3.4 - CompTIA A+ Core 1
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
Hard Disk Drive (HDD)

A non-volatile magnetic storage device that operates using rapidly rotating platters.
Non-volatile storage
A type of storage that retains data even when not powered.
Random-access
The capability to retrieve data from any part of a drive at any time.
HDD actuator
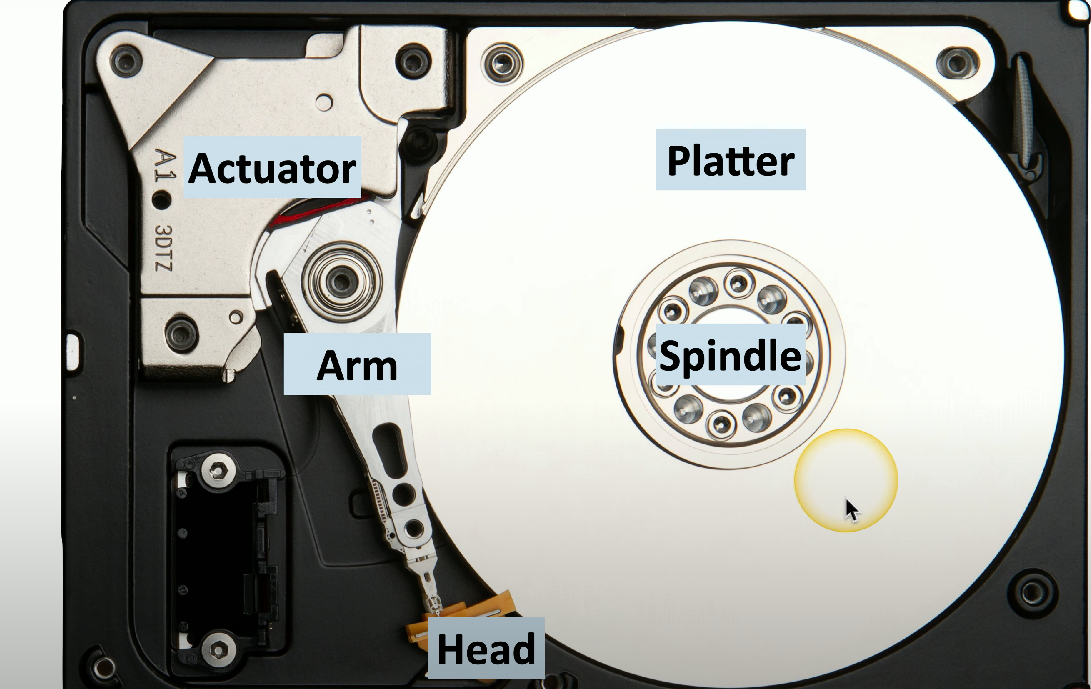
The mechanism responsible for positioning the read/write head over the correct track on the disk.
HDD platter
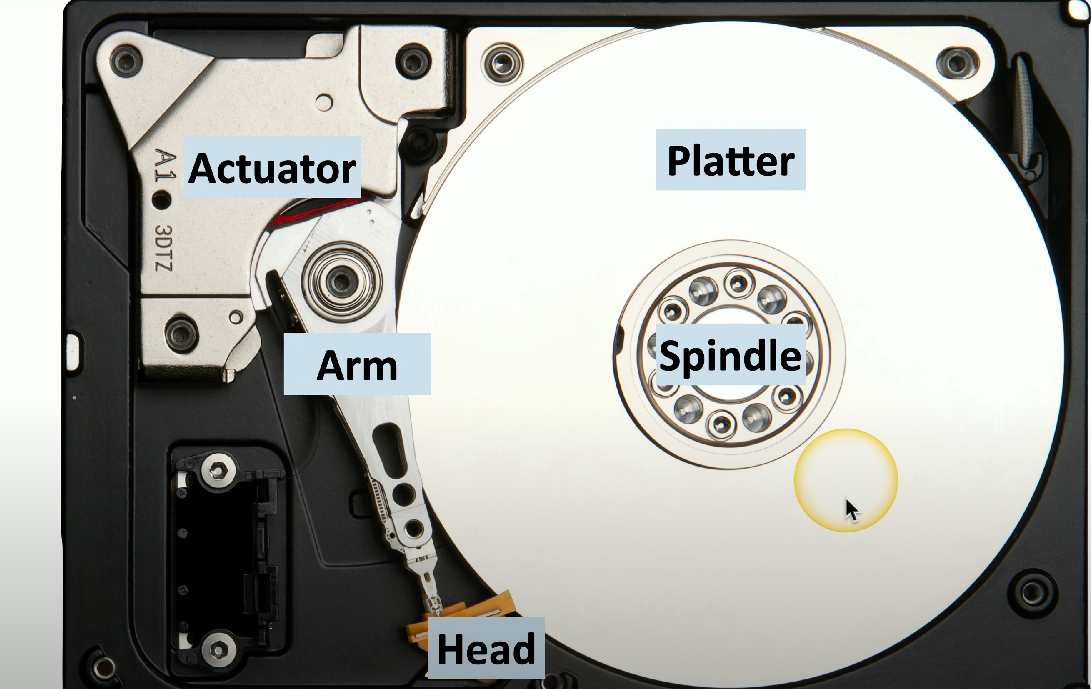
Circular disks coated with magnetic material where data is stored in concentric tracks.
HDD spindle
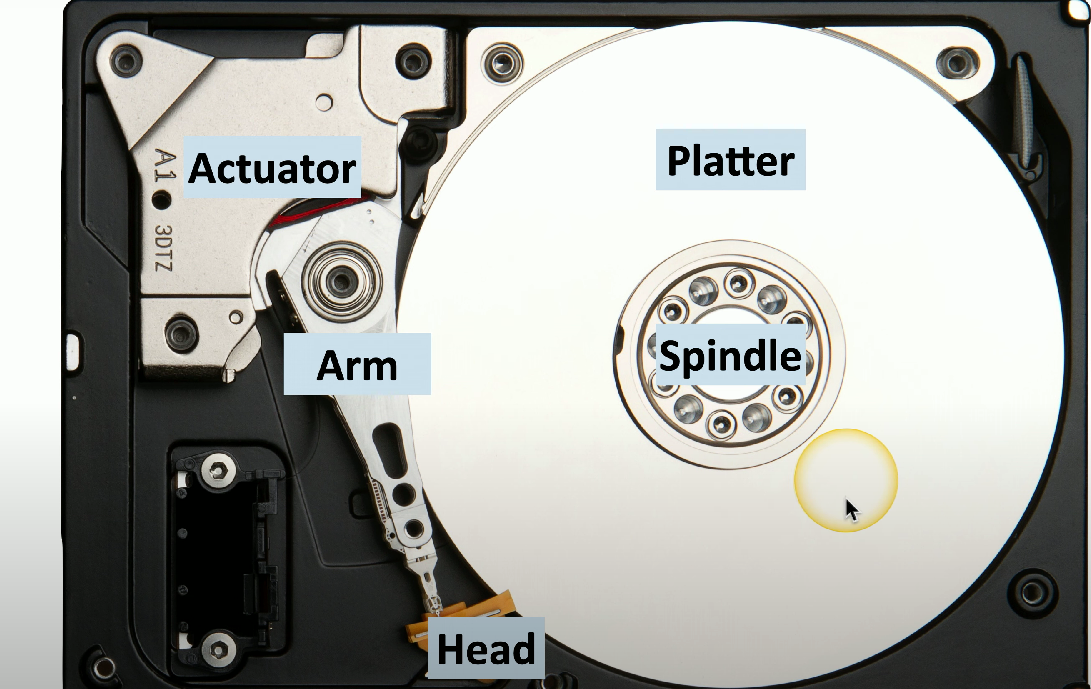
The rotating shaft that holds the HDD platters in place, enabling them to spin.
HDD arm
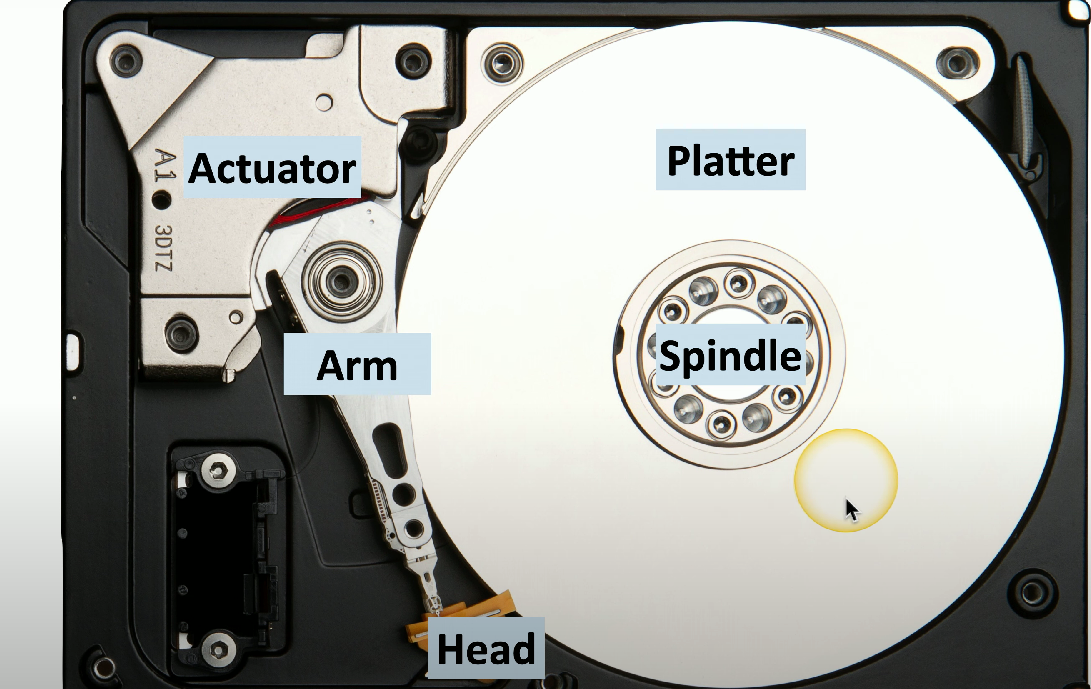
Responsible for moving back and forth to find data on the HDD.
HDD spindle speed
Regulates the latency for retrieving data; higher speeds result in lower latency.
HDD head
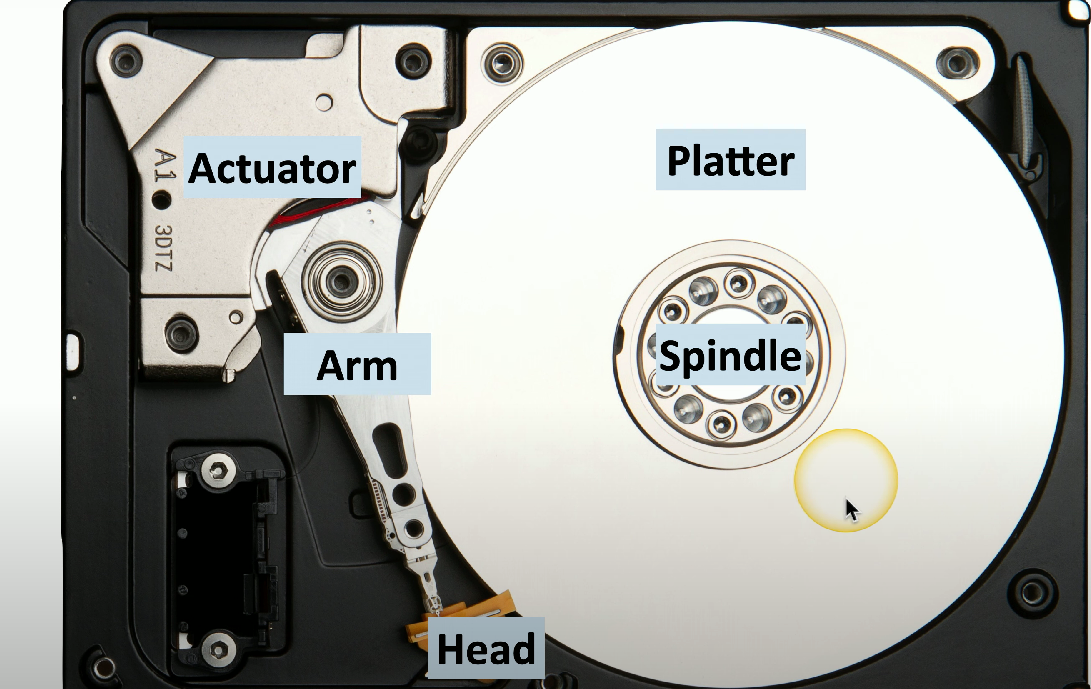
Used to precisely locate, retrieve, and write data to spinning platters.
5,400 rpm
Spindle speed providing approximately 5.55ms rotational latency.
7,200 rpm
Spindle speed providing approximately 4.16ms rotational latency.
10,000 rpm
Spindle speed providing approximately 3ms rotational latency.
15,000 rpm
Spindle speed providing approximately 2ms rotational latency.
3.5 inch form factor
Common form factor found in larger desktop computers.
2.5 inch form factor
Common form factor found in smaller laptops.
M.2 form factor
A newer form factor that can be found in both laptops and desktops.
Solid-state drive (SSD)
A non-volatile storage device containing no moving parts, using flash memory chips.
Benefits of SSDs
There are no moving parts, and very fast performance without latency from spinning drives.
Communications interface
Used to access data from an SSD/storage device.
Non-volatile memory express (NVMe)
A communication interface designed to optimize the performance of SSDs. Lower latency, and can use am M.2 form factor.
Peripheral Component Interconnect Express (PCIe)
An expansion bus standard used to connect external devices to a motherboard.
Mini-serial Advanced Technology Attachment (mSATA)
A compact SSD interface that reduces the size compared to SATA drives.
Flash drives
External storage devices using EEPROM that are non-volatile and require no power to maintain data. Limited number of writes.
Optical drives
Devices that use laser technology to read and write data on discs, albeit at slower speeds.
EEPROM
Electrically erasable programmable read-only memory used in flash drives.
Data storage method in optical drives
Data is encoded in pits and lands on the disc surface.
CD-ROM
A format of optical disc used primarily for storing digital data.
DVD-ROM
A format of optical disc used for storing larger amounts of data than CDs.
Blu-ray
A high-capacity optical disc format designed for storing high-definition video.
Redundant Array of Independent Disks (RAID)
Technology used to combine multiple hard drives into a single unit for improved performance and redundancy.
Why RAID is not a backup
RAID uses data that is actively retrieved or stored - it is not a backup of data in a separate location.
RAID 0
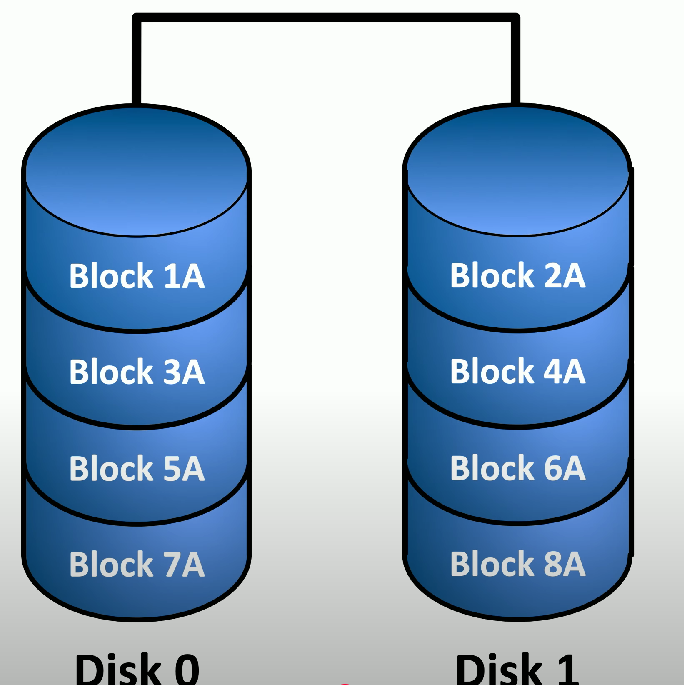
Striping - a RAID system that stripes data evenly onto multiple disks to enhance performance but provides no redundancy.
RAID 1
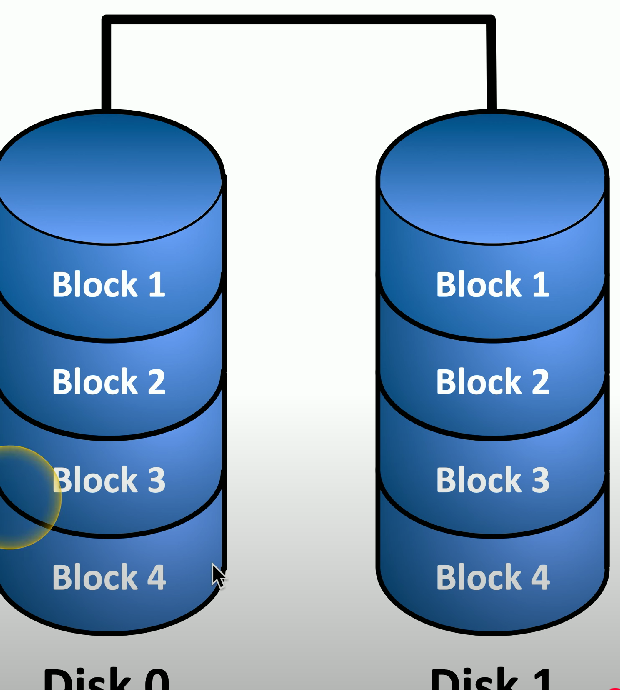
Mirroring - a RAID system that mirrors data between two or more drives, offering high redundancy and requiring double disk space.
RAID 5
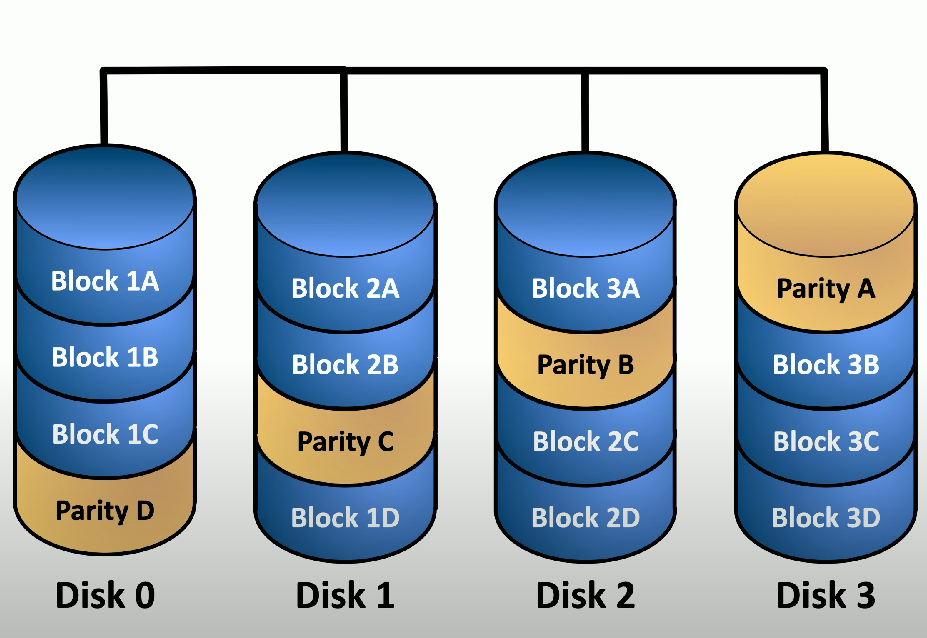
Striping with parity - a RAID system that stripes data across multiple drives while storing a single parity block for high redundancy and efficient space utilization.
RAID 6
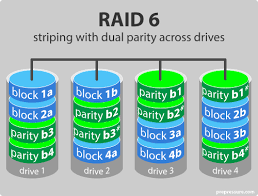
Striping with double parity - RAID system that uses double parity blocks, allowing two drives to fail without data loss but may slow performance.
RAID 10 (RAID 1+0)
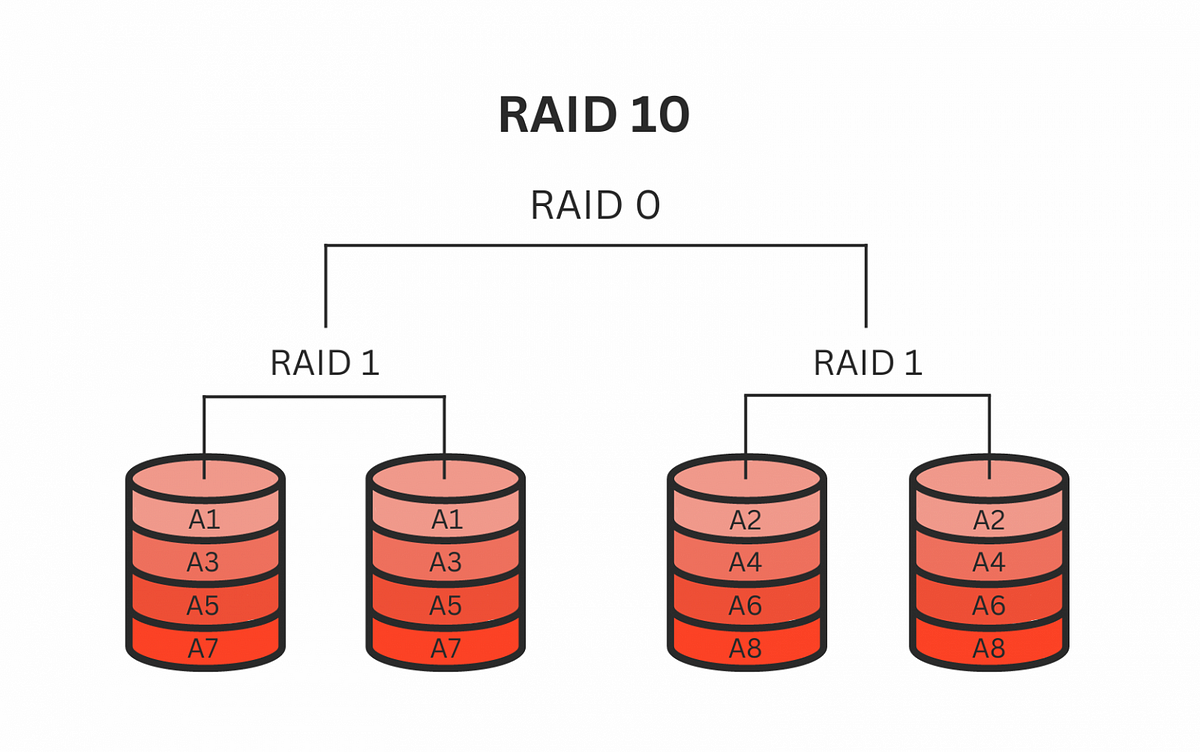
A stripe of mirrors - combines RAID 0 (striping) with RAID 1 (mirroring) for high redundancy and high speed, requiring at least four drives.
Data Redundancy in RAID
The ability to recover data after a drive failure, present in RAID 1, RAID 5, and RAID 6.
Performance Enhancement in RAID
The improved speed in data access and retrieval, primarily seen in RAID 0.
Parity in RAID systems
Extra data stored in RAID arrays that allow for data recovery in case of a single drive failure, used in RAID 5 and RAID 6.
RAID system requirements
Different RAID configurations require a specific number of drives, with RAID 10 needing at least four.