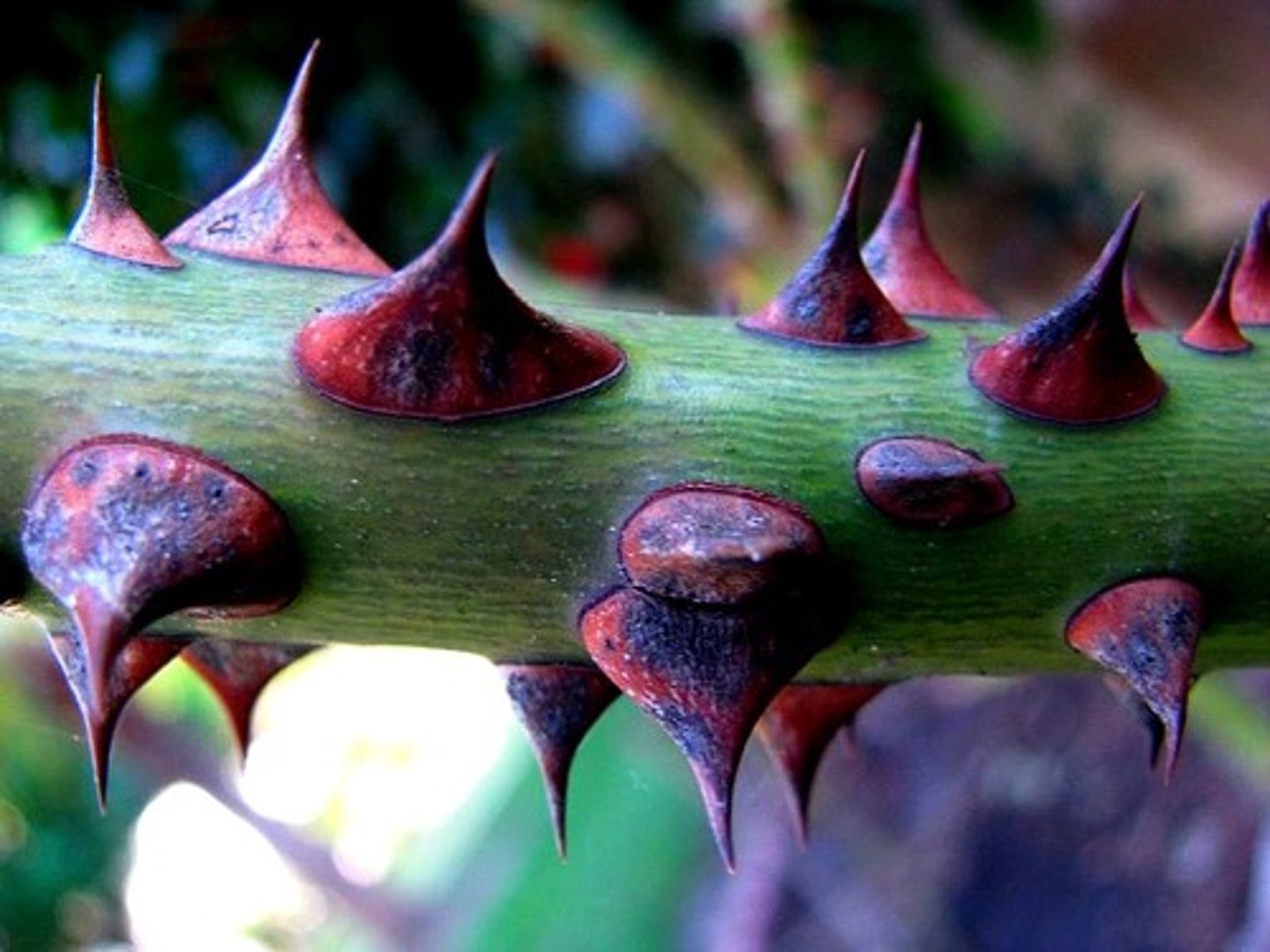
Plant Defence Response - Thorn / Fine Hair
deters insects & animals from eating
- unpleasant/painful to eat
- physical

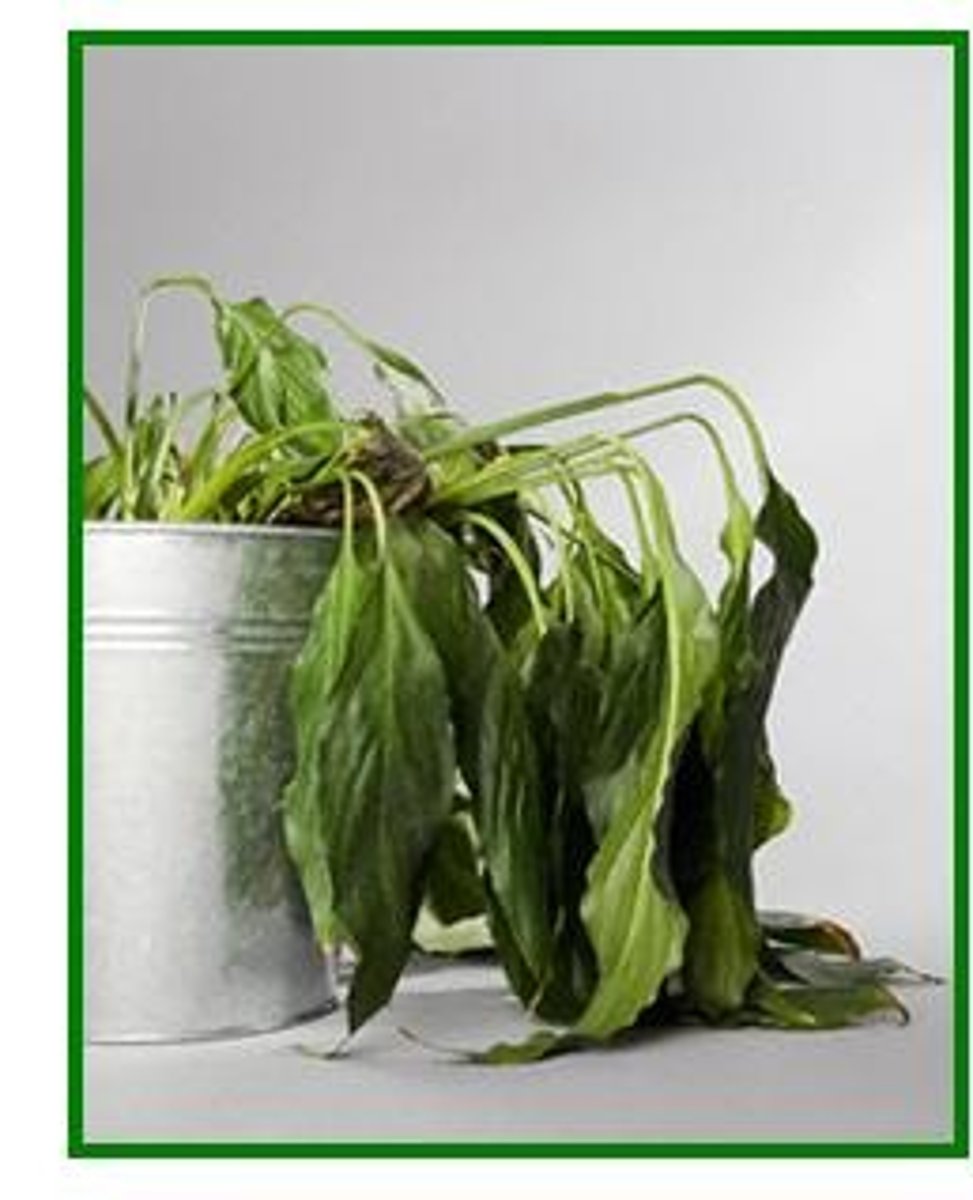
Plant Defence Response - Drooping Leaves with Touch
- frightens animals
- dislodges insects
- unappealing
- mechanical

Plant Defence Response - Mimicking Unhealthy Plants
- look's unappealing
- deters insects & animals
- mechanical
