Reptiles Lab Practical
1/98
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
99 Terms
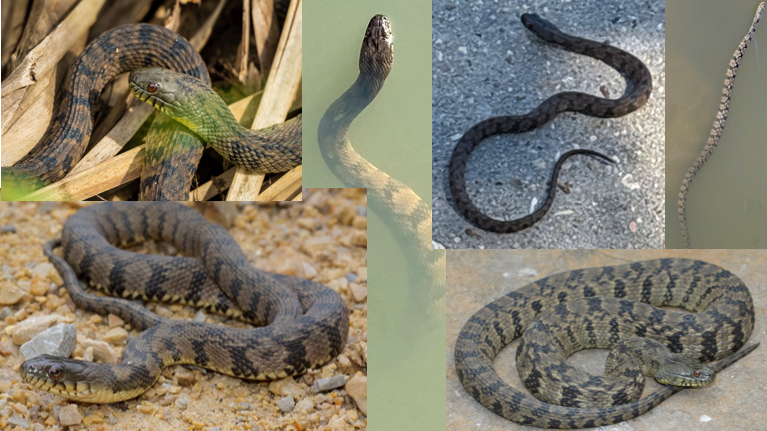

non-venomous, adult males have raised papillae under chin
Nerodia rhombifer
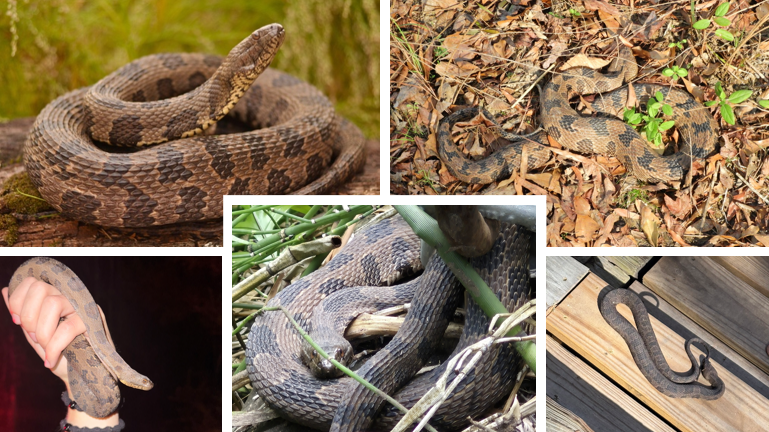

primarily consume catfish, non-venomous
Nerodia taxispilota

non-venomous, 2 dark brown and 2 tan/yellow stripes on sides
Nerodia clarkii
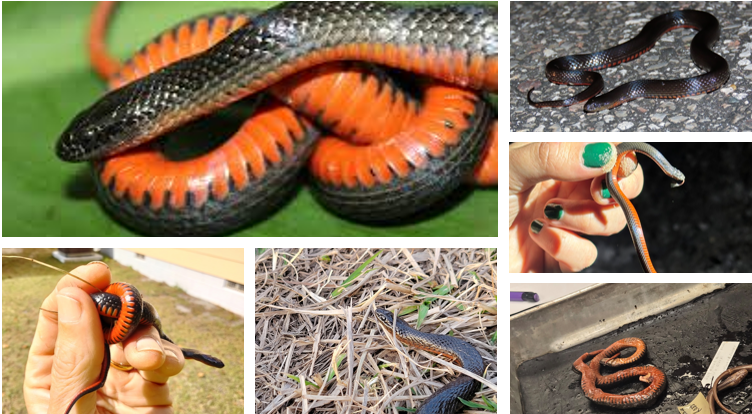

non-venomous
Liodytes pygaea

tan ventral with two rows of black, large eyes, consume freshly molted crayfish, non-venemous
Liodytes Rigida
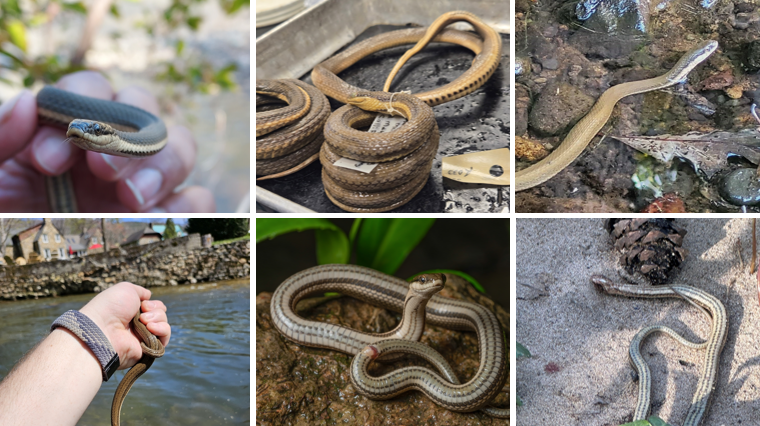

three narrow dark dorsal stripes, with yellow lateral stripes. Four brown stripes on venter. consume freshly molted crayfish, non-venomous
Regina septemvitatta
This genus has strongly keeled scales, a wide broad head that is distinct from the neck, and a divided anal plate
Nerodia
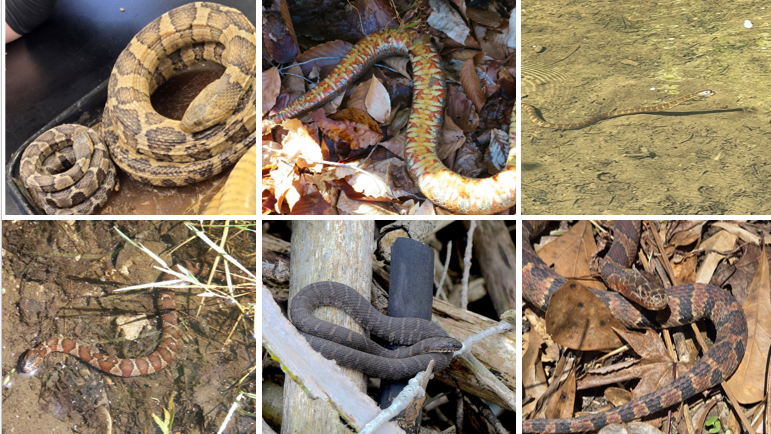

yellow or cream venter with two rows of half-moon markings, swollen labial scales
Nerodia sipedon
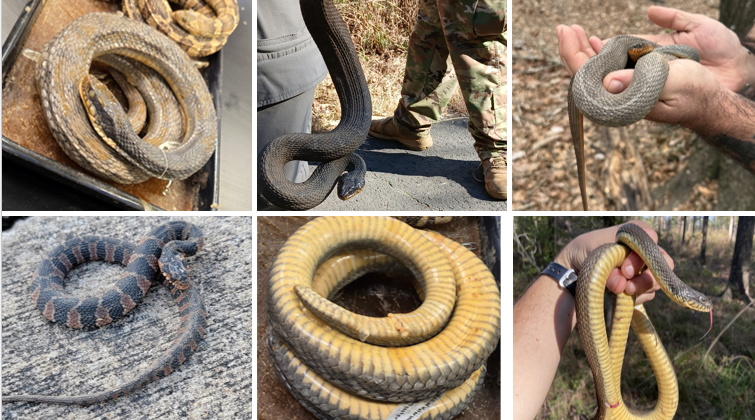

venter can be red, yellow, or orange
Nerodia erythrogaster
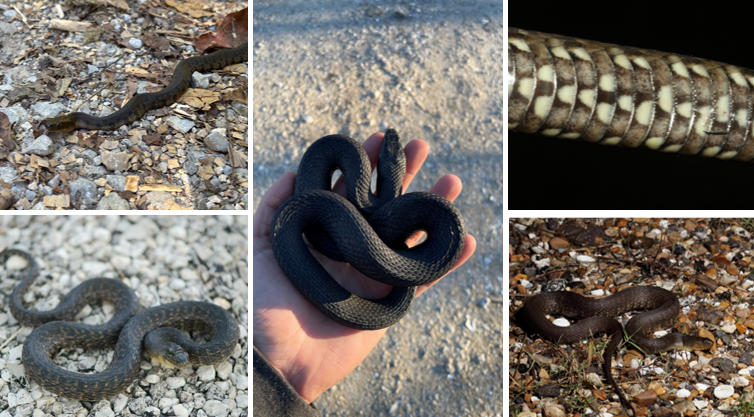

subocular scales separate eyes from labial scales, dark venter with light half moons
Nerodia cyclopion
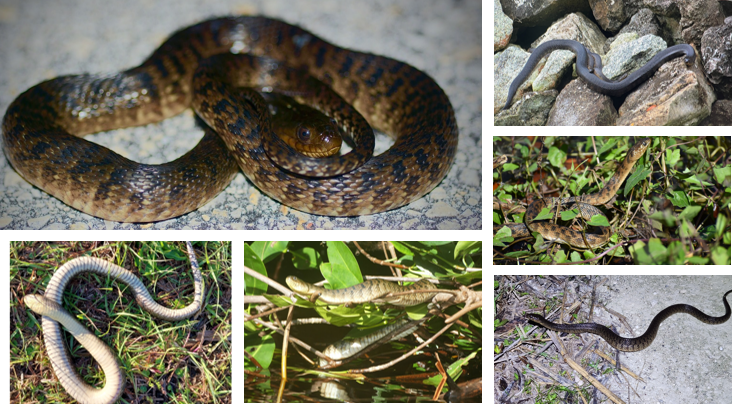

subocular scales separate eyes from labial scales, venter is light and mostly unicolor
Nerodia floridana
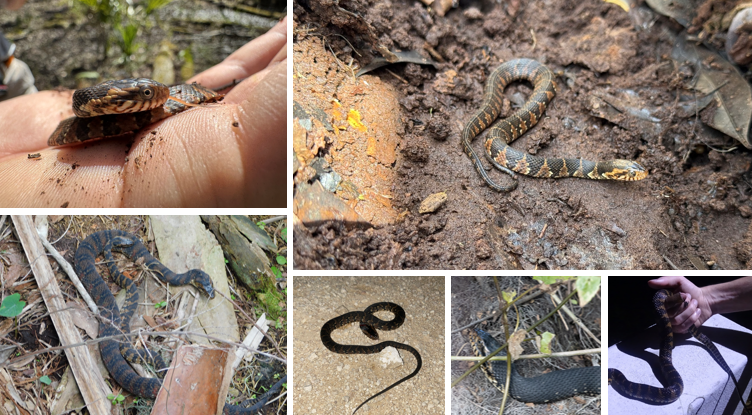

red, brown, or black crossbands, often with a black border, postorbital dark stripe
Nerodia fasciata
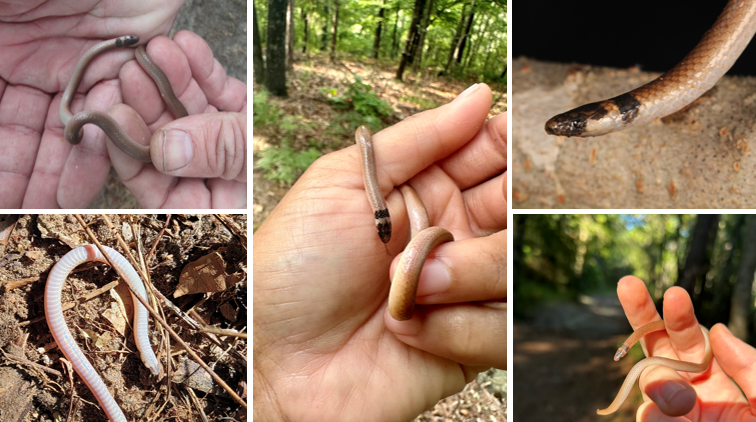

fossorial, eats inverts, nonvenomous to humans, prefers sandy/loose soil, collar/band behind head
Tantilla coronata
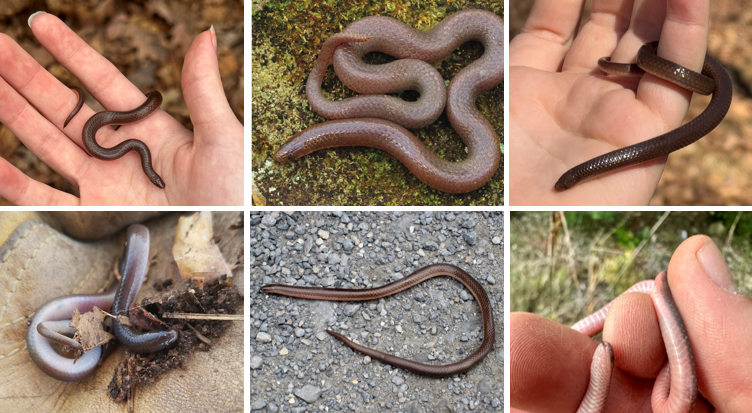

fossorial, feeds on soft bodied inverts, name means pleasin/charming, forests with high leaf litter + canopy cover, spine tipped tail
Carphophis amoenus
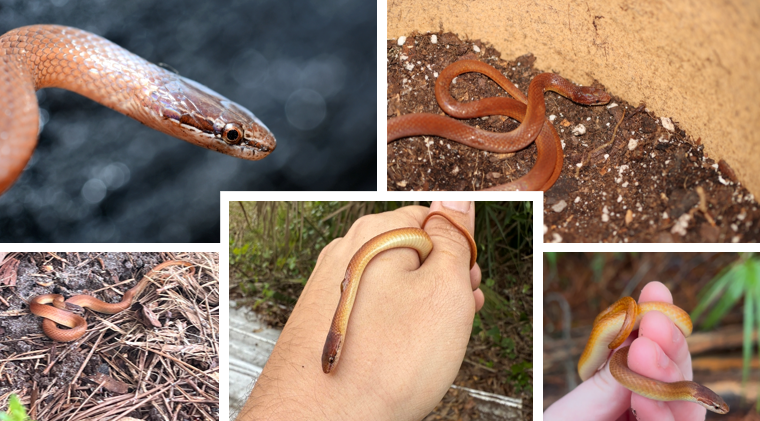

fossorial, pine and mixed pine hardwood forests, toxic saliva (not dangerous to humans), dark stripe through eye.
Rhadinaea flavilata
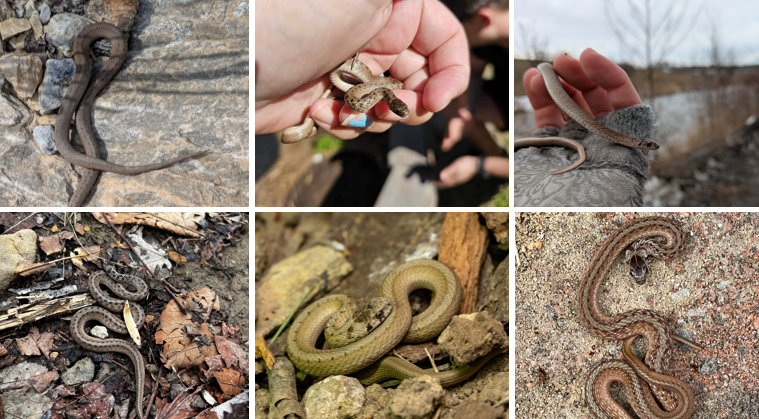

fossorial, commonly found in urban areas, wetlands, grasslands, forests, viviparous, eats slugs, snails, and earthworms, light center stripe bordered by black spots, keeled dorsal scales. Small black spots on sides.
Storeria dekayi
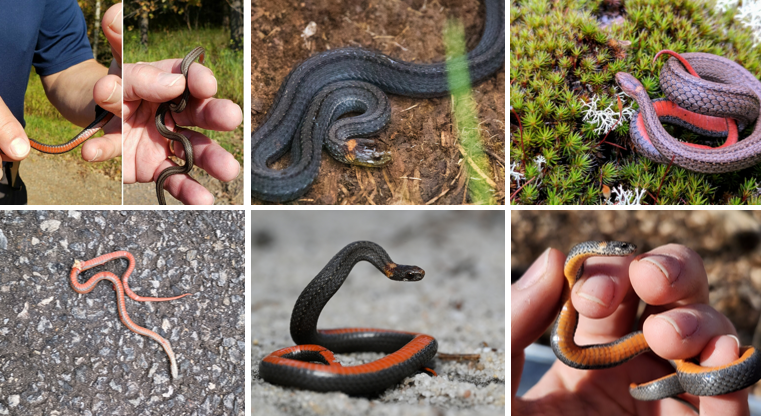

fossorial, can’t burrow on their own, eats slugs, keeled scales, bright red belly for death feigning, some can have a ring behind head
storeria occipitomaculata

fossorial, forested and urban habitats, viviparous, almost exclusively eats earthworms, keeled dorsal scales, round pupil
Virginia striatula
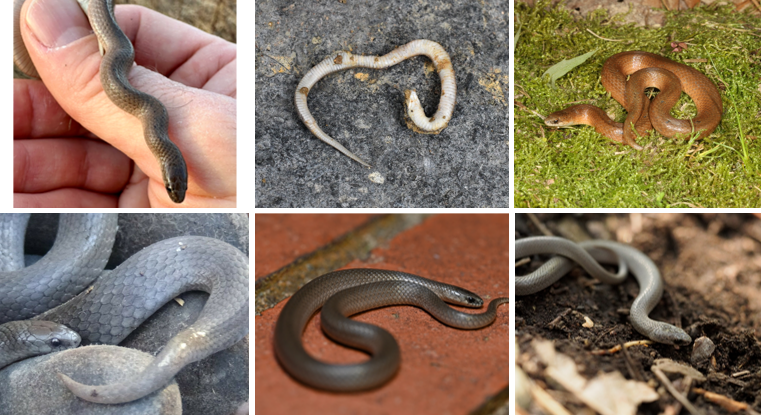

fossorial, prefer loose sandy soils, east earthworms and soft-bodied arthropods, viviparous, scales are not keeled.
Virginia valeriae
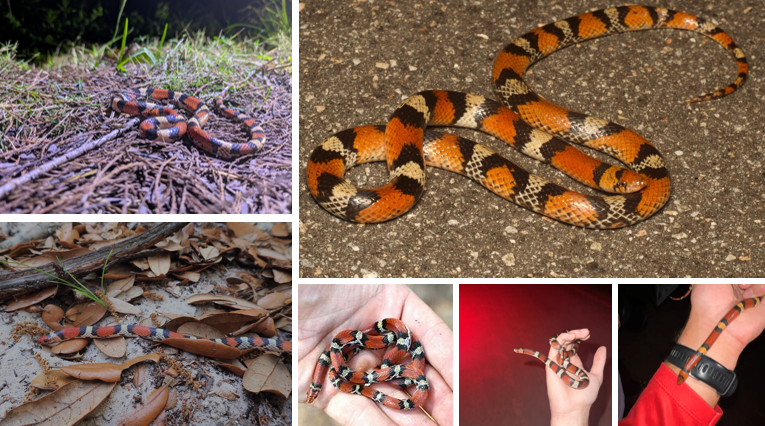

nonvenomous, inhabits dry sandy soils, burrower, alternating red, black, and white bands in a saddle pattern. constrictor eats small reptiles, amphibians, and lizard eggs.
Cemophora coccinea
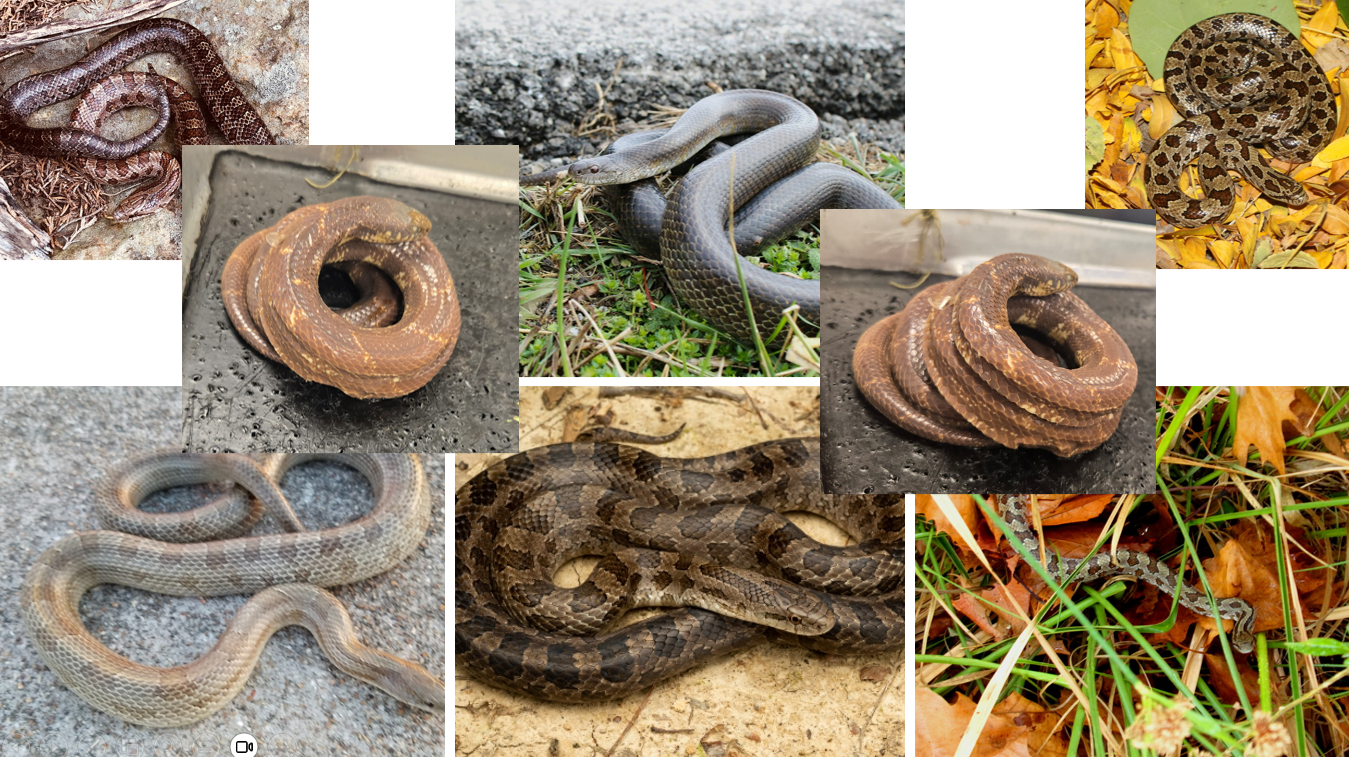

prefers loose, sandy soils in open woodlands, grasslands and fields. burrowers. non-venomous constrictor. has ‘eyeliner’
Lampropeltis calligaster
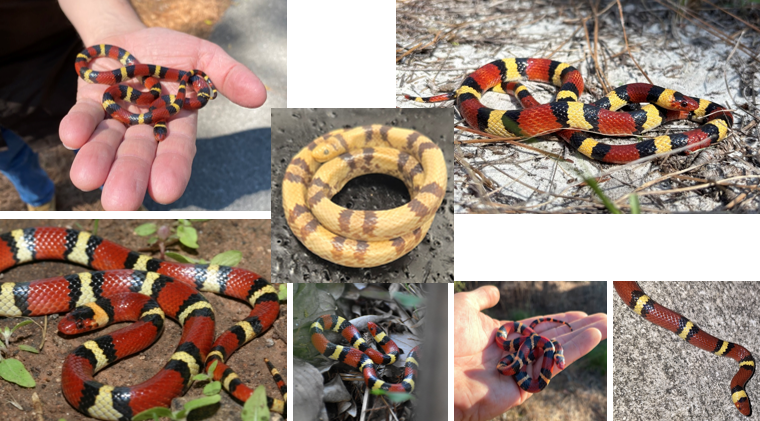

found at low elevation near open ground or brushy undergrowth, thrives in forests, woodlands, grasslands, and shrublands. Head is solid black or red, not banded like the body. Eats small reptiles, amphibians, rodents, and bird eggs. non-venomous constrictor.
Lampropeltis elapsoides

constrictor that eats small rodents and other snakes, including venomous ones. thrives in deciduous forests, mixed woodlands, farmlands, and suburban areas. alternating black and white/yellow bands, head is typically black and unpatterned.
Lampropeltis getula
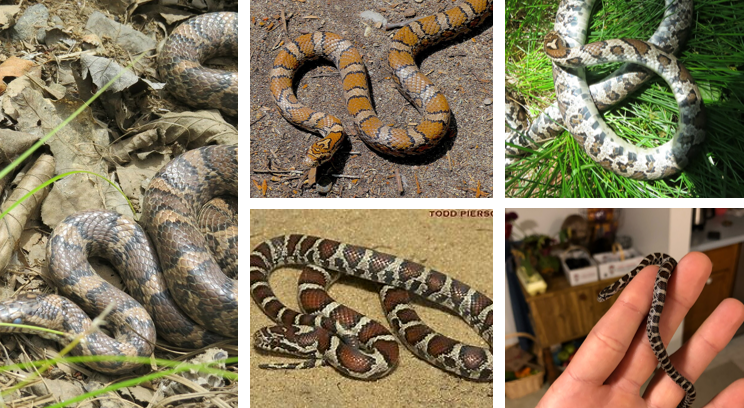

non-venomous constrictor, found in grasslands, meadows, farmlands, rocky outcroppings, hillsides, and near water sources. alternating red, black, and white/yellow bands.
Lampropeltis triangulum
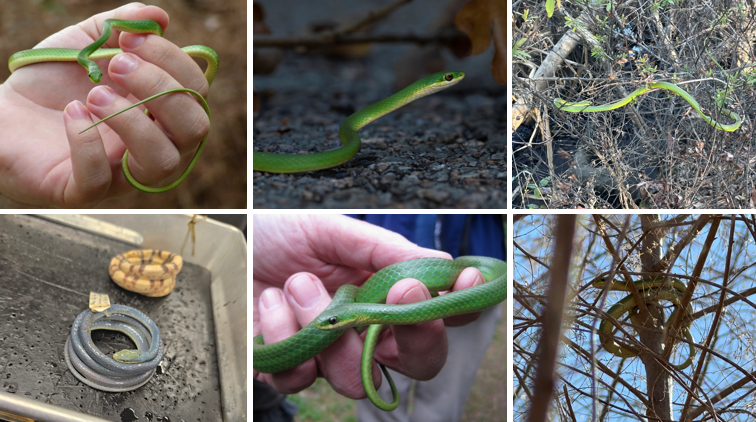

keeled scales, long, slender tail adapted for climbing, semi-arboreal found in woodlands, shrubs, and vine-covered areas. Tail makes up about 1/3 of length
Opheodrys aestivus
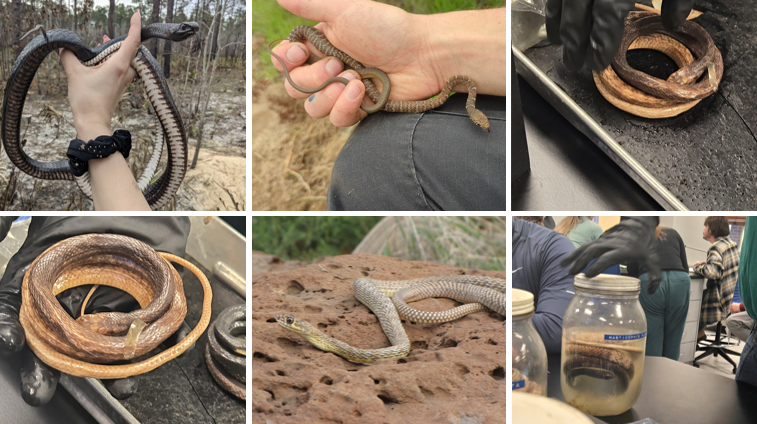

lives in rocky, open hillsides, hill prairies, and glades. Usually has a red or tan tail. Braided pattern on tail. non venomous
Coluber flagellum
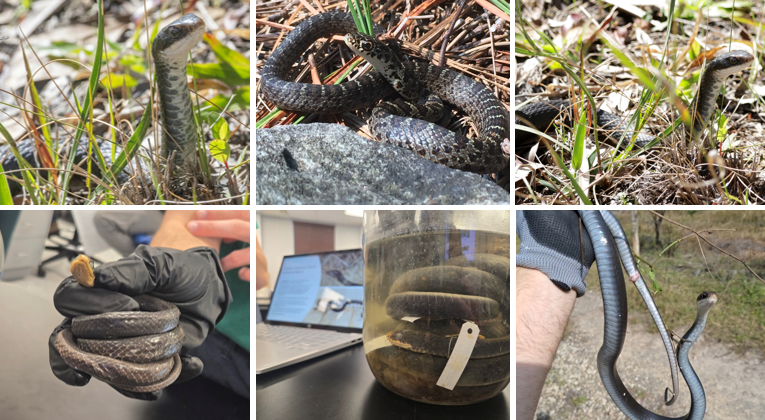

lives in pine flatwoods, hardwood hammocks, prairies, and sandhills. White markings on chin and throat. Periscoping behavior. non-venomous
Coluber constrictor
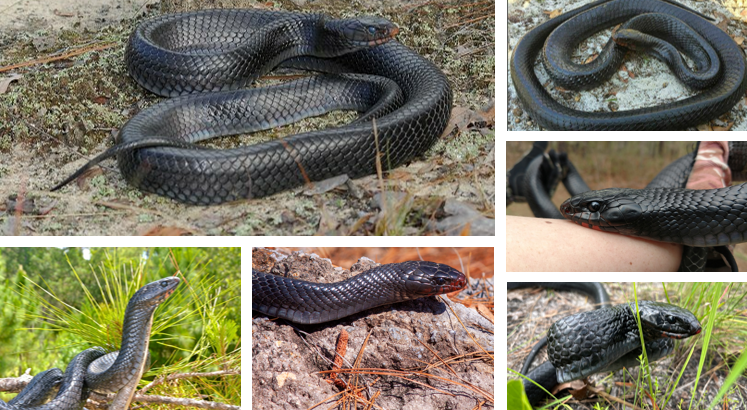

lives in sandy soils, flatwoods, thickets, cane fields, and high ground with well drained soil. Red or orange blush on face and neck. staple for longleaf pine forests. Non-venomous, eats venomous snakes and frogs.
Drymarchon couperi
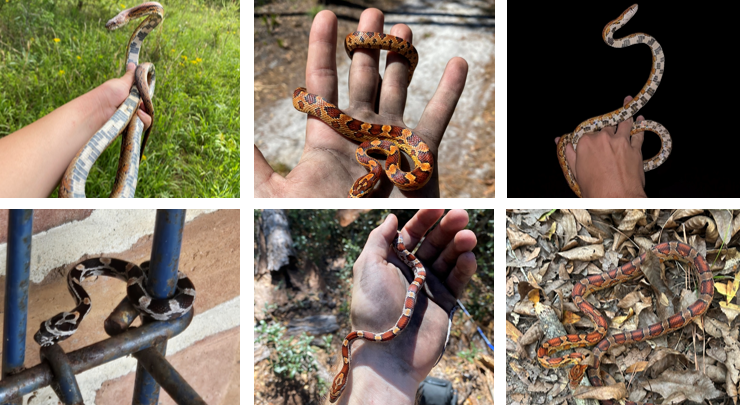

lives in wooded groves, rocky hillsides, meadowlands, tropical hammocks, barns and abandoned buildings. Has a pattern of large red blotches outlined in black, checkerboard pattern on belly. non-venomous, like to choke prey
Pantheropis guttatus
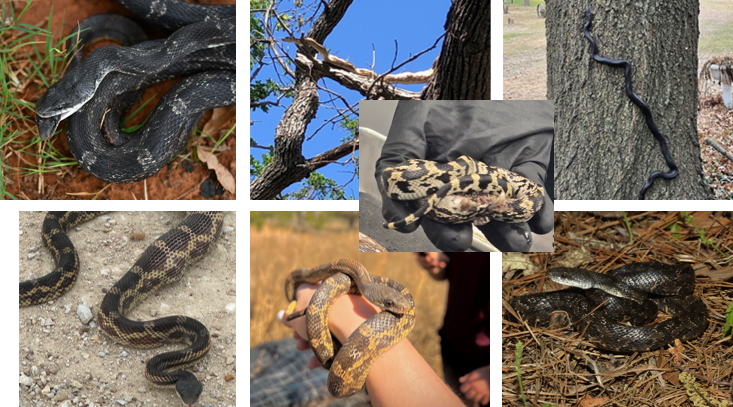

lives in farmland, hardwood forests, forested wetlands, can live in urban areas. checkerboard belly with black splotches on back. excellent swimmers and climbers, eat small mammals, birds, frogs, eggs, and rats. non-venomous, will freeze when threatened
Pantheropis obsoletus
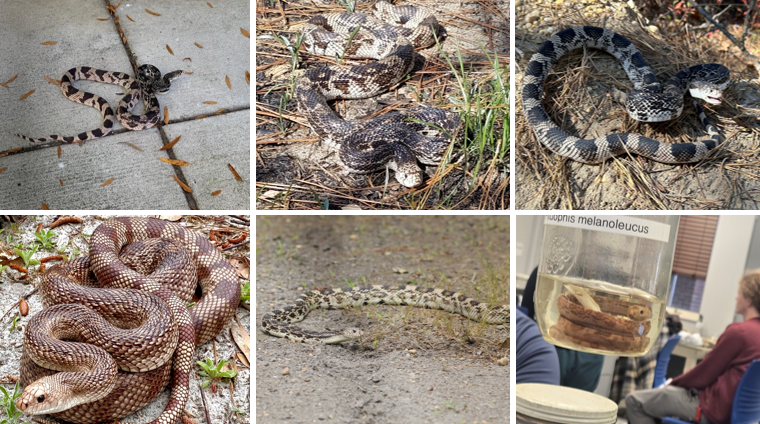

lives in sandy, pine-oak woodlands, pine flatwoods, open brushlands, cultivated fields, and rocky deserts. keeled dorsal scales, one anal plate. their predators are striped skunks. non-venomous.
Pituophis melanoleucus

ventral is orange/yellow with black spots. oviparous, no parental care. fossorila, lives in moist terrestrial habitats. eats small snakes, frogs, salamanders, lizards, and worms.
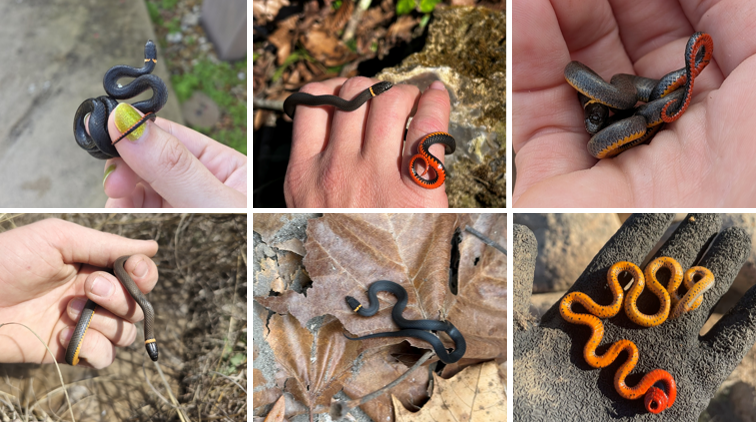
Diadophis punctatus
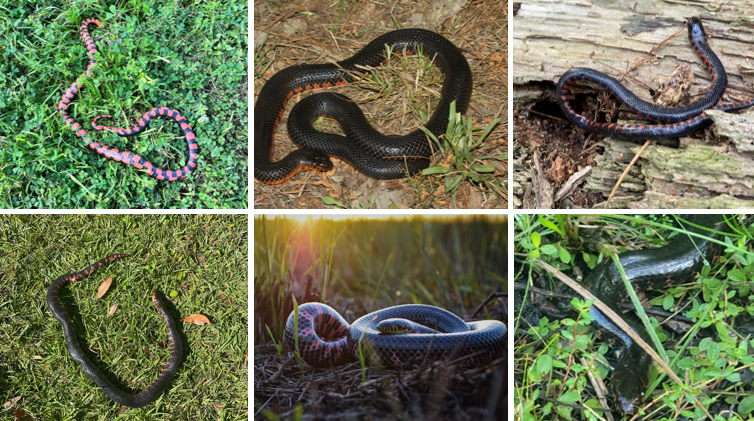

alternating red and black bars on ventral, oviparous, parental care until eggs hatch. live in swamps, marshes, mud-bottom creeks etc. Primarily eat Siren and Amphiuma salamanders
Farancia abacura
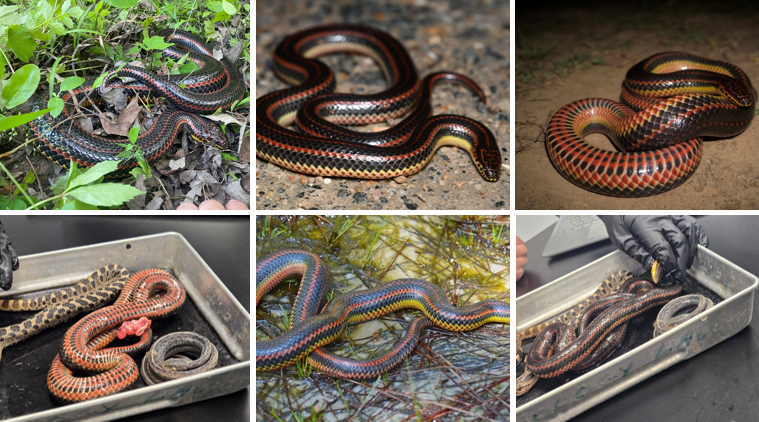

oviparous, parental care until eggs hatch. found in rivers or creeks, eats eels, fish, tadpoles, and salamanders.
Farancia erytrogramma
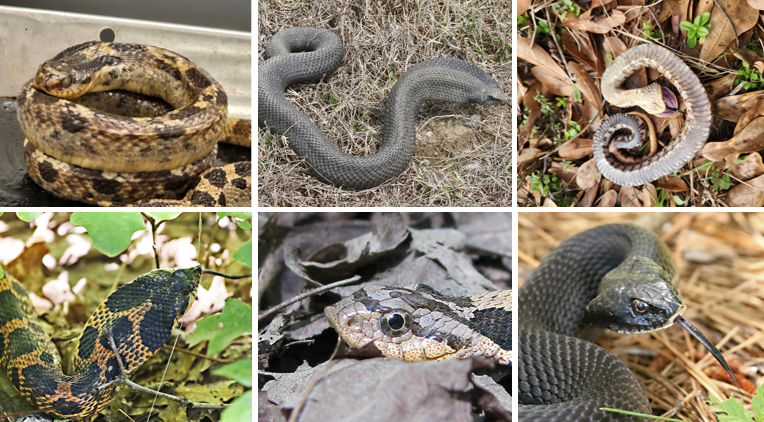

distinguishing feature is the protrudin rostral scale, keeled scales, dark color pattern on head. play dead. venomous, but not to humans. oviparous, no parental care. Terrestrial, sandy soils, primarily eat toads.
Heterodon platirhinos

sharply upturned rostral scale, uniform pattern of large black blotches alternating with smaller blotchess, keeled scales. pay dead, venomous but not to humans. oviparous, no parental care. Semifossorial in sandy hills, woodlands, flooded plains, and forested areas. primarily eat Anaxyrus toads and spadefoot toads.
Heterodon simus
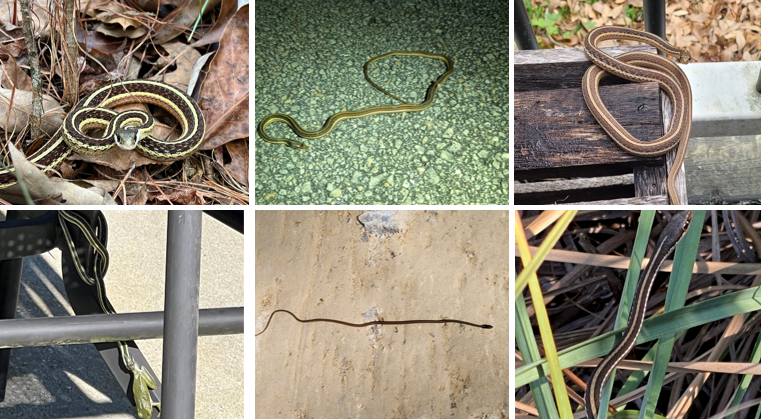

three light line running down body, one in middle, two on sides. white chin and white spot beside eye. keeled scales. unmarked belly. viviparous, no parental care after birth. semiaquatic, prefers swamps, marshes, weedy lake shores, wet meadows, and streams. Eats fish, worms, and amphibians
Thamnophis saurita

cross-hatching pattern, three lines, one middorsal and two on sides. viviparous, no parental care after birth. terrestrial, commonly found in wetlands, hillsides, marshes. Eats worms, frogs, toads, salamanders, and other snakes.
Thamnophis sirtalis

venomous, dark rounded blotches, rusty middorsal stripe, very small rattle
Sistrurus miliarius

forests, rocky outcrops, and wetlands. venomous, eats small mammals. chevron crossbands, black tipped tail
Crotalus horridus

eats small mammals, birds, and reptiles. venomous. diamondback
Crotalis adamanteus

tail only has black and yellow rings, black face w/ yellow stripe behind. venomous. red on yellow
Micrurus fulvius
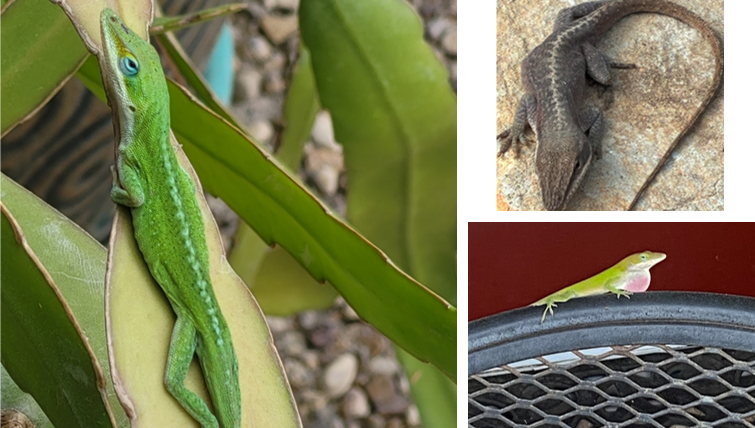

pointy face, males have red dewlap. green or brown, can change color
Anolis carolinensis

pointed head, middorsal crest, has a dorsal stripe, sometimes has a reddish orange cap
Norops sagrei
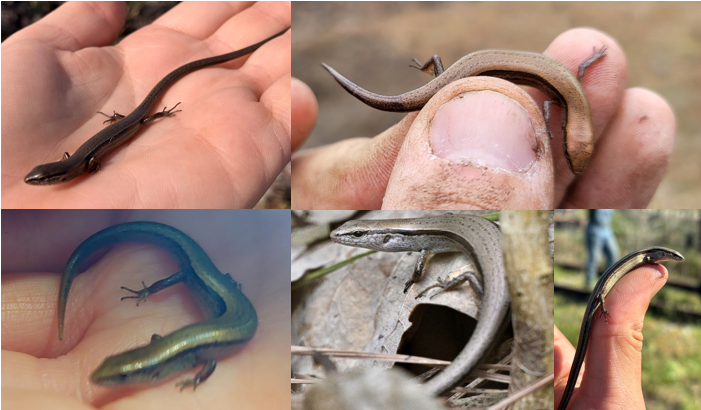

dorsolateral stripes, yellow or white belly, can regrow tail, lower eyelid has a transparent window-like structure
Scincella lateralis
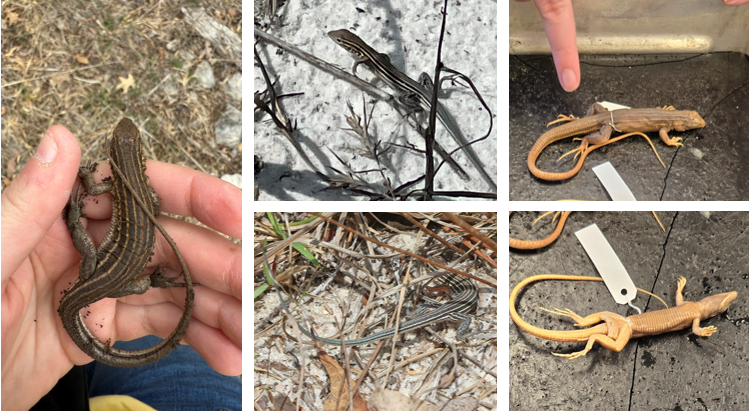

ventral are scales are bigger than dorsal scales and in nice rows, scales on tail are in rows, 6 dorsal lines,
Aspidoscelis sexlineata
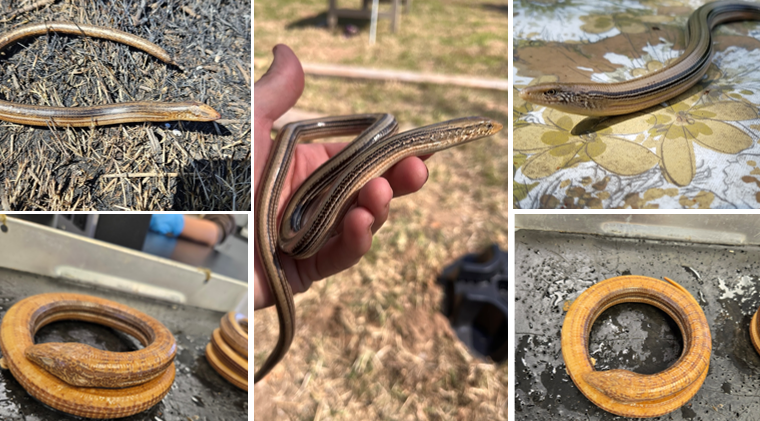

lives in dry pine woods, old fields, and near ponds/streams, squarish scales, deep groove on each side of body, irregular crossbars are present, the venter can have two rows of dark spots forming longitudinal stripes below the lateral grooves. legless lizard
Ophisaurus attenuatus
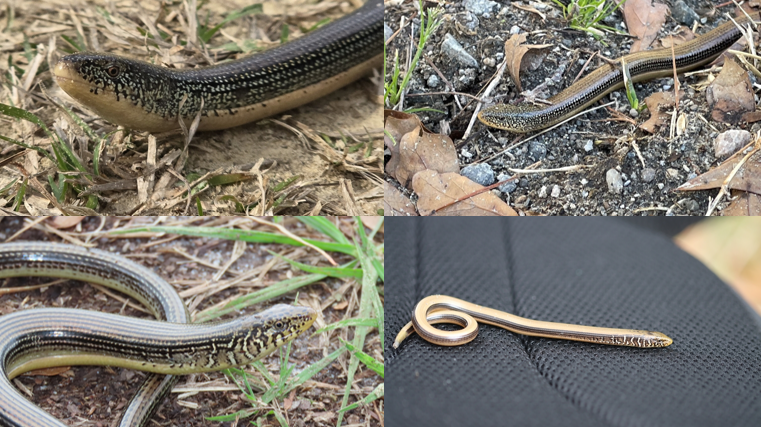

live in damp or mesic habitats, squarish scales, deep groove on sides, 2-3 lateral dark stripes, several longitudinal rows of spots, “salt and pepper” look
Ophisaurus ventralis
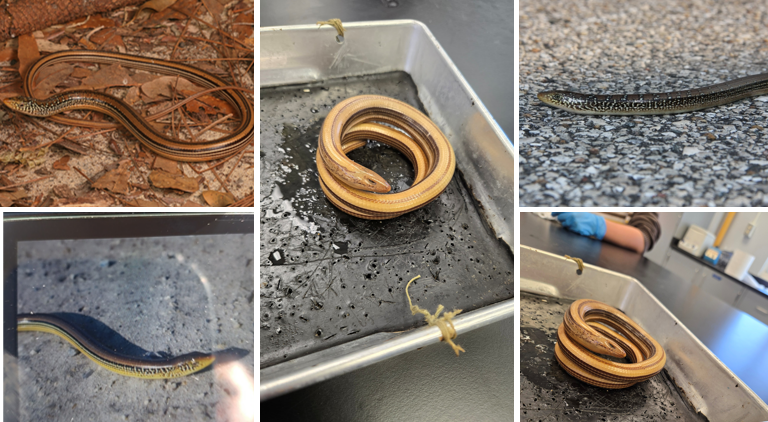

lives in flat woods or pitcher plant bods, squarish scales, yellowish towards tip of snout, 2-3 light stripes are bordered by dark spots below the lateral fold.
Ophisaurus mimicus
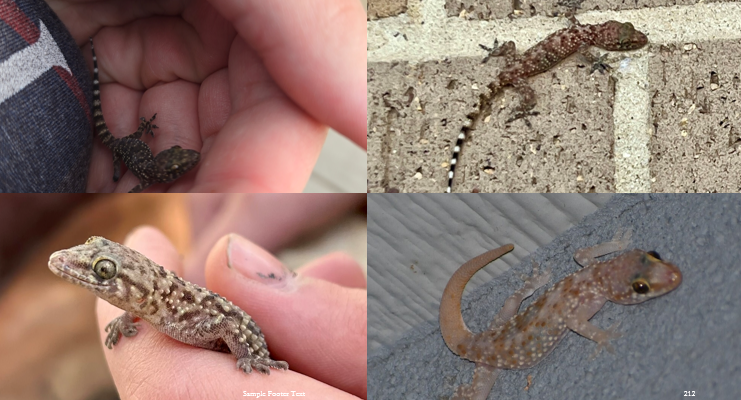

seeks darkness to hide, drops tail, oviparous, visual eaters
Hemidactylus turcicus
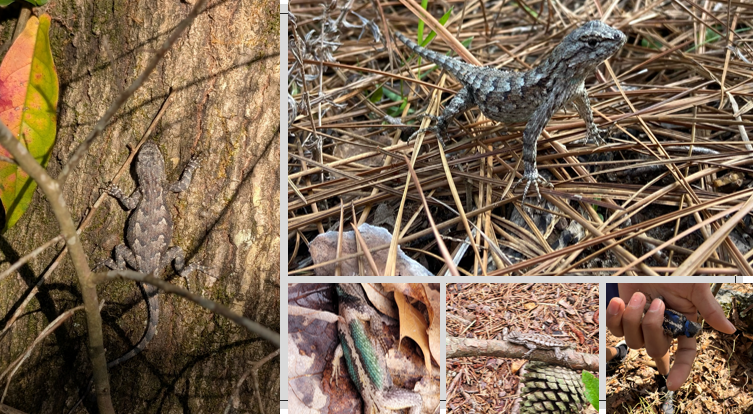

diurnal (active during the day), temperate to subtropical habitats, greenish blue or black ventral
Sceloporus undulatus
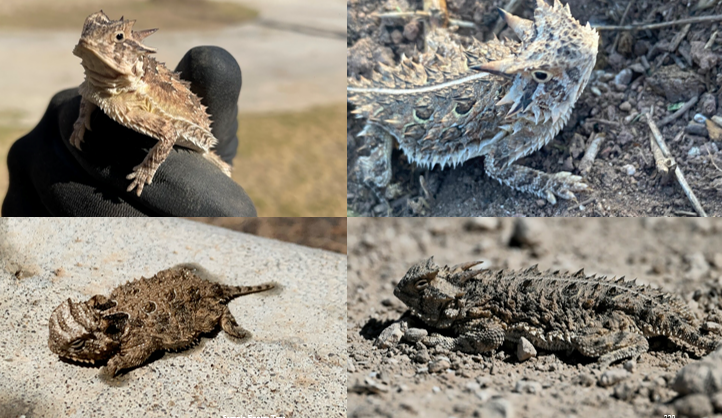

horny, can squirt blood from eyes, eats ants, termites, beetles, and grasshoppers,
Phrynosoma cornutum
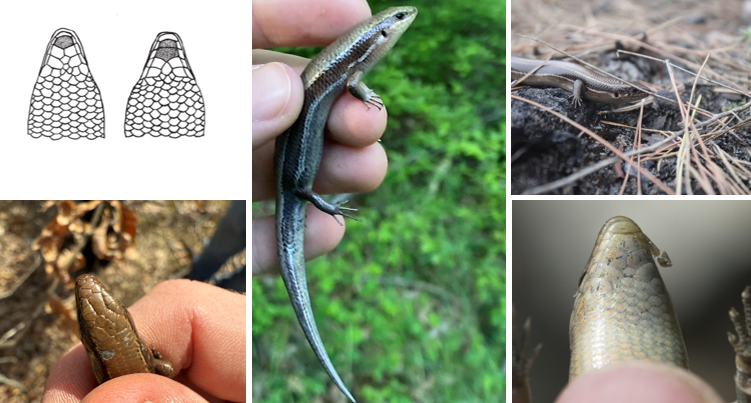

gray/brown w/ 2 stripes on each side, single post-mental scale, carnivorous, oviparous
Plestiodon anthracinus
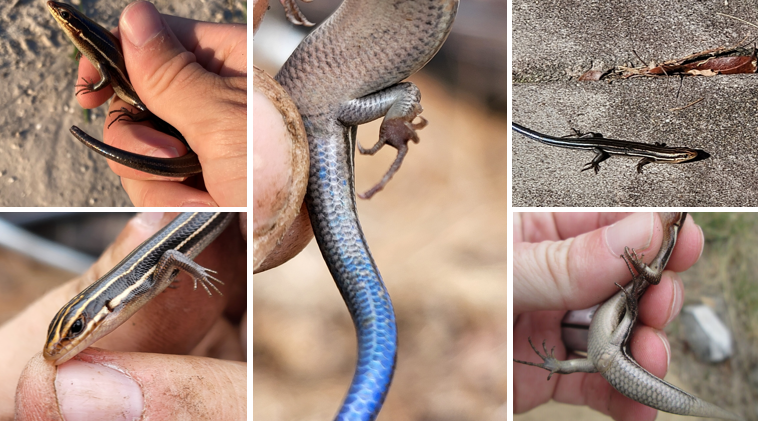

consistently sized scales on underside of tail, most common in wooded areas, carnivorous, oviparous, 5 upper labial scales
Plestiodon inexpectatus
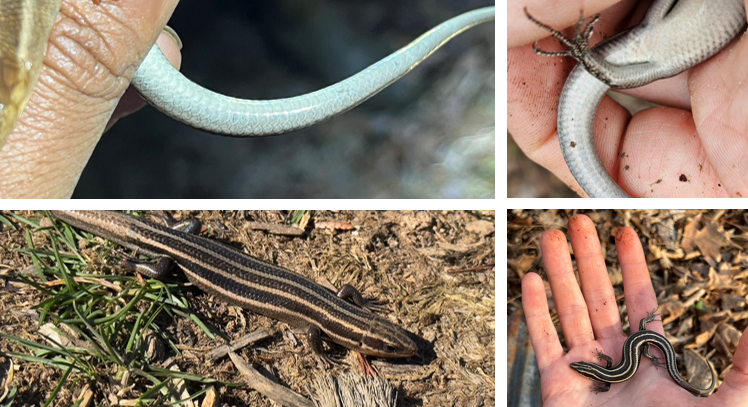

five pale stripes down body, enlarged row of scales on underside of tail, most common in wooded areas, carnivorous, oviparous.
Plestiodon fasciatus
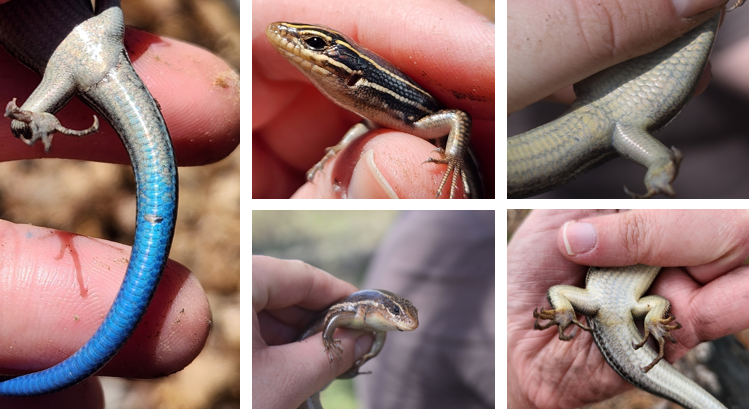

enlarged row of scales on underside of tail, six labial scales, males can have a reddish head, more arborial than other skinks, common in wooded areas, carnivorous, oviparous
Plestiodon laticeps

two light stripes on each side, red/orange tail, rarely climb, carnivorous, oviparous
Plestiodon egregius

fossorial, looks like a worm, small pointed spur on tip of tail, eyes covered with translucent scales, parthogenesis, eats eggs, larvae, and pupae of ants and termites
Ramphotyphlops braminus

ambush predator, defensive tail vibration, live young, Hersheys kiss pattern, deciduous forest and mixed woodland
Agksitrodon contortrix

mostly eats fish and frogs, vibrating tail, active at night, broad dark stripes on sides of head, swims on top of water
Agkistrodon piscivorous
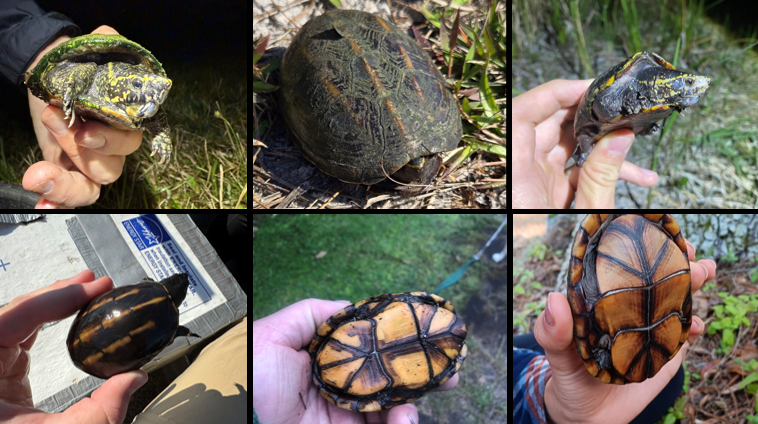

slow-moving water, found in Choctawatchee River drainage, semi-aquatic, omviore, temp sex determination
Kinosternon baurii
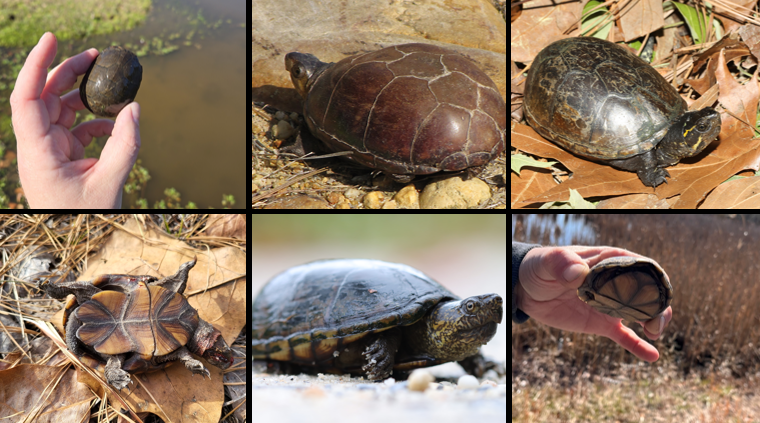

slow moving bodies of water, semi-aquatic, more active at night, seldom bask. temp sex determination, omnivores, strongly hooked upper jaw
Kinosternon subrubrum
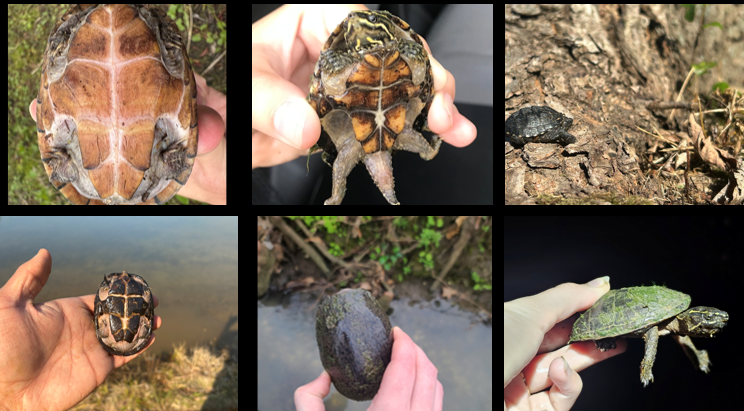

slow moving water, temperature sex determination, omnivores, extremely aquatic, seldom bask, stinky. plastron can’t close, stripes originate from snout. barbels on chin and neck
Sternotherus odoratus

large carapace, up oto19”, 3 keels, eyes located dorsally, moderately hooked snout, long tail equal to carapace length, highly aquatic
Chelydra serpentina

large carapace, up to 25.5”, 3 large keels, supermarginal scutes, strongly hooked upper jaw, dermal projections on head and neck, specially adapted tongue (wormlike)
Macrochelys temminckii

found in the apalachicola river, large carapace, up to 25.5”, 3 large keels, supermarginal scutes, strongly hooked upper jaw, dermal projections on head and neck, specially adapted wormlike tongue
Macrochelys apalachicolae

armored body (osteoderms/scutes), muscular flat tail, largest reptile in the US up to 19’, short thick limbs, rounded snout. there’s an introduced populsation in Lake Hillabee, Oxford
Alligator mississippiensis

slow moving or still freshwater, bottoms of streams and still water bodies, Escatawpa River in Mobile and Washington counties. barbels on chin, no gular scute on plastron, carapace high keeled and about as tall as it is wide
Sternotherus carinatus
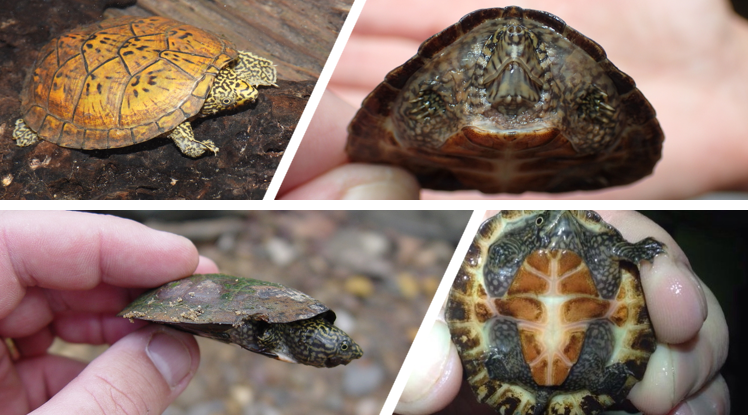

only found in permanent steams in the Black Warrior River system above the fall line, barbels on chin only, has gular scutes, strongly flattened shell. top of head is greensih with a dark reticulum, top of snout spotted or blotched
Sternotherus depressus
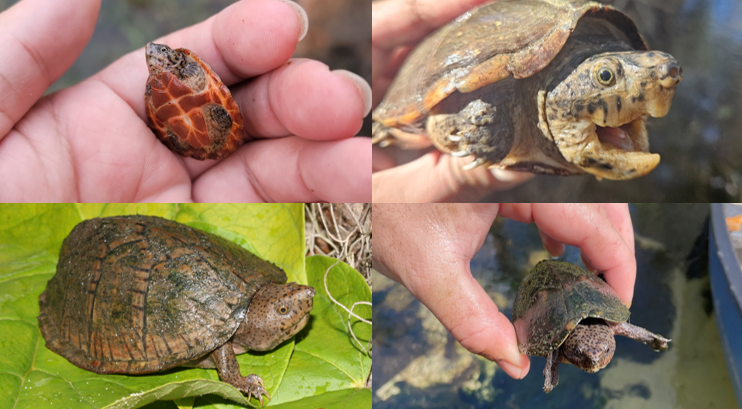

slow moving or still freshwater, bottoms of streams and still bodies of water, found East of the Mobile Bay to the Appalachicola, Fish, and Perdido Rivers. Barbels on chin only, has gular scutes, carapace is wider than it is tall but not strongly flattened. distinct dark spots posterior to eyes
Sternotherus minor
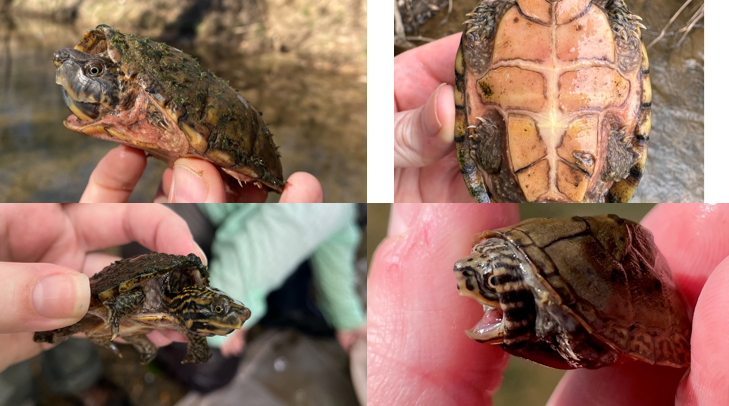
slow moving or still freshwater, bottoms of streams and still bodies of water, any river, creek, or pond in AL. barbels on chin only, has gular scutes, shell is not strongly flattened, curved dark stripes posterior to eyes, neck boldy marked with light and dark stripes.
Sternotherus peltifer

slow moving or still freshwater, bottoms of streams and still water bodies, endemic to Choctawatchee and Escambia River Basins in southern AL and FL’s panhandle. dark spotted head with light groud coloring, some degree of striping on face and neck, has gular scute, vertebral keel present, reduced or lacking lateral keels
Sternotherus intermedius
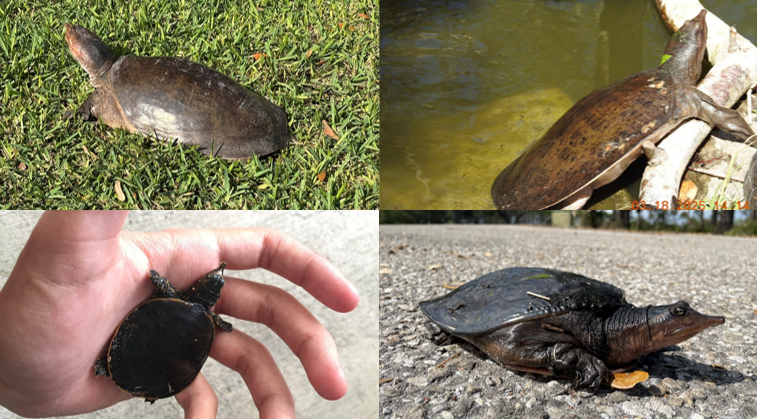

large, leathery skin, flattened, narrower at anterior, spade like feet, restricted to lower coastal plain, slow streams, lakes, and ponds, heavily aquatic, sandy substrates. genetic sex determination, omnivorous but mainly meat.
Apalone ferox
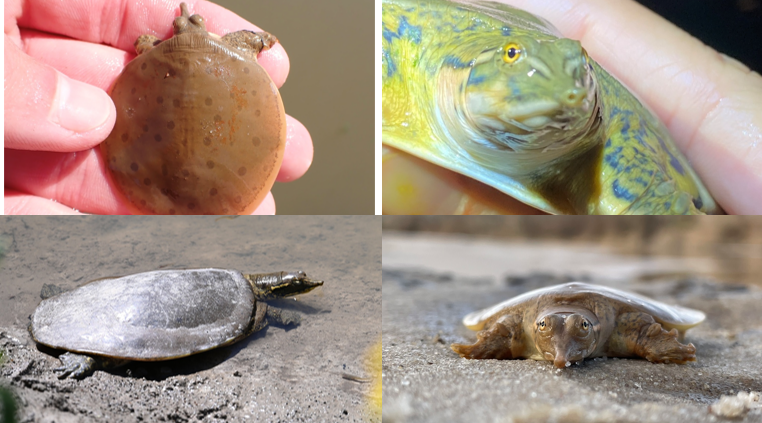

no tubercules, leathery skin, bold, dark-bordered light stripe behind eyes, round nostrils, Tennessee River Drainage, strongly aquatic stream dweller, carnivorous, genetic sex determination
Apalone mutica
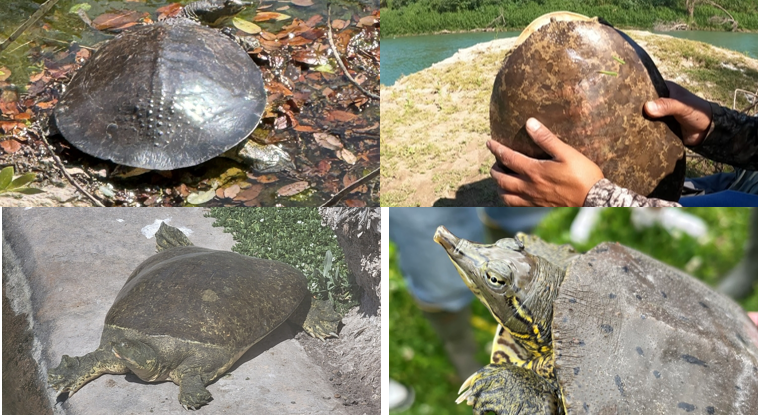

large, leathery skin, c-shaped nostrils, spiny conelike projections on edge of carapace, pale lines bordered by black running down sides of neck, ecological generalist, generally found in slow waters, genetic sex determination, omnivores
Apalone spinifera

2+ black lines along posterior border of carapace, scattered ring shaped spots on carapace, yellow and brown spots/stripes up to nose, temperate climate freshwater biomes, carnivorous, genetic sex determination
Apalone spinifera aspera

large, terrestrial, notably scaled head, large flattened toenails, elephantine back feet, gular projection of shell behind head, oblong shell shape, herbivorous, temp sec determination
Gopherus polyphemus

feet are modified wing-like flippers, carapace has 5 pair pleural scutes and 3 on plastron bridge, front of carapace is concave, temp sex determination, carnivorous
Caretta caretta
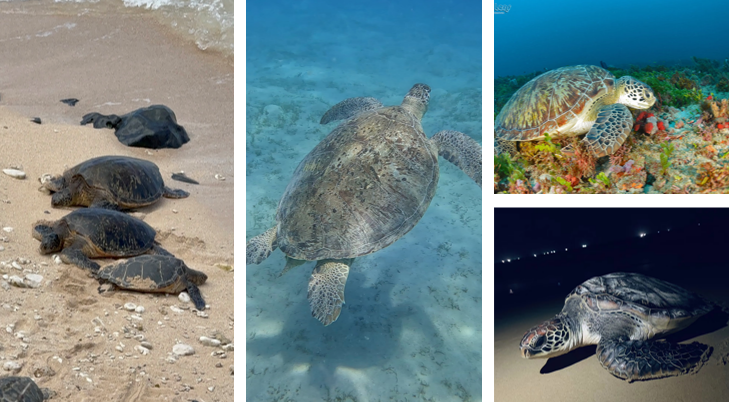

carapace is light to dark brown with mottled blotches and four pleural scutes, shallow tropical shores, temperature sex determination,
Chelonia mydas

heart shaped carapace with 4 pleural scutes, reddish brown marking on shell w/ small tan and yellow spots, temp sex determination, coral reef habitats,
Eretmochelys imbricata
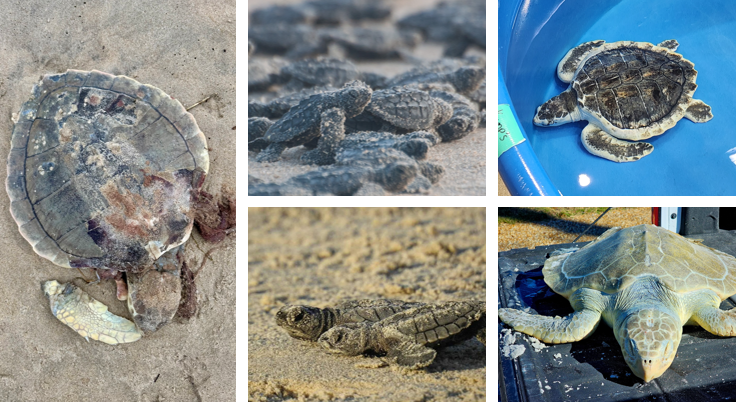

5 pairs of pleural scutes, 4 scutes on the white plastron bridge, circular grey carapce. nest along gulf of mexico, long migratory periods.
Lepidochelys kempii

no scutes, carapace has 7 longitudinal ridges, 5 ridges on plastron, temp sex determination,
Dermochelys coriacea
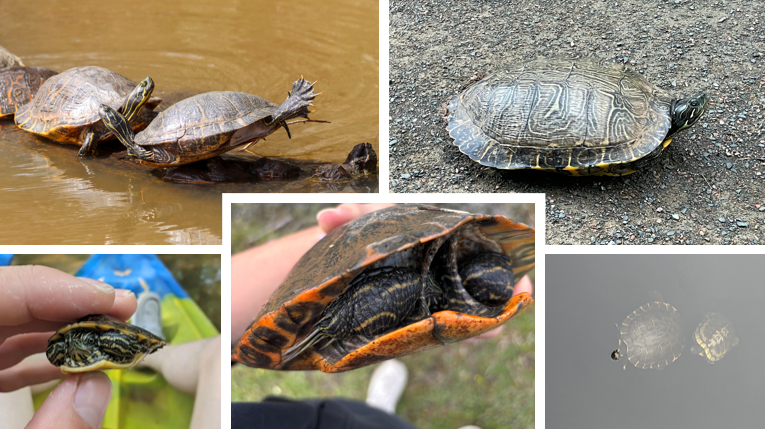

oval shaped carapace, somewhat serrated. C on the second pleural scute. plastron is yellow, can have dark markings on seams. no bar through eye. live in streams and large lakes, often bask, usually swim away when approached. herbivores
Pseudemys concinna

oval carapace, somewhat serrated. vertical bar on second pleural scute that is forked at either or both ends. iris has transverse dark bar. Found in the lower coastal plain, Occur in large ponds, oxbows, sloughs, and small sluggish rivers. mostly herbivorous as adults. dark markings on anterior marginal scutes
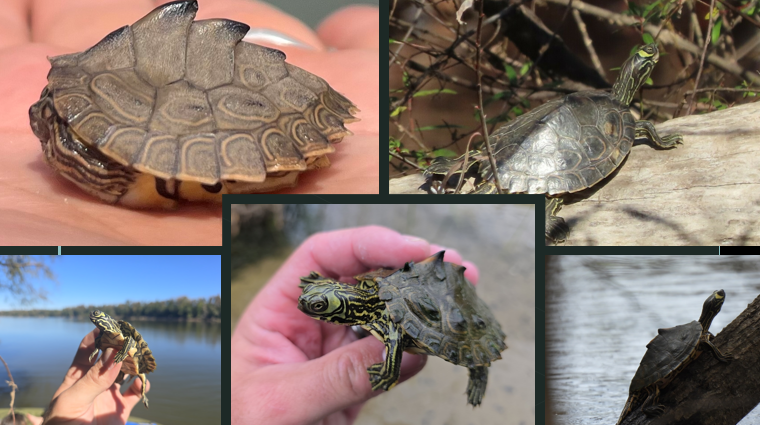
Pseudemys floridana

oval and slightly serrate carapace, reddish plastron that may have dark markings, light vertical bar can be present on second pleural scute, underside of marginals have dark rings, iris has transverse dark bar, found in Mobile Bay drainage, Pascagoula River, Back Bay of Biloxi watershed, inhabits fresh to moderately brackish water. fond of basking, AL’s state reptile, prefers aquatic vegetation. “buck teeth”
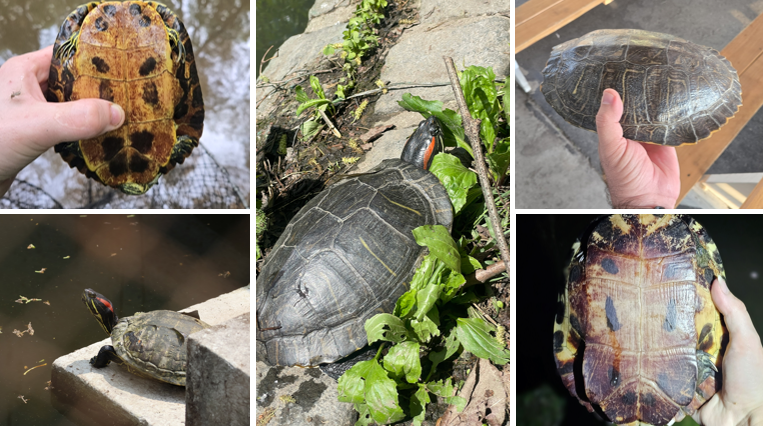
Pseudemys alabamensis

two subspecies, carapace round to oval, iris with transverse bar, upper jaw has terminal notch, large plastron with dark spots or smudges on each scute, iris with transverse dark spots, herbivorous and carnivorous, inhabit lakes, swamps, ponds, sloughs and shallow streams
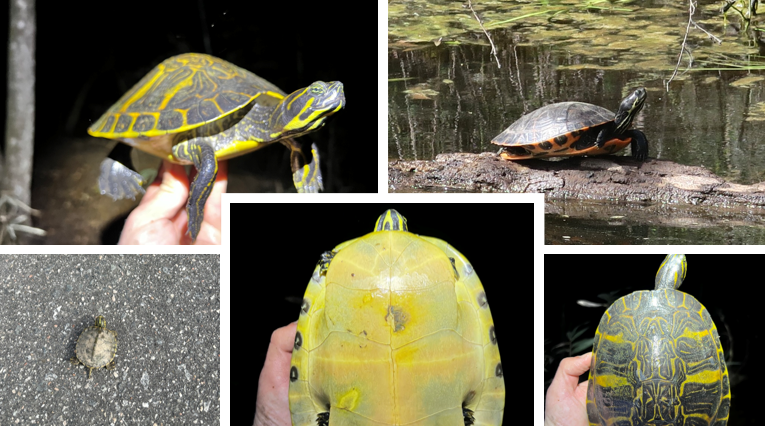
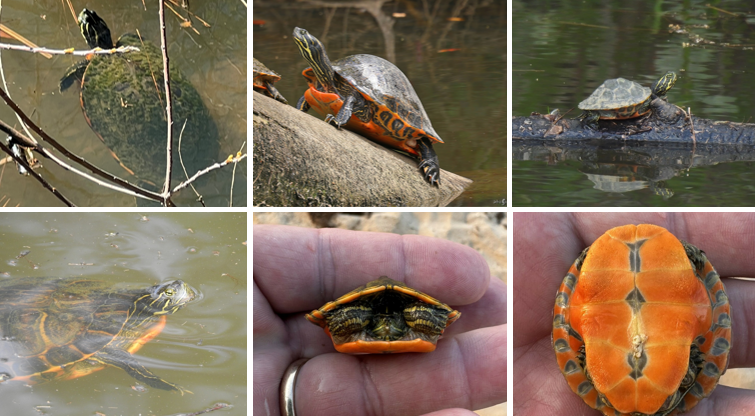
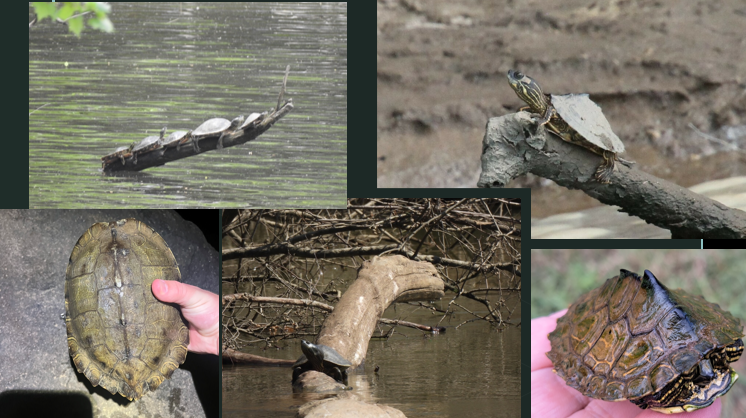
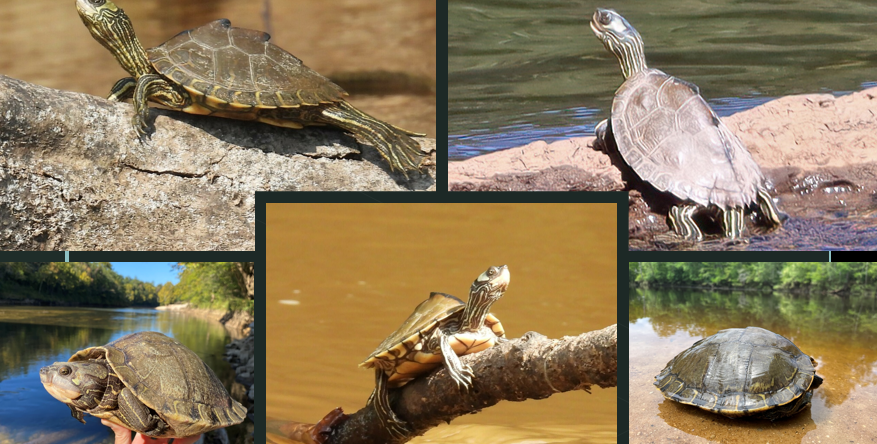
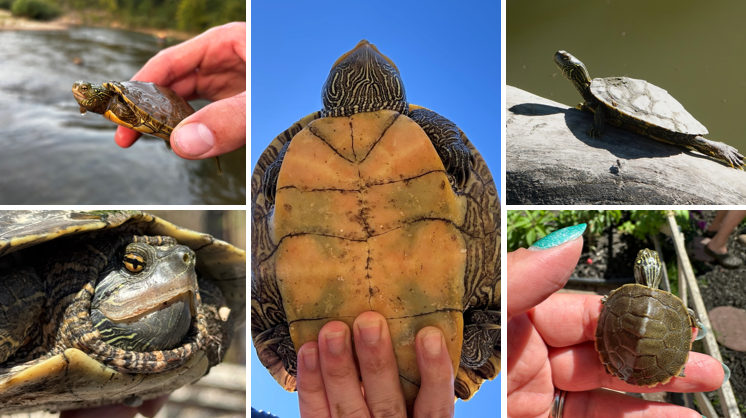
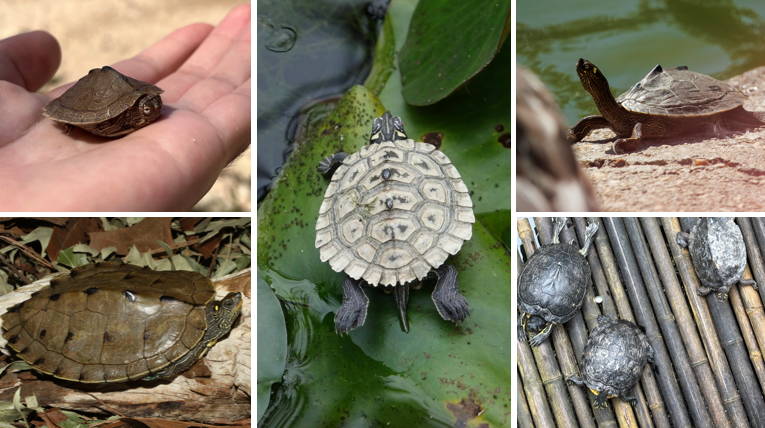
Trachemys scripta

carapace has medium keel, accentuated by spines on some vertebrals, pleural scutes have yellowish c-shaped markings, upper marginals are squarish, plastron is yellow with dark lines following the seams, green/yellow blotch behind eyes, U-shaped yellow bar under chin. exclusively in streams with lots of mollusks, fond of basking. carnivorous, adult males and juveniles are insectivorous, adult females almost exclusively eat mollusks and snails.
Graptemys barbouri

carapce has medium keel accentuated by spines, longitudinal black stripe on carapace, pleurals are unmarked or with light rectangular markings that follow the seams, yellow concentric markings on upper surface of marginals, wide concentric black markings on underside of marginals. yellow/green blotch between eyes, and behind eyes, v-shaped pattern on chin. Found in Mobile Bay drainage, inhabit creeks and rivers with lots of mollusks for females to eat, males and juveniles eat insects and arthropods. temp sex determination, males=cooler nest
Graptemys pulchra

carapace with median keel accentuated by spines, carapace has longitudinal black stripe, pleural scutes have wide yellow rings and light reticular markings following seams. yellow bar markings on upper surface of marginals, dark smudge marks on posterior marginals. plastral markings limited to dark marks following seams. blotches between and behind eyes, oval spots on head aligned to anterior paramedial stripes, v-shaped mark on chin. Found in Yellow, Conecuh, and Choctawatchee-Pea drainages, females show great fidelity to their basking logs. females can store sperm to use later for fertilization
Graptemys ernsti

week middorsal keel along vertebrals, carapace is weakly serrated on posterior border, pattern of circular, semicircular and reticulate yellow/orange on carapace. Plastron yellow with dark markings on seams. undersurface of marginals have concentric circular or semicircular dark markings at seams, unattached yellow spot behind eyes. Found in Tennessee River system, and Black Warrior, Cahaba and Coosa Rivers above fall line. fond of basking, inhabits streams bordered by forest, temp sex determination, males=cooler.
Graptemys geographica

carapace has a median keel accentuated by prominent knobs or blunt spines on the vertebrals, serrate carapace on posterior end, circles or semicirculars on the pleurals, undersurface of marginals have concentric dark rings on seams, bridge has dark lines, rectangular to oval yellow spot behind eyes, three yellow spots on lower jaw. live in Tennessee River, lives in large impoundments and low-gradient streams. fond of basking, temp sex determination
Graptemys ouachitensis
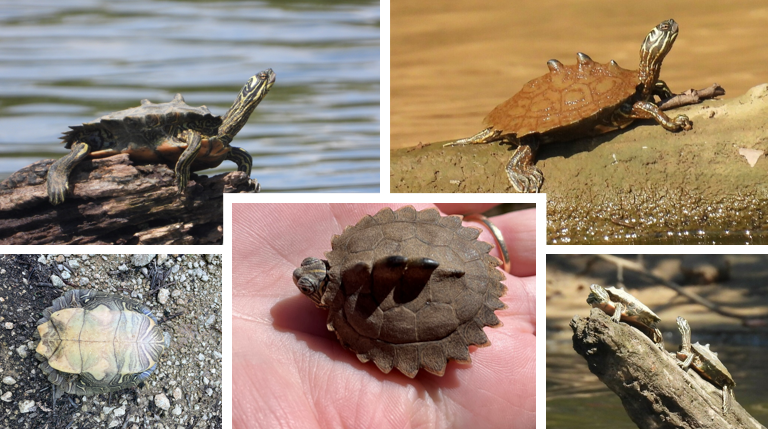

restricted to Alabama and Tombigbee Rivers, knob-like projections on the vertebrals, serrate carapace on posterior end, pleurals have yellow or white circles, side of vertebrals have light reticular markings. plastron is yellow with dark lines, concentric dark rings on underside of marginals, postocular yellowish crescent-shaped marks. South of fall line in Coosa, Tallapoosa, and Cahaba Rivers. Fond of basking,
Graptemys nigrinoda
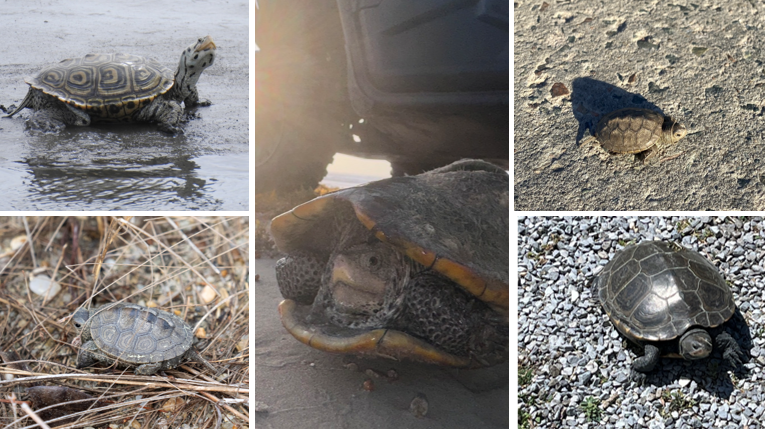

oval shell with sides that are nearly parallel, deep furrows between scutes of carapace, weak keels on carapace, spots on plastron and skin. Inhabit wetlands of the Gulf Coast, restricted to salt marshes and estuarine habitats, temp sex determination.
Malaclemys Terrapin
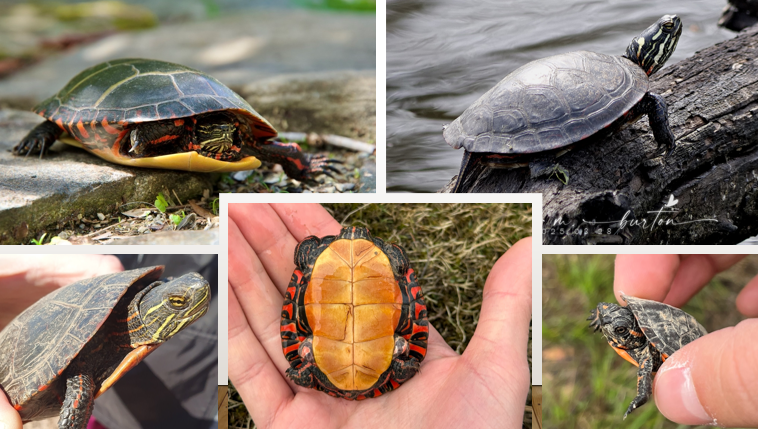

lives in lakes, ponds, sloughs, oxbows with mud/silt bottoms and aquatic vegetation, eats mainly arthropods, mollusks, vegetation. burrows into muddy bottoms of wetlands during winter, thin yellow bands between vertebral scutes, yellow spots behind eye,
Chrysemys picta

lakes, ponds, oxbows, slughs with mud/silt bottoms and abundant aquatic vegetation, eat arthropods, mollusks, aquatic vegetation, burrow in the mud in cold weather, red, orange, or yellow median stripe on dorsal, yellow stripe behind each eye,
Chrysemys dorsalis
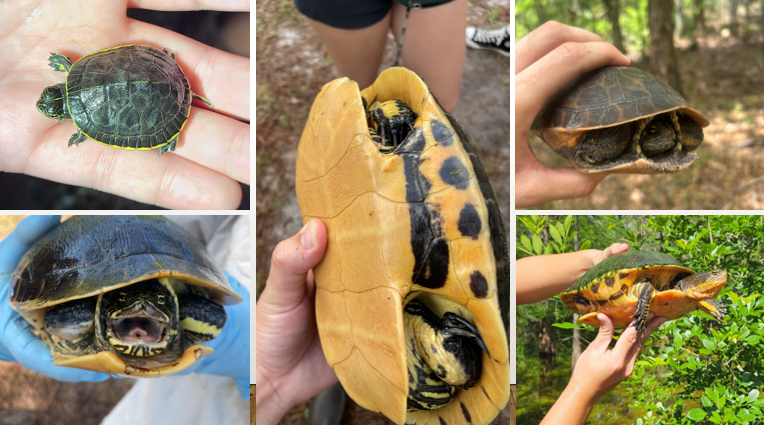

shallow, weedy ponds, swamps, and burrow pits w/ standing water, not big swimmers. suction feeders, aquatic inverts, females mostly crayfish, males and juveniles mostly dragonfly larvae. oval shaped carapace, shell rimmed w/ yellow, posterior surface of thighs w/ vertical yellow stripes
Deirochelys reticularia
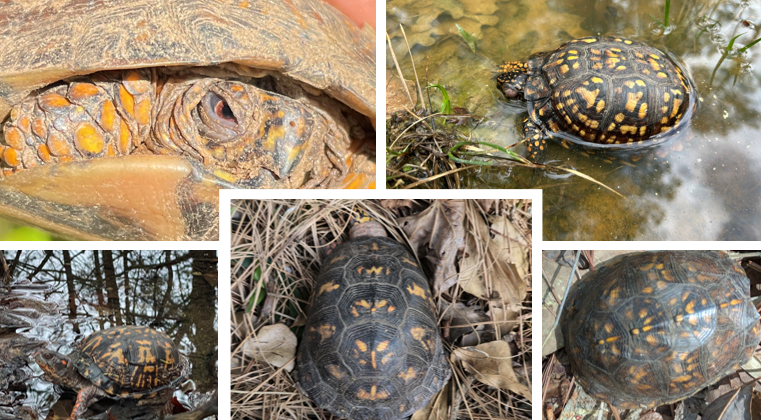

yellow blotches on shell kinda look like little handprints, males have bright red eye, females have brown eye, yellow stripe from head to tail on back of shell. 4 toes on hind feet, temp sex determination.
Terrapean carolina
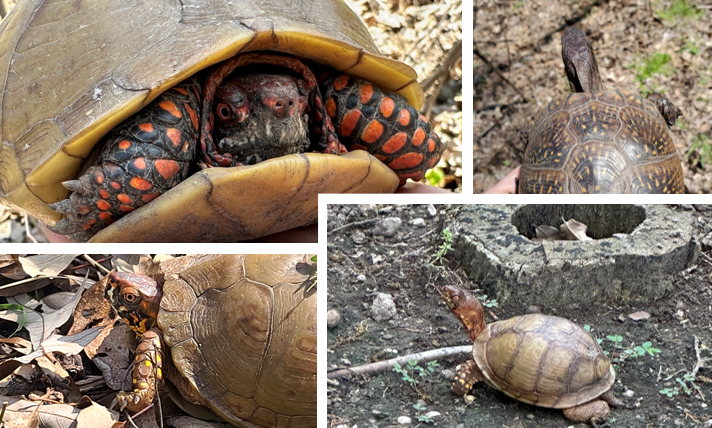

very bulbous shell, three toes on hind feet, males often have red, yellow, or orange faces
Terrapean carolina triunguis
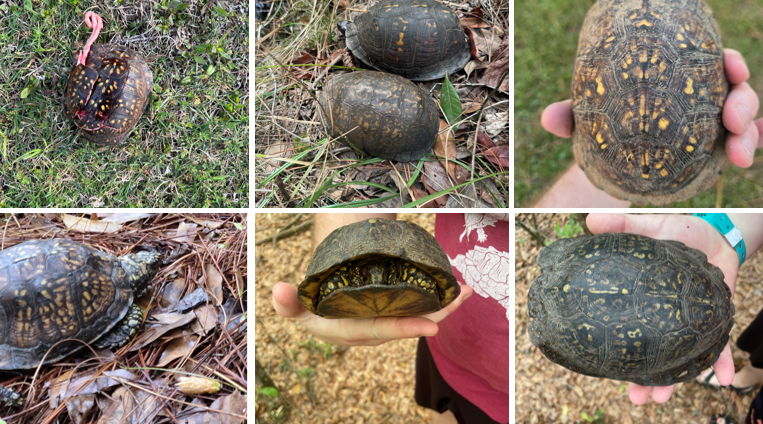

dark shell with little to no blotching, four toes on each foot, found in gulf coast, males w/ red or yellow eyes, females have dark colored eyes,
Terrapean carolina major