(16.10.11) The Pineal Gland and Pancreas
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
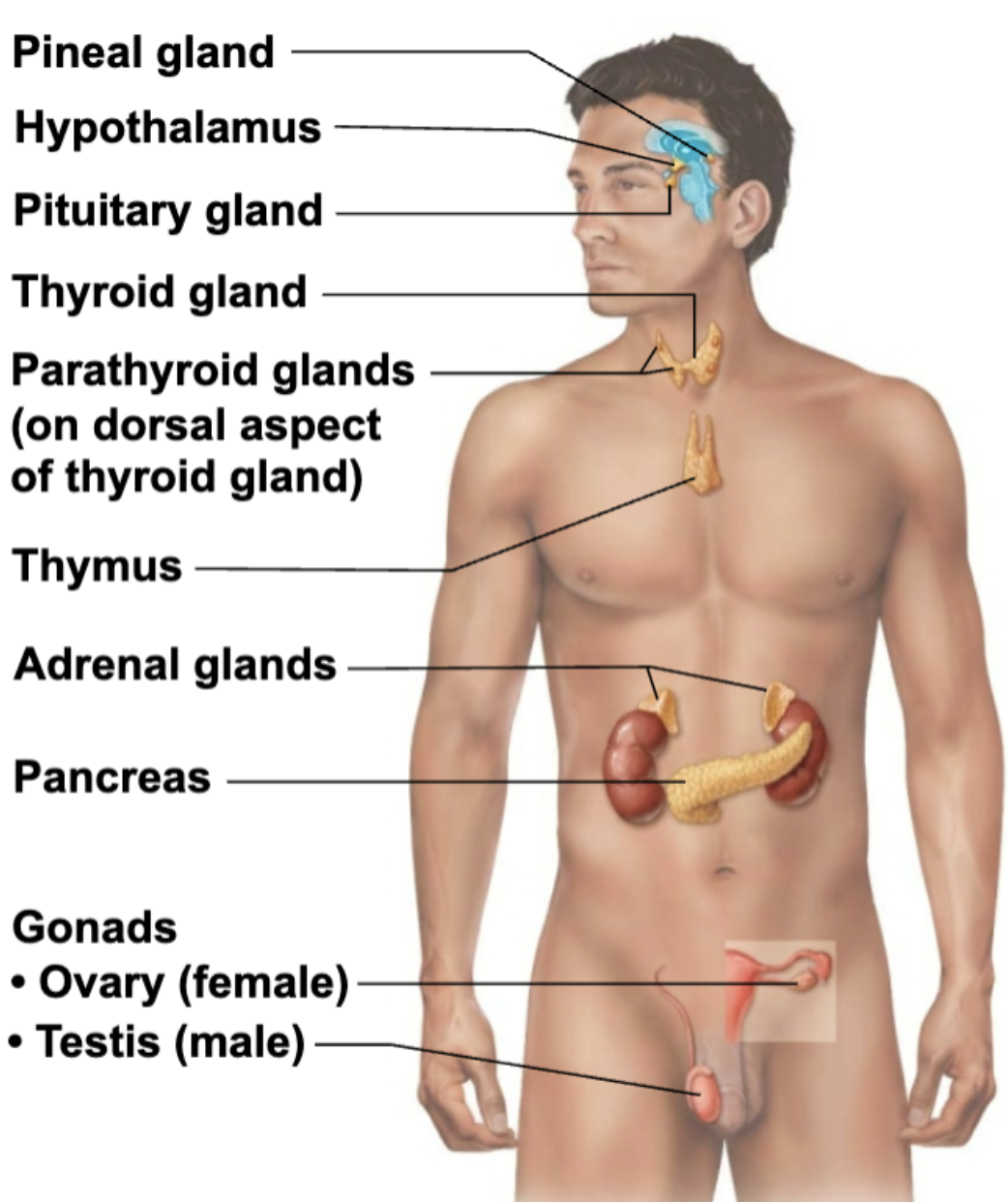
Describe Structure and Function of Pineal Gland
STRUCTURE
Small gland hanging from roof of third ventricle
FUNCTION
Pinealocytes secrete melatonin, derived from serotonin
Describe the importance of Melatonin
Timing of sexual maturation and puberty
Day/Night cycles
Physiological processes that show rhythmic variations
Production of antioxidant and detoxification molecules in cell
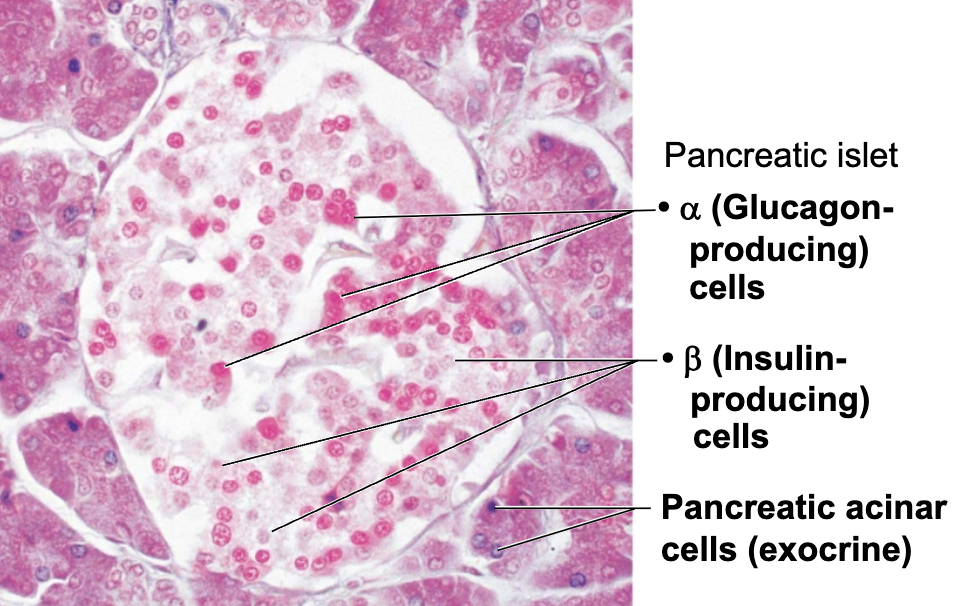
Describe Structure and Function of the Pancreas
STRUCTURE
Triangular gland located partially behind stomach
FUNCTION
Has both exocrine and endocrine cells
Acinar cells (exocrine)
Pancreatic islets (endocrine cells)
Role of Acinar cells
Exocrine cells
Produce enzyme-rich juice for digestion
Role of Pancreatic islets and list Hormones produced
FUNCTION
Contain endocrine cells
HORMONES
Alpha cells → produce glucagon (hyperglycemic hormone)
Beta cells → produce insulin (hypoglycemic hormone)
Explain Regulation of Release of Glucagon
STIMULATED by
Decreased BG levels
Rising amino acid levels
Sympathetic nervous system
INHIBITED by
Elevated BG levels
NEGATIVE FEEDBACK
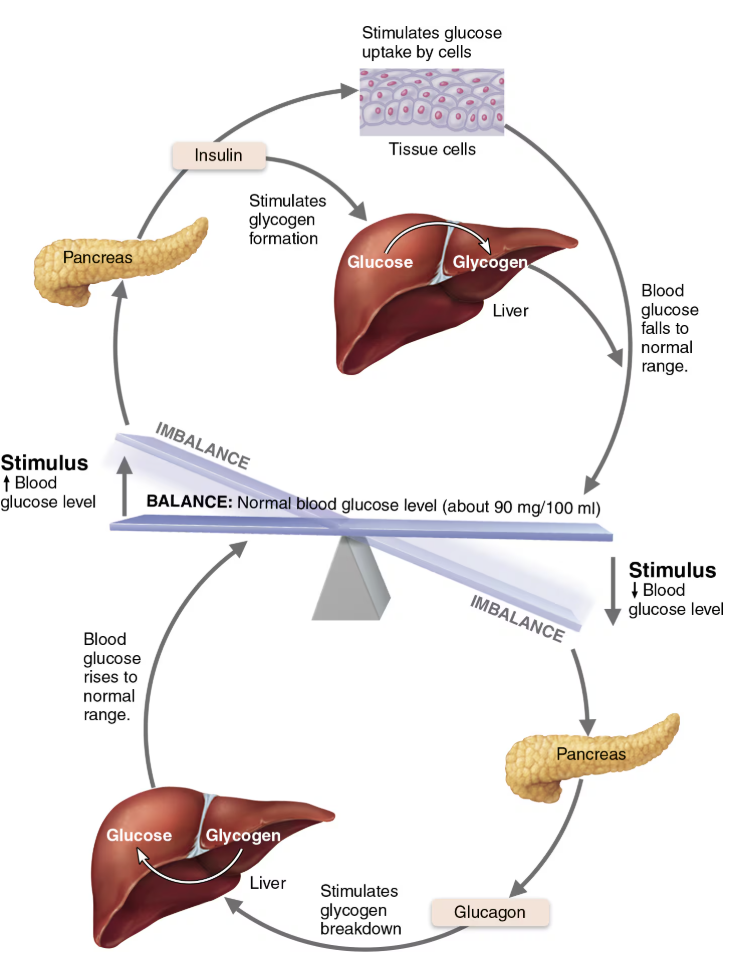
Glucagon Target and Effect
Raises blood glucose levels by traveling from the pancreas into the bloodstream to targeting liver to:
Glycogenolysis → Break down glycogen into glucose
Gluconeogensis → Synthesize glucose from lactic acid and other non-carbohydrates
Release glucose to the blood
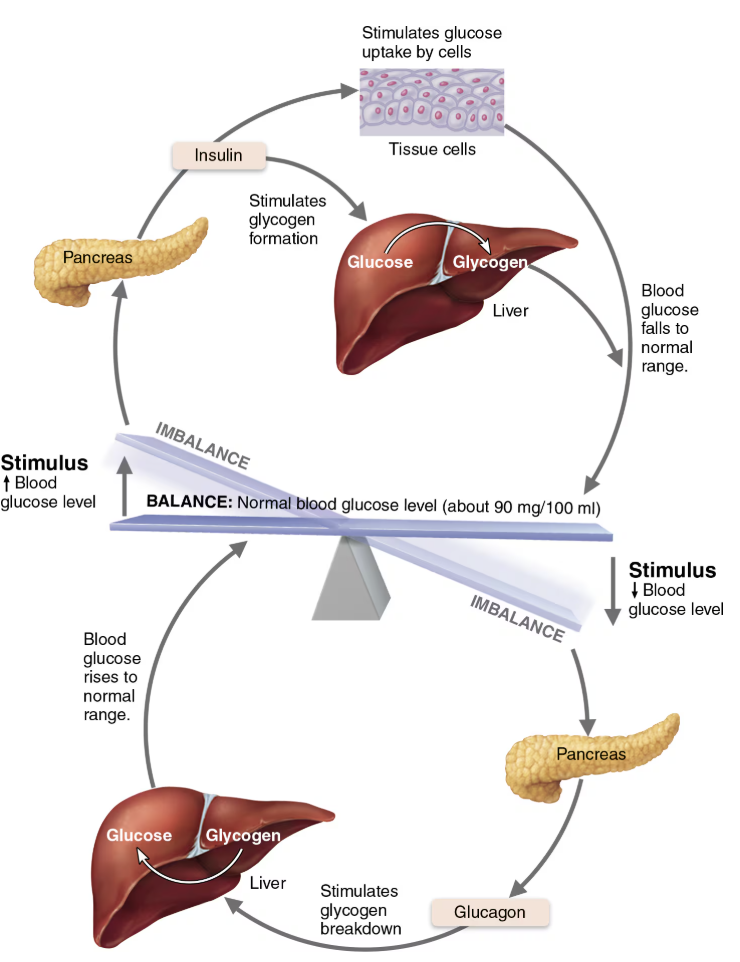
Explain Regulation of Release of Insulin
STIMULATED by
Increased BG
Synthesized as proinsulin that is then modified
INHIBITED by
Low BG levels
NEGATIVE FEEDBACK
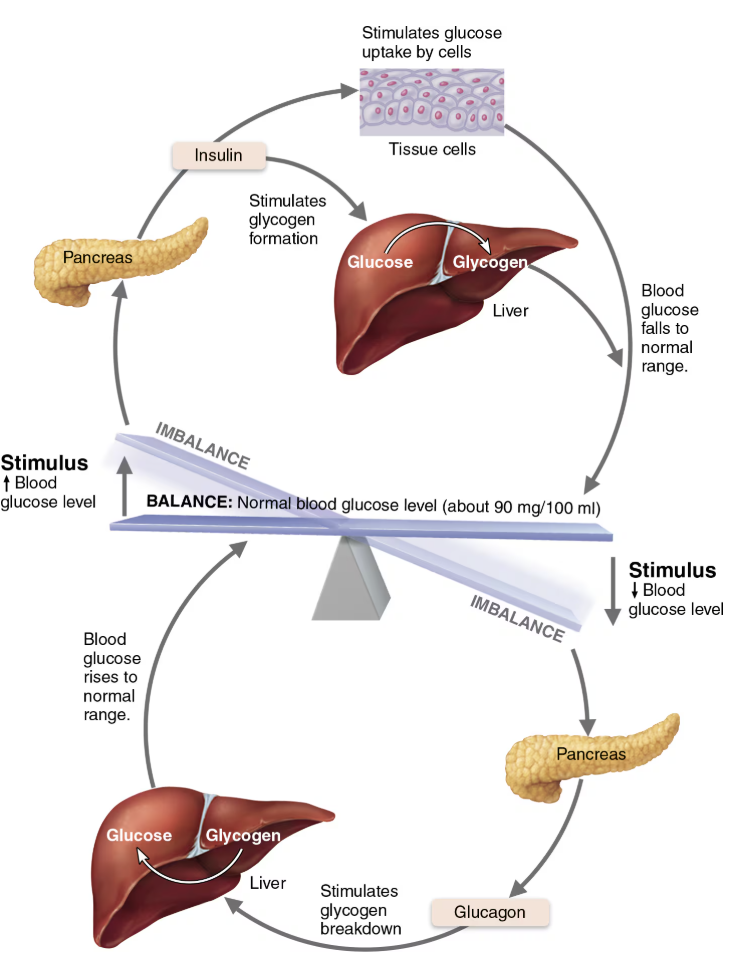
Insulin Target and Effect
Lowers blood glucose levels by traveling from the pancreas into the bloodstream to target the liver, muscles, and adipose tissue
Inhibits breakdown of glycogen to glucose
Inhibits conversion of amino acids or fats to glucose
Enhances membrane transport of glucose into fat and muscle cells
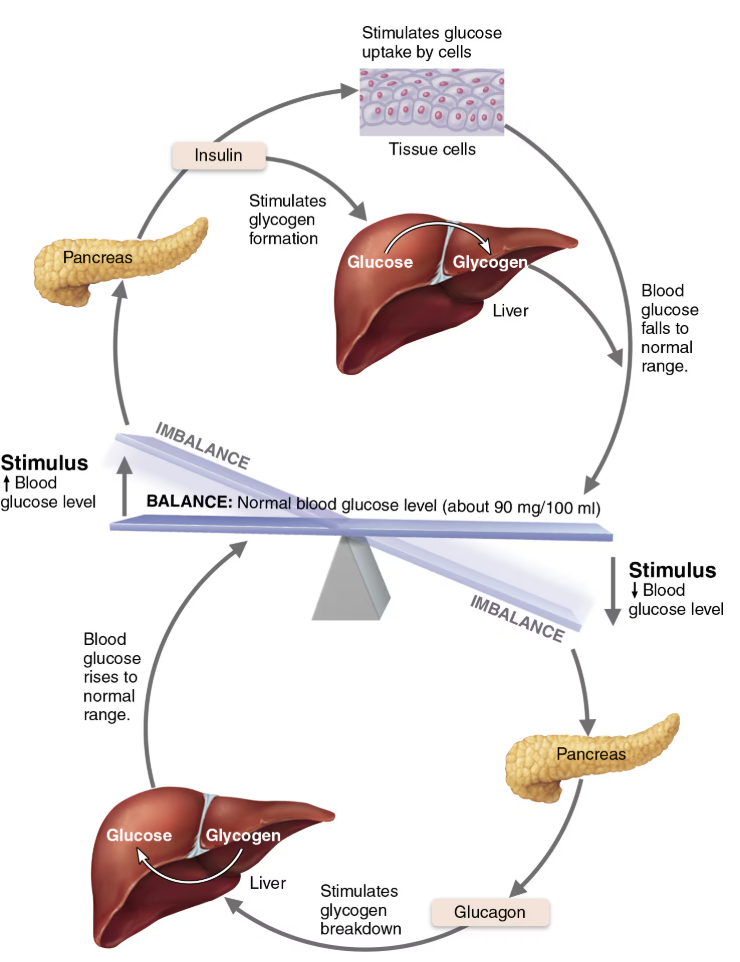
Compare and contrast the effects of the two major pancreatic hormones
Glucagon
STIMULATED by
Decreased BG levels
Rising amino acid levels
Sympathetic nervous system
INHIBITED by
Elevated BG levels
NEGATIVE FEEDBACK
Raises blood glucose levels by traveling from the pancreas into the bloodstream to targeting liver to:
Glycogenolysis → Break down glycogen into glucose
Gluconeogensis → Synthesize glucose from lactic acid and other non-carbohydrates
Release glucose to the blood
Insulin
STIMULATED by
Increased BG
Synthesized as proinsulin that is then modified
INHIBITED by
Low BG levels
NEGATIVE FEEDBACK
Lowers blood glucose levels by traveling from the pancreas into the bloodstream to target the liver, muscles, and adipose tissue to:
Inhibits breakdown of glycogen to glucose
Inhibits conversion of amino acids or fats to glucose
Enhances membrane transport of glucose into fat and muscle cells
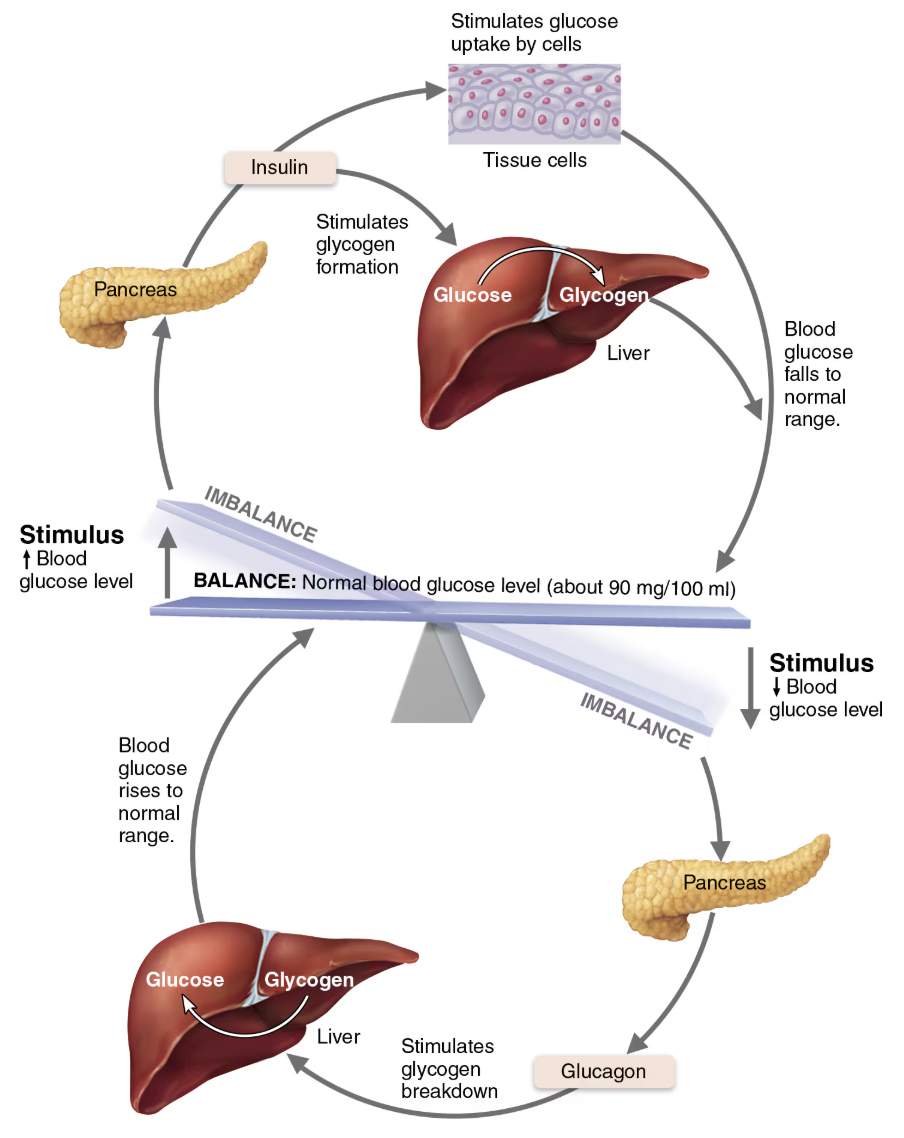
What are Factors that Influence Insulin Release
Elevated BG levels → Primary stimulus
Raising blood levels of amino acids and fatty acids
Hormones glucagon, epinephrine, GH, thyroxine (T4), glucocorticoids
Somatostatin and sympathetic nervous system inhibit insulin release
Causes and Effect of Hyposecretion of Insulin
Diabetes mellitus (DM)
A chronic metabolic disorder characterized by high blood sugar (glucose) levels due to an imbalance between insulin production and insulin resistance
CAUSES
Hyposecretion of insulin: Type 1
Hypoactivity of insulin: Type 2
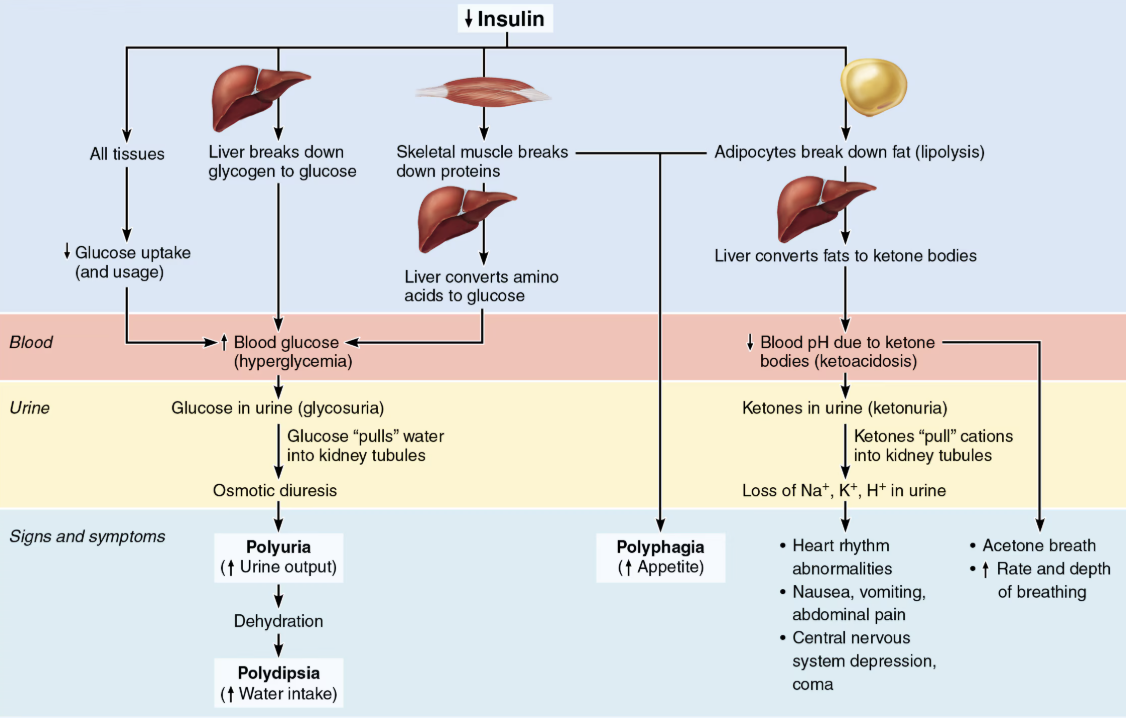
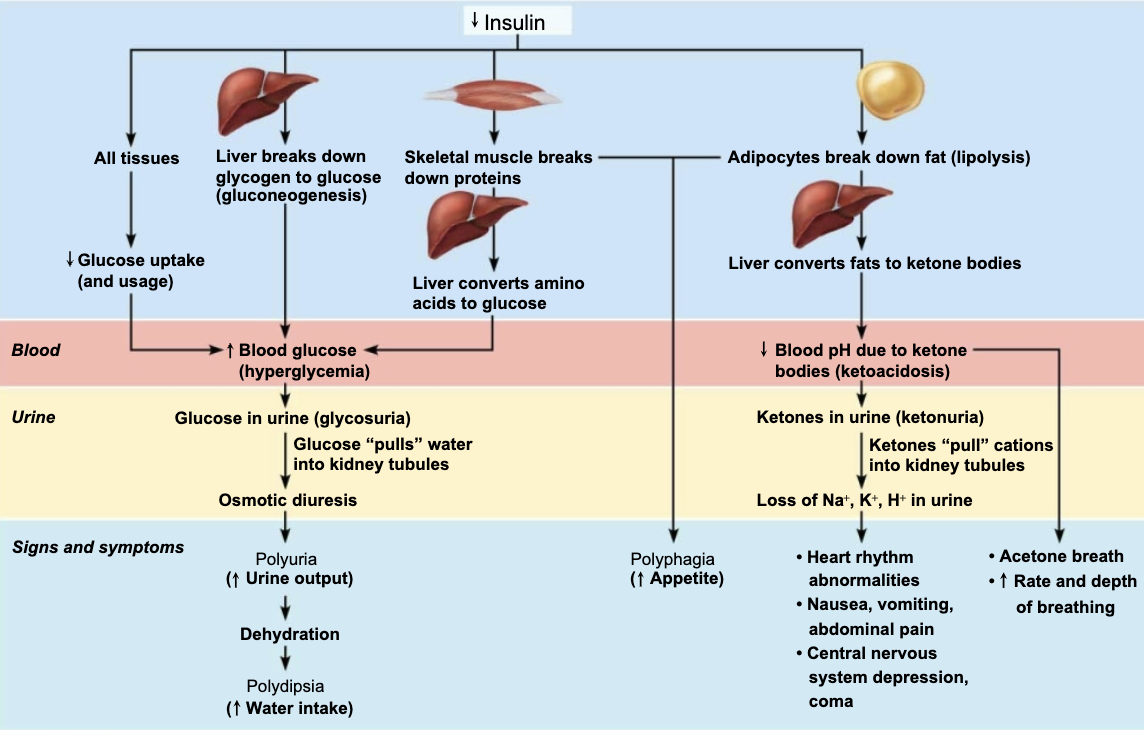
List the symptoms of Diabetes Mellitus
Polyiria: huge urine output
Glucose acts as osmotic diuretic
Polydipsia: excessive thirst
From water loss due to polyuria
Polyphagia: excessive hunger and food consumption
Cells cannot take up glucose and are “starving”
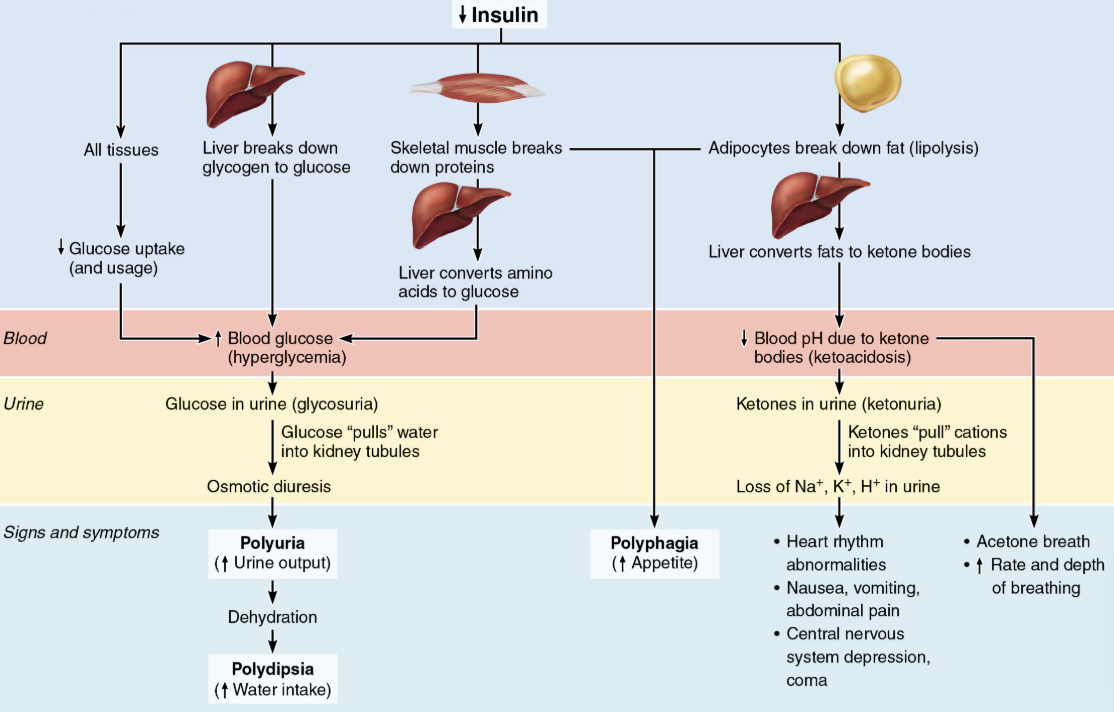
Explain Ketoacidosis
When sugar cannot be used as fuel, as in Diabetes Mellitus, fats are used, causing lipidemia → high levels of fatty acids in blood
Fatty acid metabolism results in formation of ketones (ketone bodies)
Ketones are acidic, and their build-up in blood can cause ketoacidosis
Also causes ketonuria: ketone bodies in urine
Causes and Effect and Treatment of Hypersecretion of Insulin
Hyperinsulinism → Excessive insulin secretion
Anxiety
Nervousness
Disorientation
Unconsciousness
Even death
CAUSES:
Hypoglycemia
Rare → islet cell tumor
TREATMENT:
Sugar ingestion
Explain the difference between Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes
Type 1
A form of diabetes mellitus in which the pancreas makes little or no insulin due to the destruction of pancreatic beta (β) cells by the immune system
Hyposecretion of insulin
Type 2
A form of diabetes mellitus in which insulin receptors are resistant to or unable to respond to insulin
Hypoactivity of insulin
Explain the treatment strategies for Diabetes Mellitus
Type 1
Continuous glucose monitors
Frequent insulin injections (up to four times daily, or better yet, by a continuous infusion pump)
Coupling glucose sensors to an insulin pump to make a true artificial pancreas
Pancreatic islet cell transplants
Type 2
Weight loss
Regular exercise
Healthy diet
Medications