Conception and Fetal Development, Genetics
1/47
Earn XP
Description and Tags
10 questions
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
48 Terms
fetal development wk 4
beginning development of GI tract
Heart is developing
Somites develop → beginning vertebrae
Heart is beating and circulating blood
eyes and nose begin to form
arm and leg buds are present
fetal development wk 6`
trachea is developed
liver produces blood cells
trunk is straighter
digits develop
tail begins to recede
fetal development wk 12
eyelids are closed
tooth buds appear
fetal heart tones can be heard
genitals are well-differentiated
urine is produced
spontaneous movement occurs
fetal development wk 16
lanugo (baby hair) begins to develop
blood vessels are clearly developed
active movements are present
fetus makes sucking motions
swallows amniotic fluid
produces meconium
fetal development wk 20
subQ brown fat appears
**quickening is felt by mother (baby starts moving)**
nipples appear over mammary glands
fetal heartbeat is heard by fetoscope
fetal development wk 24
eyes are structurally complete (should be able to open eyes)
vernix caseosa covers skin
alveoli are beginning to form
fetal development wk 28
testes begin to descend
LUNGS ARE STRUCTURALLY MATURE (not functionally mature) → if baby is preterm, delaying to 28 weeks can improve prognosis
fetal development wk 32
rhythmic breathing movements (breathe in and out amniotic fluid)
ability to partially control temp
bones are fully developed but soft and flexible
fetal development wk 36
inc in subQ fat → biggest WEIGHT GAIN last few wks of gestation
lanugo (baby hair) begins to disappear
fetal development wk 38
skin appears polished
lanugo has disappeared except in upper arms and shoulders
hair is now coarse and ~1inch in length
fetus is flexed
factors influencing development
quality of sperm or ovum (inc age = dec quality)
genetic code
adequacy of intrauterine environment (Mom getting adequate nutrients)
teratogens
high pollution (air/water pollution linked to preterm birth)
occupational hazards
meds
geriatric Mom/Dad age
geriatric Mom at 35 y/o
geriatric Dad at 50 y/o
ovarian cycle
Follicular phase (days 1-14)
Graffian follicle appears by day 14
Luteal phase (days 14-28)
begins on 1st day of bleeding
day 12 → lots of estrogen → pituitary gland releases LH
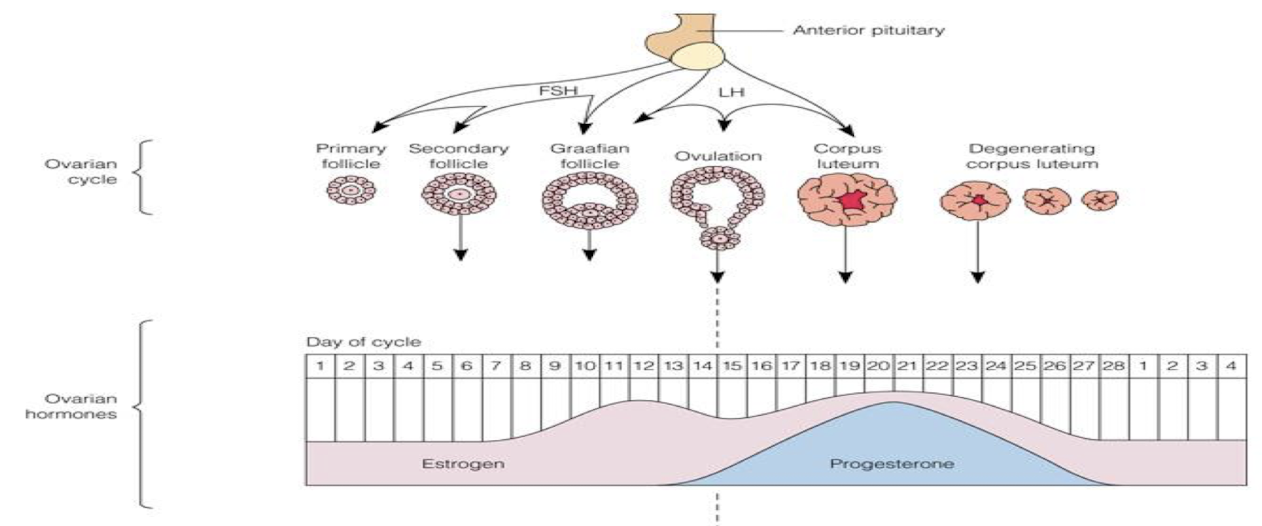
ovulation
release of ripe egg
menstrual cycle
Menstrual phase = endometrium sheds
Proliferative phase (growing) = endo-and myometrium thickens; estrogen levels peak right before ovulation
Secretory phase = progesterone dominate; estrogen drops sharply; uterus ready for implantation
Ischemic phase = estrogen and progesterone levels fall; vasoconstriction of uterine arterioles (think ischemic = less blood b/c of vasoconstriction)
GnRH
causes anterior pituitary to release FSH and LH
FSH
maturation of follicle
LH
release of mature follicle
estrogen
assists in maturation of ovarian follicles
progesterone
prepares the uterus for implantation and prepares the breasts for lactation
cervix
“door” to uterus
internal os and external os = doors; sometimes 1 is open and 1 is not
function:
lubrication of vagina
acts as bacteriostatic agent
provides an alkaline environment
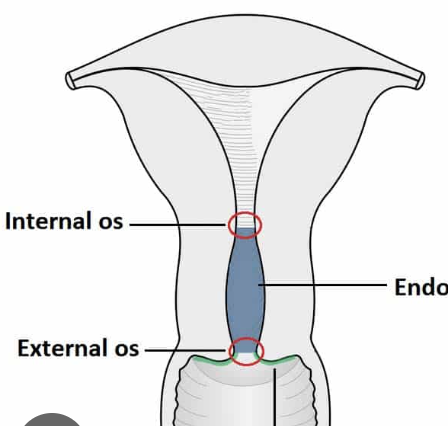
uterine corpus
body of uterus
perimetrium = peritoneum
myometrium = muscle layer
endometrium = mucosal layer
sheds in menstrual cycle
fallopian tubes
transport of the ovum to the uterus
site for fertilization
nourishing environment for ovum/zygote
ovaries
store and develop follicles
secrete hormones → estrogen and progesterone
male external genitals
penis and scrotum
male internal reproductive organs
testes
epididymis
vas deferens → gets cut / clamped in vasectomy
ejaculatory ducts
urethra
accessory glands
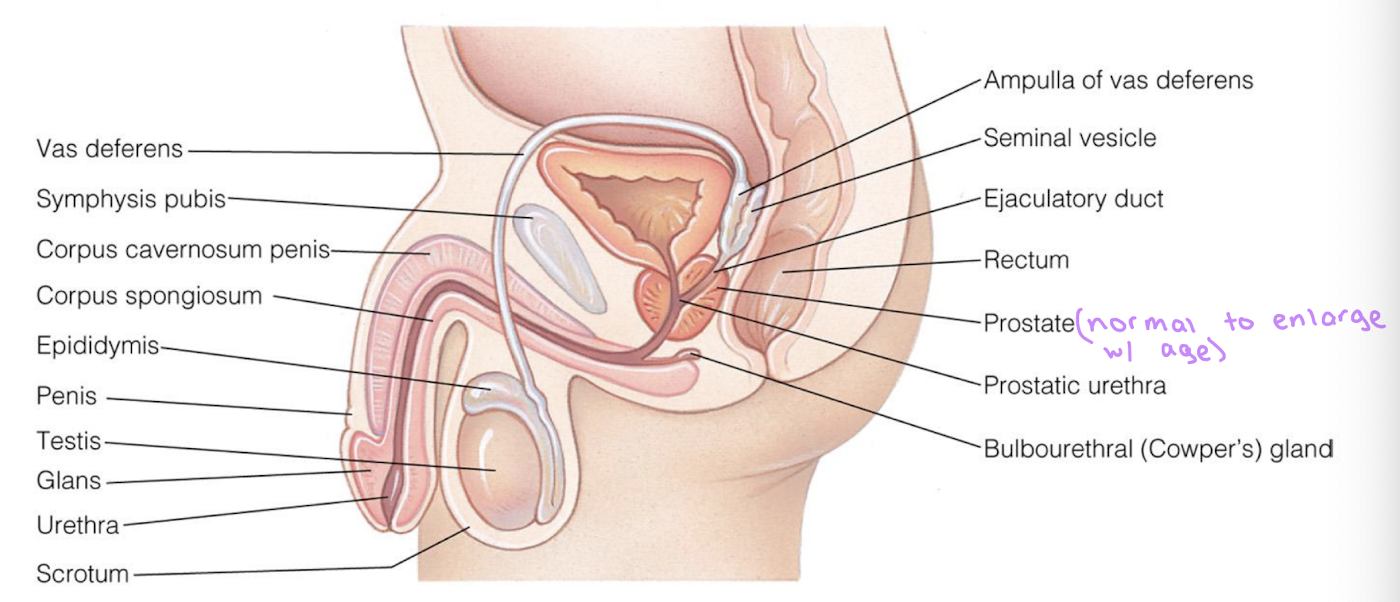
epididymis
stores sperm for 2-10 days
mitosis
exact copies of original cell
meiosis
production of new organism
1st division = mitosis
2nd division = chromatids separate and move to opposite poles → cells divide, forming 4 daughter cells
end up with haploid cells (half genetic material)
oogenesis
ovary gives rise to oogonial cells → cells develop into oocytes
meiosis begins and stops before birth
cell division resumes at PUBERTY → development of Graafian follicle (mature follicle)
spermatogenesis
production of sperm
1st meiotic division = primary spermatocyte replicates and divides
2nd meiotic division = secondary spermatocytes replicate and divide
produce 4 spermatids
fertilization
sperm and ovum unit to form zygote
sperm must pass through cervix (open while ovulating) to uterus
one fallopian tube empty; one contains egg
sperm binds to sperm receptors on egg
zona pellucida hardens after fertilization → prevents more sperm from entering
secondary oocyte completes second meiotic division → forms nucleus of ovum → nuclei of ovum and sperm unite → membranes disappear → chromosomes pair up
ova are fertile for 12-24hr
sperm are fertile for 72hr
takes place in ampulla of fallopian tube
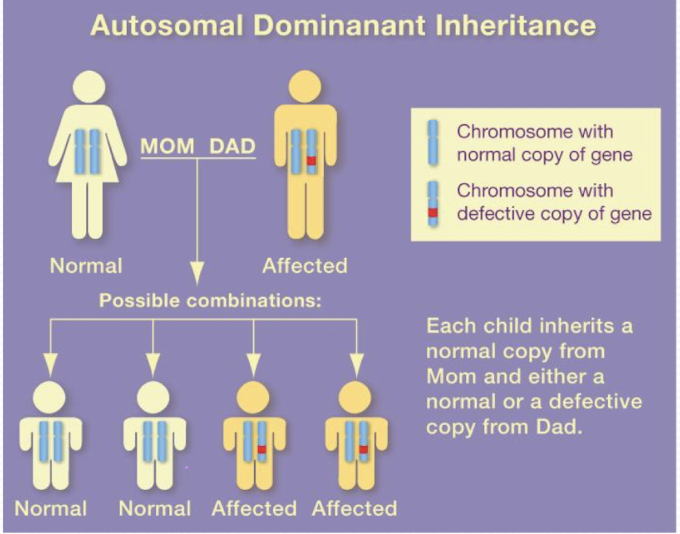
autosomal dominant disorders
Multigenerational
50% change of passing on gene
Males and females EQUALLY affected
Varying degrees of presentation
Ex: Huntington’s, Achondroplasia (dwarfism)
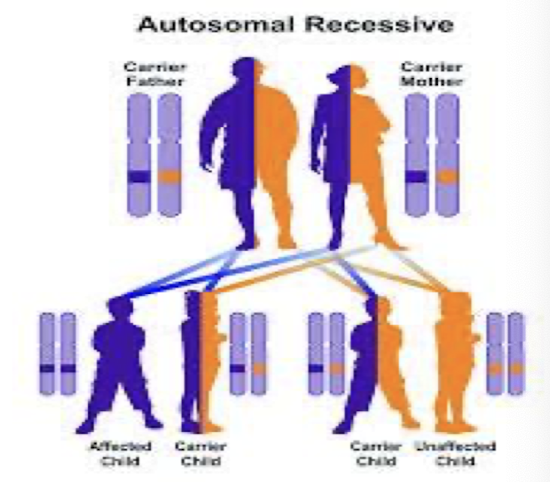
autosomal recessive disorders
Carrier parents
25% chance of passing on abnormal gene
25% chance of an affected child
If a child is clinically normal, 50% chance child is carrier
Males and females EQUALLY affected
Ex: sickle cell, cystic fibrosis, Tay-Sachs
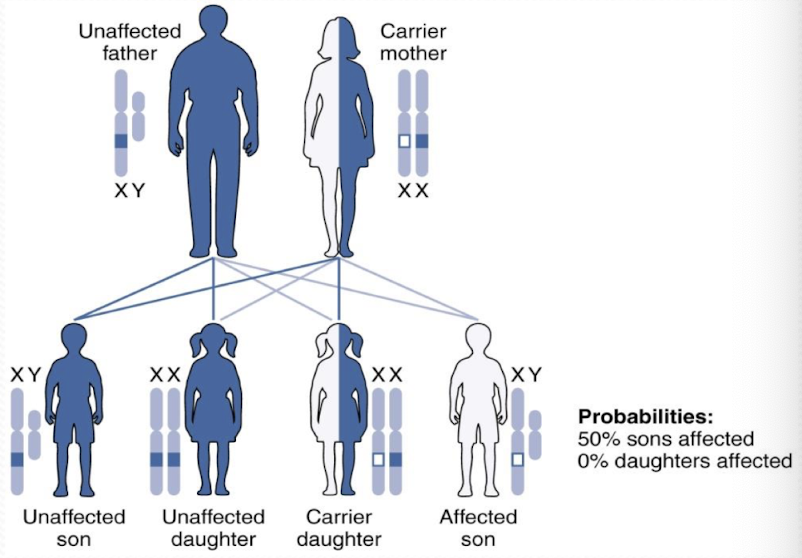
X-linked recessive disorders
NO male-to-male transmission
MORE COMMON IN MALES
50% chance carrier mother will pass the abnormal gene to sons → affected
50% chance carrier mother will pass abnormal gene to daughters → carrier
Ex: hemophilia, DMD
implantation
occurs 7-10 days after fertilization
blastocyst burrows into endometrium
endometrium now called decidua
placenta
metabolic and nutrient exchange
maternal portion = decidua
fetal portion = chorionic villi (shiny, whitish blue)
fetal surface covered by amnion (bag of water)
placental functions
nutrition, excretion, fetal respiration , production of fetal nutrients and hormones
umbilical cord
body stalk fuses with embryonic portion of the placenta
provides circulatory pathway from chorionic villi to embryo
ONE VEIN = delivers oxygenated blood to fetus
TWO ARTERIES = carry waste products away from fetus to placenta

indications for preconceptual genetic testing
Geriatric pregnancy = Maternal age 35+
Family hx
Known or suspected Mendelian genetic disorder
Birth defects and/or mental retardation
Previous pregnancies
Previous child with chromosomal anomaly
Previous child with metabolic disorder
2 or more first trimester spontaneous abortions
Parental genetics
Couples with a balanced translocation
Couples who are carriers for a metabolic disorder
Abnormal MSAFP (Maternal Serum Alpha-Fetoprotein)
Screening for birth defects
Women with teratogenic risk
genetic testing — options that are JUST screening
Sequential (10-13 wks)
Nuchal translucency
PAPP-A and hCG
MSAFP quad screen (15-21 wks) = NOT diagnostic, just inc r/o
AFP, inhibin, Estriol, hCG
Free cell DNA (at 10 wks)
20 wk ultrasound (18-22wks)
genetic testing — actual test / determination
Genetic amniocentesis (15-18wks) = tap and sample amniotic fluid; past deadline for TAB
Chorionic villus sampling (10-13wks) = riskier (inc r/o SAB)
Nurse’s role in genetic counseling
Educate about tests
Provide support
Refer for counseling
Resource during and after counseling
Down syndrome
trisomy 21 = extra copy of chromosome 21
what wk of gestation is quickening felt by mother?
wk 20
what week of gestation are alveoli beginning to form?
wk 24
what week of gestation are lungs structurally mature (but not functionally)?
wk 28 → delaying premies to 28 wks GREATLY increases prognosis
what week gestation does largest weight gain begin?
wk 36