Muscular System - Antatomy
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
53 Terms
Frontalis function
raises eyebrows (upward)
Temporalis function
elevates mandible (upward)
Occipitalis function
tenses and retracts scalp (downward)
Platysma function
depresses mandible
Trapezius function
extension at the neck
Splenius Capitis function
extension at the neck
Sternocleidomastoid function
both contract = flexion at the neck
one contract = rotation at the neck
Orbicularis oculi function
open/close eye
orbicularis Oris function
purses lips
Buccinator function
compresses cheek
Zygomaticus function
smile
Functions of the muscular system (5)
Movement
Generating Heat
Posture/Support
Guards entrances/exits
supports soft tissue
Properties of Muscle Tissue (4)
contractility (get shorter)
extensibility (get longer)
elasticity (bounce back)
excitability (respond to stimuli)
Masseter
Elevates mandible
What thoracic muscles can you see both anterior and posterior (3)
Deltoid
Trapezius
Serratus Anterior
What thoracic muscles are only seen from the posterior (8)
Latissimus Dorsi
Infraspinatus
Supraspinatus
Teres major
Teres minor
Rhomboid
Splenius Capitis
Levator Scapulae
What thoracic muscles can only be seen from the anterior (4)
Pectoralis major
Pectoralis minor
External/Internal oblique and transverse abs
Rectus abdominis
List the ab muscles from deep to superficial
transverse →internal oblique →external oblique
Gracilis (most medial) function (2)
adduction at hip
flexion at knee
Tensor fascia late function
hip abduction
Sartorious function
flexion at hip and knee
Rectus femoris function (2)
flexion at the hip
extension at knee
4 muscles that make up the quads
vastus lateralis
vastus medialis
vastus intermedias
rectus femoris
vastus lateralis function
extension at knee
vastus medialis
extension at knee
vastus intermedialis
extension at knee
Iliopsoas function
flexion at hip
Tibialis anterior function
dorsiflexion (flexion at foot)
Gluteus maximus function
extension at hip
Gluteus medius function
abduction at hip
Biceps femoris (most lateral) function
flexion at the knee
extension at the hip
Semitendionosus
flexion at the knee
extension at the hip
Semimembranosus function
flexion at the knee
extension at the hip
What make up your hamstrings (3)
Biceps femoris
semimembranosus
semitendinosus
Gastrocnemius function
plantar flexion
flexion at the knee
soleus function
plantar flexion
The anterior arm muscles do what
flexion
The muscles that make up the anterior of the arm (7)
brachialis
brachioradialis
biceps brachii
pronator teres
flexor Carpi ulnaris
palmaris longus
flexor Carpi radialis
pronator function
rotate medially (inward)
Supinator function
rotate laterally (outward)
what one flexor muscle can you see posteriorly on the arm
flexor carpi ulnaris
What function do the posterior arm muscle do
extend
epimysium
outermost layer - surrounds entire muscle
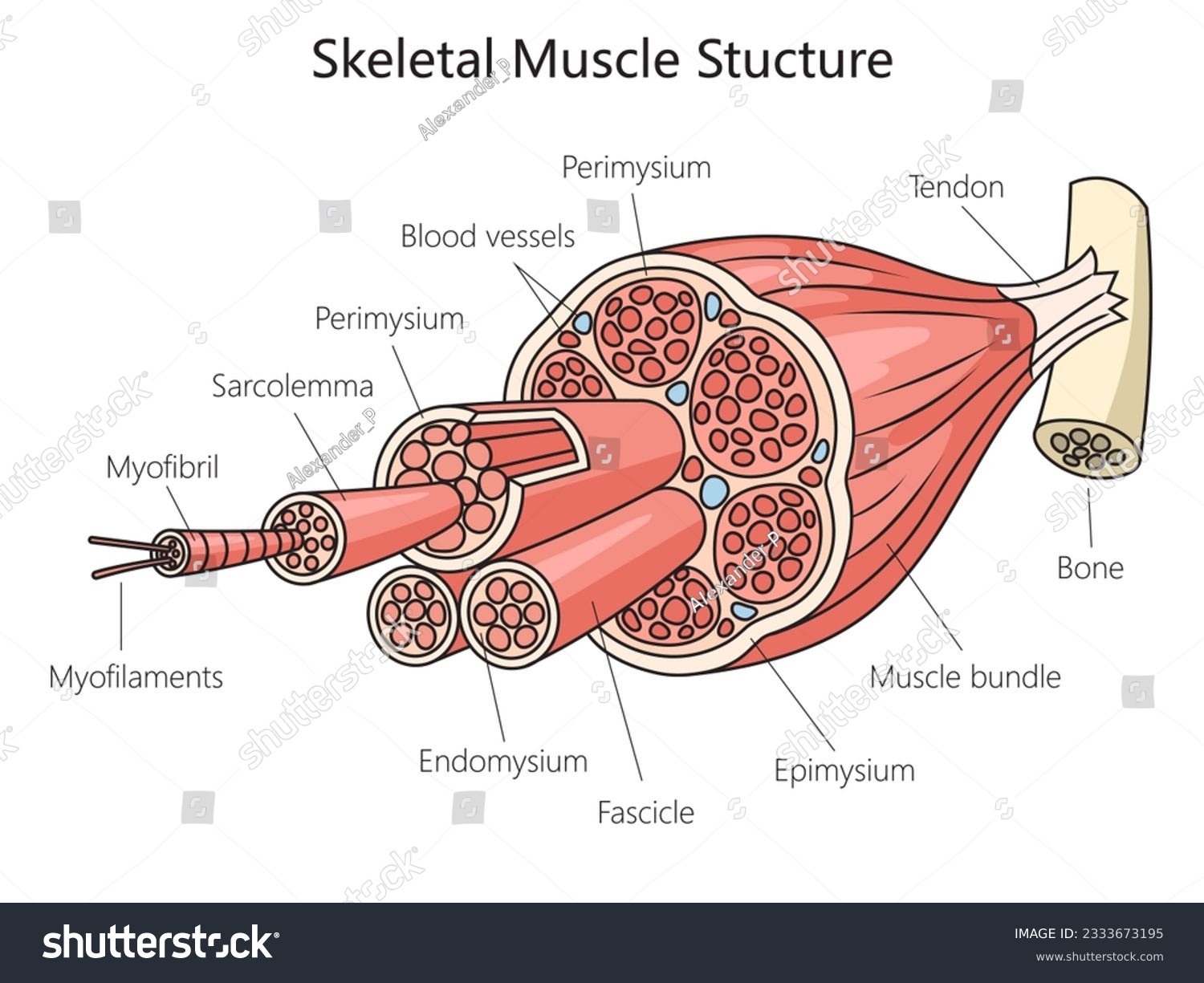
fascicle
bundles of muscle fibers
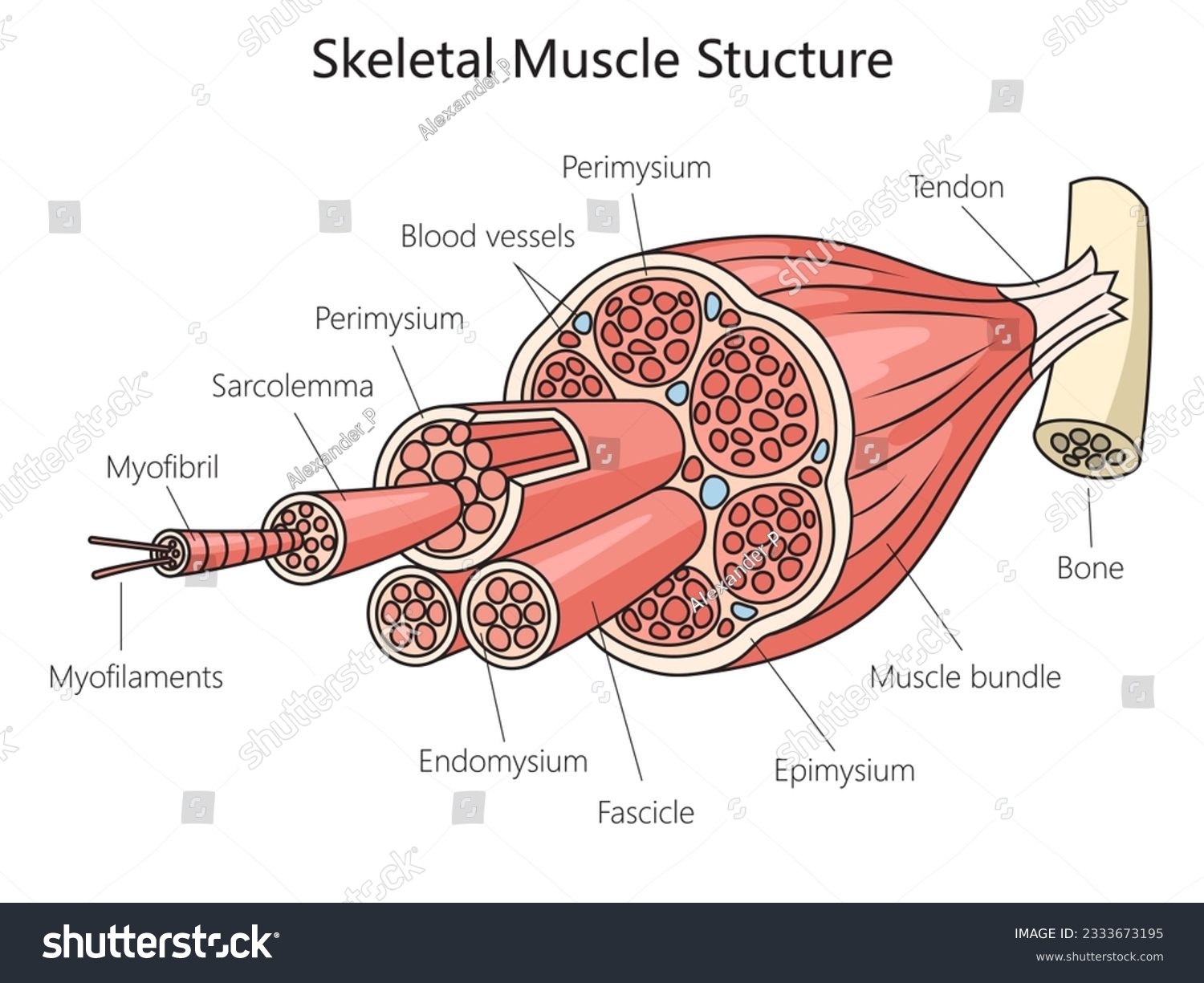
perimysium
separates and surrounds fascicles
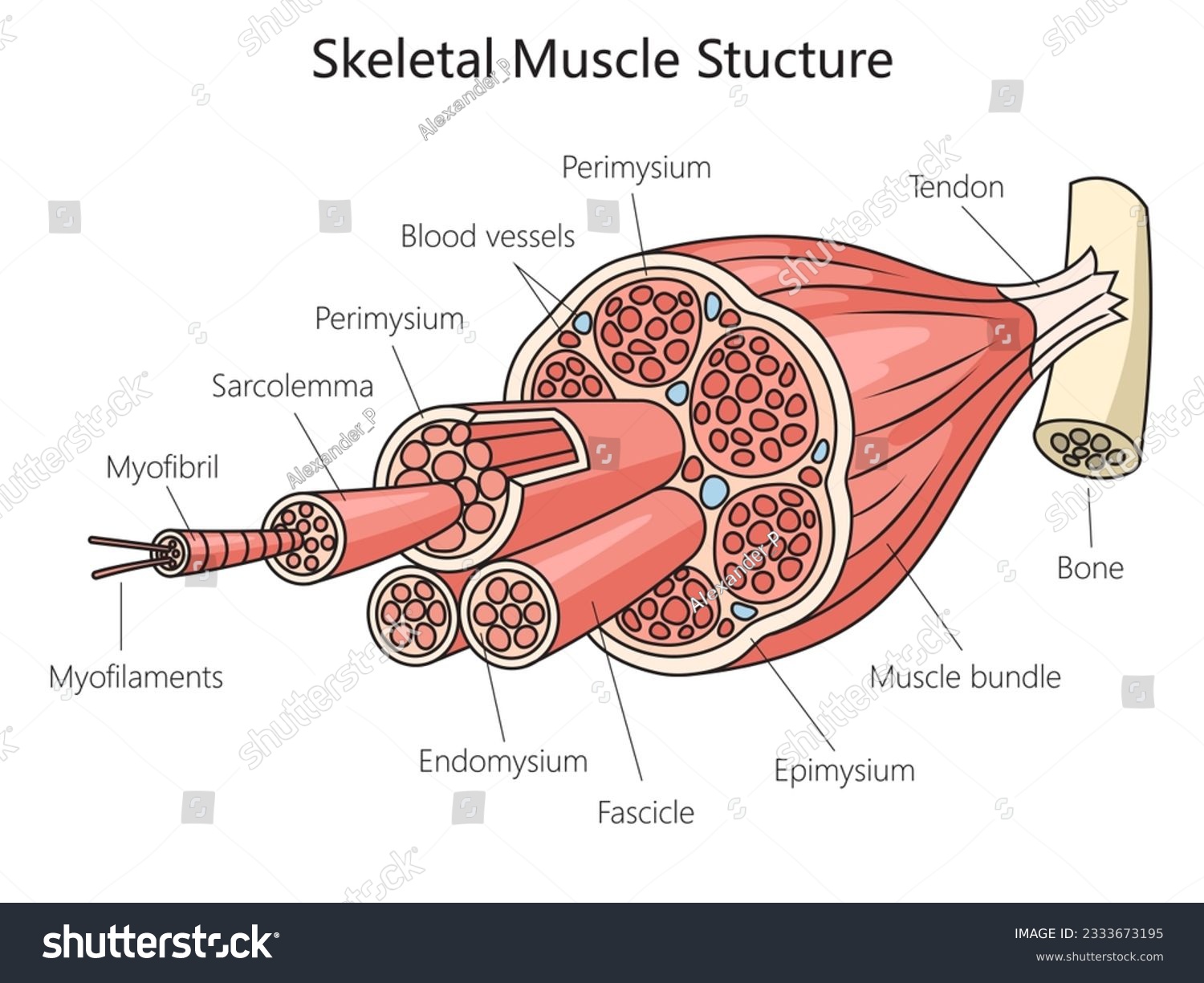
muscle fiber
cells
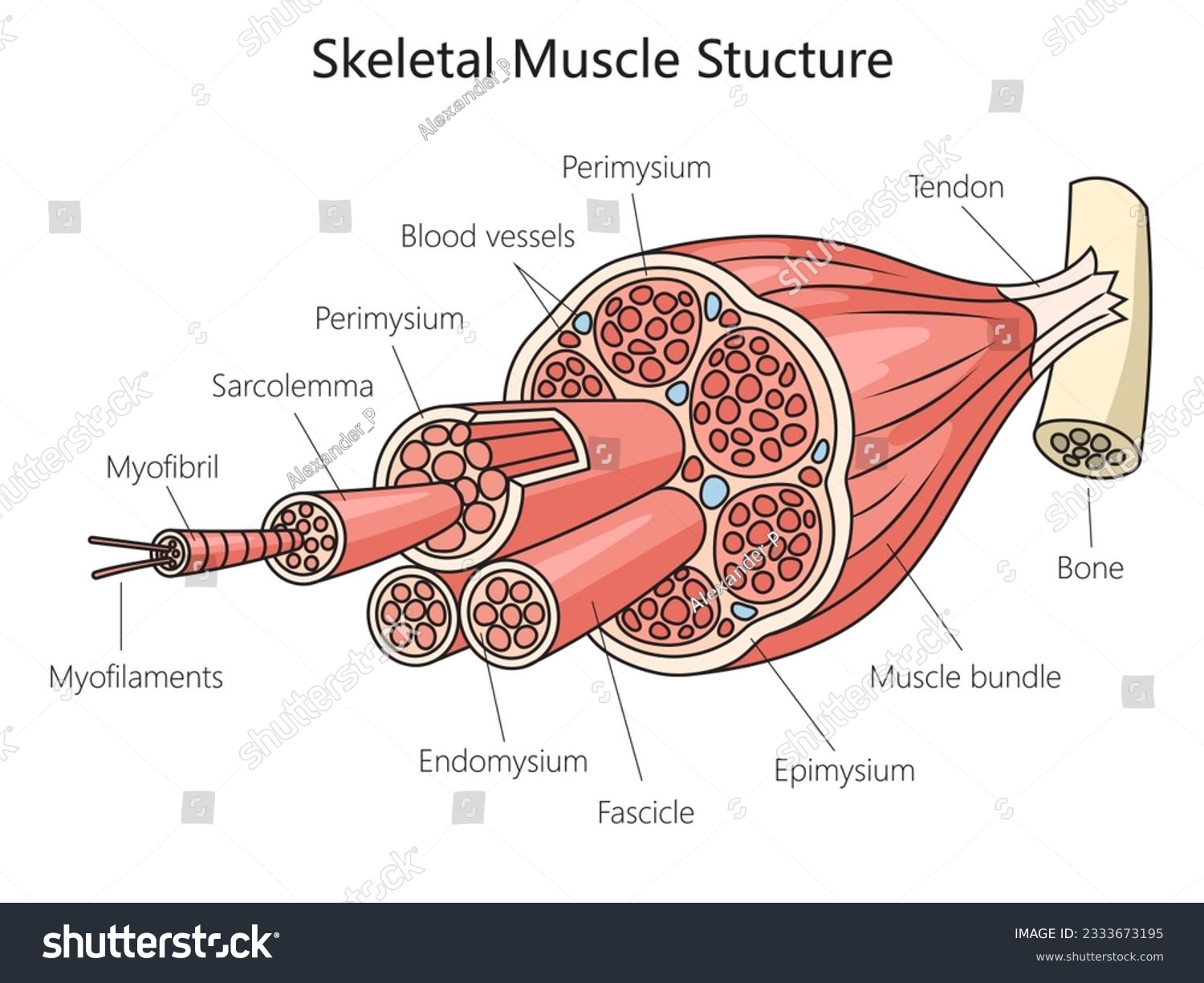
endomysium
surrounds each individual muscle fiber
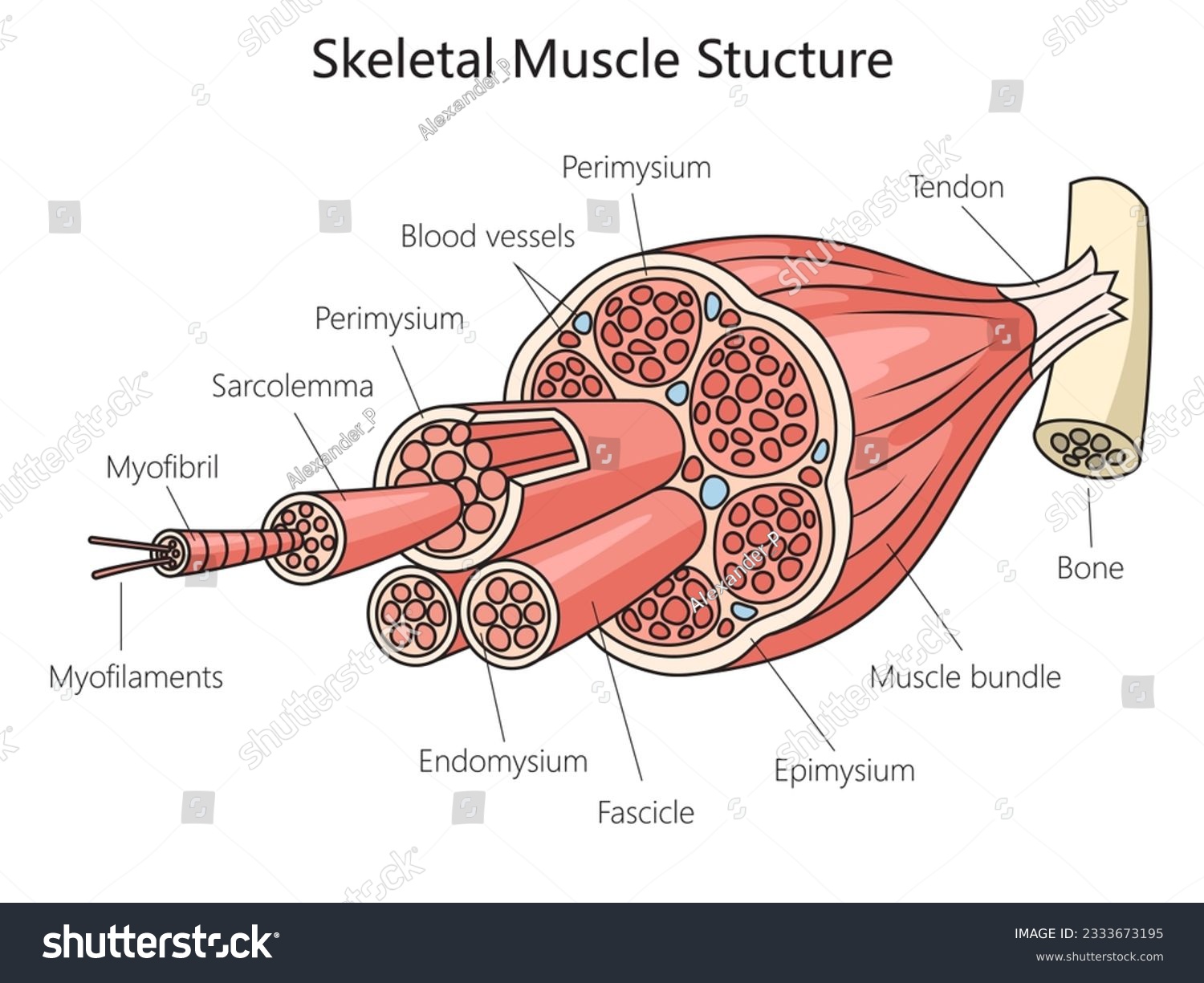
sarcolemma
muscle fiber membrane
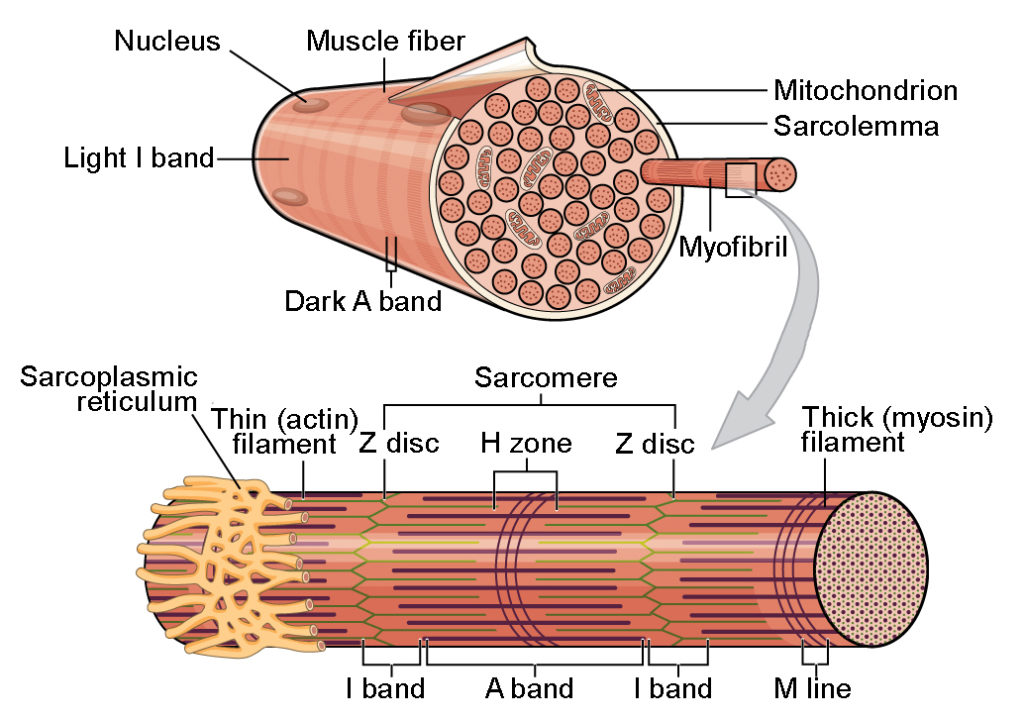
sarcoplasm
muscle cell cytoplasm
sarcoplasmic reticulum
specialized endoplasmic reticulum
myofibrils
within the sarcoplasm are parallel fibers - multinucleated
steps in the sliding filament theory (5)
sarcoplasmic reticulum releases calcium
Calcium bind to troponin →moves tropomyosin out of the way
myosin head bind to actin →crossbridge
“power stroke”→myosin release energy (ratcheting)
ATP →resets"
process of neuromuscular junction (5)
electrical signal travels down the axon
synaptic vesicles release ACh in synaptic cleft
ACh binds to receptors
ACh receptors initiate contraction of fibers (T tubules)
ACh is removed from cleft by AChE