2. oncogenesis
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
Cancer
Heterogeneous group of disorders characterized by uncontrolled cell division
resulting in overgrowth of cells with genetic mutations that give them
advantage over normal cells
Genetic disease, but not inherited!
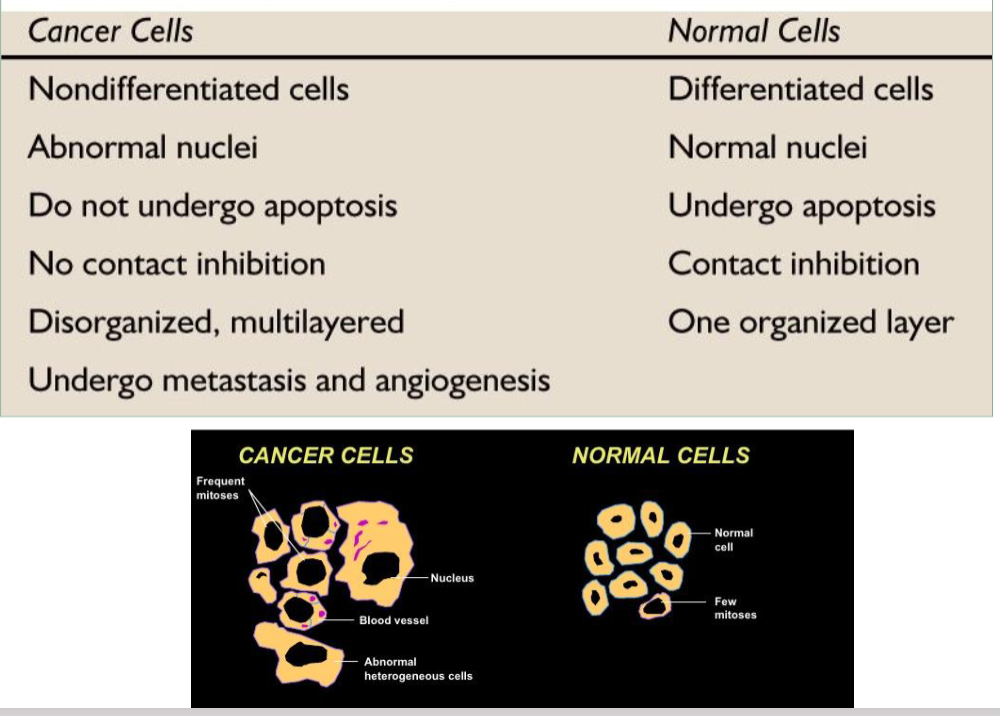
cancer cells vs normal cells
cancer risk factors
Genetic predisposition
Viral infections
Age
Environmental:
– Tobacco
– Diet
– Obesity
– Alcohol
– UV-radiation
– Ionizing radiation
– Pollutants
cancer characteristics
multi-hit model
clonality
autonomy
Multi-hit model
accumulation of mutations in a number of genes over time
Initial malignant cell
accumulations of mutations
Clonality
all cells in a tumor are clones of a single cell
Autonomy
ability to override normal regulatory mechanisms
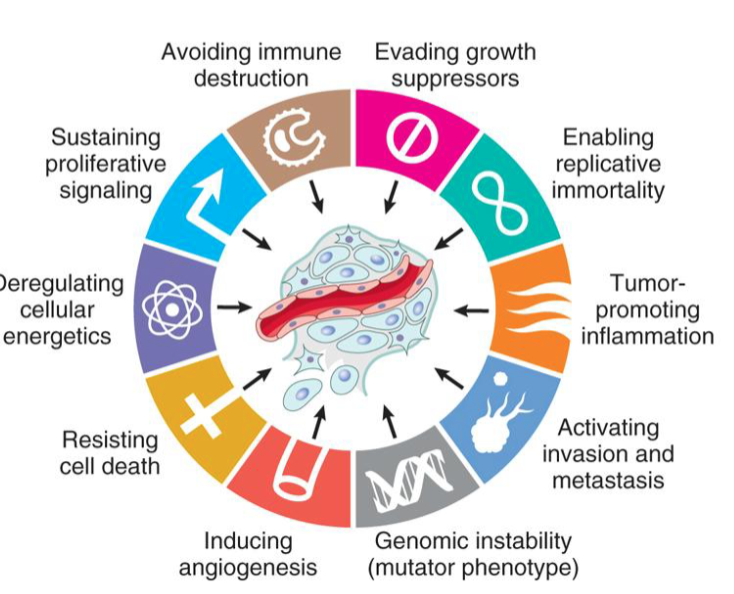
hallmarks of cancer
Genes mutated in cancers
Proto-oncogenes
Tumor-suppressor genes
Cell cycle controlling genes
Apoptotic genes
DNA-repair genes
Telomerase regulating genes
Vascularization–promoting genes
MicroRNAs
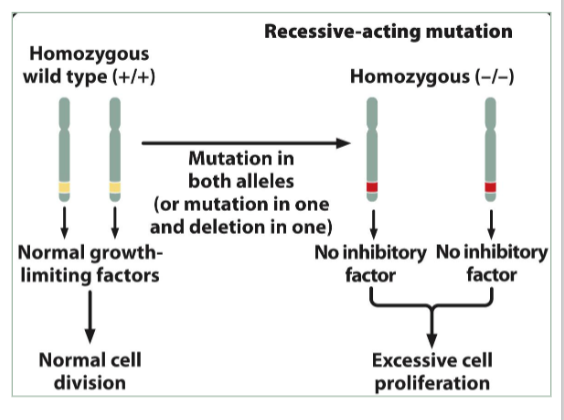
tumor suppressor genes
Loss-of-function = cancer (the brakes)
Suppress inappropriate cell proliferation + induce the repair of damaged DNA
Recessive-acting genes
Loss of heterozygosity (LOH)
function of BRCA 1 + cancer related
TSG
DNA repair, transcription factor
breast + ovarian
function of p53 + cancer related
TSG that regulates cell division
many types
function of RB + cancer related
TSG that regulates cell division
retinoblastoma
TSG mutation is either ____ or ______
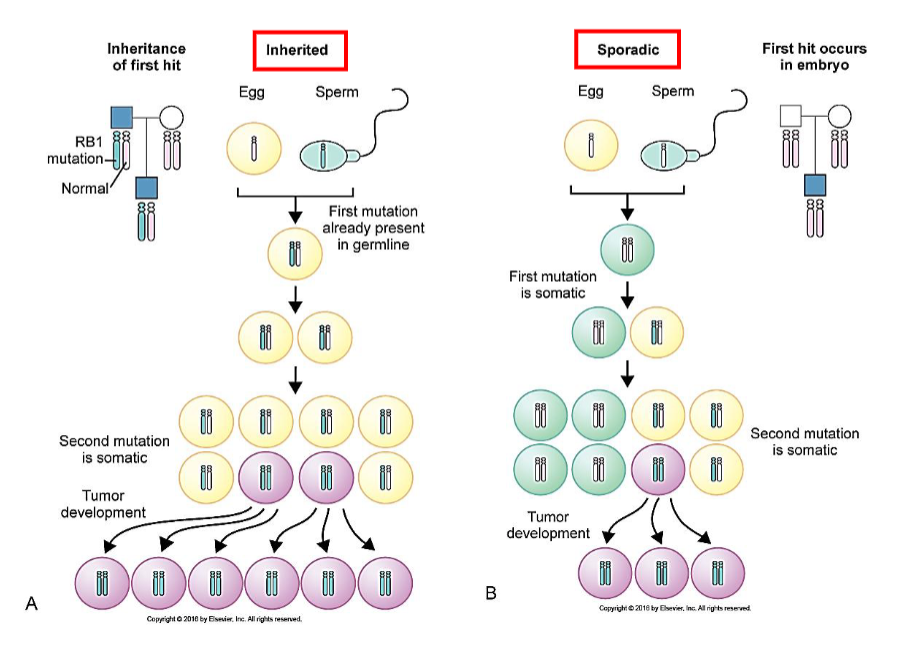
Li-Fraumeni
Germline mutation of TP53
Increased rate of colon, breast, brain cancers (50% by age 30)
Proto-oncogenes
Responsible for basic cellular functions
growth factors, receptors, intracellular kinases, TFs
gain of function → oncogenes (cancer, the gas)
Oncogenes
Stimulate cell division
Dominant-acting genes (need one copy)
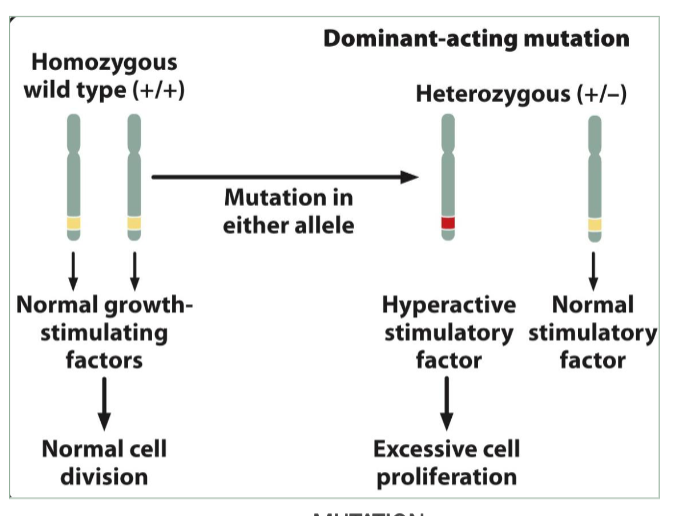
myc
transcription factor (proto oncogene)
lymphomas,leukemia,neuroblastome (oncogene)
ras
GTP binding + GTPase (proto oncogene)
many types (oncogene)
proto-oncogene activation mechanisms
Activation mechanisms
Promoter/enhancer insertion
Gene amplification
Point mutations
Chromosomal translocations
Viral-induced oncogenes
Both DNA and RNA viruses can cause cancer
Introduction of a new “transforming” gene into the host cell
Change in gene expression of host genes
Mutating and rearranging proto-oncogenes
Inserting strong promoters near proto-oncogenes
Induce impaired DNA repair and chronic inflammation
Cell-cycle regulatory genes
Cycling expression of cyclins/cdks (downstream effectors of those pathways) control different checkpoints in cell cycle
Mutations that promote unregulated passage from G1 to S phase are
oncogenic in ~80% of human cancers
Signal transduction pathways
Signaling pathways that respond to growth factors (Ras/MAPK pathway)
Transforming mutations:
– Growth factors
– Growth factor receptors
– Adaptor proteins
– Kinases
– Transcription factors
DNA-repair genes
loss of function = cancer
Cancer cells have higher-than-normal mutation rates
– Low replication fidelity
– Inefficient repair
DNA repair systems produce double-strand breaks, which can result in chromosomal rearrangements
Telomerase
Reactivation of telomerase in 90% of tumors
normally active only in germ cells and stem cells
what is the most common noncoding mutations in cancer?
Somatic mutations in the proximal promoter of the human telomerase reverse transcriptase gene (hTERT), the catalytic subunit of telomerase
Apoptosis
Programmed cell death
regulated energy-dependent sequence of events for cells to self-destruct
steps of apoptosis
Initiation: through death receptors (TNF1-R), GF deprivation, or loss of mitochondrial integrity
Signal integration –balance between proapoptotic and antiapoptotic signals to decide on whether to proceed
Execution mediated by caspases (proteases)
how do cancer cells bypass apoptosis
by inactivating caspases
epigenetics
Influence of life-style and environmental exposure on gene expression
Angiogenesis
New blood vessel formation by endothelial cells and extracellular matrix
Tumors >1mm3 need a new vessel
Angiogenic factors
VEGF, TGF-b, bFGF, IL-8
Angiogenesis inhibitors
interferons
Defining characteristics of malignancy
invasion + metastasis
Invasion
malignant cells disrupt the basement membrane and penetrate the underlying stroma
Loss of adhesion to basal membrane (low E-cadherin)
Local ECM proteolysis (high MMPs)
Metastasis
active transport of malignant cells through tissues barriers at distant sites
Intravasation
malignant cells enter the circulation and migrate to new location
Extravasation
migration from the circulation into the local ECM
Oral cancer – molecular pathways
1. p53/ Rb/ cyclin D
2. Promoter hypermethylation
3. Mitochondrial mutations
p53/ Rb/ cyclin D
75% missense p53 mutations = initiating event (already in pre-cancerous lesions)
Rb inactivation mostly in HPV-positive cancers
Cyclin D overexpression – poor prognosis factor for tongue
Mitochondrial mutations
variants of mitochondrial DNA