Comprehensive Study Guide on Respiratory Disorders: Key Terms and Nursing Care Techniques
1/71
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
72 Terms
Describe the airway of infants
It is highly compliant meaning it doesn't keep its shape and can pinch off
What type of breathers are infants?
Obligate nose breathers
Describe the anatomy and physiology of infants noses
•Obligate nose breathers
•Produce less mucus
•More susceptible to infections
•Sinuses are not developed
•Small nasal passages prone to obstruction
Infants throat
What will increase the risk for airway obstruction?
Enlarged tongue
When is it best to perform an assessment/inspection on an infant?
When they are asleep
What is the first sign of a serious illness in infants?
Changes in breathing including depth and rate
What are the signs of respiratory distress in infants?
•Anxiety
•Restlessness
•Nasal Flaring
•Tracheal tugging
Signs of respiratory distress in infants
How will their appearance change?
They can become pale or cyanotic
What is the intervention for an infant that is having contractions?
Oxygen therapy
Describe rhonchi
•Low pitched snoring
•Common in secretions
•Continuous sounds heard on inspiration and expiration
Describe wheezing breath sounds
•Whistling sounds
•Common in asthma and inflammation
•Heard on expiratory
•Can be heard on inspiratory as well but having both is worse
Describe fine crackles breath sounds
•Crackle sounds
•Common in pneumonia
•NOT continuous
Infants/children with respiratory distress
What will a chest radiograph (x-ray) show?
•Hyperinflation
•Atelectasis
•Infiltration (pneumonia)
Infants/children with respiratory distress
What will a blood gas test show?
•Carbon dioxide retention
•Hypoxemia
Oxygen saturation
What should it be kept at?
Above 92% when awake
Above 88% when asleep
Instant test for presence of streptococcus A antibody in pharyngeal secretions
Throat swab for rapid strep testing
Why is humidity used for respiratory distress?
It will help liquefy secretions for ease in clearance.
What are the common medical treatments for respiratory distress?
•Oxygen
•High humidity
•Suctioning
•Chest physiotherapy and postural drainage
•Saline gargles or lavage
•Chest tube
•Bronchoscopy
What is suctioning used for and when will you use it?
Used for babies with RSV. This treatment will be used before bottle feedings
Promotes mucus clearance by mobilizing secretions with the assistance of percussion or vibration accompanied by postural drainage
Chest physiotherapy
Relieves throat pain via salt water gargle
Saline gargles
Normal saline introduced into the airway, followed by suctioning
Saline lavage
Benefits of a nasal cannula
Child can eat and talk without interrupting oxygen delivery

Negatives of a nasal cannula
•FI02 inconsistent
•Drying of nasal mucosa
Nasal cannula maximum rate
4-6L/min
Negatives of a Simple Mask
Must be removed for eating
FI02 inconsistent
Simple mask flow rate
6-10L/min (mask must fit snugly)
Benefits of venturi mask
Delivers precise high flow rates of O2
Simple facemask with valves at the exhalation ports and an oxygen reservoir bag with a valve to prevent exhaled air from entering the reservoir
Non rebreather mask
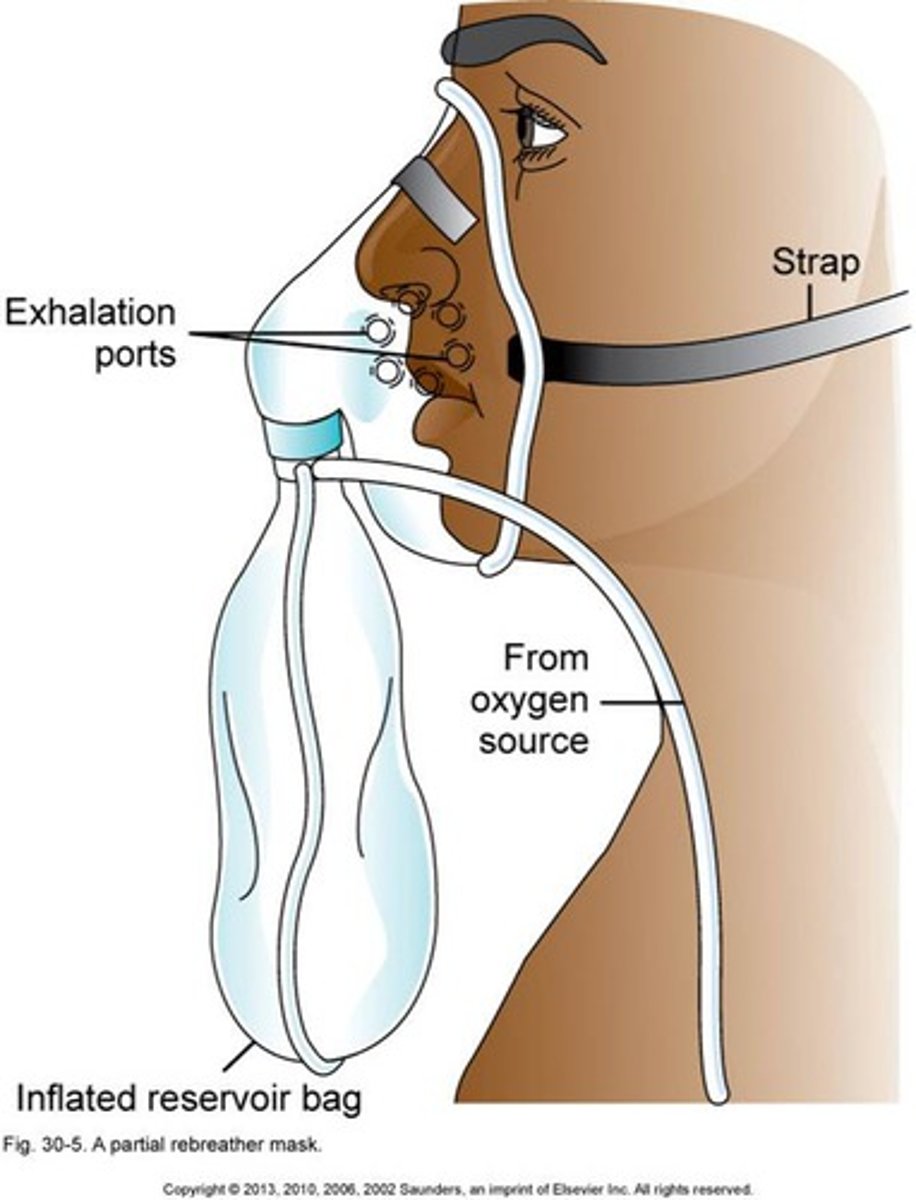
Which type of oxygen delivery method is a short term solution?
Nonrebreather mask
Nonrebreather mask flow rate
15L/min
Which type of oxygen delivery method is used for severe respiratory distress?
High flow oxygen
High flow oxygen
What is the maximum flow rate for a child?
2L/kg/min
Describe high flow oxygen
•Used for severe respiratory distress
•NOT used as first intervention
•Heated and humidified
•Larger cannula prongs
•Flow and FI02 can be adjusted separately
Risk factors for respiratory disorders
•Prematurity
•Chronic illness
•Developmental disorders
•Passive exposure to cigarette smoke
•Immune deficiency
•Crowded living conditions or lower socioeconomic status
•Daycare attendance
What type of chronic illnesses are risk factors for respiratory distress?
•Diabetes
•Sickle cell anemia
•Cystic fibrosis
•Congenital heart disease
•Chronic lung disease
What type of developmental disorders are risk factors for respiratory distress?
Cerebral palsy (affects mobility)
Risk factors for tuberculosis
•HIV infection (immunocompromised)
•Incarceration and institutionalization
•Positive recent history of TB
•Immigration or travel to endemic countries
•Exposure at home to people with any of the above factors
Acute infectious disorders
•Common cold, sinusitis
•Pharyngitis, tonsilitis, laryngitis
•Respiratory syncytial virus
•Influenza
•Coup syndromes
•Pneumonia, bronchitis
Chronic respiratory disorders
•Allergic rhinitis
•Asthma
•Chronic lung disease (bronchopulmonary dysplasia)
•Cystic fibrosis
•Apnea
What is croup?
Viral infection and inflammation of the upper respiratory tract
Pneumothorax
What are the signs?
•Chest pain
•Tachypnea
•Retractions
•Nasal flaring
•Grunting
Risk factors for pneumothorax
•Chest trauma
•Intubation and mechanical ventilation
•History of chronic lung disease
Treatment for pneumothorax
•Chest tube
•Nonrebreather oxygen therapy (small pneumothorax only)
What is Bronchiolitis (RSV)?
Inflammation of the bronchioles
Bronchiolitis (RSV)
What is the first sign?
Clear runny nose
What symptoms will develop with Bronchiolitis?
•Pharyngitis
•Low grade fever
•Poor feeding
•Coughing
•Wheezing
Bronchiolitis
When does a cough develop?
1-3 days into illness
Bronchiolitis
When do the symptoms become worse?
Day 4-5 of illness
Bronchiolitis
How is it treated?
•Fluids
•Oxygen
•Suctioning (do it before feeding)
Children under 5 years old are diagnosed with what type of asthma?
Reactive airway disease
Why are children under 5 diagnosed with reactive airway disease instead of just asthma?
It's possible they will grow out of it
Chronic inflammatory airway disorder
Asthma
Exaggerated bronchoconstrictive response to stimuli seen in asthma
Airway hyperresponsiveness
Signs of asthma
•Airway hyperresponsiveness
•Airway edema
•Mucus production
•Tachypnea
•Cough
•Increased work of breathing
•Wheezing
Asthma
What is it triggered by?
•Allergens
•Illness
•Exercise/activity
What is an asthma score based off?
Work of breathing, O2 sat on room air, breath sounds, lung sounds
How is asthma treated?
•Short acting bronchodilators (rescue medications)
•Maintenance medications (everyday use)
What are the type of maintenance medications used for asthma?
•Long acting bronchodilators
•Inhaled corticosteroids
Cystic fibrosis
What type of disorder is this?
Autosomal recessive
What is cystic fibrosis?
Autosomal recessive disorder that produces excess mucous and decreases pancreatic enzymes
What will cause cystic fibrosis?
•Problems in exocrine glands
•Decreased pancreatic enzymes
•Hypersecretion of glands
Cystic fibrosis
What are the treatments through PO?
•Pancreatic enzyme supplementation
•ADEK vitamin supplementation
•Well balanced, high calorie, high protein diet
Cystic fibrosis
What are the treatments through inhalation?
•Inhaled bronchodilators
•Inhaled dornase alfa (pulmonary enzyme)
•Inhaled antibiotics
Cystic fibrosis
What treatment will help break up the mucus?
Chest physiotherapy
Tonsillectomy Nursing Care
How do you promote airway clearance?
Placing the patients on side lying or prone position
Tonsillectomy treatment involves coughing T/F
False. You want to maintain fluid volume and coughing cam cause damage
Tonsillectomy Nursing Care
How will you maintain fluid volume?
•Discourage coughing
•Encourage fluids
Tonsillectomy Nursing Care
What type of fluids do you want to avoid?
Citrus, brown or red fluids
Tonsillectomy Nursing Care
How can you relieve pain?
Ice collar and analgesics
Tonsillectomy Nursing Care
What does frequent swallowing indicate?
Bleeding!
Tonsillectomy Nursing Care
Why do you want to frequently inspect the throat?
To check for bleeding