The History and Models of the Atom
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
Dalton's Model
Elements combine in fixed ratios to form compounds.
Rutherford's Gold Foil Experiment
Demonstrated the nucleus' existence in atoms.
Quantum-Mechanical Model
Describes electron locations as probability distributions.
Isotopes
Atoms of the same element with different neutrons.
Democritus
500 B.C.
Proposed the concept of indivisible atoms.
(he had no proof of showing his idea)
Thomson's Model
Introduced the plum pudding or chocolate chip cookie model
Bohr Model
Electrons orbit the nucleus in defined paths.
Atomic Symbol
One or two-letter representation of an element.
Hyphen Notation
Element name followed by mass number (e.g., C-12).
Nuclear Symbol
Notation showing element, mass number, and atomic number.
Cations
Positively charged ions from losing electrons.
Anions
Negatively charged ions from gaining electrons.
Electron Configuration
Distribution of electrons among atomic orbitals.
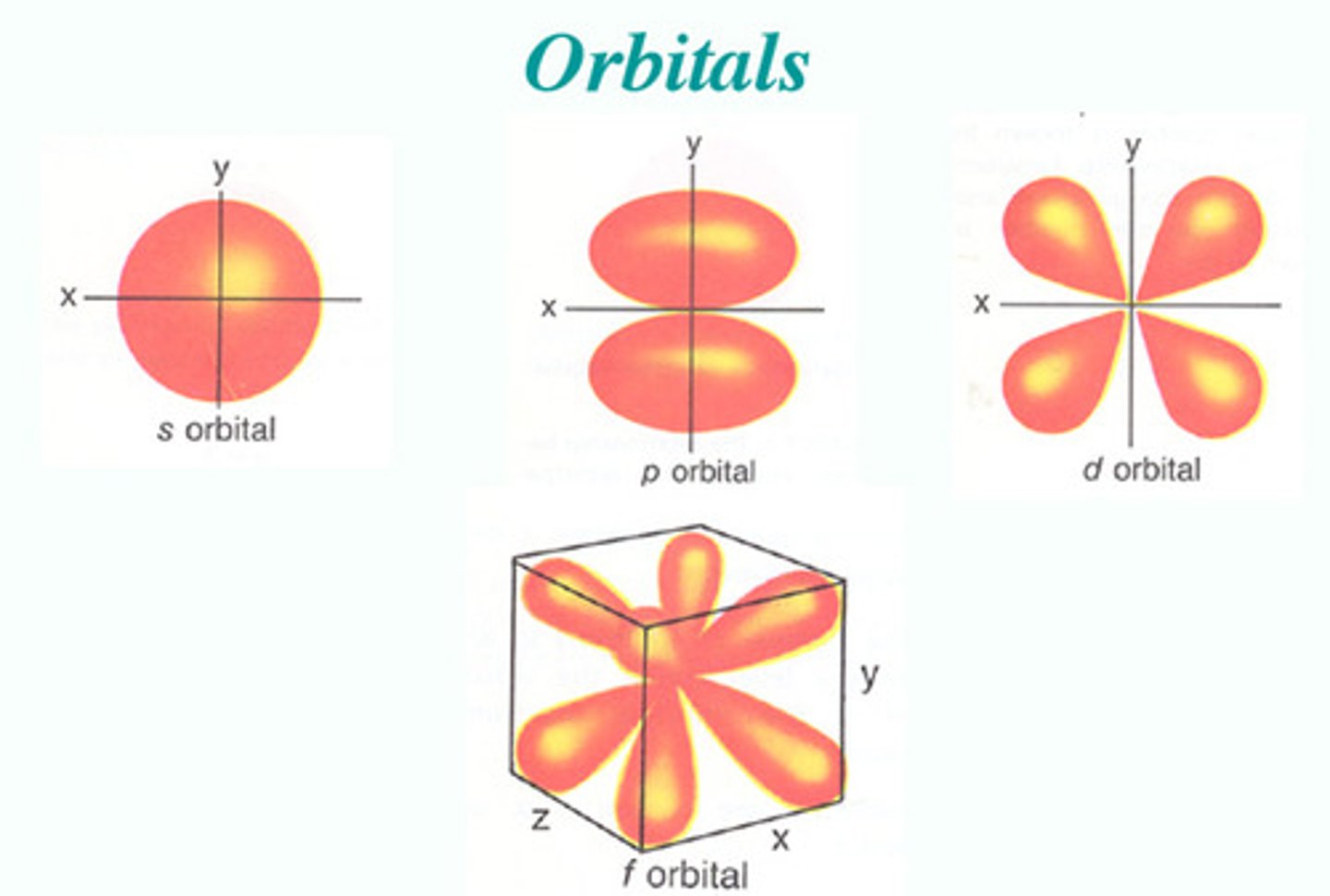
Orbital Shapes
Geometric representation of electron probability regions.
Orbital Sizes
Indicates energy levels of electrons in atoms.
Shorthand Electron Configuration
Abbreviated notation using noble gas symbols.
Unpaired Electrons
Electrons that occupy separate orbitals singly.
Ground State
Lowest energy configuration of electrons in an atom.
Excited State
Higher energy state when electrons absorb energy.
The is when the electrons are in the lowest energy orbitals
ground state
The is achieved when the electrons jump to higher-energy orbitals
excited state
Atomic Theory
Foundation explaining matter's composition and behavior.
Building Blocks
Conceptual representation of atomic structure and interactions.
Energy Emission
Unique light colors emitted during electron transitions.
Electron Jump
Movement of electrons between energy levels.
Periodic Table
Organizes elements based on atomic structure and properties.
How many different orbital shapes?
(four) s, d, f, p