cerebrum
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
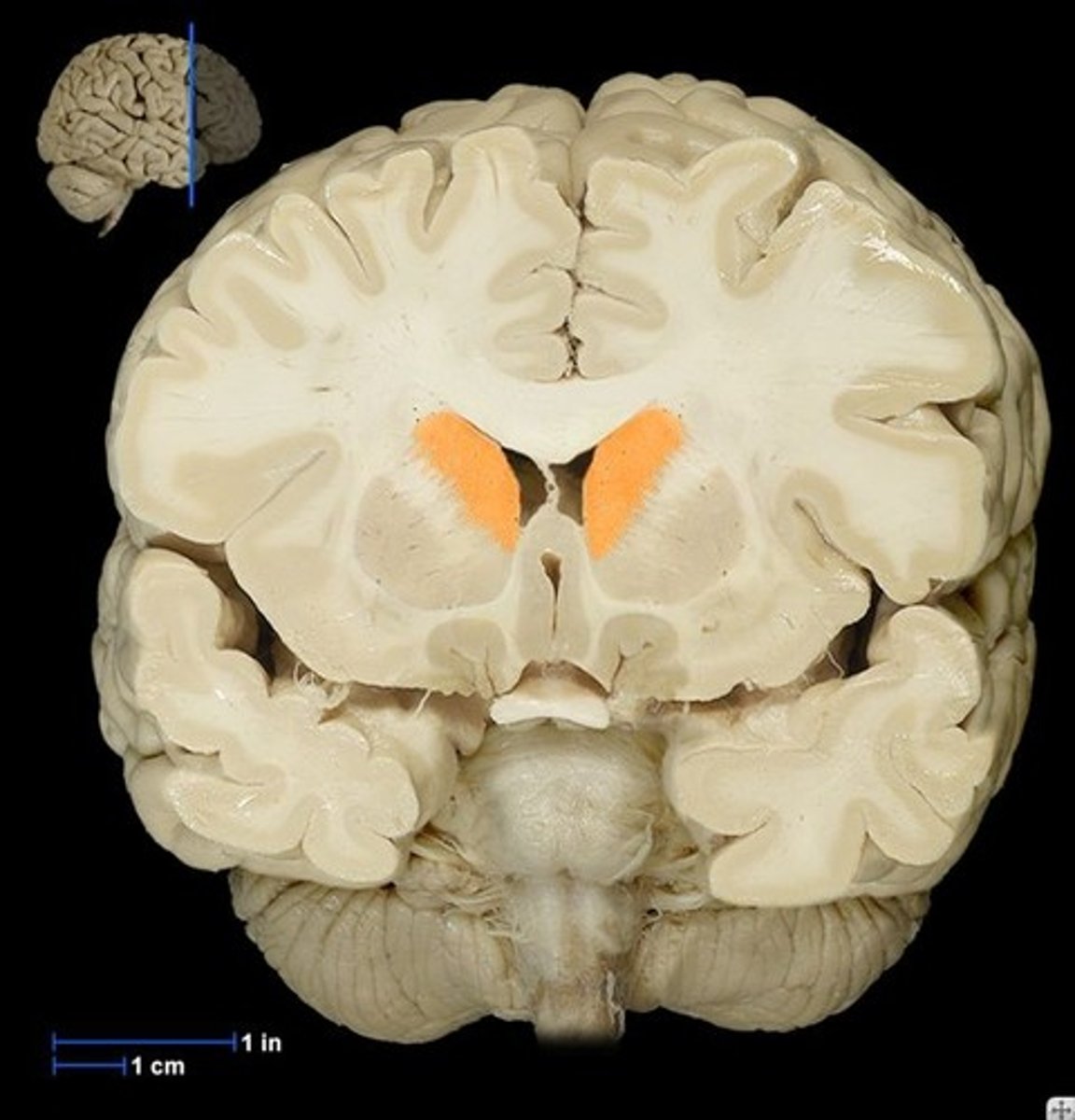
basal nuclei
islands of gray matter buried within the white matter
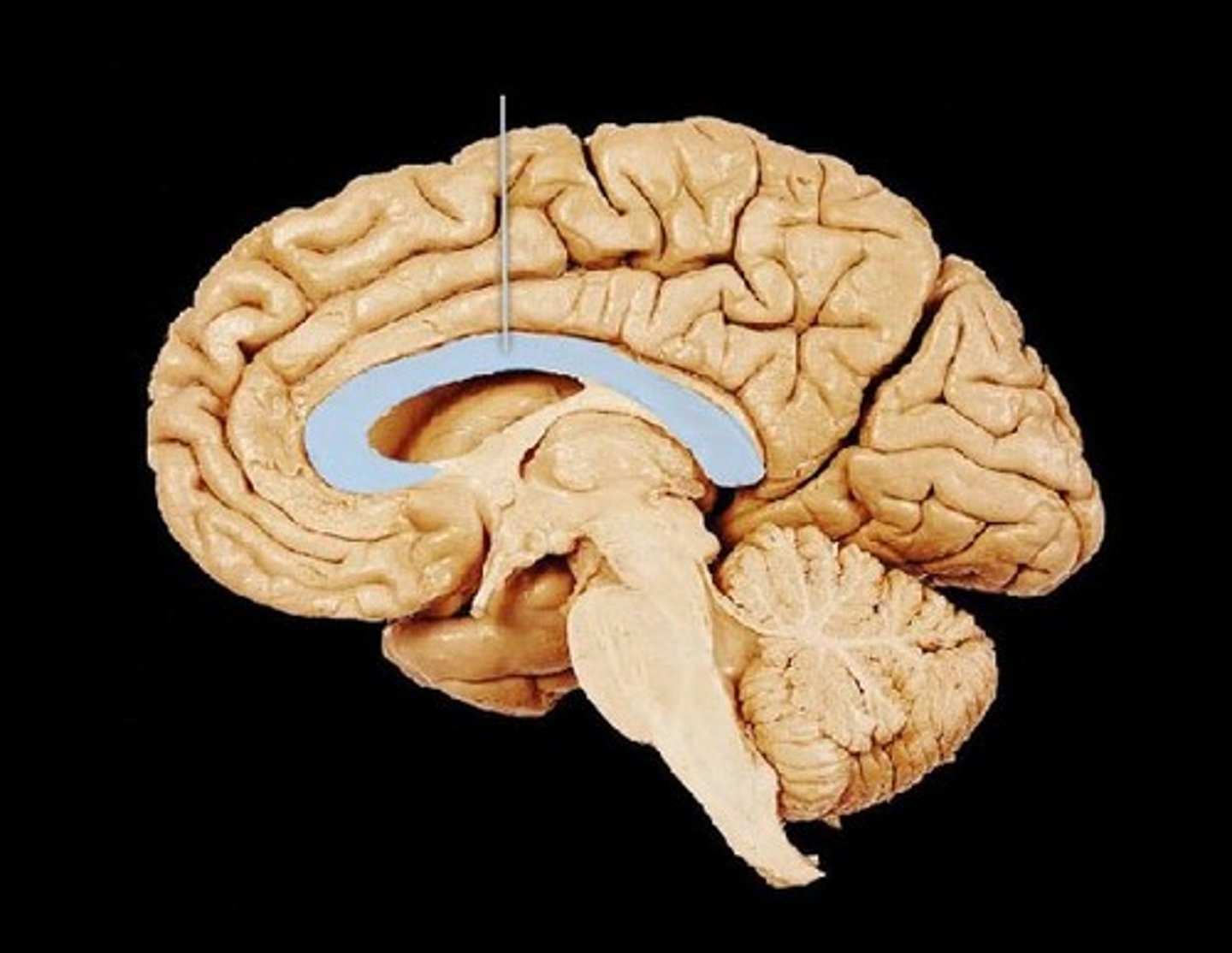
corpus callosum
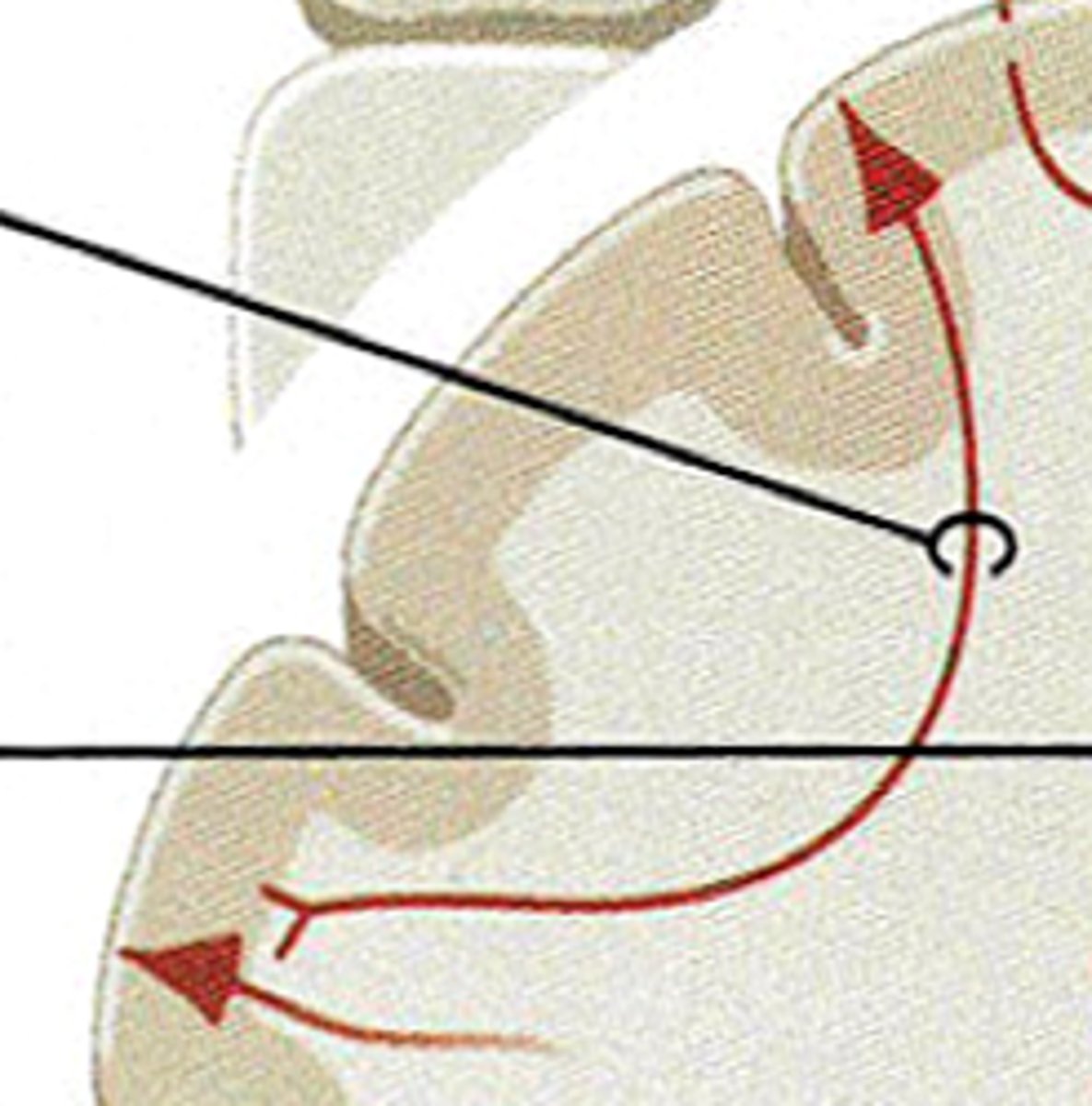
association fibers
connect different parts of the same hemisphere
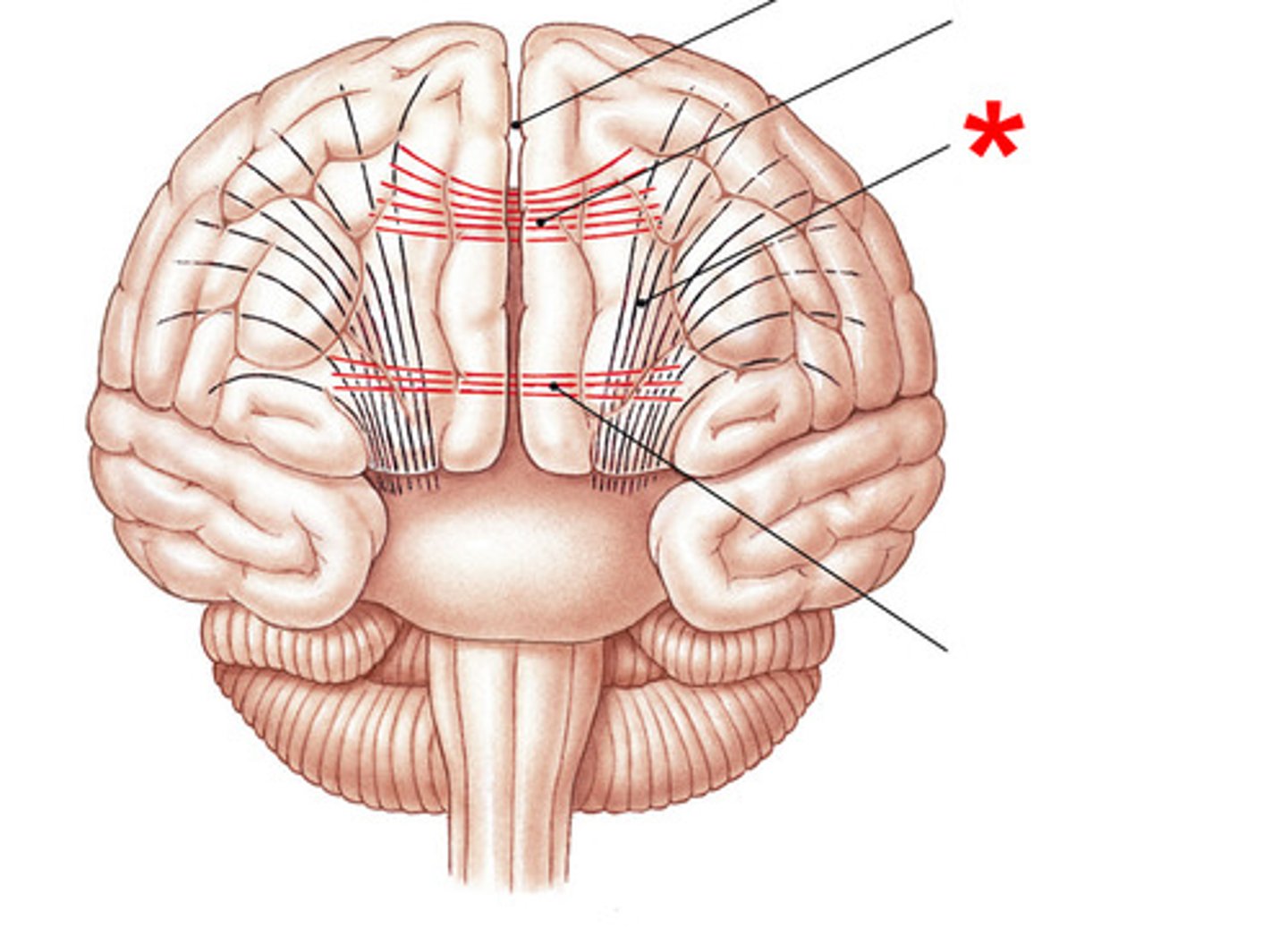
commisural fibers
conduct impulses between the hemispheres and form corpus callosum
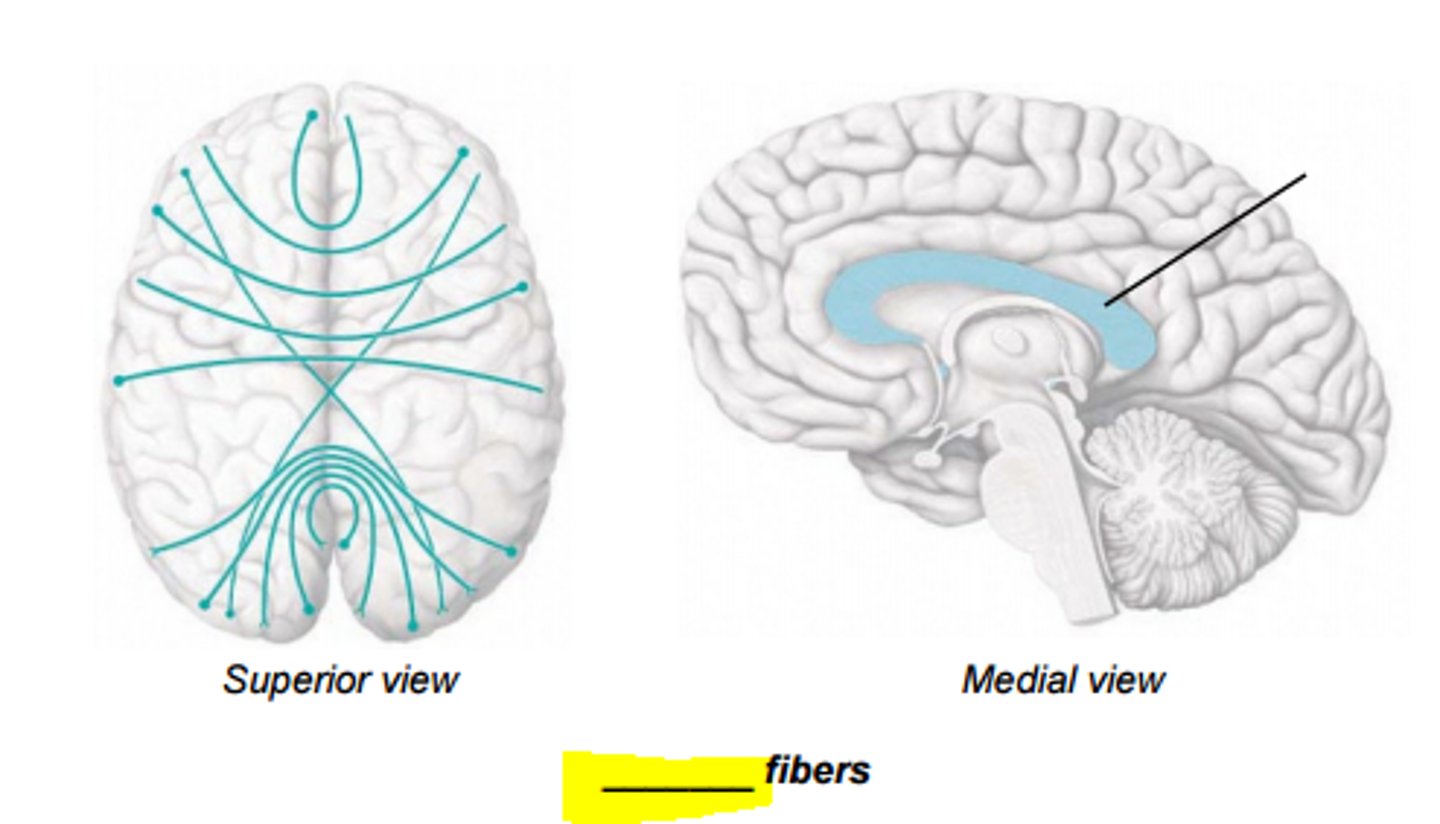
projection fibers
vertical fibers that connect hemispheres with lower brain or spinal cord
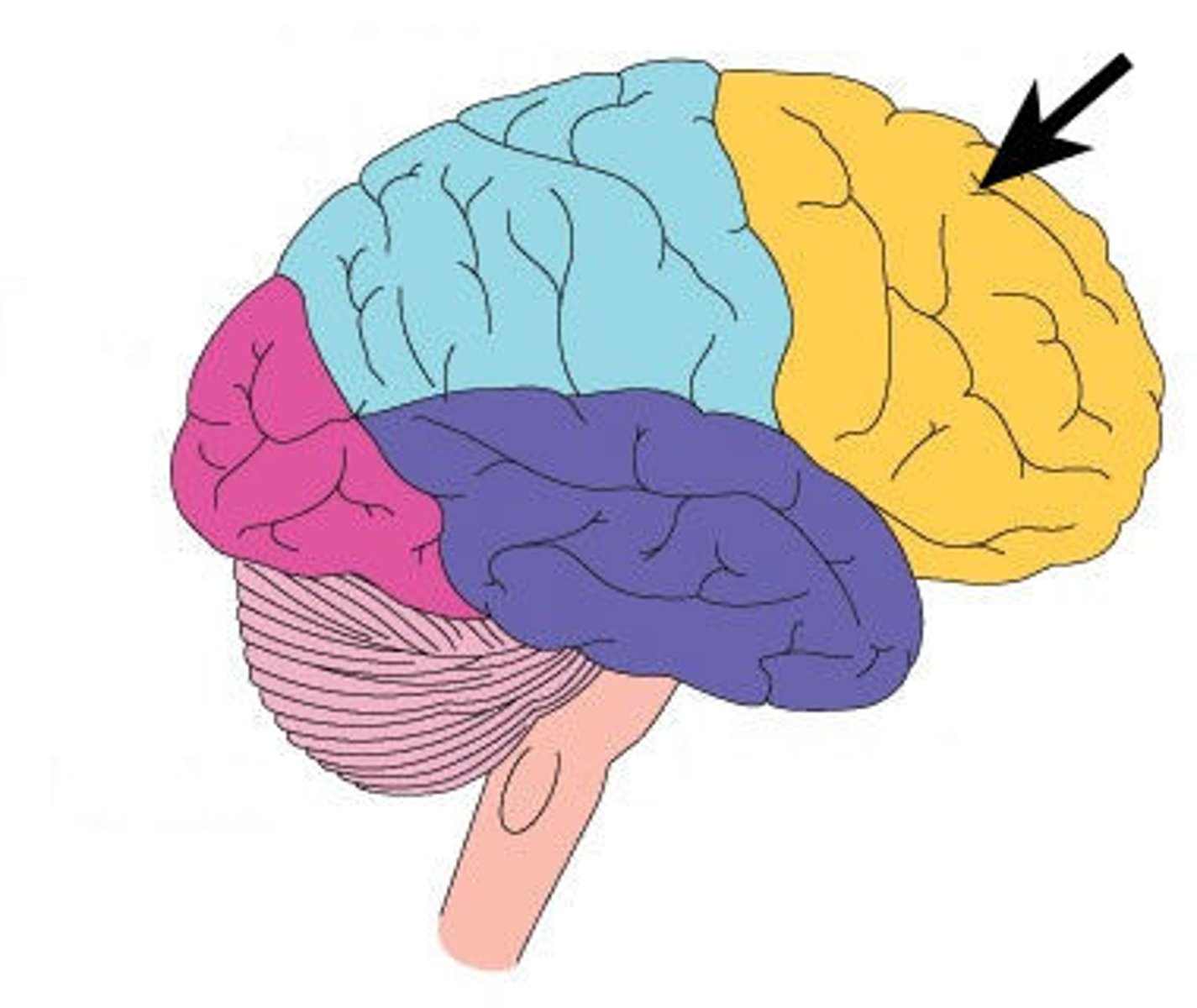
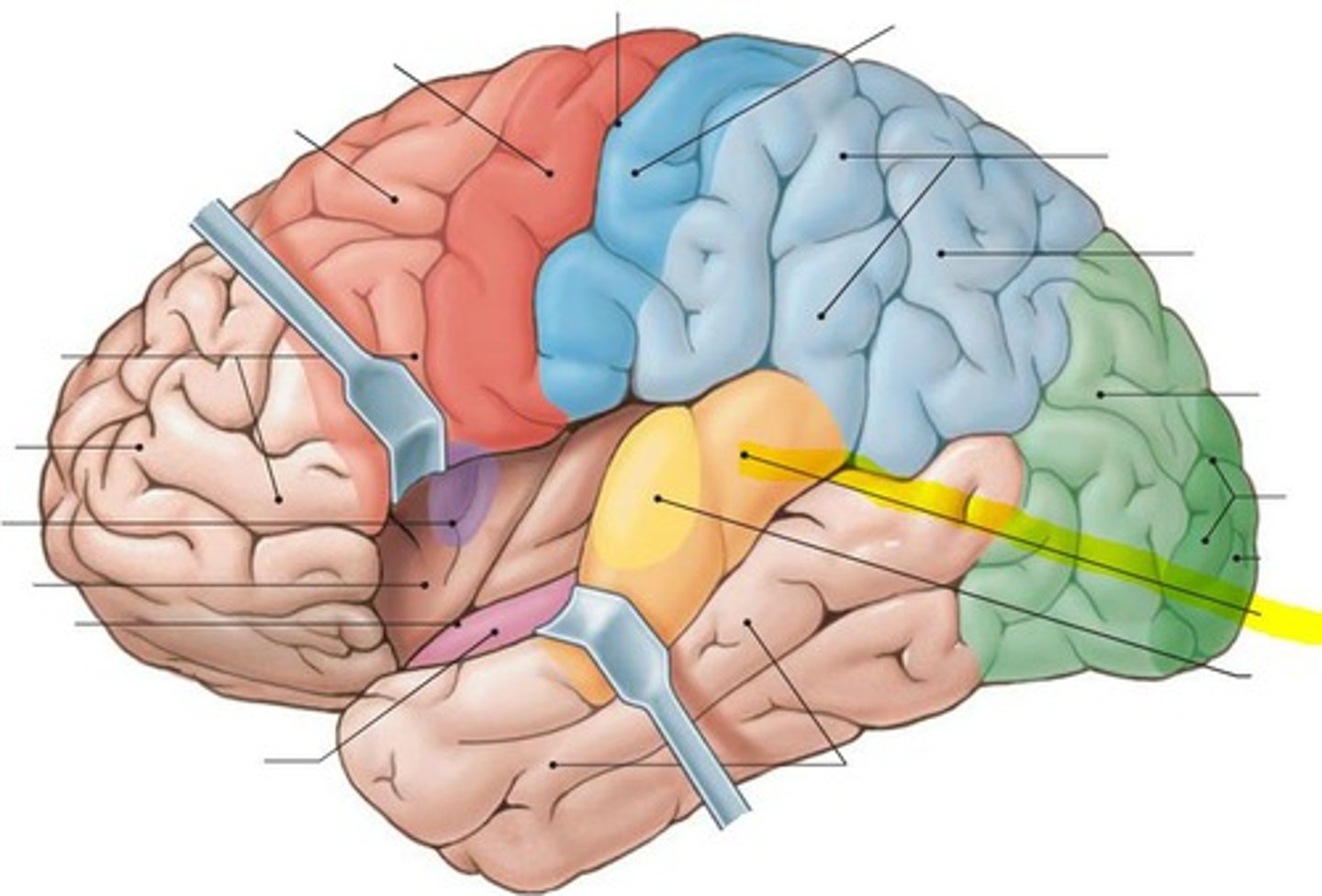
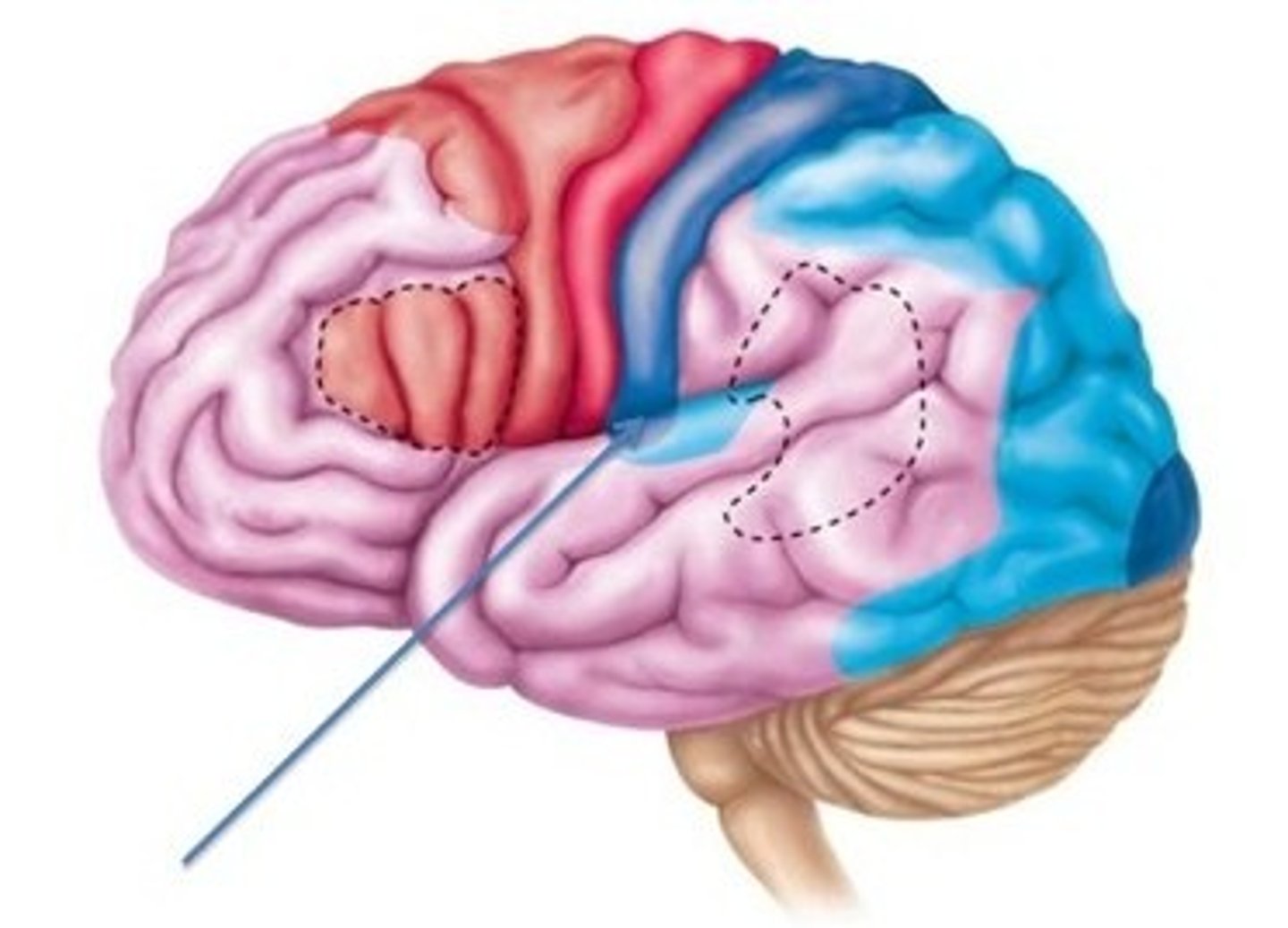
frontal lobe
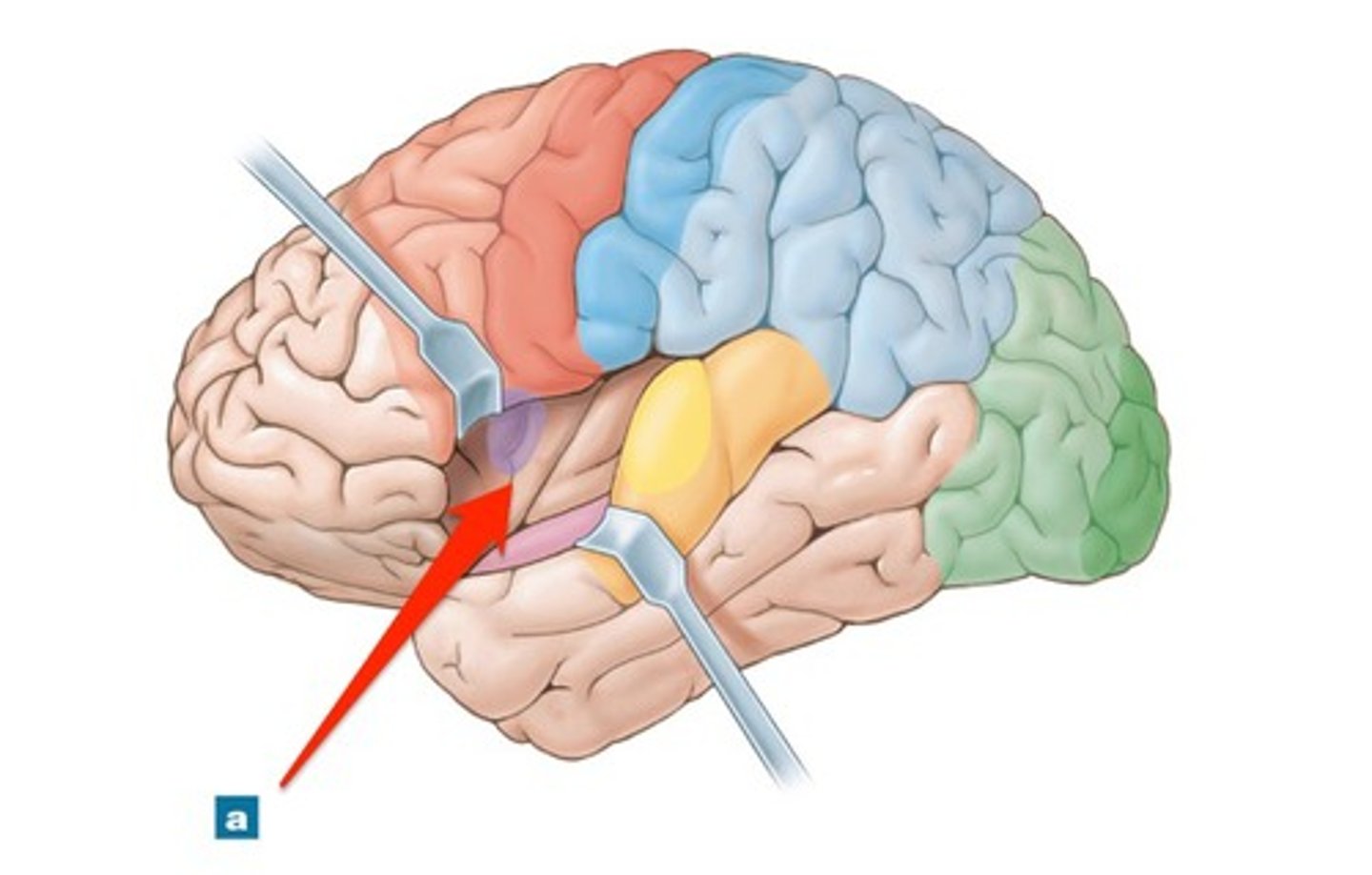
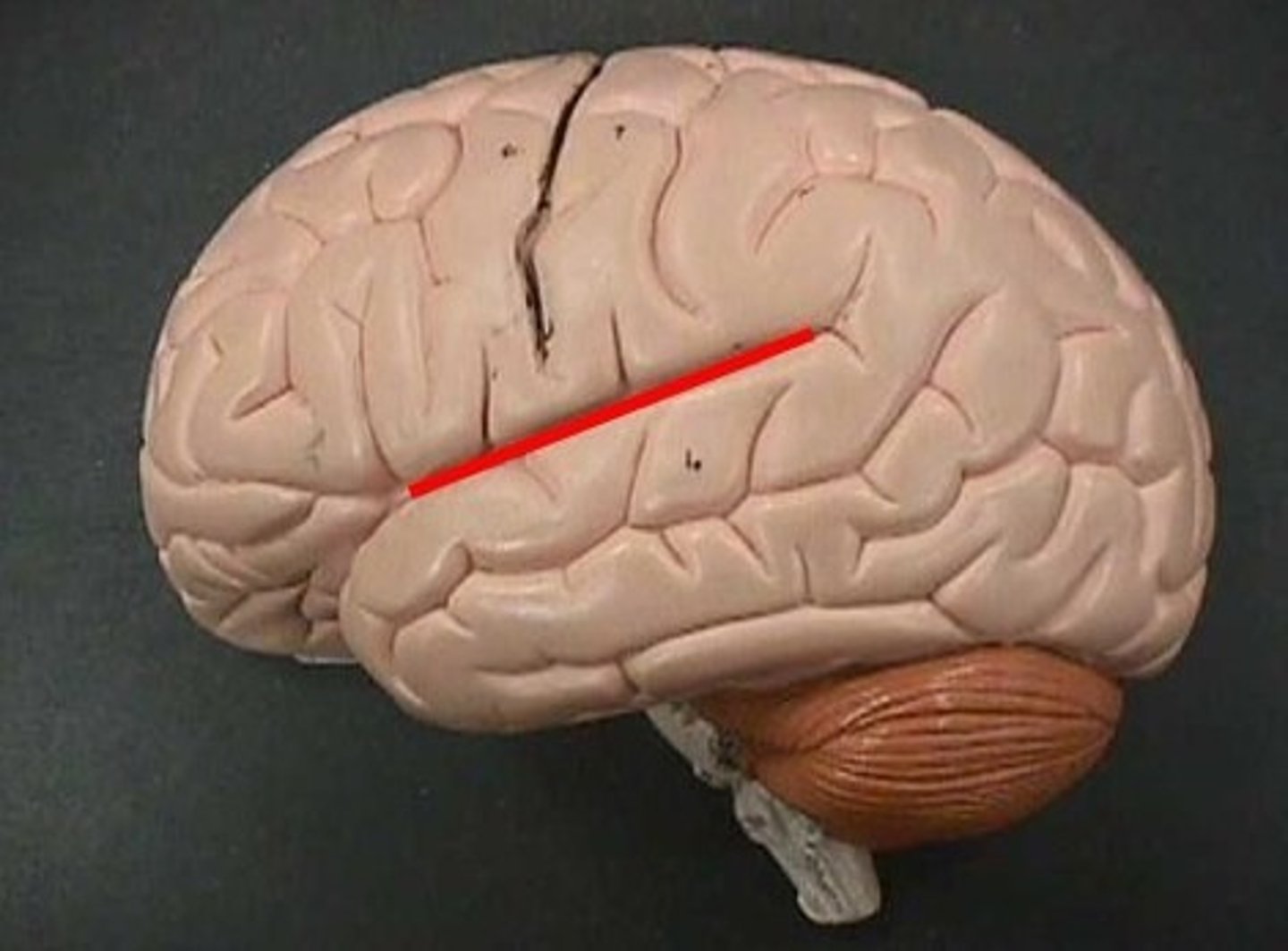
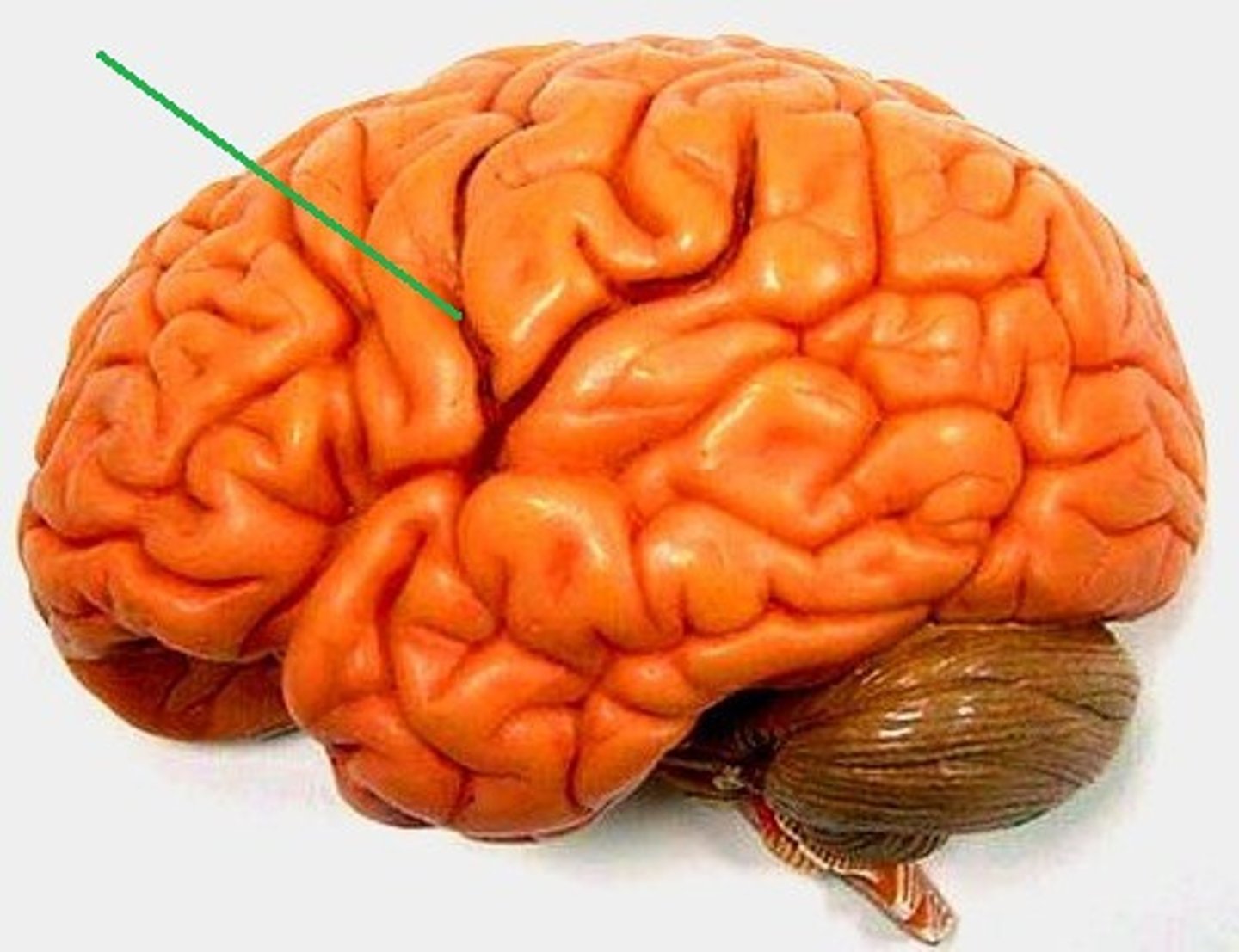
lateral cerebral sulcus
separates the frontal lobe from the temporal lobe
precentral gyrus
primary motor cortex
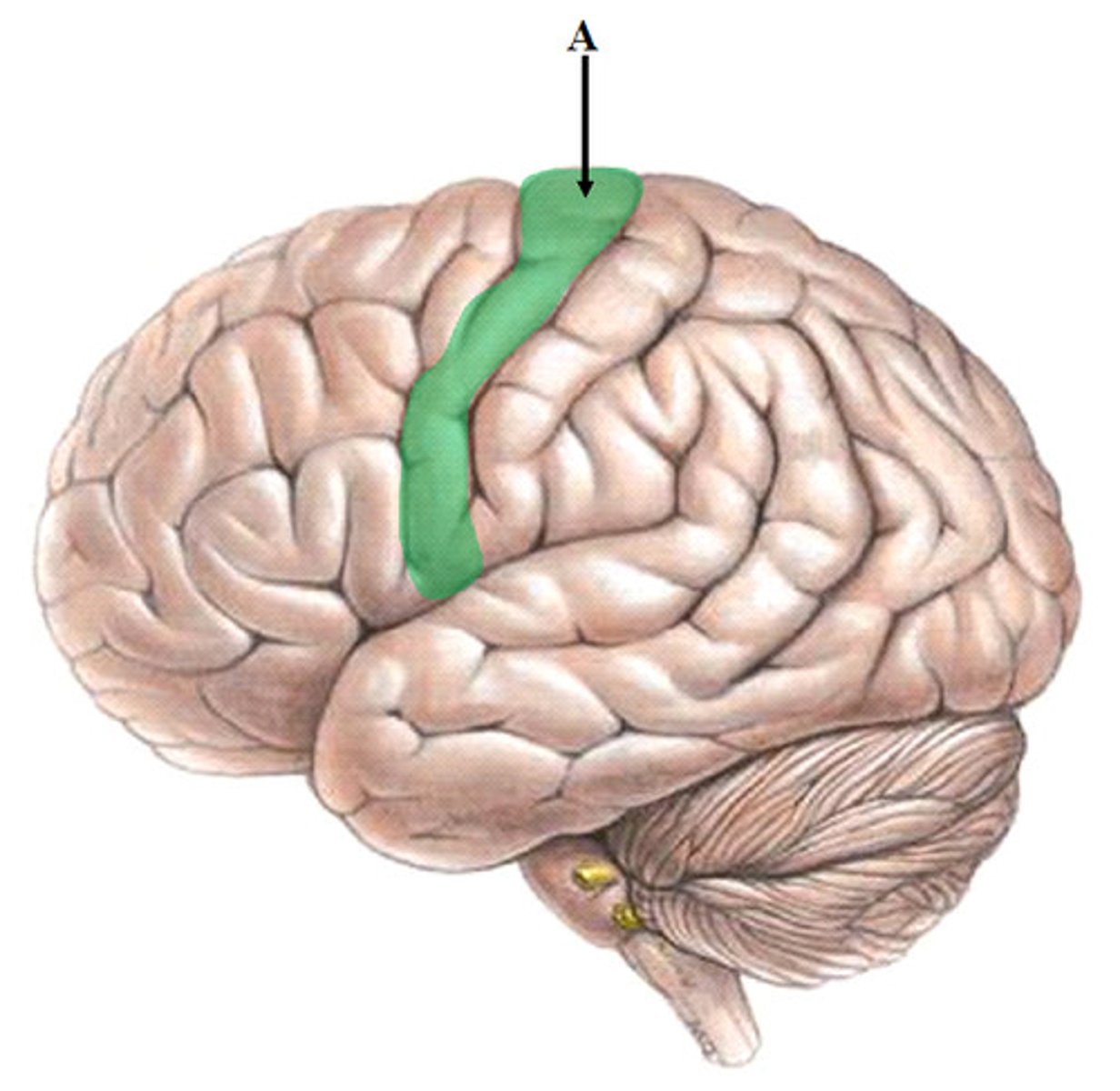
central sulcus
separates frontal and parietal lobes
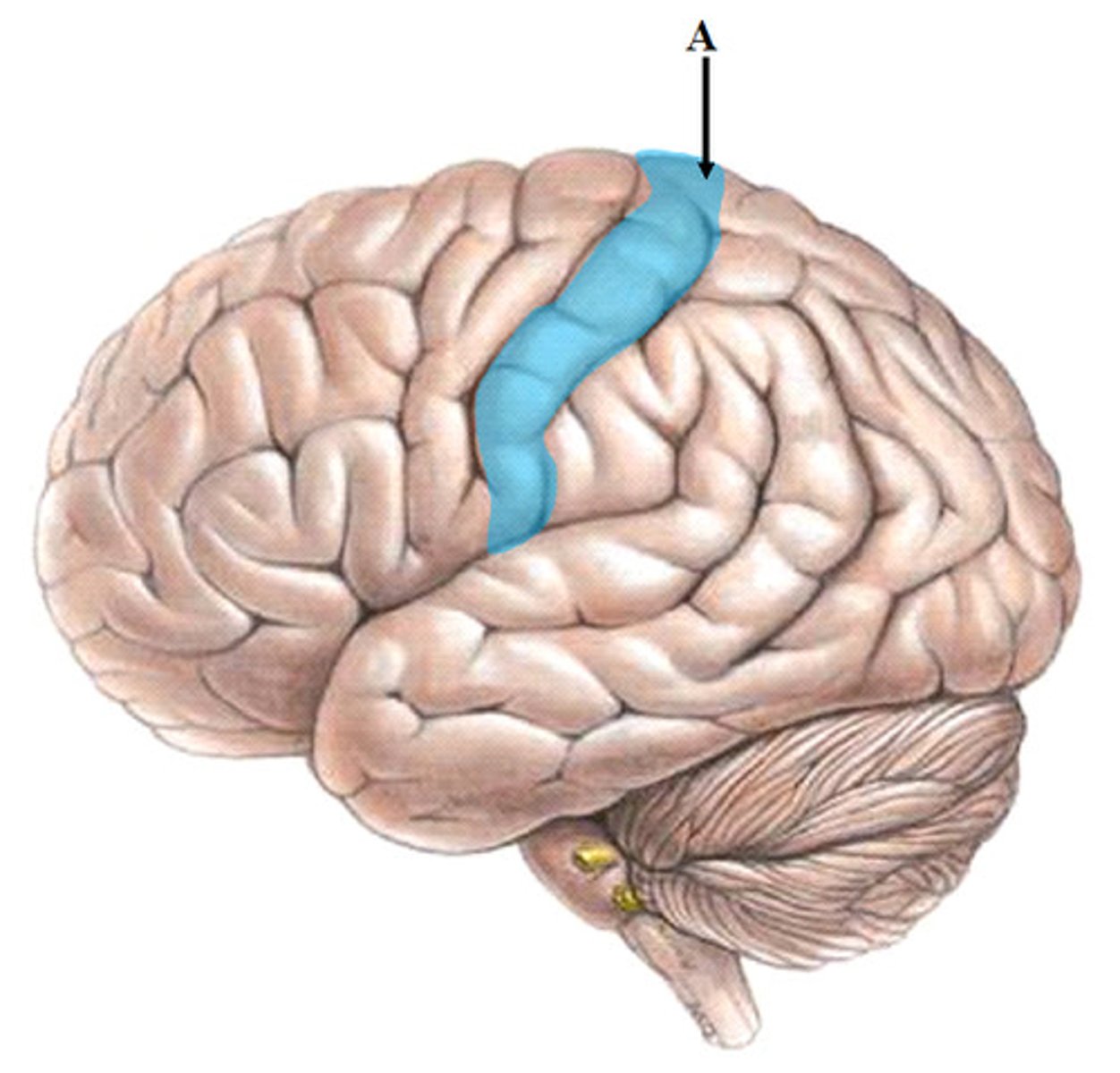
postcentral gyrus
primary somatosensory cortex
temporal lobe
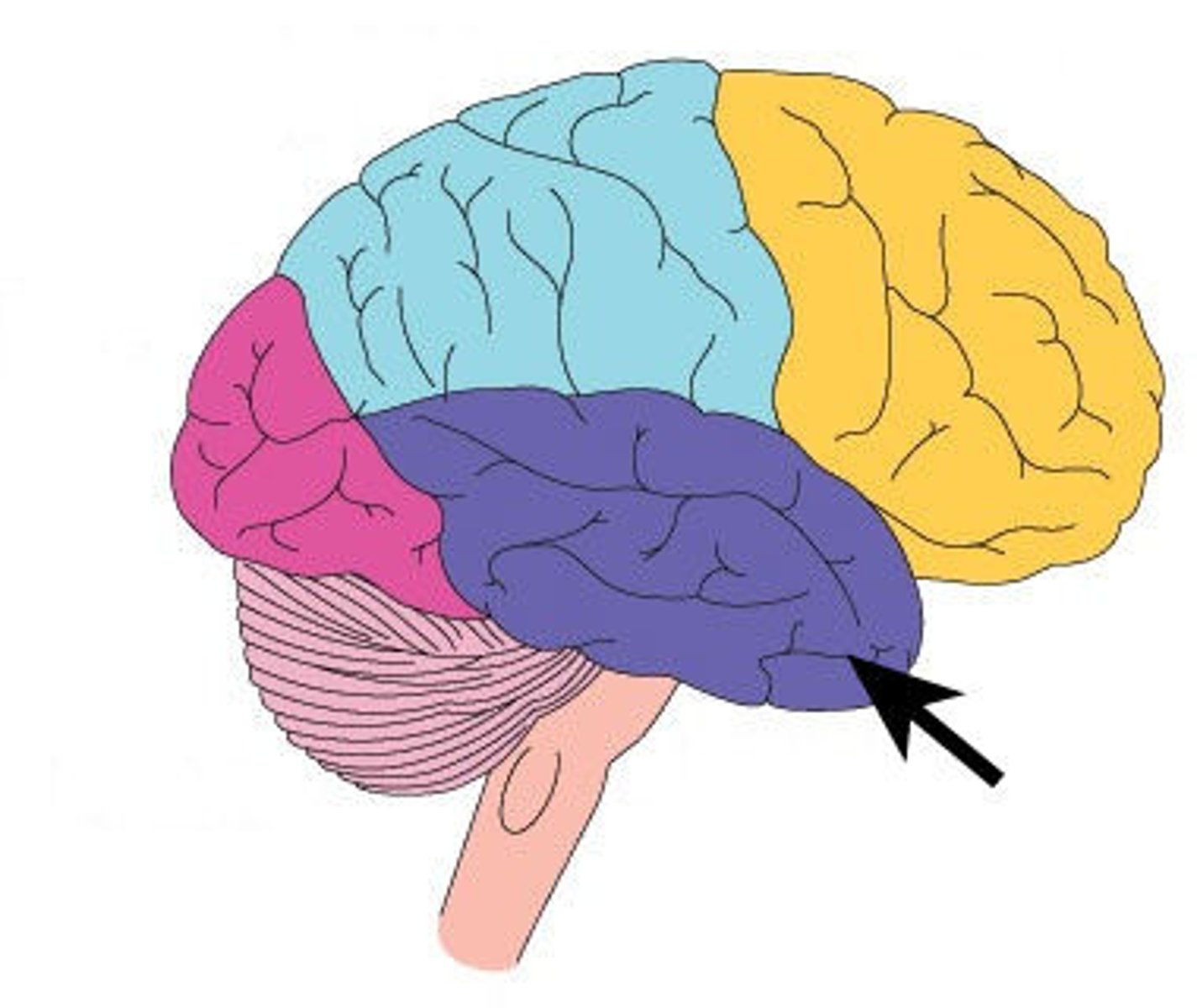
parietal lobe
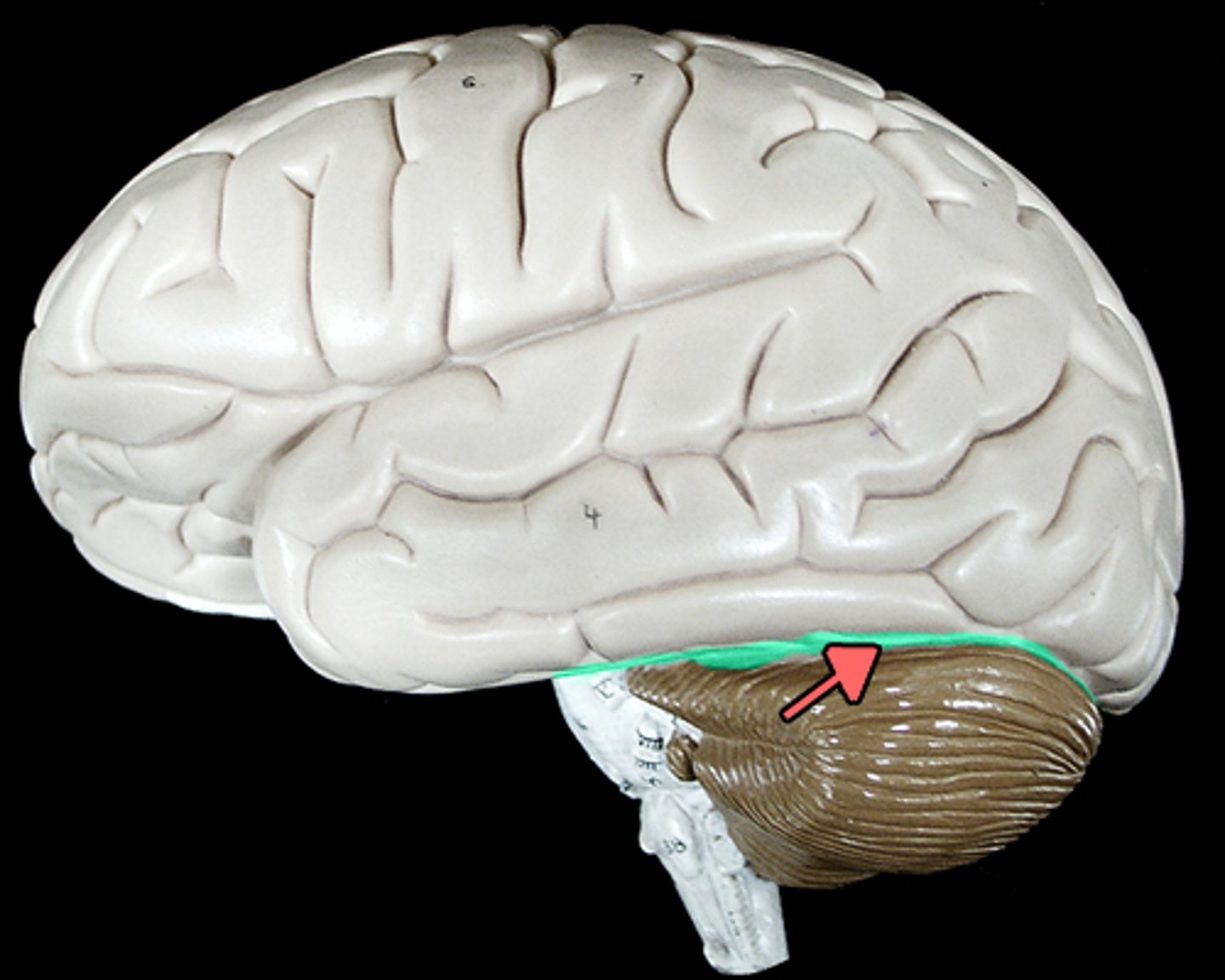
transverse fissure
separates cerebrum from cerebellum
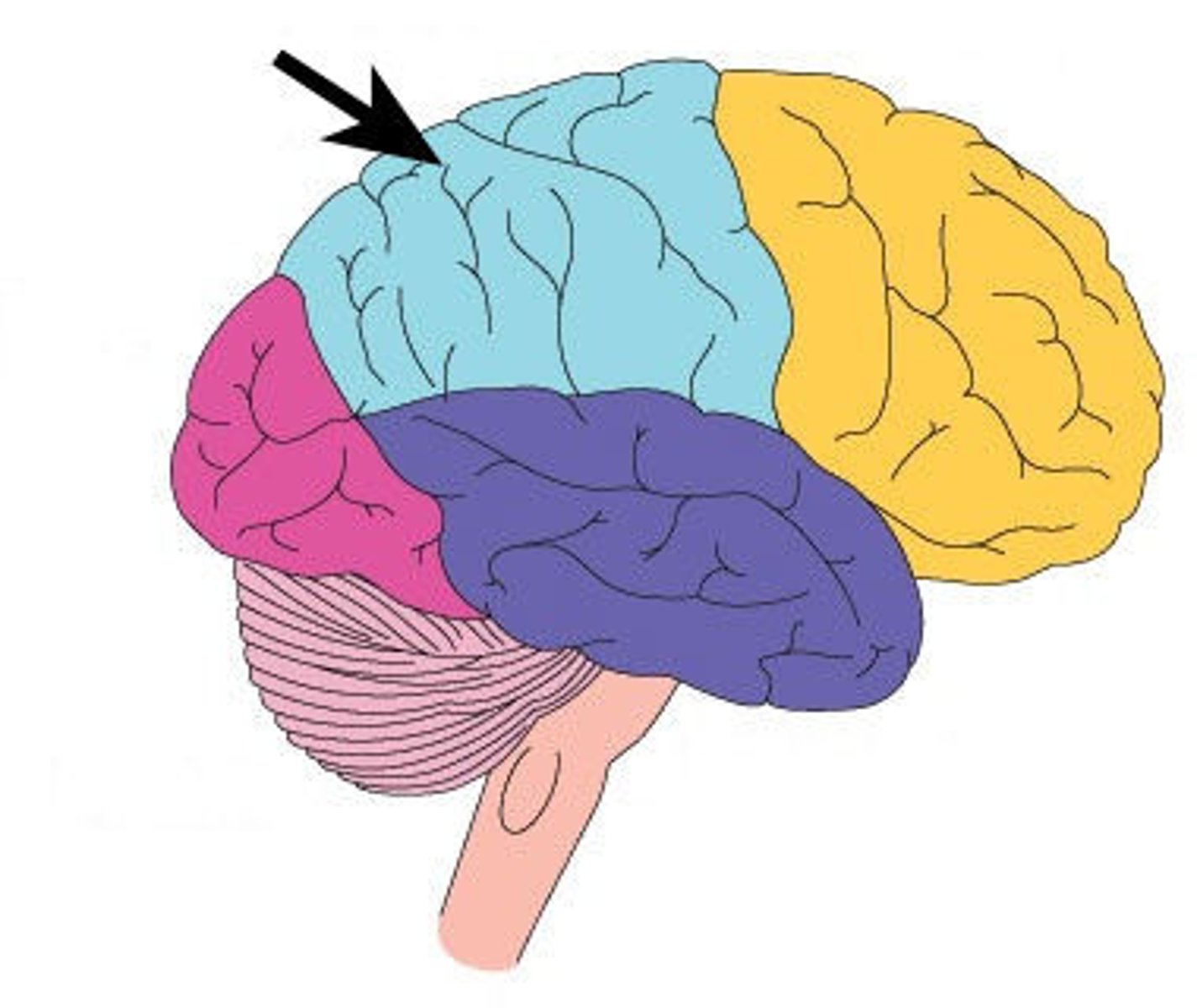
parietal-occipital sulcus
separates parietal and occipital lobes
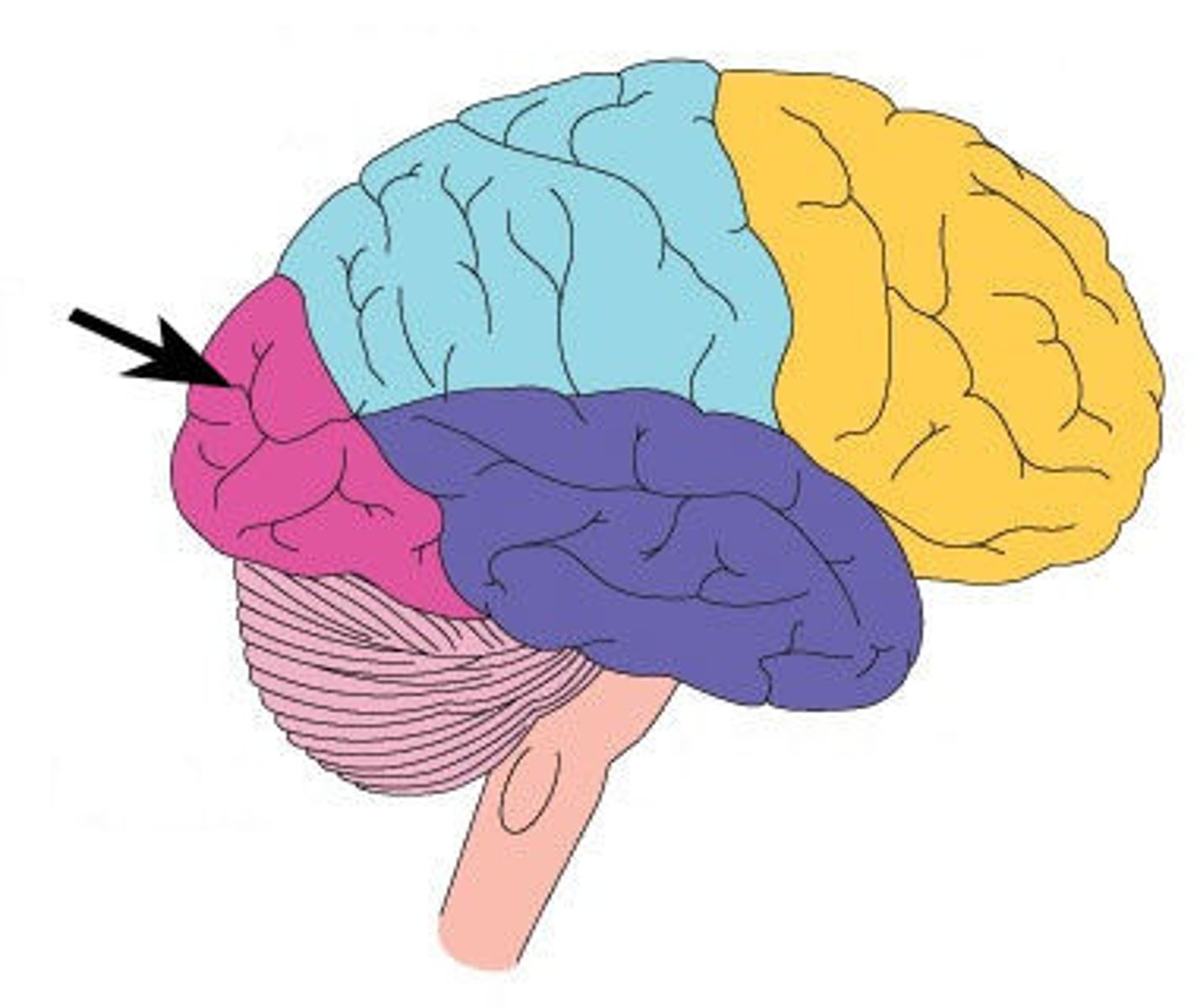
occipital lobe
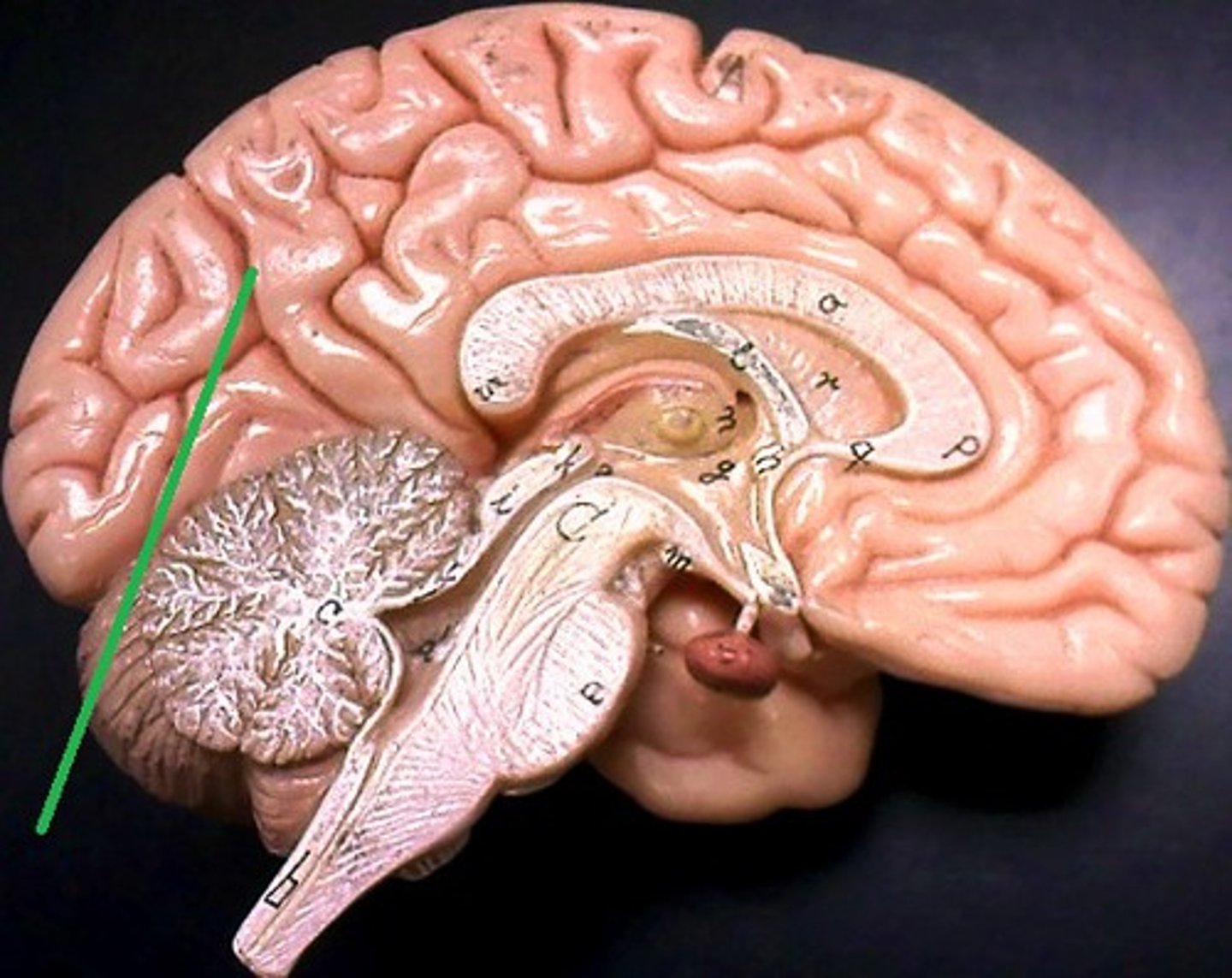
longitudinal fissure
separates cerebral hemispheres
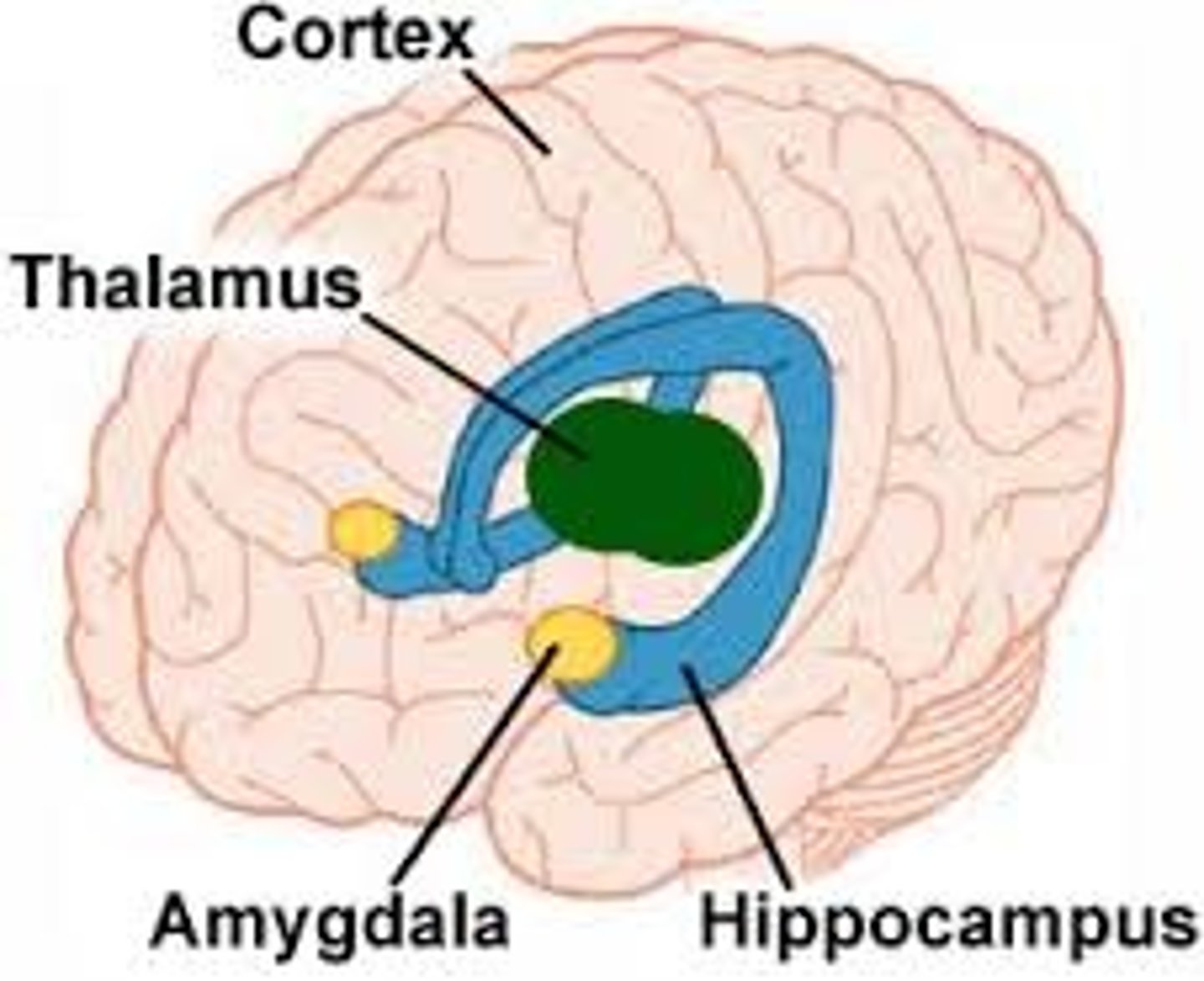
limbic system
A doughnut-shaped system of neural structures at the border of the brainstem and cerebral hemispheres; associated with emotions such as fear and aggression and drives such as those for food and sex. Includes the hippocampus, amygdala, and hypothalamus.
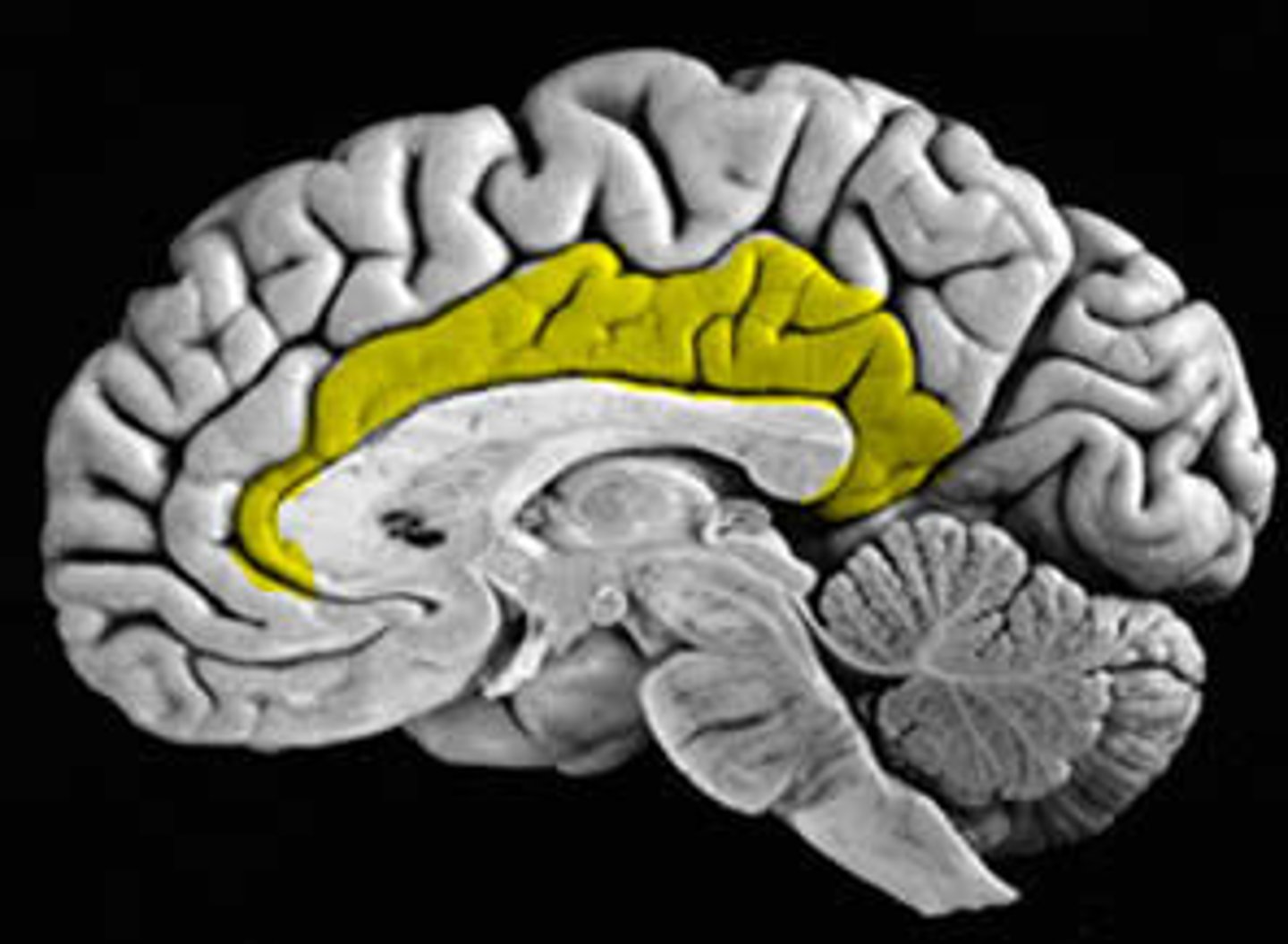
cingulate gyrus
a strip of limbic cortex lying along the lateral walls of the groove separating the cerebral hemispheres, just above the corpus callosum
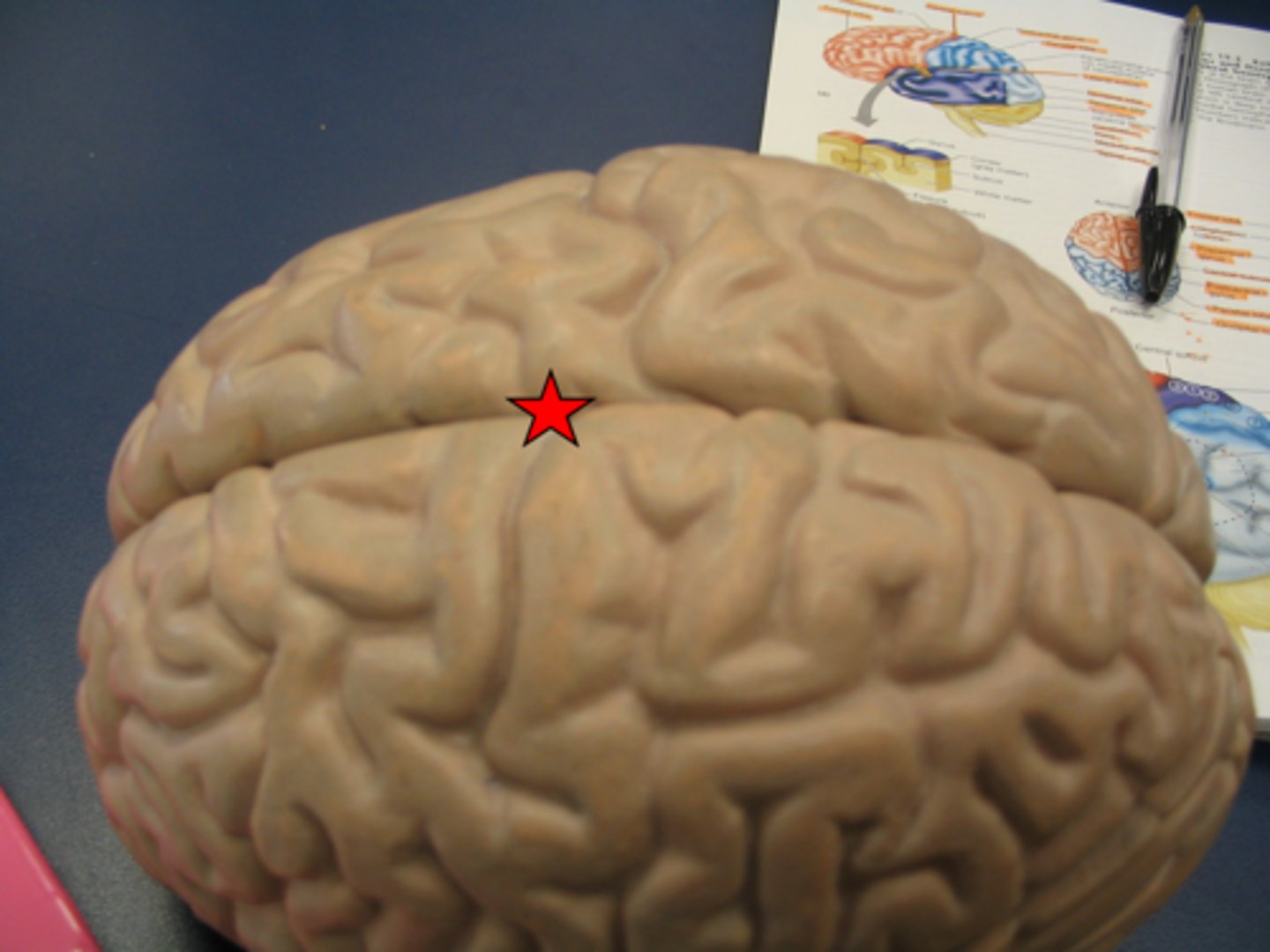
Somatic motor association area (premotor cortex)
responsible for coordinating learned movements
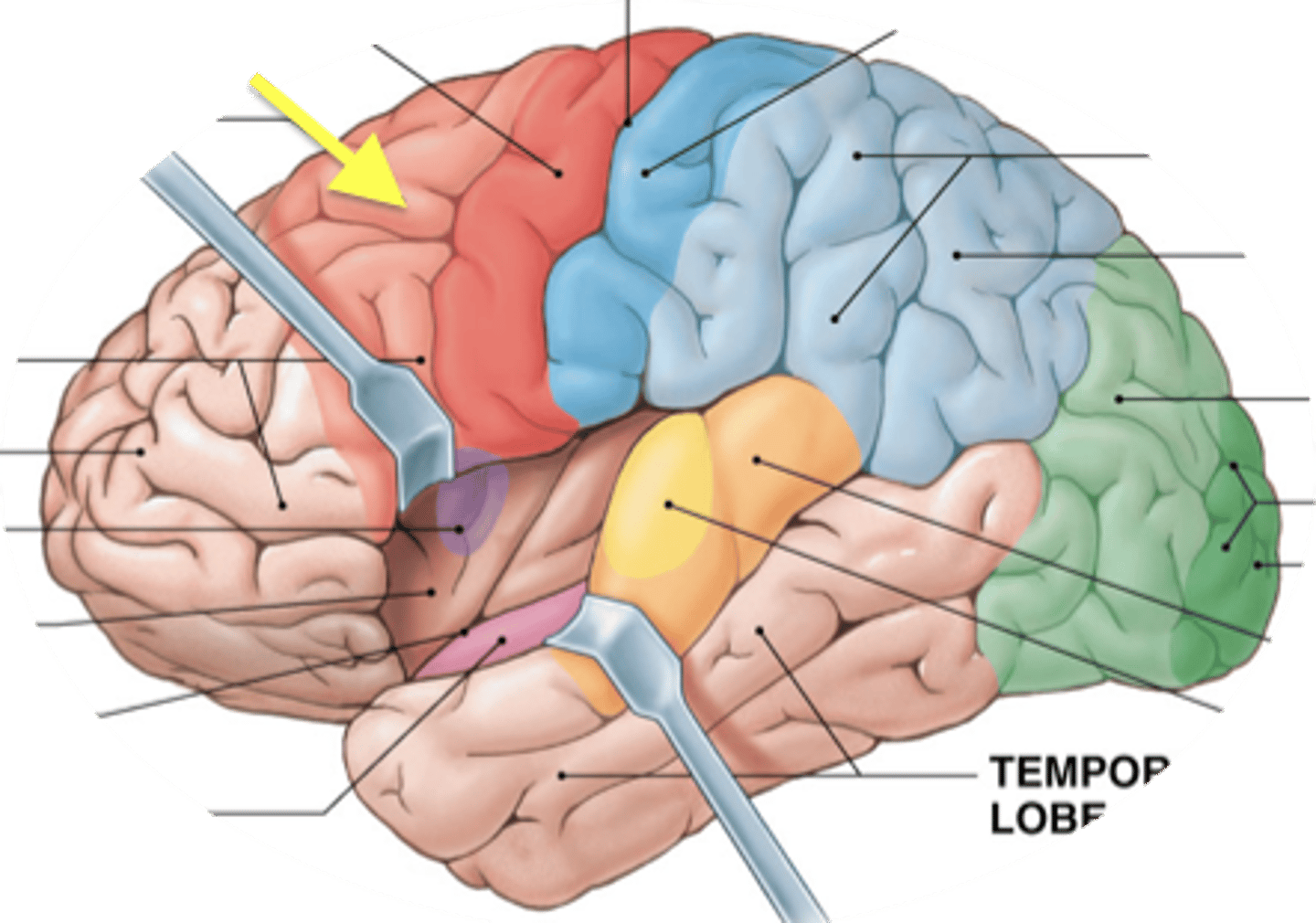
somatic sensory association area
monitors activity in the primary sensory cortex; involved with special senses: hearing, smelling, sight...
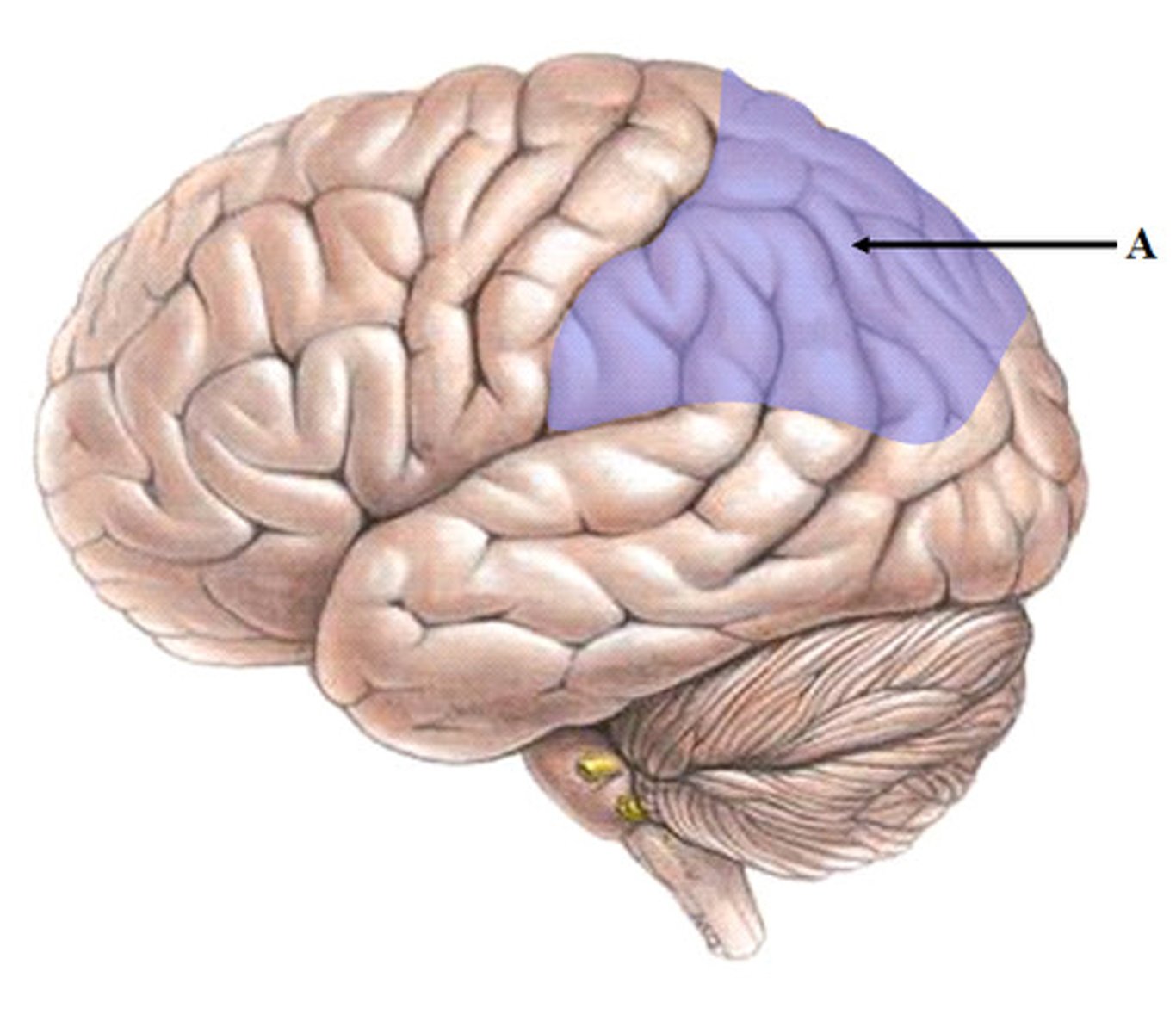
visual associtation area
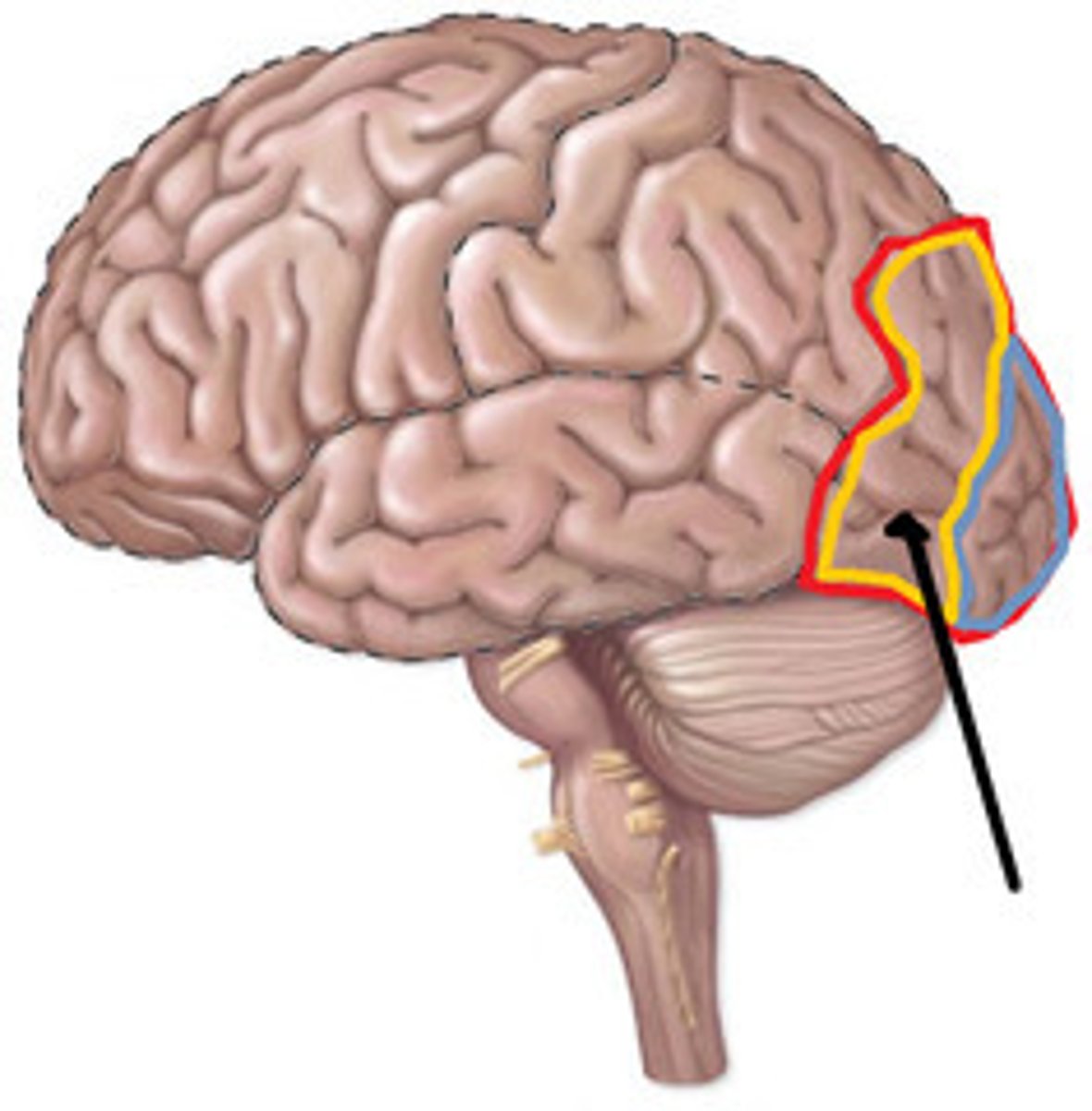
primary visual cortex
the region of the posterior occipital lobe whose primary input is from the visual system
auditory association area
stores memories of sounds and permits perception of sounds
primary auditory cortex
the region of the superior temporal lobe whose primary input is from the auditory system
olfactory cortex
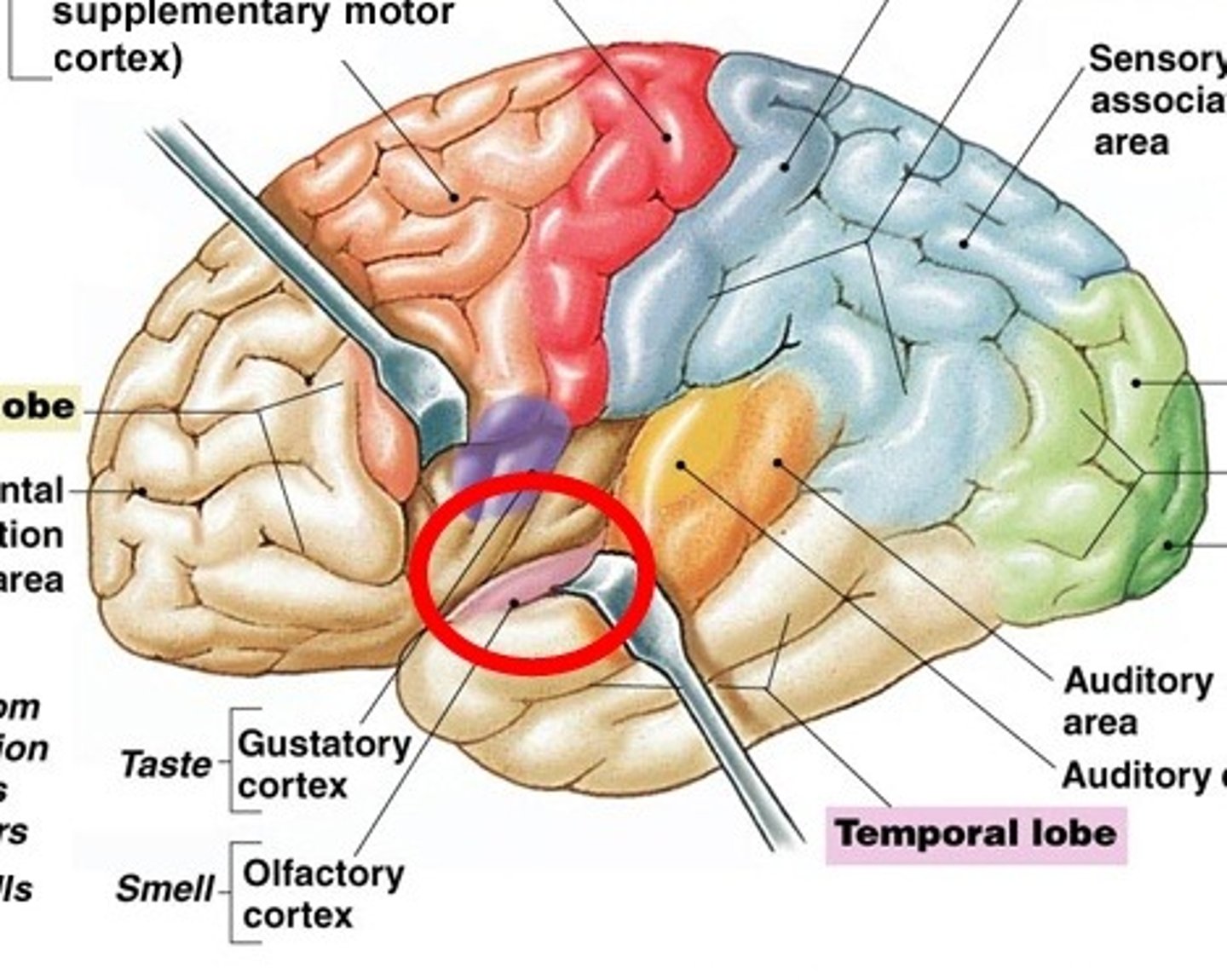
gustatory complex
to taste