Transport in Animals
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
43 Terms
Oxygenated blood
exits from the lungs through the pulmonary veins to the left atrium to mitral valve to left ventricle to aortic valve to aorta to general circulation
Deoxygenated
blood carrying little or oxygen
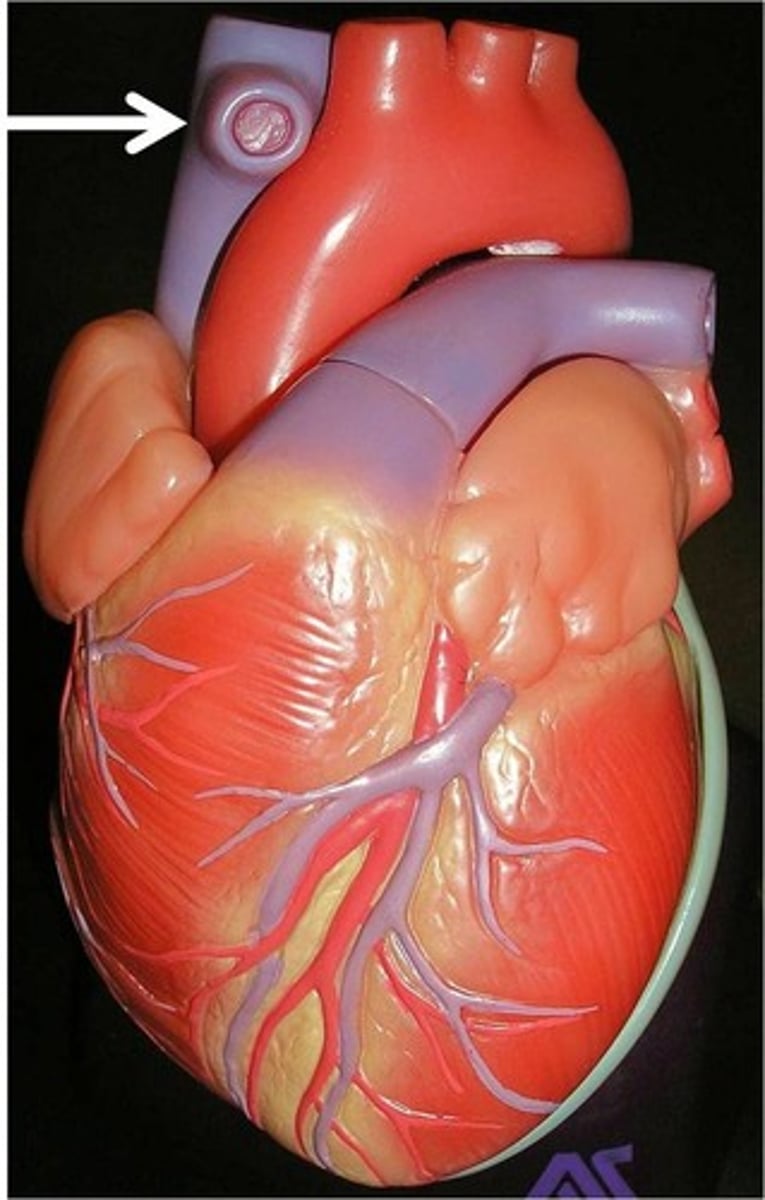
Double circulatory system
a transport system in which blood travels twice through the heart for each complete circulation of the body
Pulmonary system
Directs blood flow from the right ventricle of heart to the lungs where it is oxygenated and returns to left atrium
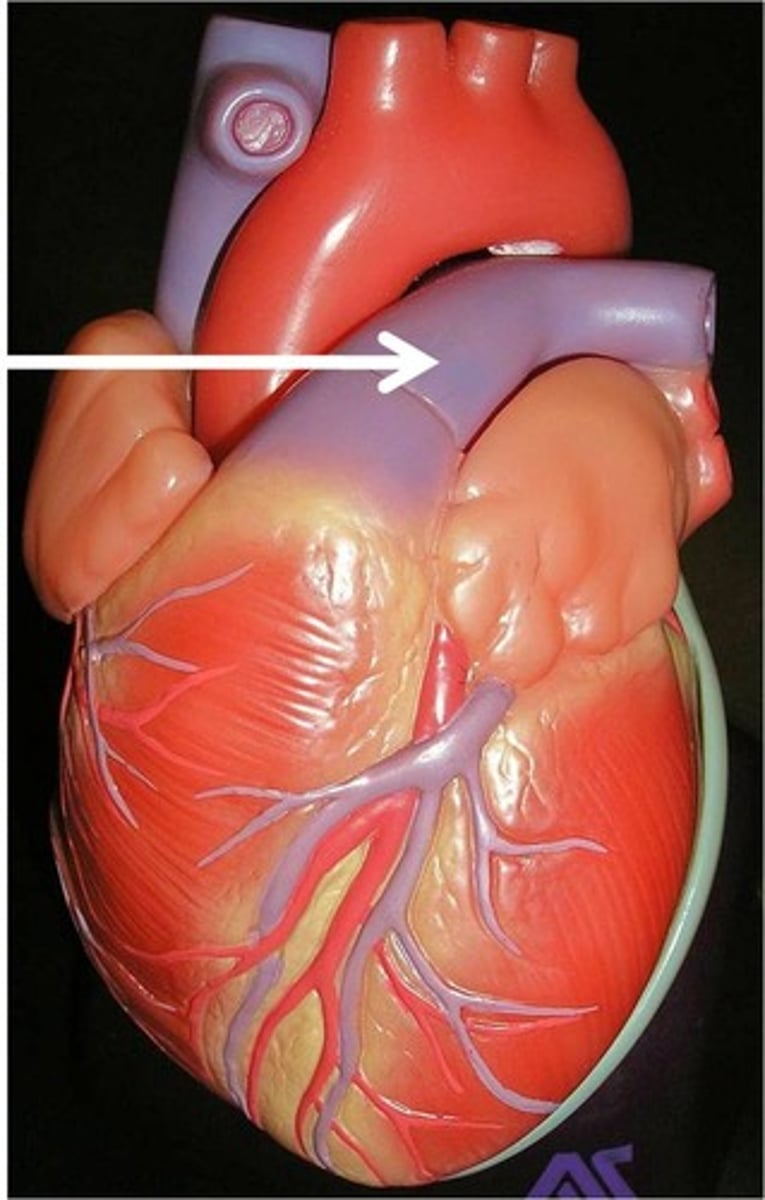
Systemic system
Larger than pulmonary system. Consists of arteries arterioles, capillaries, venules and veins.
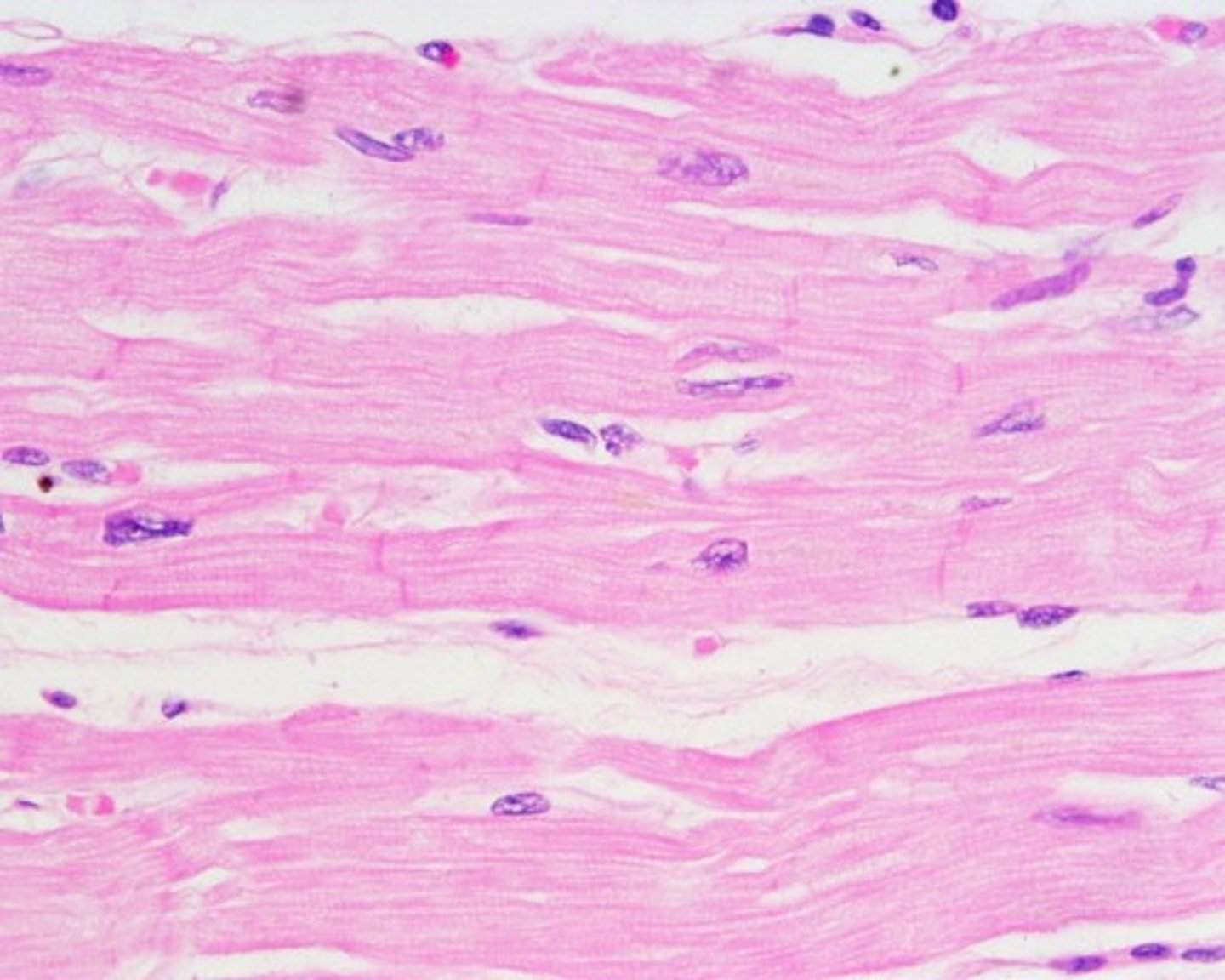
Cardiac muscle
Muscle tissue found only in the heart
Left atria
receives blood returning to the heart from the pulmonary veins
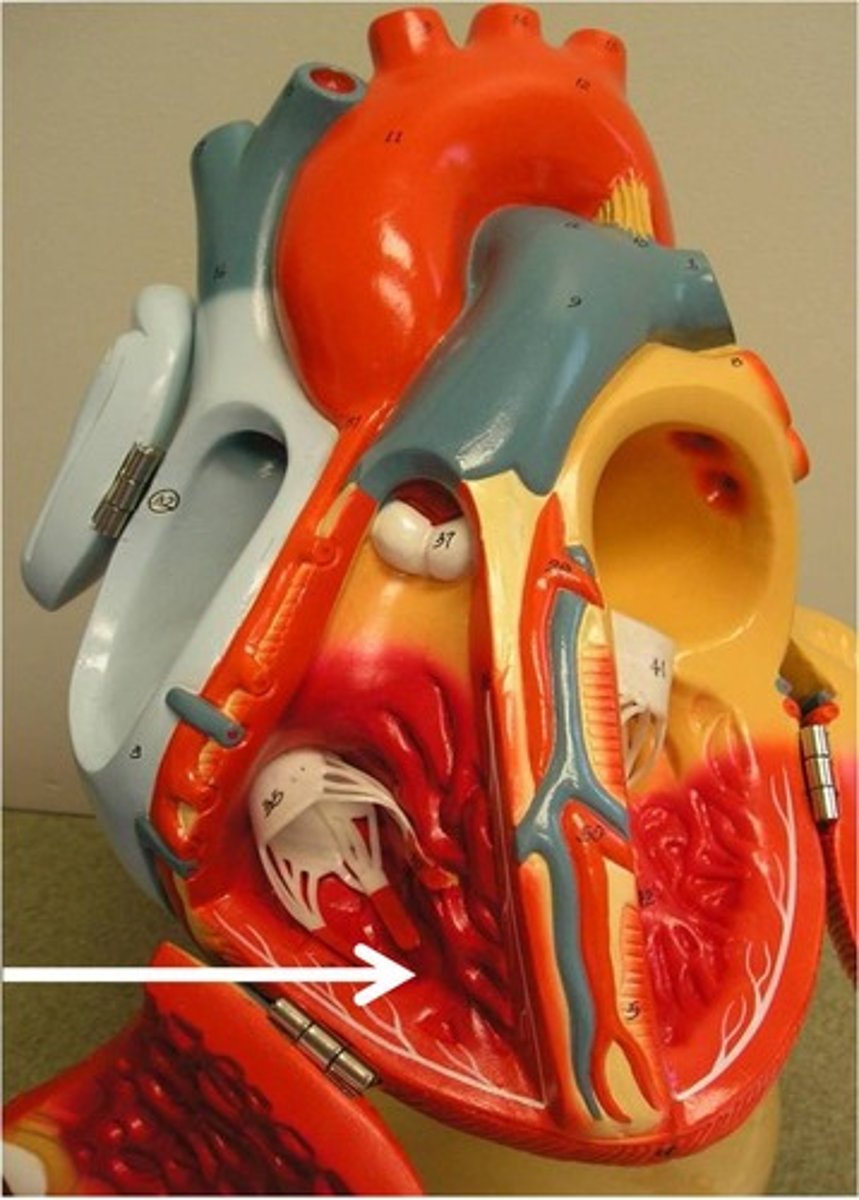
Left ventricle
the chamber of the heart that receives arterial blood from the left atrium and pumps it into the aorta
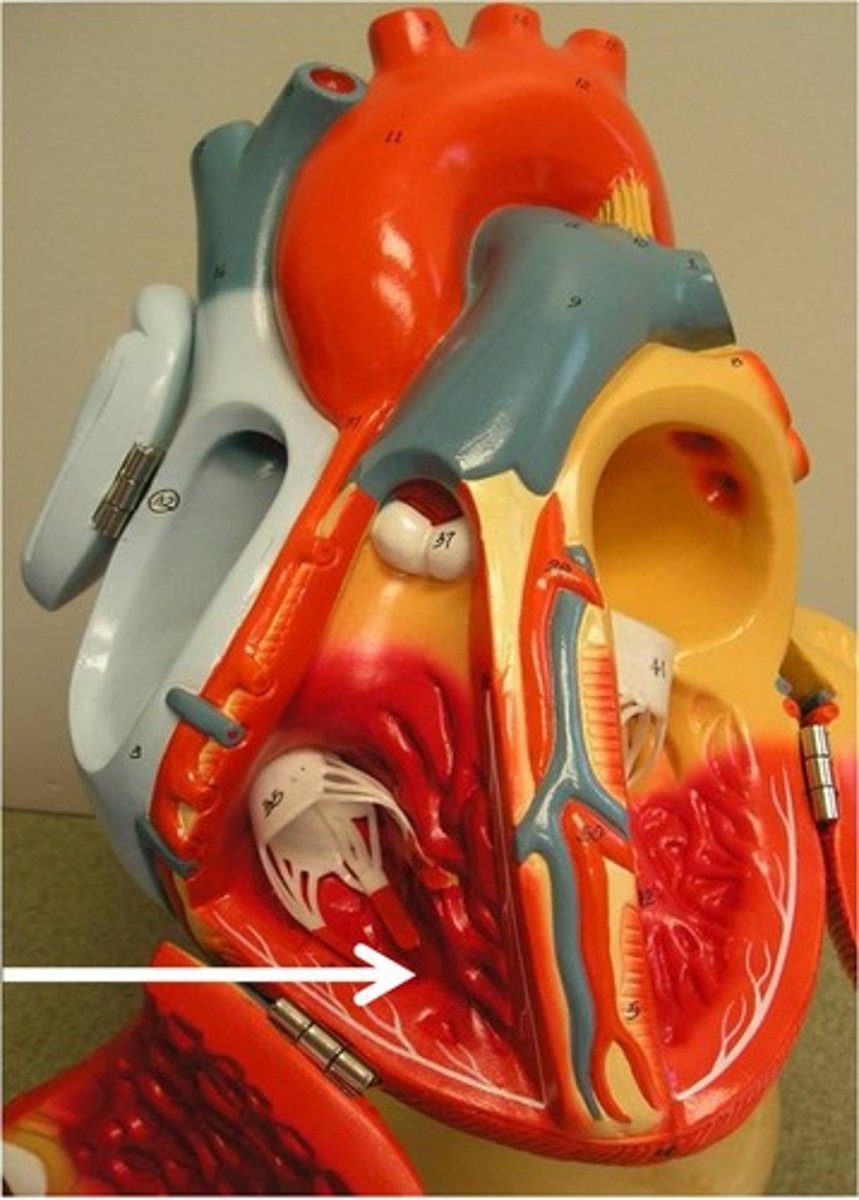
Right atria
recieves blood returning to heart
Right ventricle
the chamber of the heart that receives venous blood from the right atrium and pumps it into the pulmonary artery
Arteries
Blood vessels that carry blood away from the heart
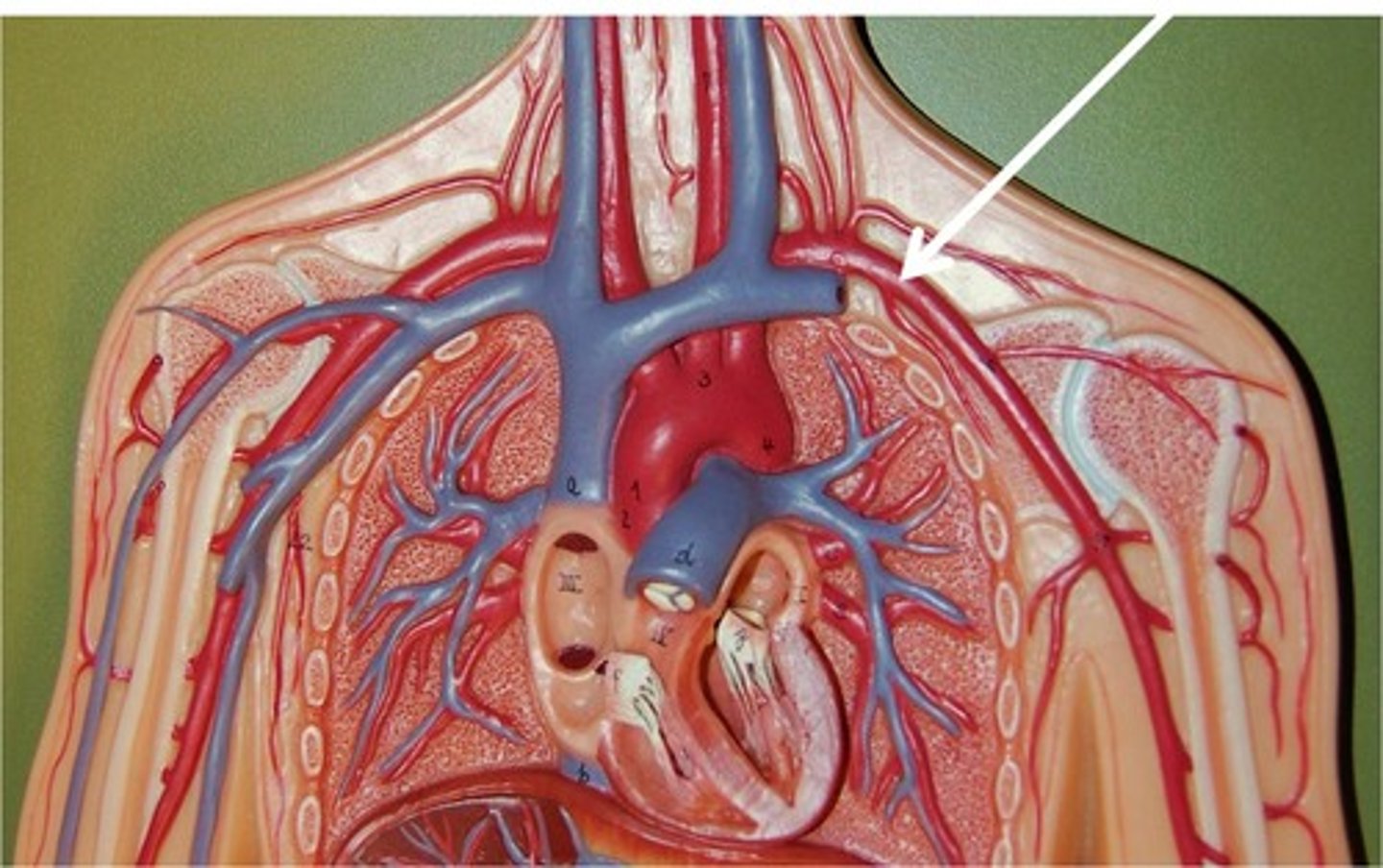
Veins
Blood vessels that carry blood back to the heart
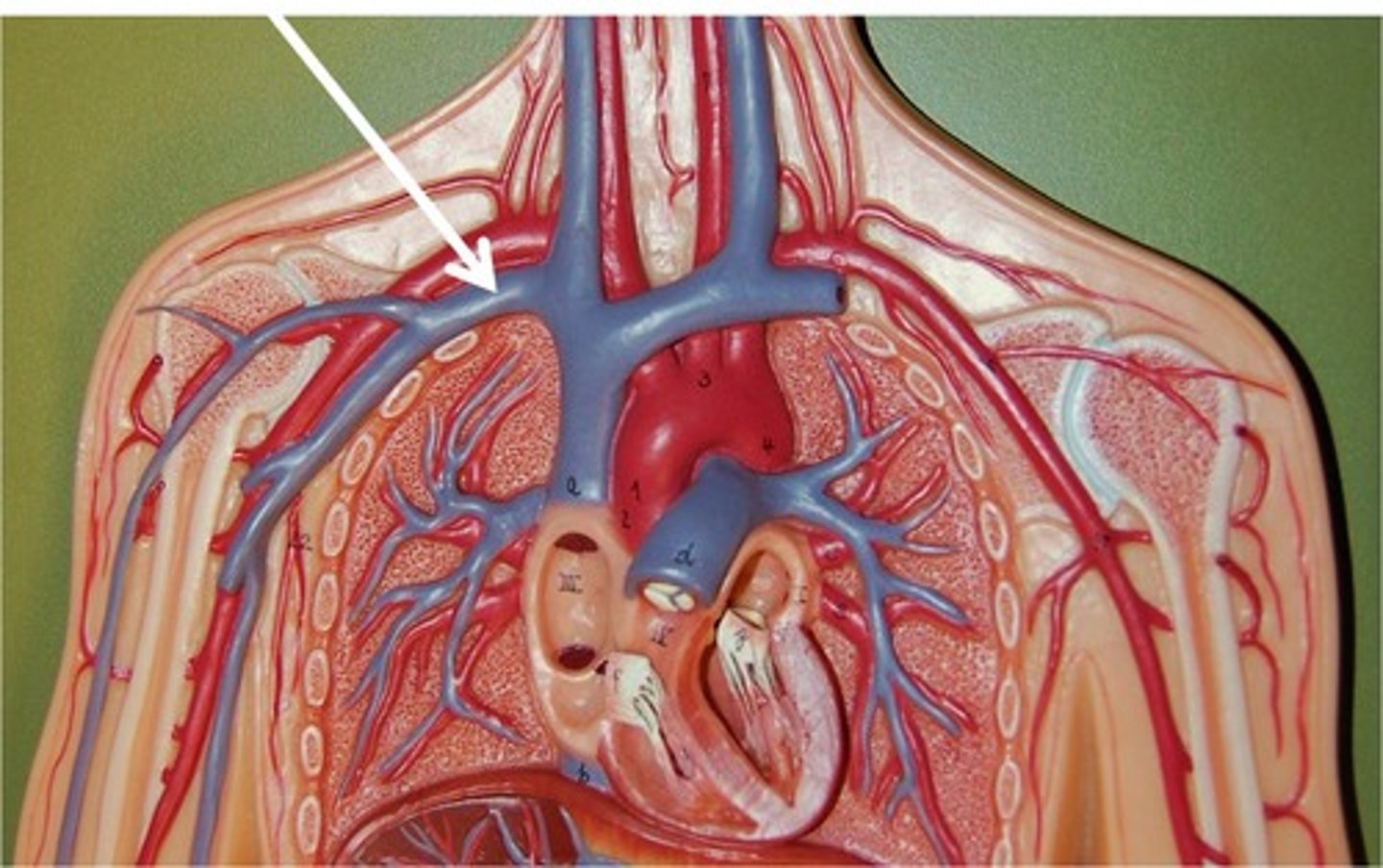
Capilaries
microscopic blood vessels convey between artiers and veins
Aorta
The largest artery in the body
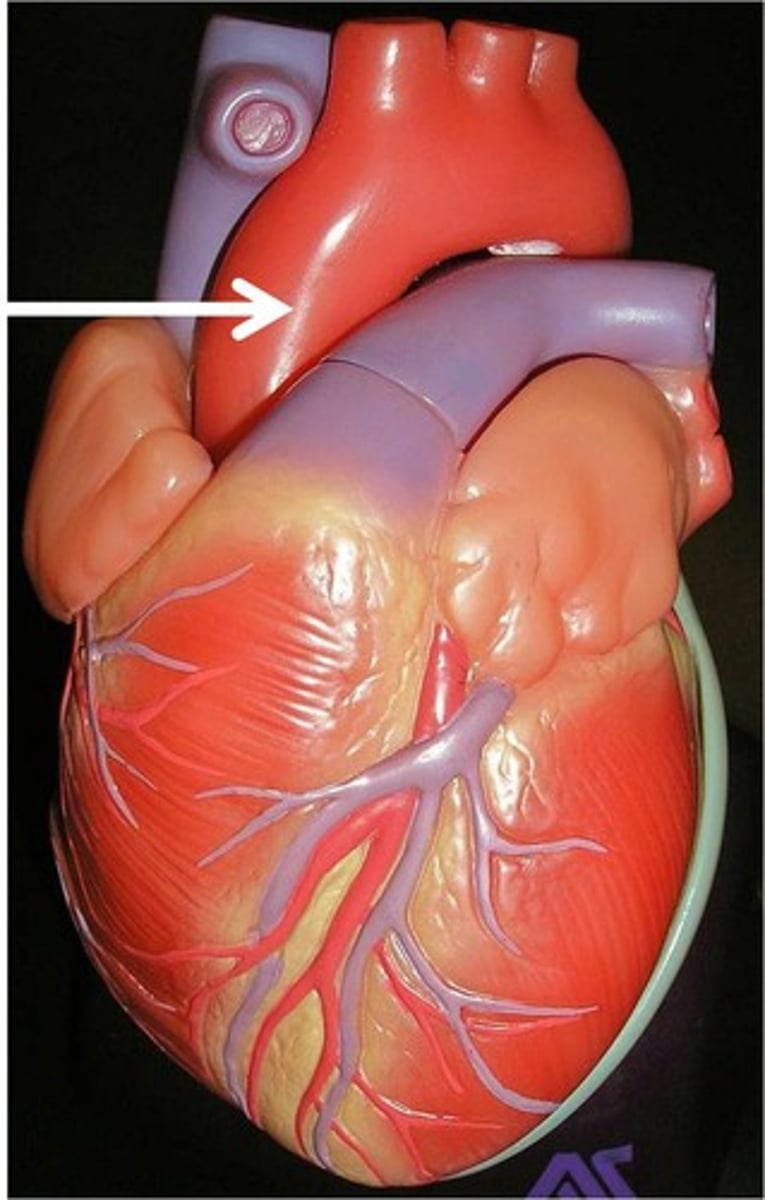
Vena Cava
One of two large vessels (superior and inferior) that return deoxygenated blood to the right atrium of the heart.
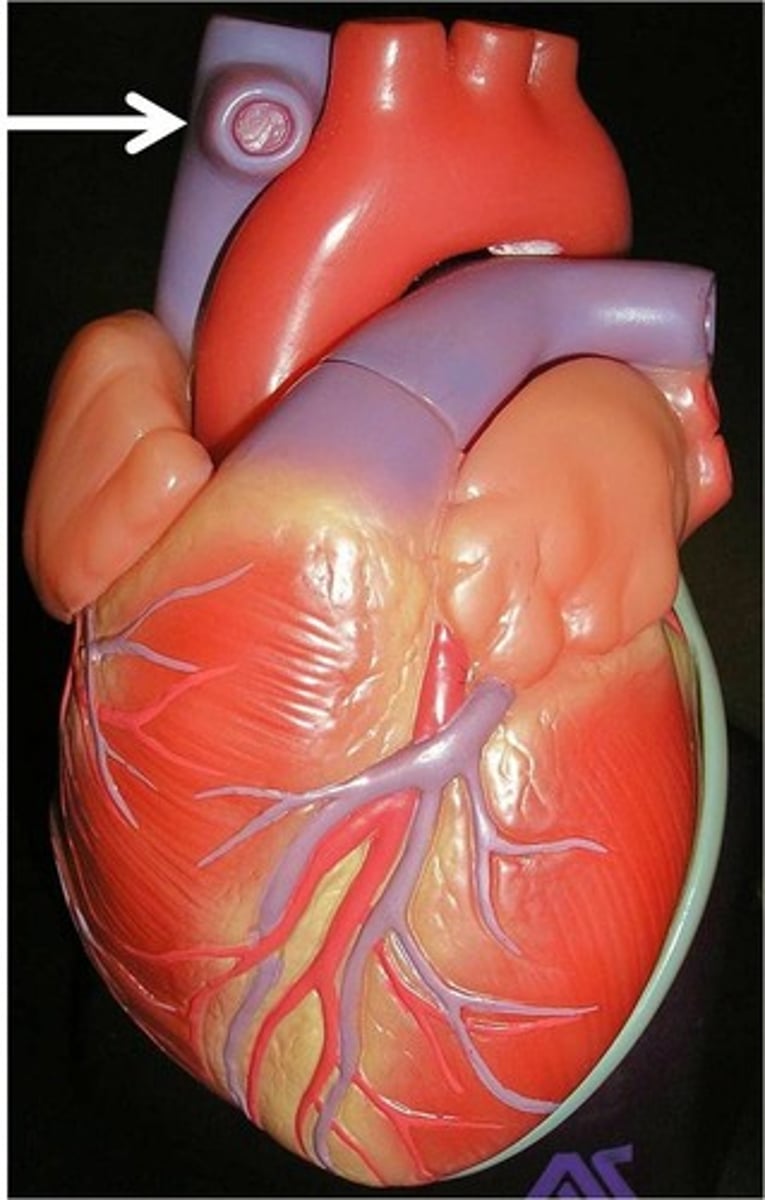
Pulmonary artery
carries deoxygenated blood from the right ventricle to the lungs.
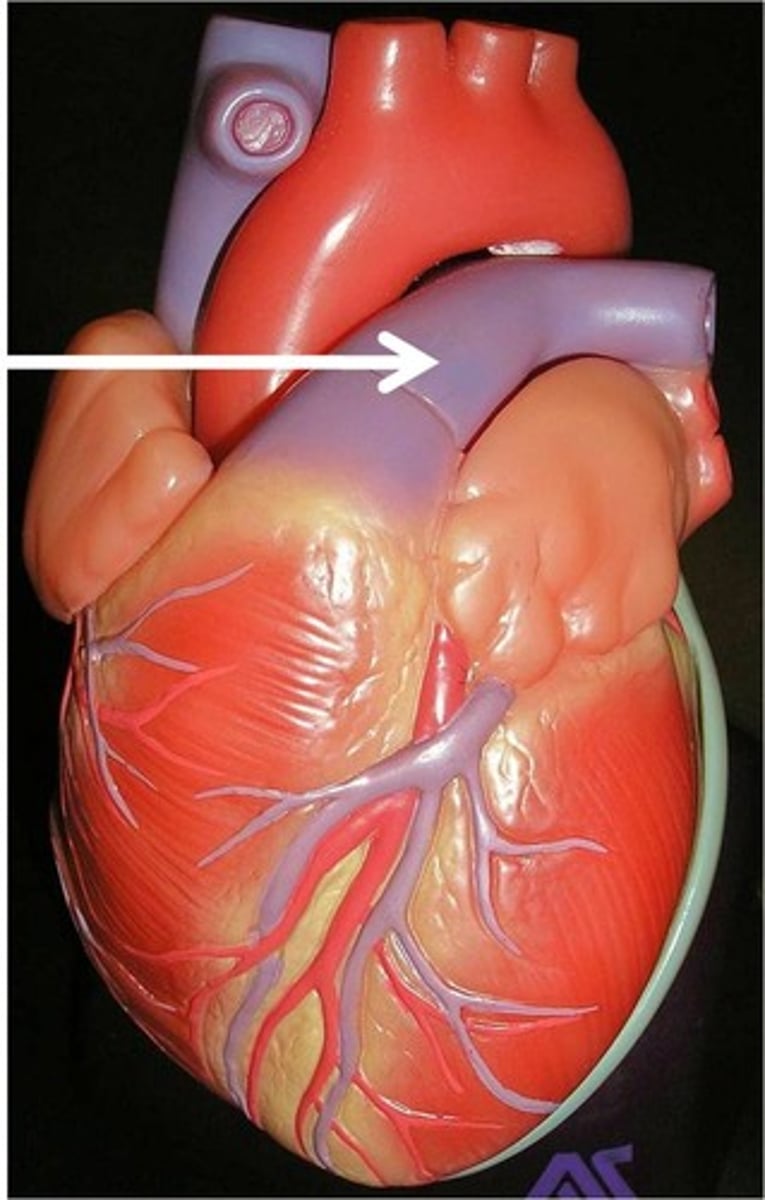
Pulmonary vein
Deliver oxygen rich blood from the lungs to the left atrium
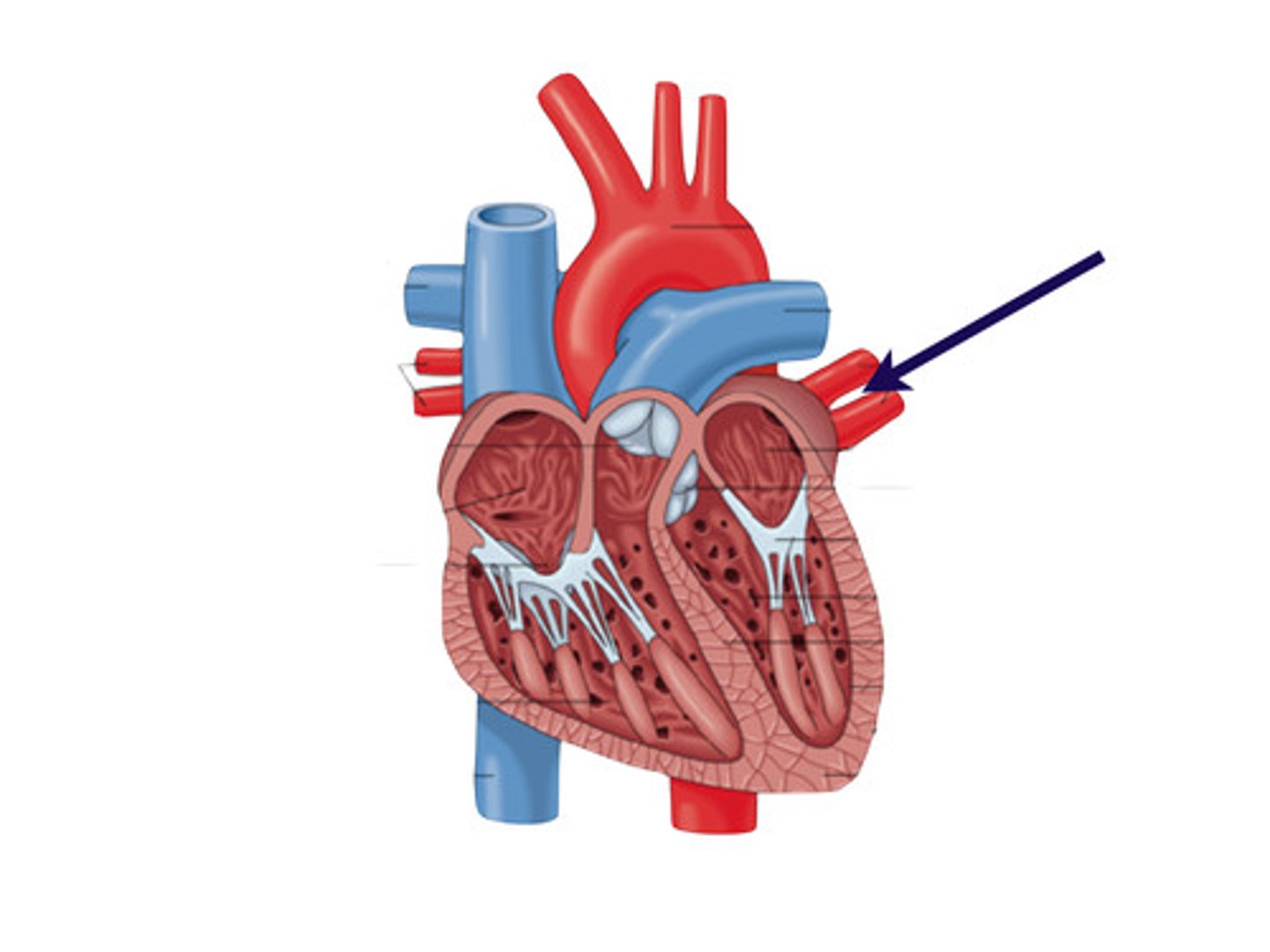
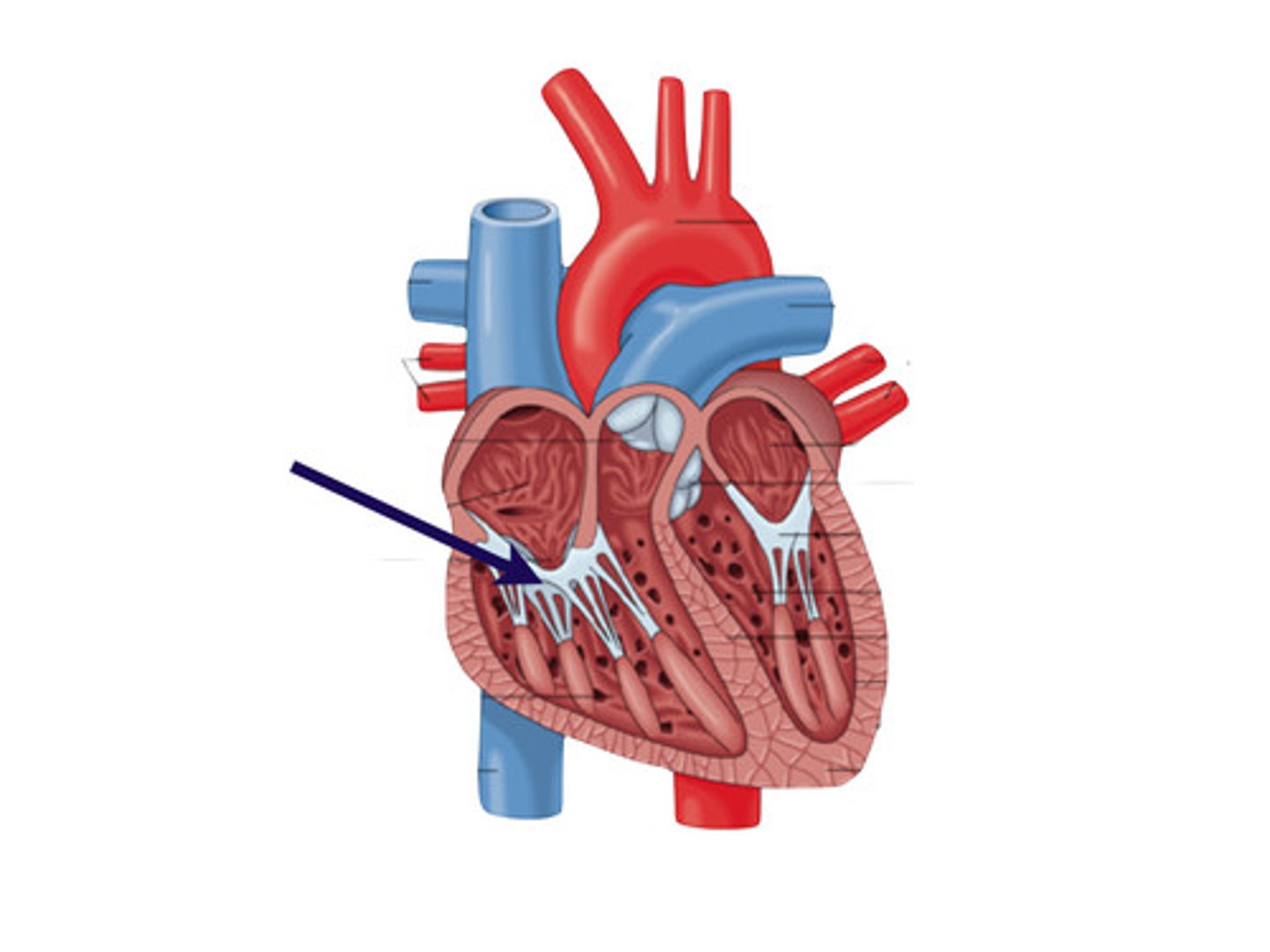
Coronary artery
blood vessel running diagonally down the ventral side of the heart from its upper left to lower right that supplies blood to the heart muscle; separates the two ventricles
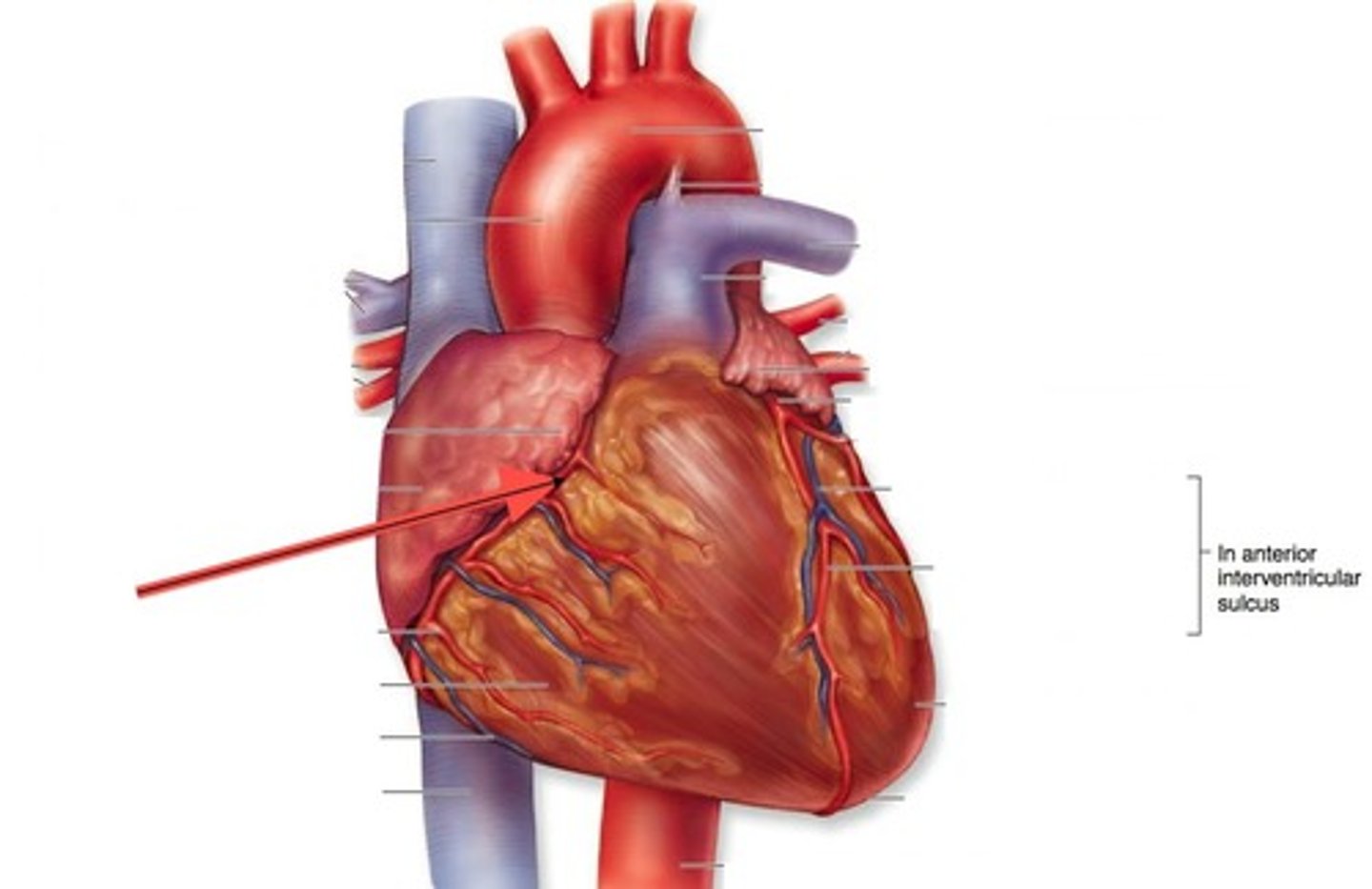
Septum
Divides the right and left chambers of the heart
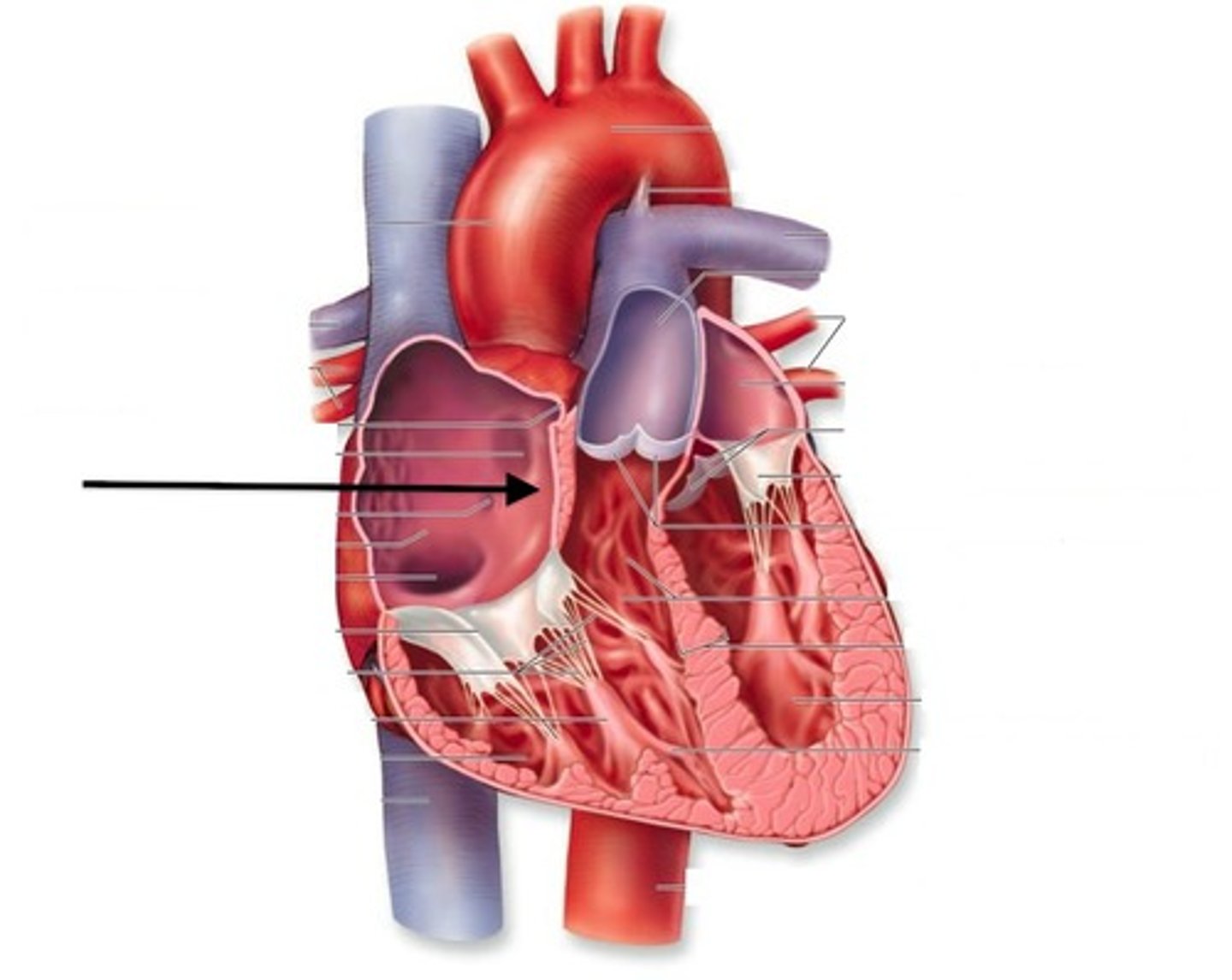
Mitral/bicuspid valve
A valve in the heart that guards the opening between the left atrium and the left ventricle that prevents the blood in the ventricle from returning to the atrium.
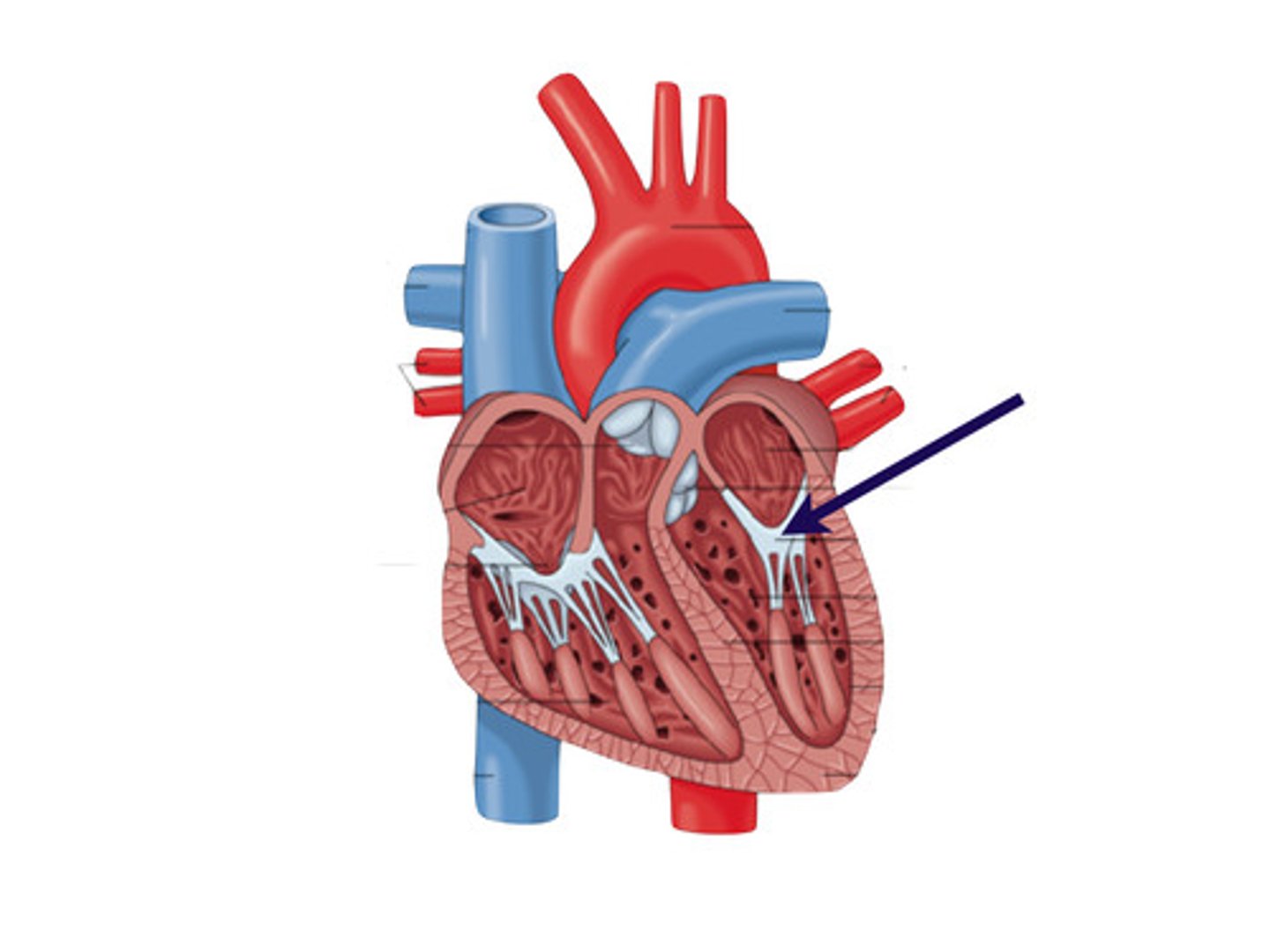
Tricuspid valve
A valve that is situated at the opening of the right atrium of the heart into the right ventricle and that resembles the mitral valve in structure but consists of three triangular membranous flaps.
Coronary Heart Disease (CHD)
the clogging of the vessels that nourish the heart muscle; the leading cause of death in many developed countries
Systole
The stage of the heart cycle in which the heart muscle contracts and the chambers pump blood.
Diastole
The stage of the heart cycle in which the heart muscle is relaxed, allowing the chambers to fill with blood.
Atrioventricular valves
Valves located between the atrial and ventricular chambers on each side of the heart, prevent backflow into the atria when the ventricles are contracting.
Platelets
fragments of blood cells that are involved in clotting
Plasma
Fluid portion of blood that transports many materials like hormones, amino acids and most of the carbon dioxide waste.
Renal artery and vein
vessels that supply blood to and from the kidneys
Red blood cells
Blood cells that carry oxygen from the lungs to the body cells. Concave discs that contain hemoglobin
White blood cells
Blood cells that perform the function of destroying disease-causing microorganisms and infectious diseases (pathogens)
Phagocytes
A type of cell within the body capable of engulfing and absorbing bacteria and other small cells and particles.
Pathogens
A virus, bacterium, prion, fungus, viroid, parasite or anything that causes disease in its host.
Fibrin
A fibrous, non-globular protein involved in the clotting of blood. It is formed by the action of the protease thrombin on fibrinogen which causes the latter to polymerize.
Fibrinogen
A soluble protein present in blood plasma.
Tissue fluid (Interstitial fluid)
A solution that bathes and surrounds the tissue cells of multi-cellular animals. It is found in the interstices-the spaces between cells (tissue spaces).
Lymph
A colourless fluid containing white blood cells, that bathes the tissues and drains through the lymphatic system into the bloodstream.
Lymph nodes
Oval shaped filters that cluster along the lymphatic vessels of the body, they function as a cleanser of lymph.
homeostasis
A constant internal state that is maintained in a changing environment by continually making adjustments to the internal and external body.
heart or pulse rate
the number of heartbeats or pulses felt in 1 minute
Lymphocytes
A type of white blood cell that make antibodies to fight off infections
Vaccines
dose of a disabled or destroyed pathogen used to stimulate a long-term immune defence against the pathogen. A weakened form of the virus is given to the person so their immune system can build up immunity to the virus.
Hormones
chemical messengers that are manufactured by the endocrine glands, travel through the bloodstream, and affect other tissues
Urea
waste product formed in cells, transmitted and filtered out of the blood by the kidneys