Ch7 Pt.2: Linkage & Chromosome mapping (Oct 6th)
1/11
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Part II. What is linkage and how can we test for it?
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
12 Terms
Define Linkage
what is it the result of?
Linkage: The non-random correlation of alleles of different loci in a population
-Most often the result of physical connection between loci on a single molecule of DNA.
Define Linkage Group
a set of alleles that are nonrandomly correlated and thus inherited together with greater probability than as if they were
independently assorting
what does a sufficiently inclusive linkage group constitute
a chromosome
Define
Crossing over
chiasma
recombination
Crossing over: reciprocal exchange of chromatid segments
during prophase I of Meiosis
Chiasma: site of crossing over
Recombination: the result of crossing over
what does recombination disrupt
linkage
what is sturtevants insight
probability of recombination is proportional to physical distance between two genes
Detecting linkage through a test-cross and chi-square test
1. Parental: how
provide the example
what is the dihybrid cross genotype
Cross two pure breeding strains (one for each mutant)
-Black bodied mutant: autosomal recessive bb
(wild-type here called “grey”)
-Vestigial wing mutant: autosomal recessive yy
bbYY x BByy
Describe Linkage vs Unlinked
in Po generation to F1 generation
Linked: Po generation has genes on same chromosome, so F1 generation will have genes on same chromosome as well
Unlinked: Po generation has genes on different chromosomes, so F1 generation will have its genes on different chromosomes as well
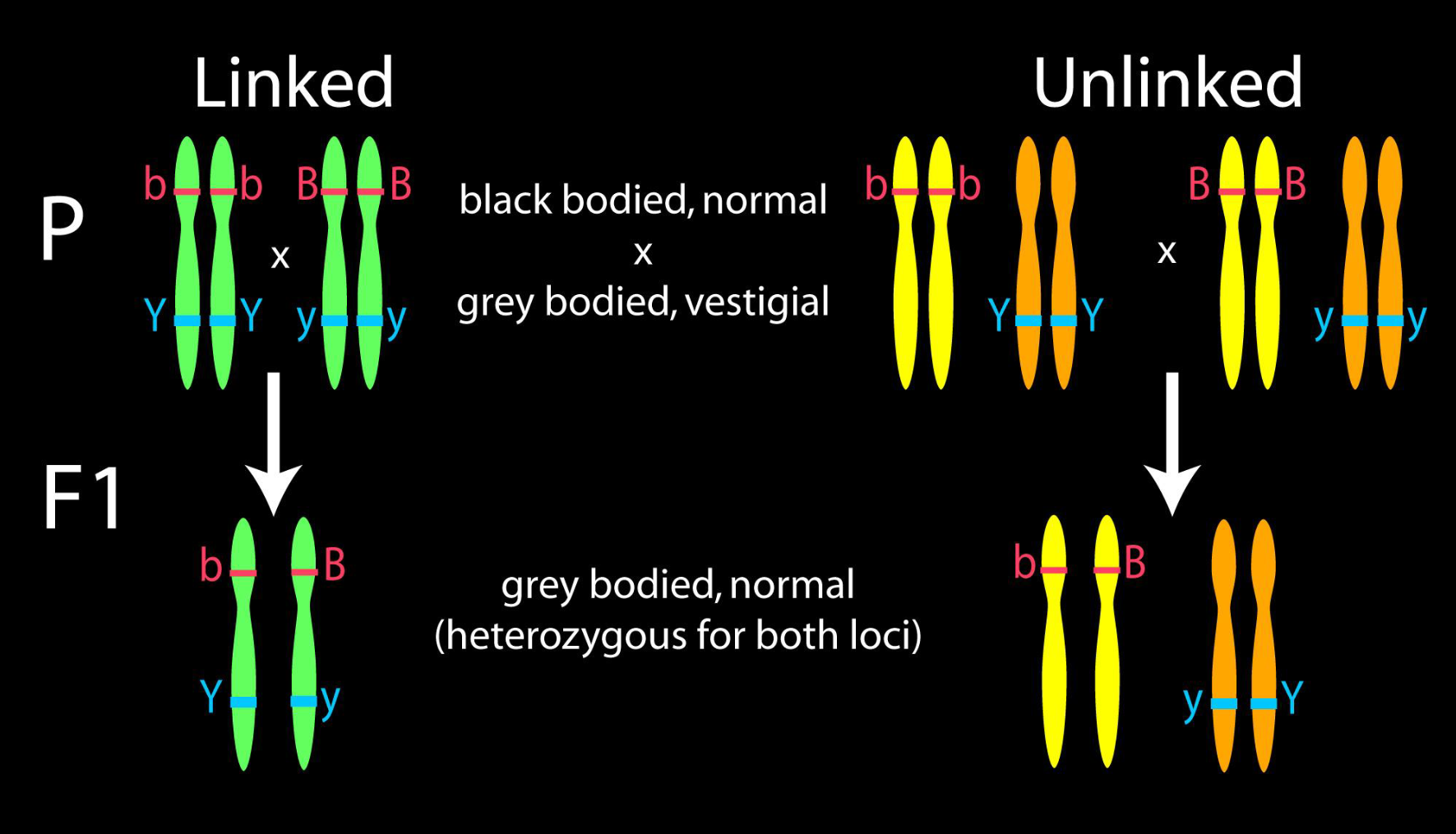
Detecting linkage through a test-cross and chi-square test
what do you cross together, for crossing over to not occur in what gender?
what does is the F2 generation, how does this help determine linked or unlinked?
2. Backcross female F1 (BbVv) with male double mutants
(bbvv). Crossing over does not occur in male Drosophila. In linked and Unlinked
If 50% to 50% ratio result: this is linked bc crossing occurs in same chromosome.
If 25% x4 ratio result: This is unlinked bc crossing over occurs in different chromosomes, parental and recombination is present here.
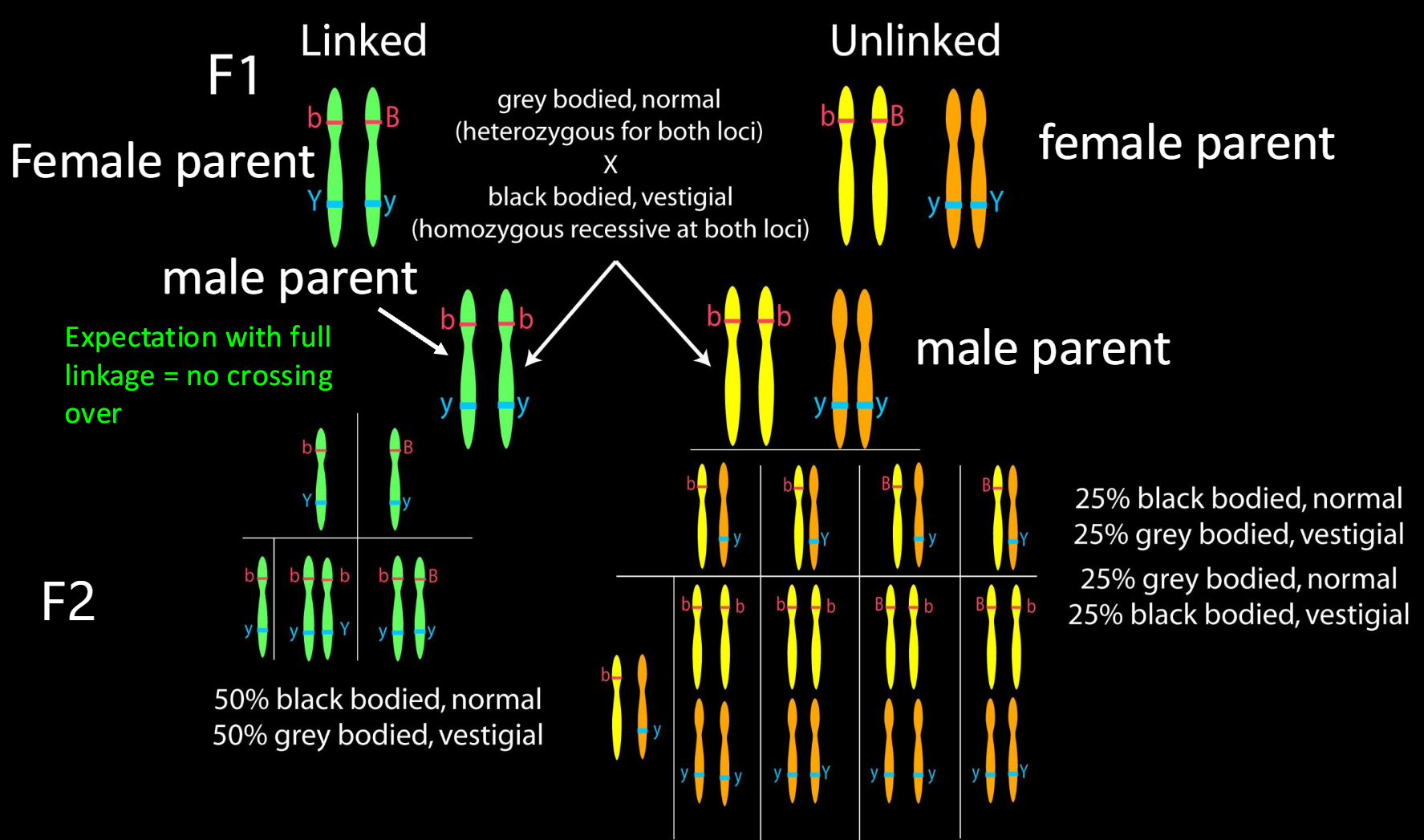
Detecting linkage through a test-cross and chi-square test
3. Expected outcome without linkage
When crossing unlinked female and unlinked male
Parental: 1 black normal: 1 grey vestigial
Recombinant: 1 grey normal: 1 black vestigial
=50% parental and 50% recombinant in F2 generation or 25% x4 total
Why use a testcross rather than a dihybrid cross to
develop null expectation?
what can u now do?
1. Limits recombination to a single parent
2. A 1:1 distribution provides a more powerful statistical test
than a 9:3:3:1 distribution
can now perform chi-square test
What percentage does recombinant not exceed and why?
Does not exceed 50%, bc it is independent assortment at that point