Market Efficiency, Consumer & Producer Surplus in Economics
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
18 Terms
Consumer Surplus
Consumer surplus is the amount a buyer is willing to pay minus the amount they actually pay.
Benefit of Consumer Surplus
It measures the benefit buyers receive from participating in a market.
Relation to Demand Curve
Consumer surplus is closely related to the demand curve.
Measuring Consumer Surplus
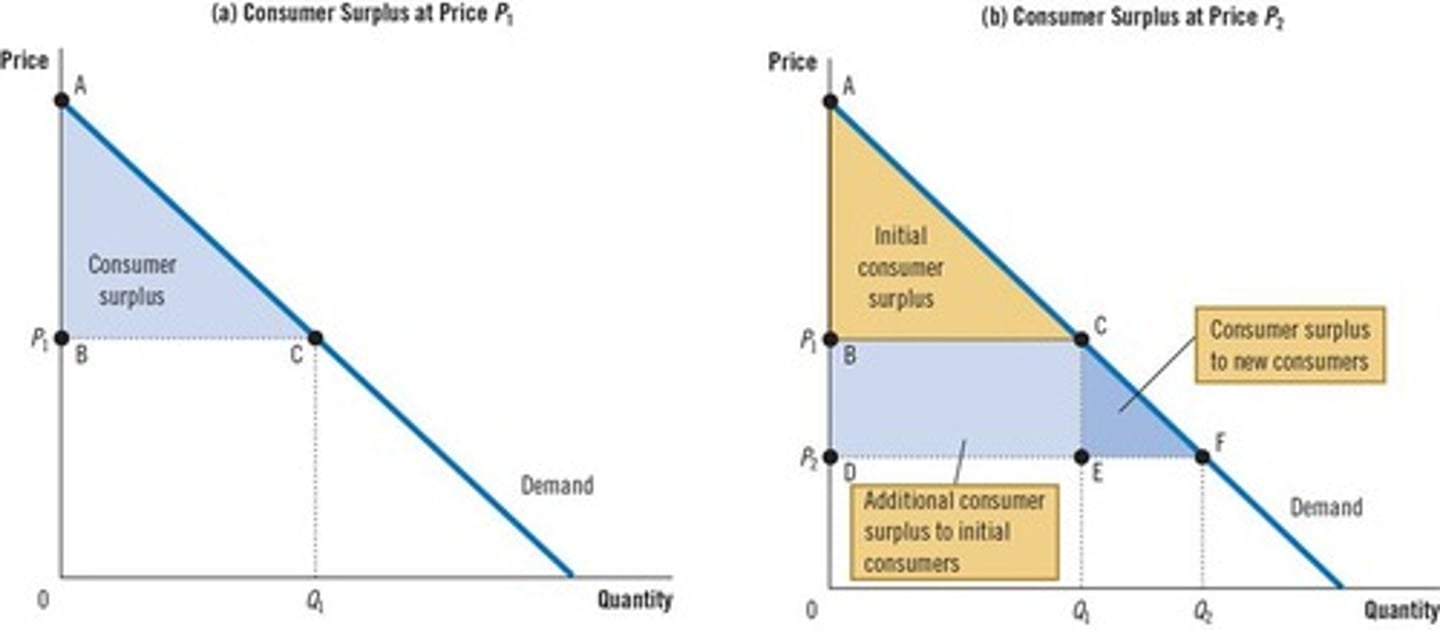
The area below the demand curve and above the price measures consumer surplus.
Marginal Buyer
It reflects the willingness to pay of the marginal buyer at any quantity.
Effect of Lower Price on Consumer Surplus
A lower price increases consumer surplus because existing buyers pay less and new buyers enter the market.
Producer Surplus
Producer surplus is the amount a seller is paid minus the seller's cost of production.
Benefit of Producer Surplus
It measures the benefit sellers receive from participating in a market.
Relation to Supply Curve
Producer surplus is closely related to the supply curve.
Measuring Producer Surplus
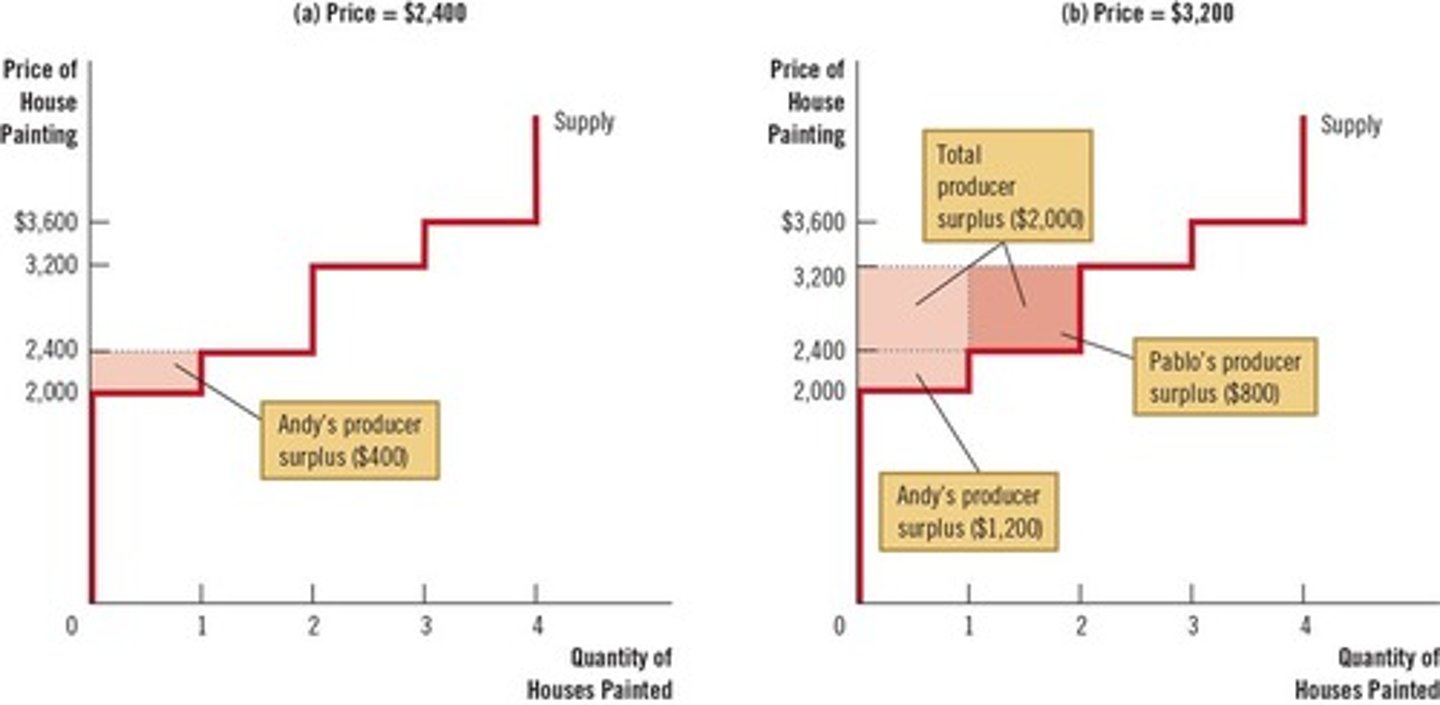
The area above the supply curve and below the price measures producer surplus.
Marginal Seller
It reflects the willingness to sell of the marginal seller at any quantity.
Market Efficiency
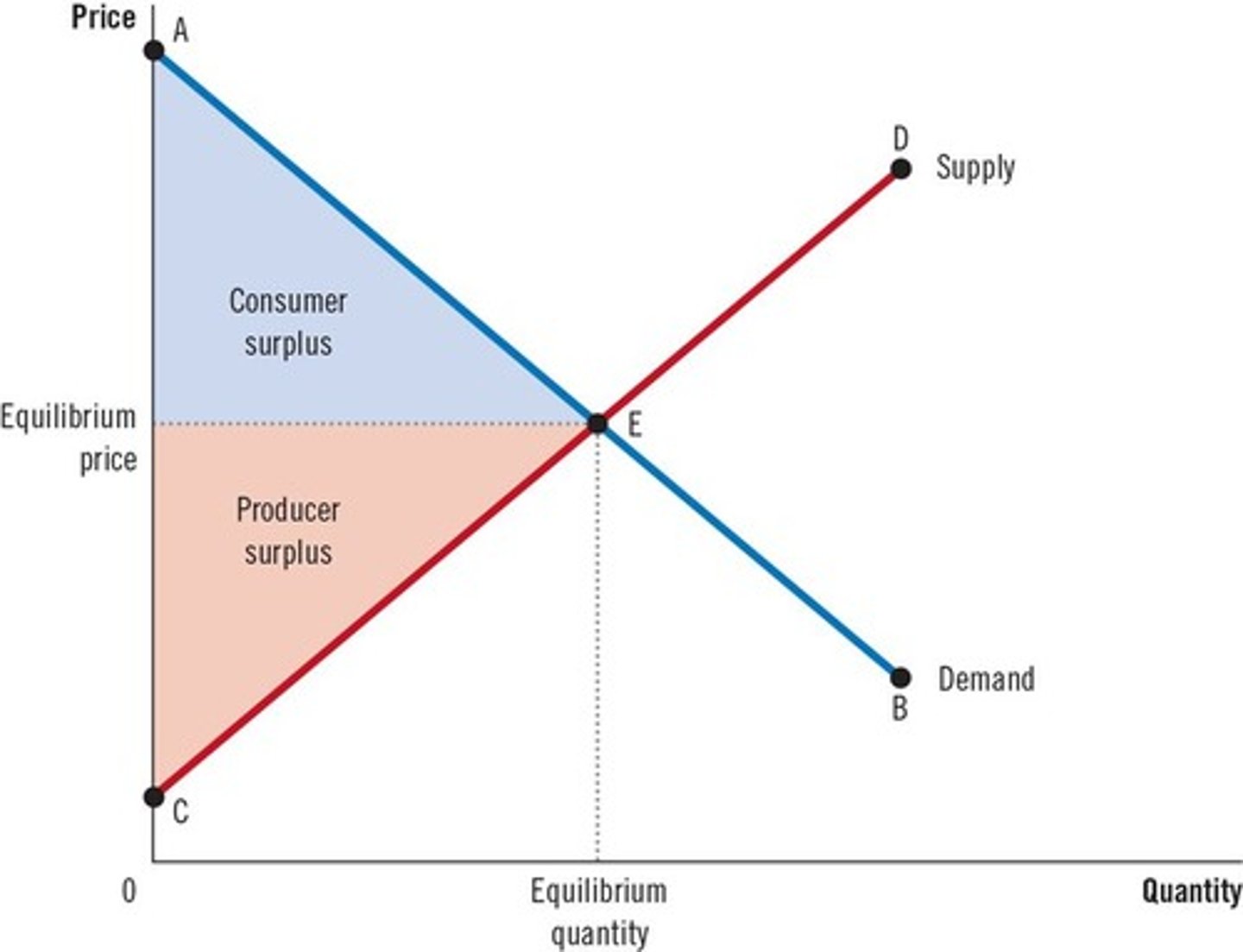
Total surplus = Consumer surplus + Producer surplus.
Efficient Allocation of Resources
An efficient allocation of resources maximizes total surplus.
Market Equilibrium
The market equilibrium maximizes the sum of consumer and producer surplus.
Invisible Hand
Adam Smith's invisible hand: In a competitive market, the forces of supply and demand allocate resources efficiently.
Competitive Markets
Competitive markets maximize total surplus and are the best way to organize economic activity.
Market Failures
Market failures, such as externalities or market power, can prevent markets from being efficient.
Public Policy and Market Failures
Public policy may be required to correct market failures.