Biology: Topic 2J Coordination and Response (Part 1A The Eye)
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
What type of organ is the eye?
A specialised sense organ that contains photoreceptors.
What is the cornea?
It refracts light and protects the eye.
Transparent and convex.
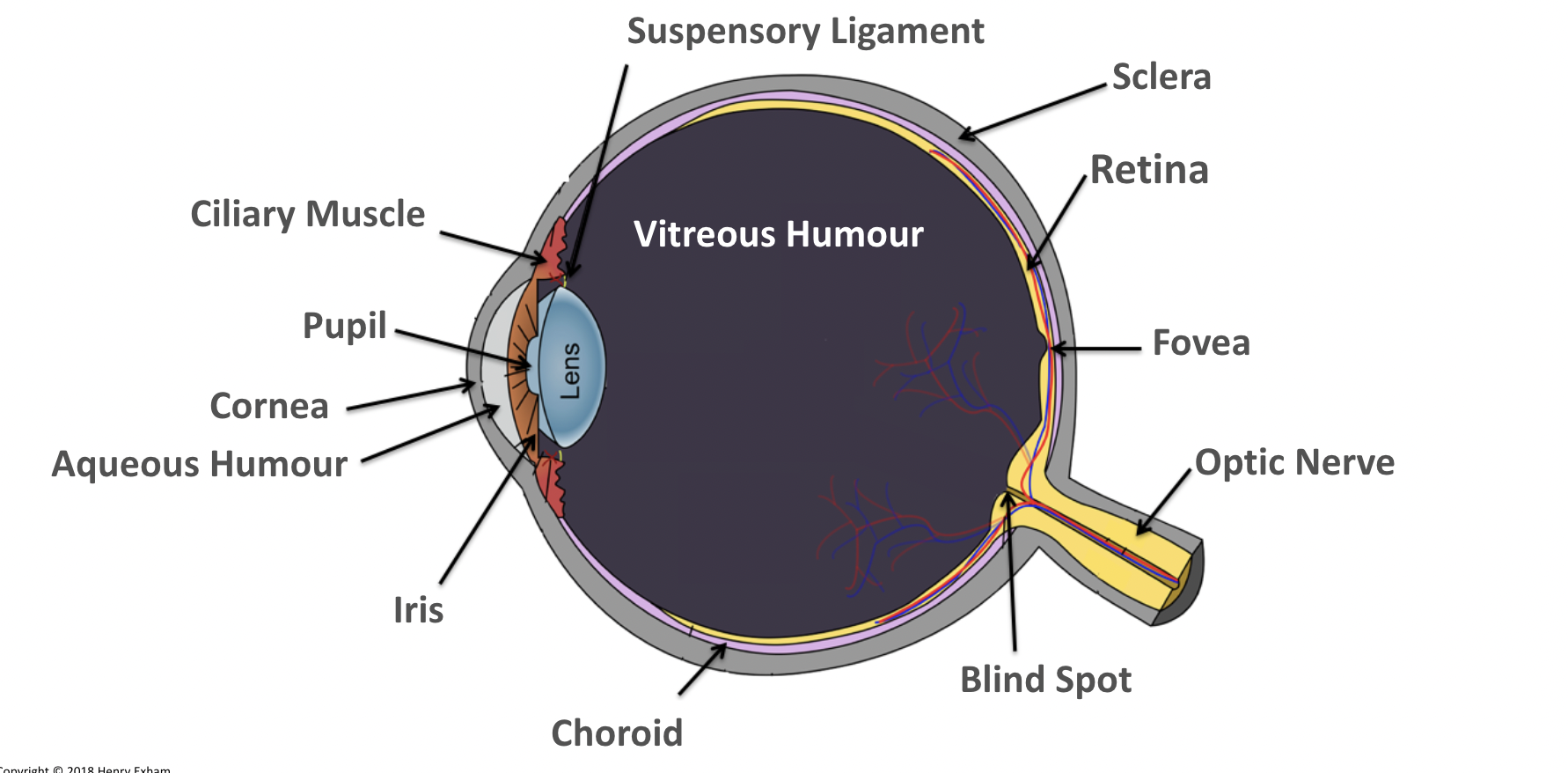
What is the lens?
Focuses light onto the retina.
Transparent biconvex disc.
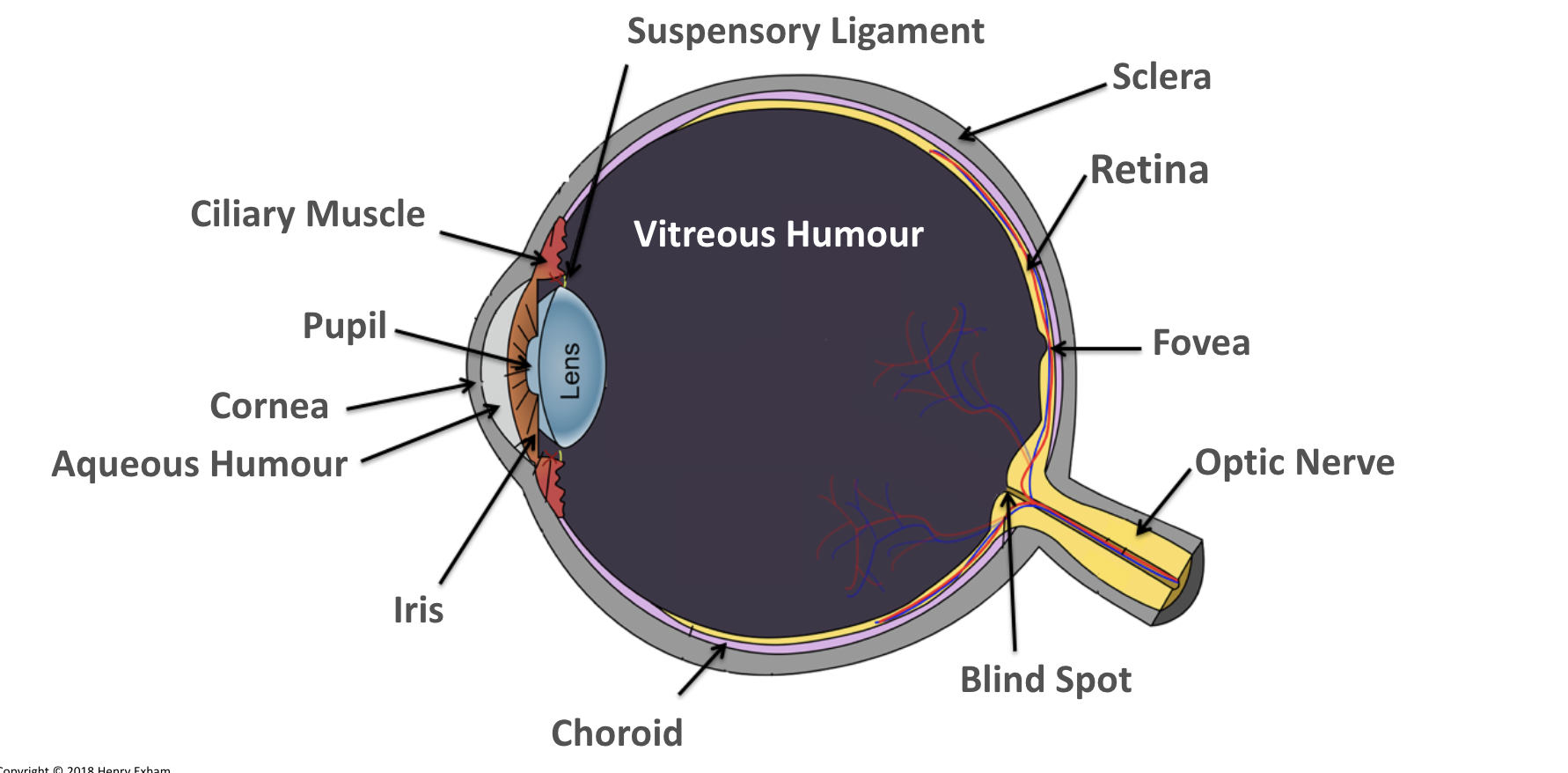
What is the retina?
A layer of tissue at the back of the eye that contains light receptor cells (rods to detect light intensity and cones to detect colour).
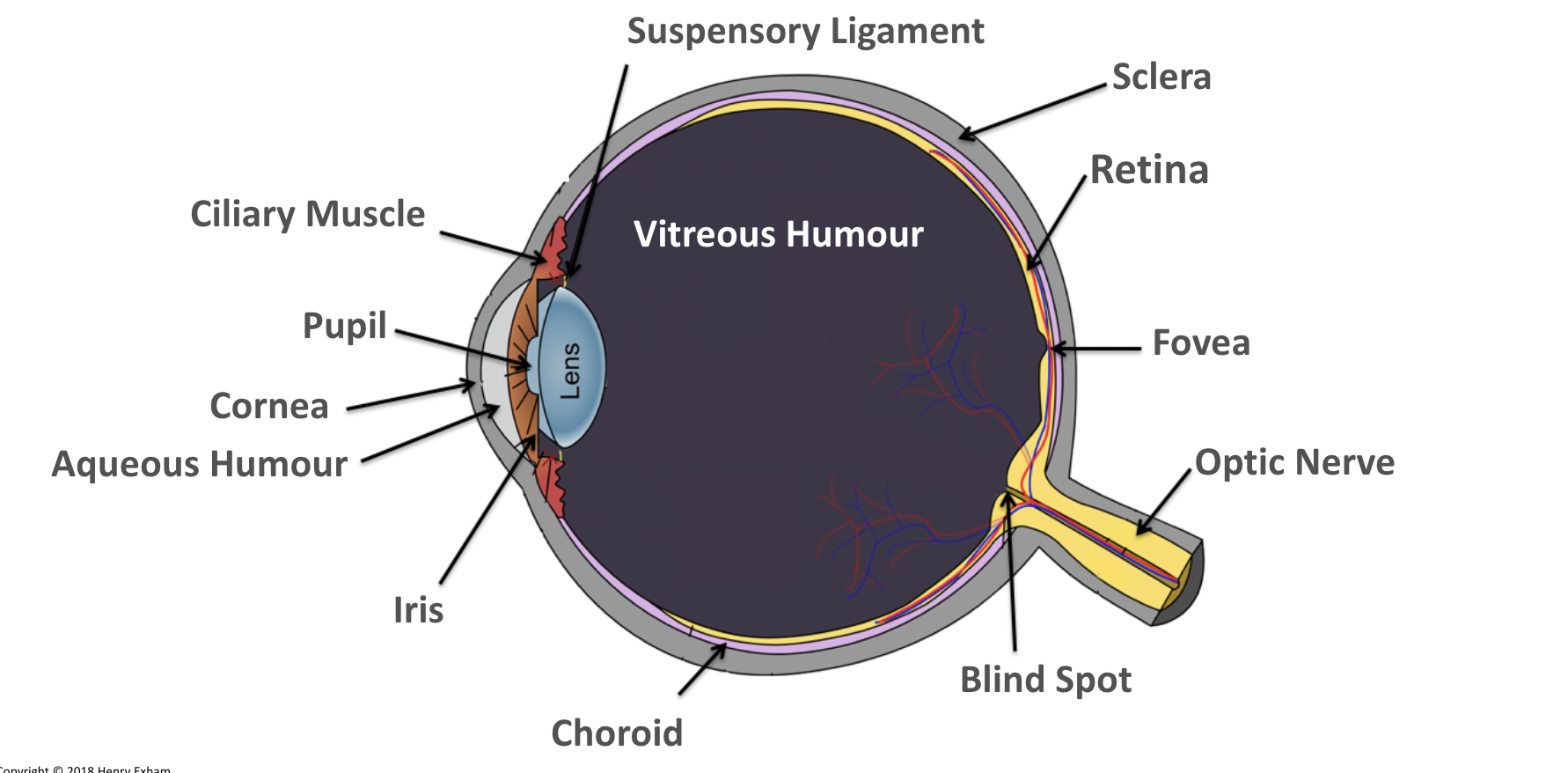
What is the aqueous humour?
Maintains the pressure in the eye and nourishes the cornea.
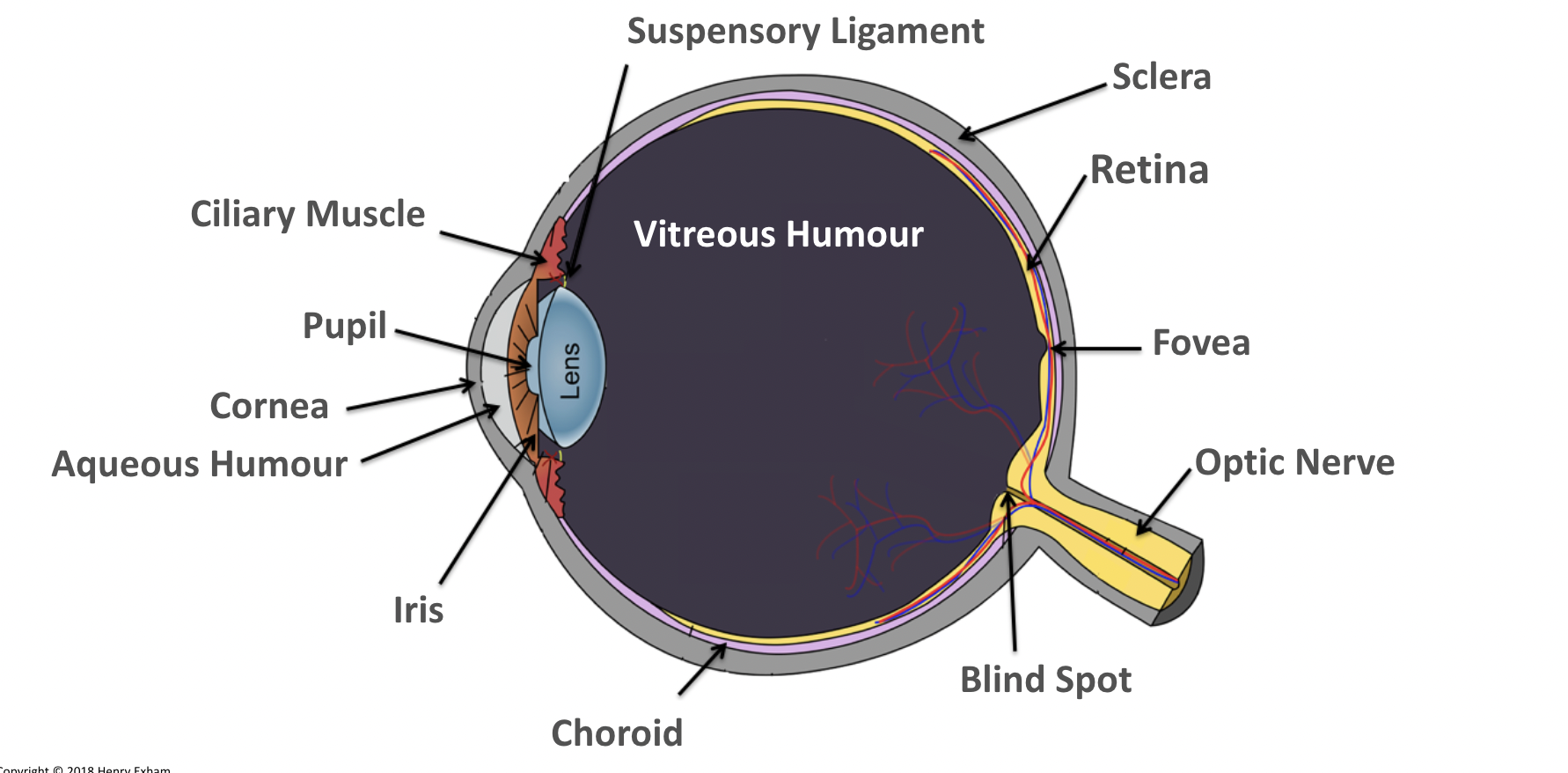
What is the vitreous humour?
Maintains the shape of the eye and attaches to the retina.
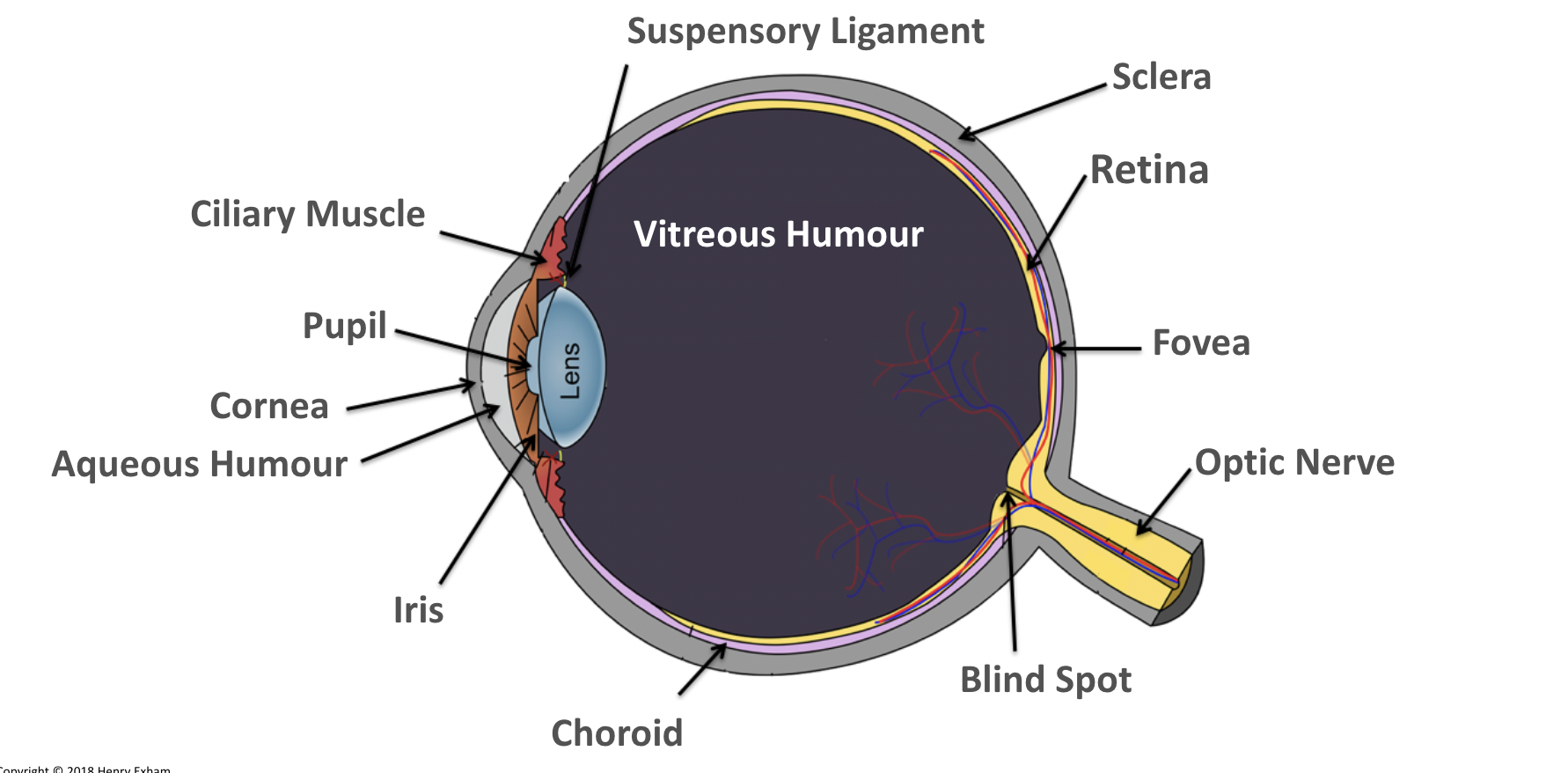
What is the ciliary muscles?
Help change the shape of the lens in accommodation.
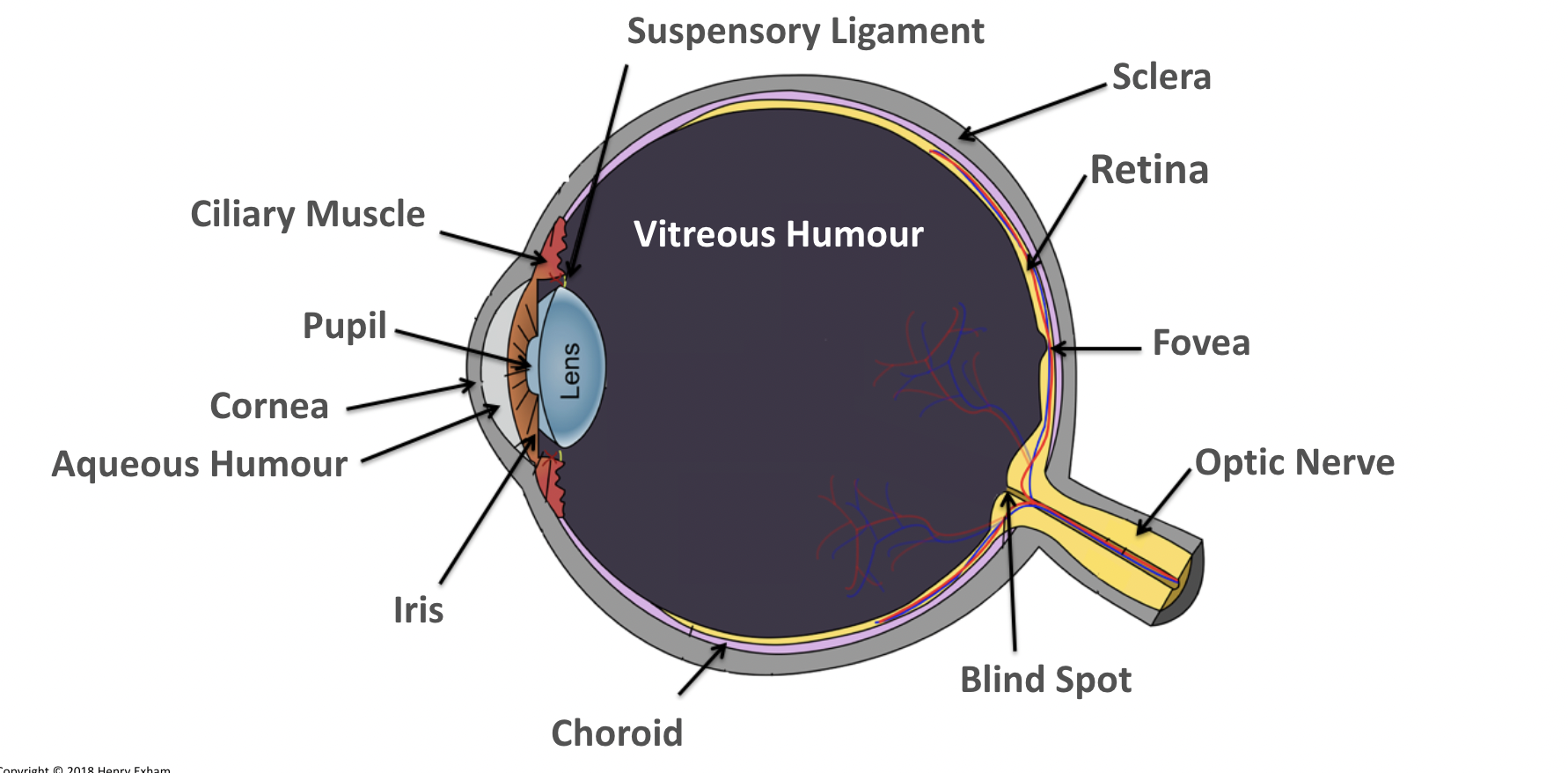
What is the sclera?
Tough outer layer that the muscles that move the eyeball attach to.
Helps maintain shape of eyeball.
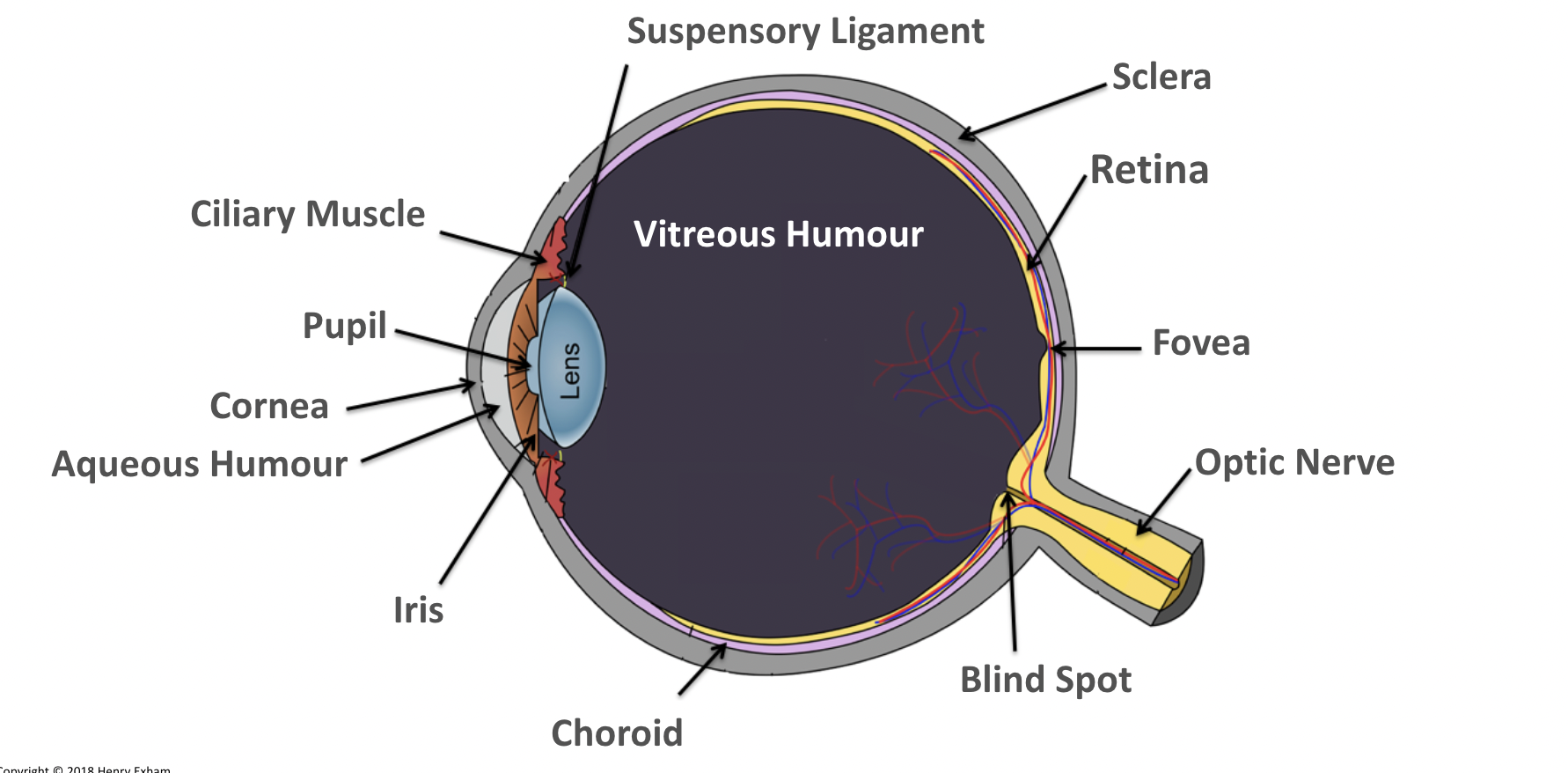
What is the pupil?
Hole in the center of the eye that lets light in.
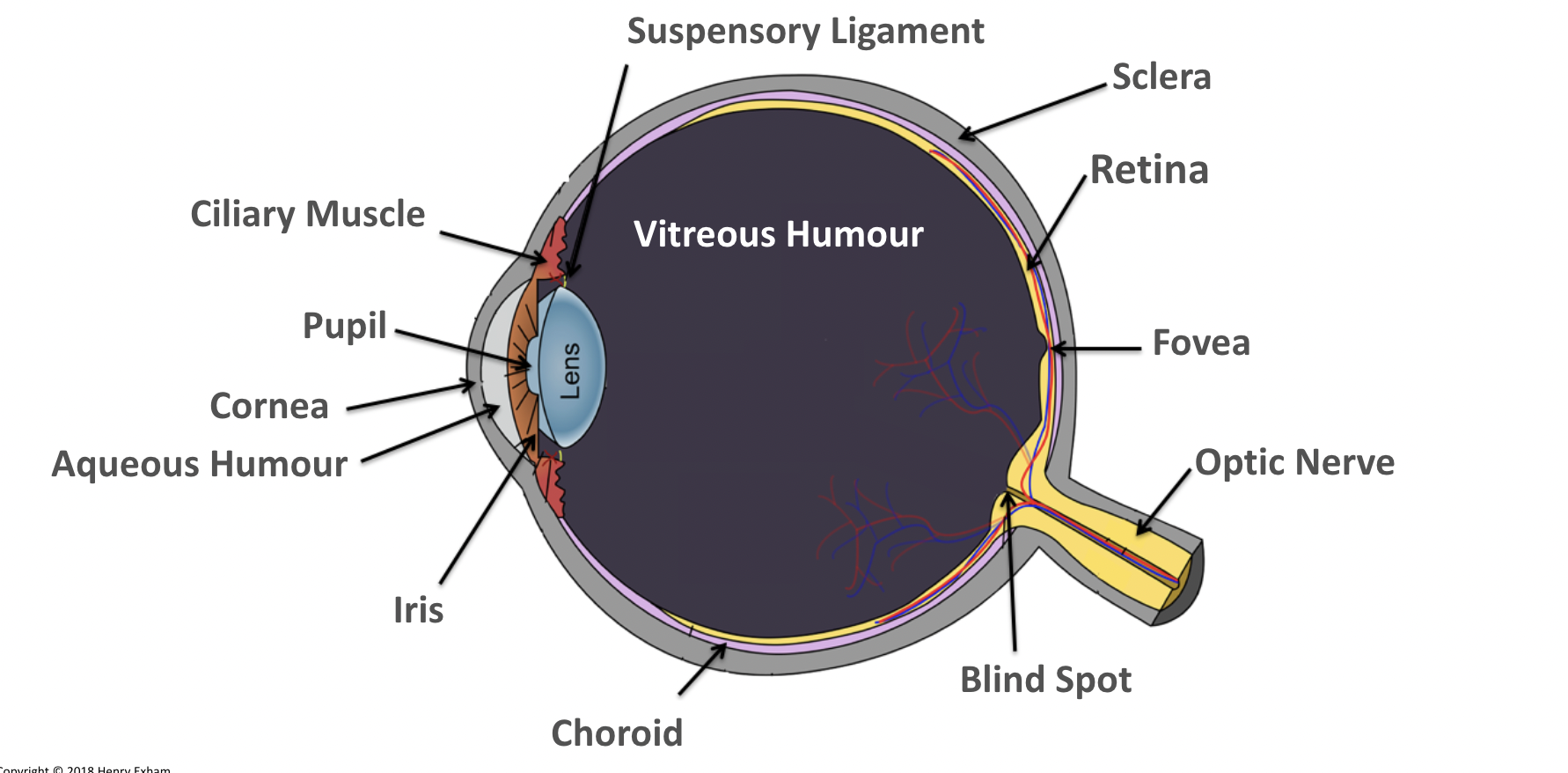
What is the iris?
Controls amount of light entering the eye by controlling size of pupil.
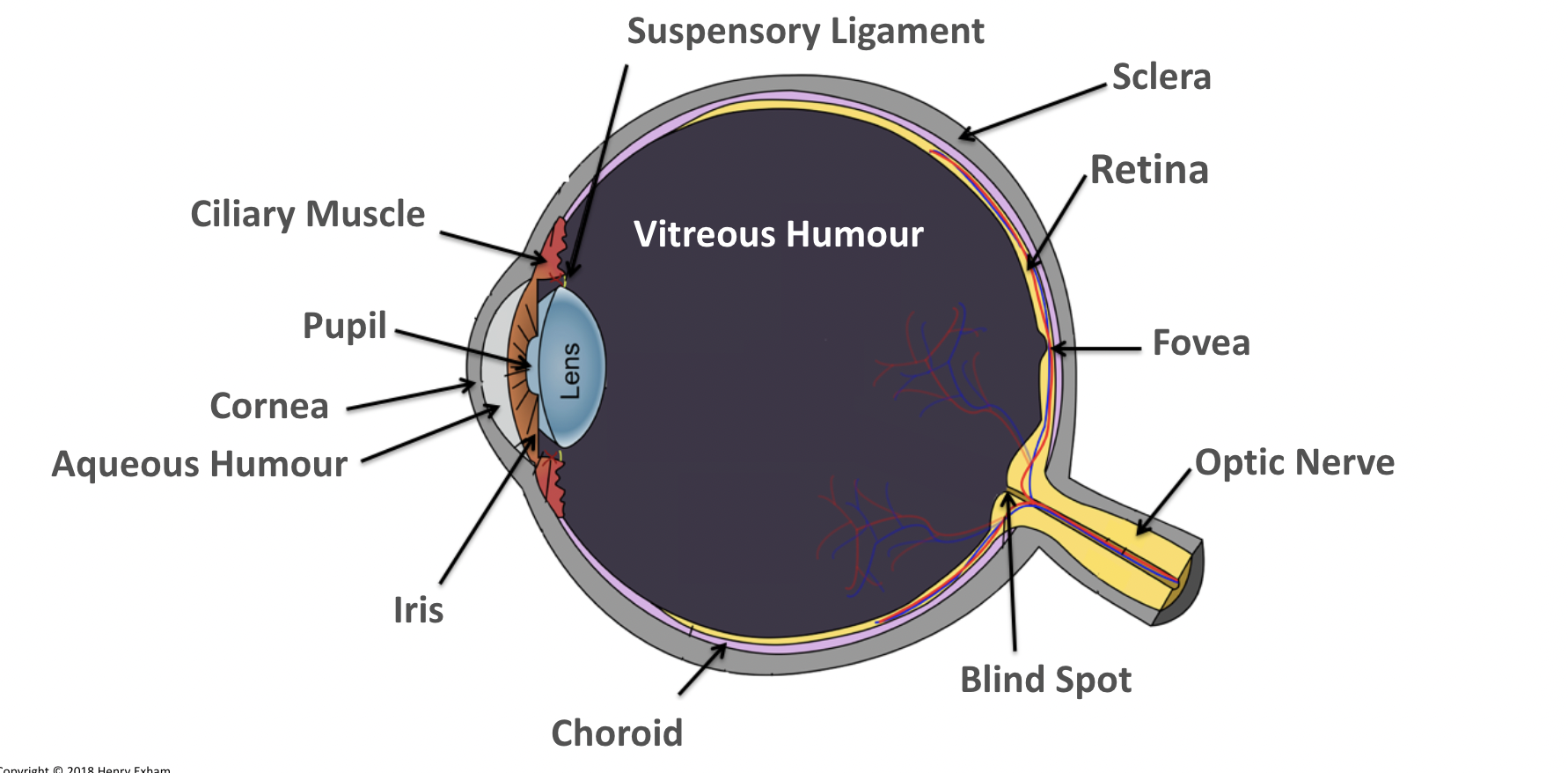
What is the suspensory ligaments?
Connect the ciliary muscles to the lens.
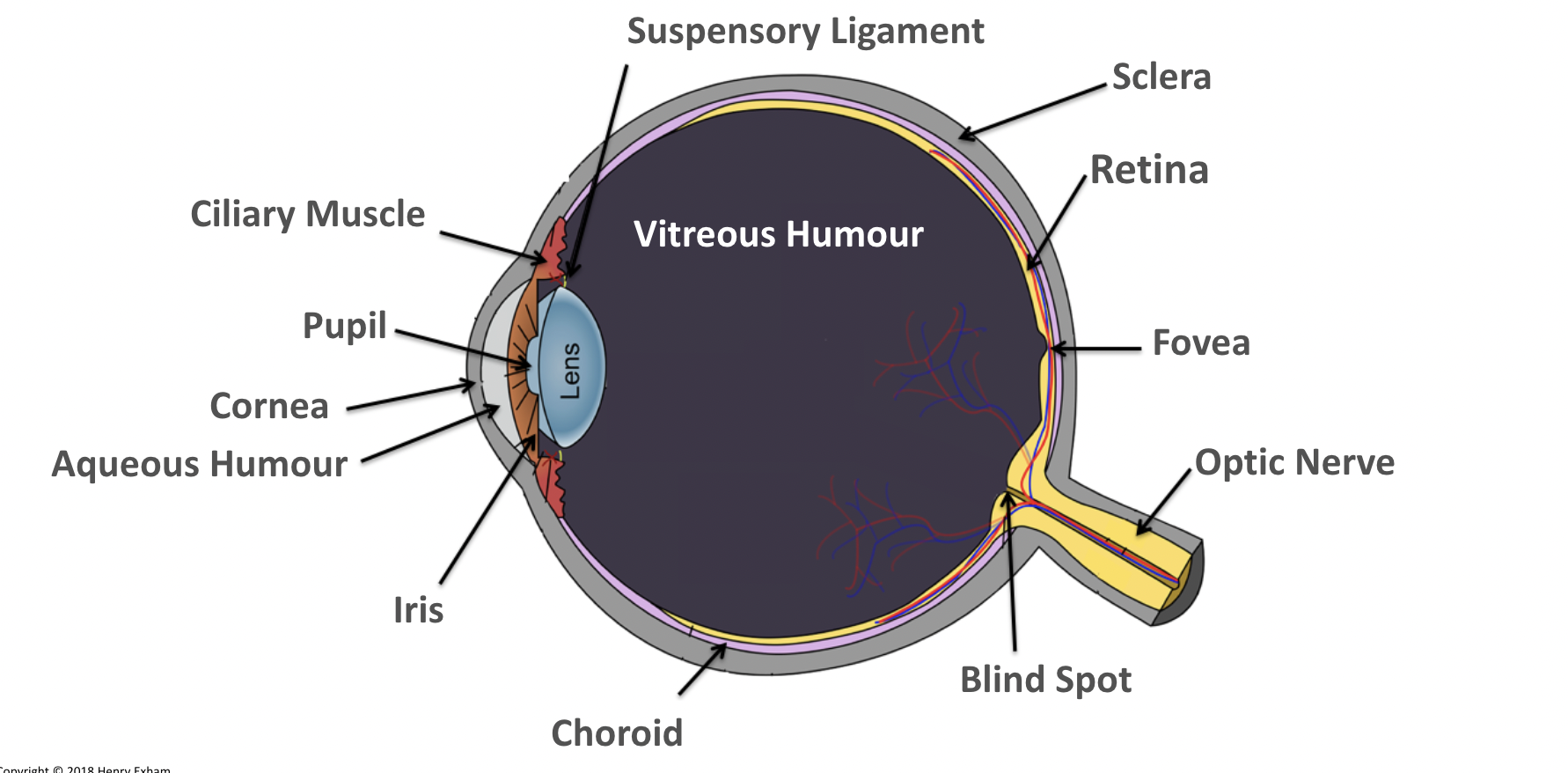
What is the conjunctiva?
Provides protection and lubrication of eye by the production of mucus and tears.
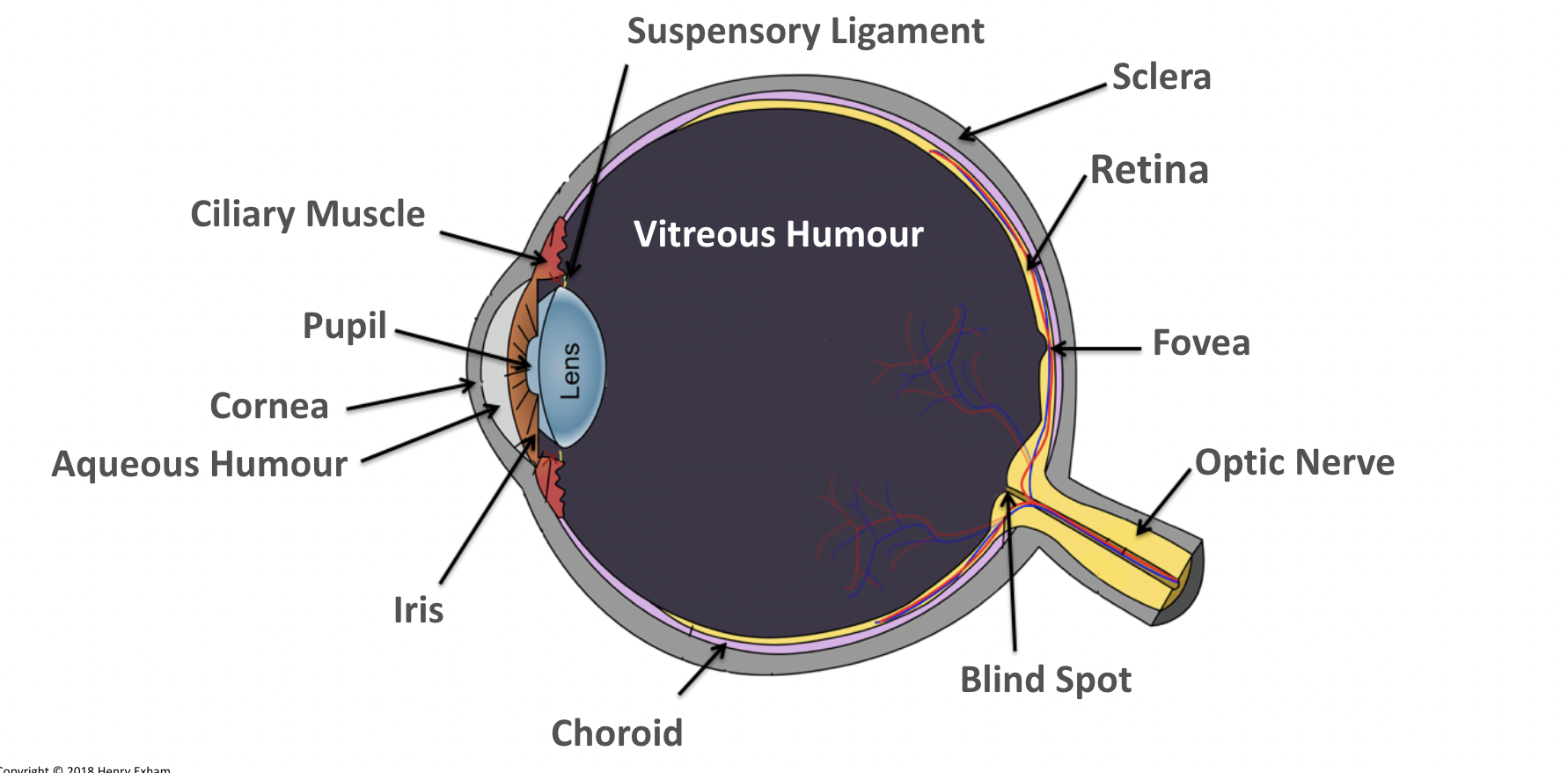
What is the fovea?
The region of retina that contains the highest concentration of cones, that contributes to sharp central vision.
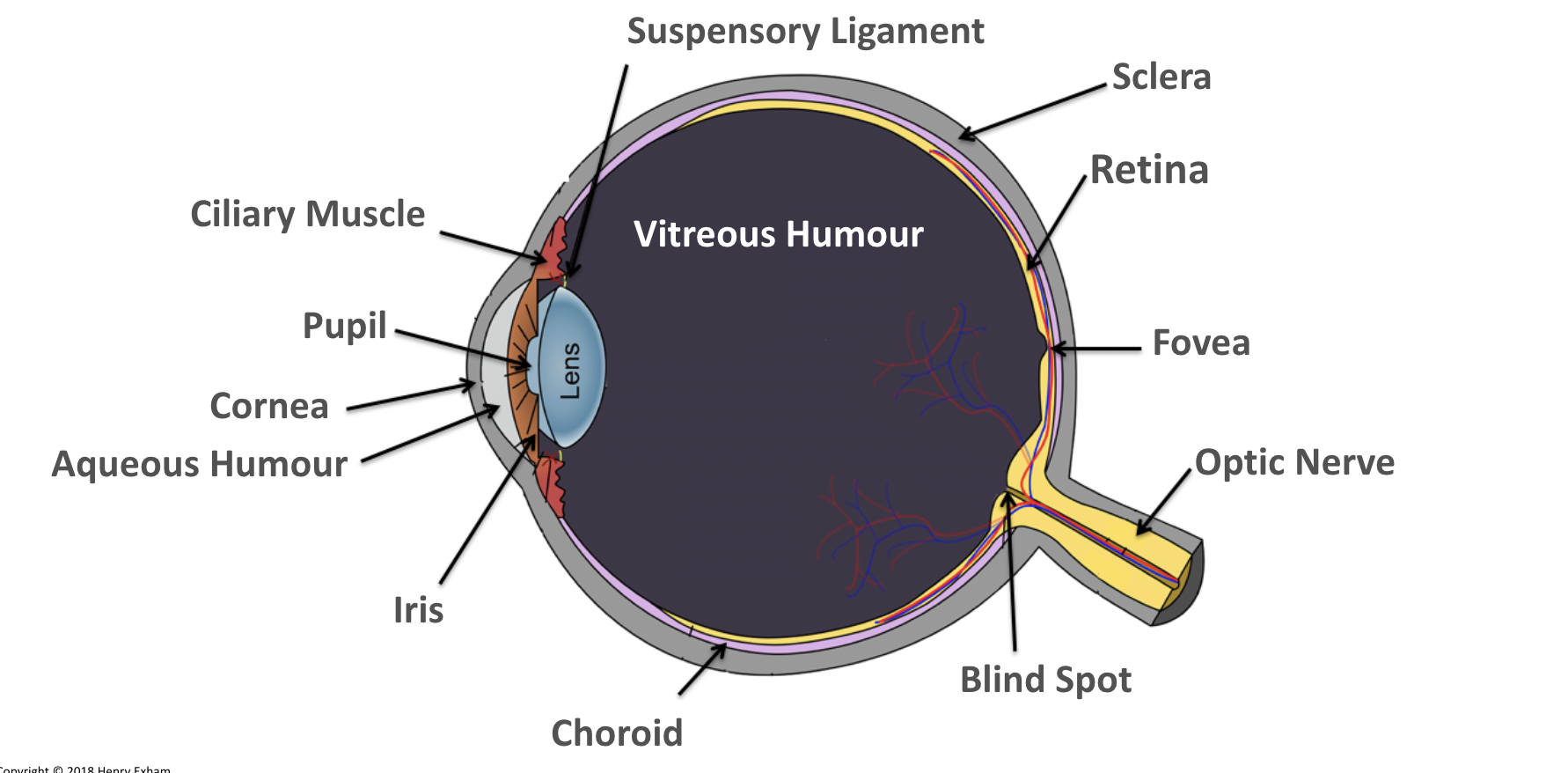
What is the iris reflex?
The iris can change the size of the pupil to control the amount of light entering the eye.
It does this using circular and radial muscles.
What happens to the radial and circular muscles in bright light?
Circular muscles contract.
Radial muscles relax.
Pupils constrict.
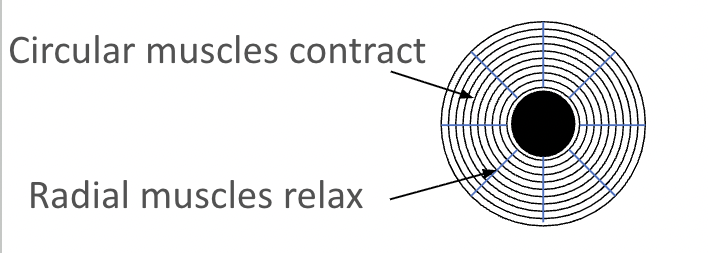
What happens to the radial and circular muscles in dim light?
Circular muscles relax.
Radial muscles contract.
Pupils dilate.
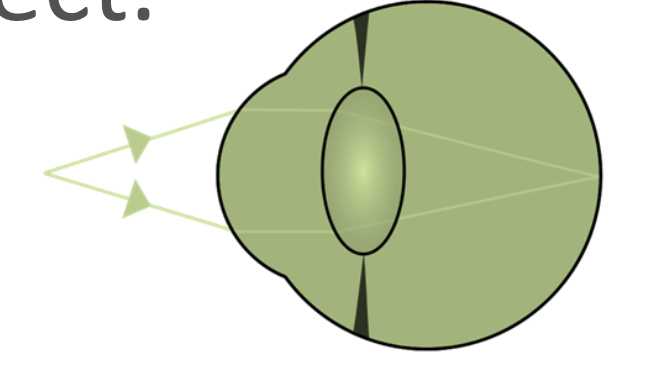
What is accommodation?
Focusing on near or distant objects.
The lens has to change shape.
Controlled by the ciliary muscles and the suspensory ligaments.
What happens to the ciliary muscles and suspensory ligaments when focusing on a near object?
Ciliary muscles contract.
Suspensory ligaments slacken.
Lens becomes fatter.
This is to refract light stronger.
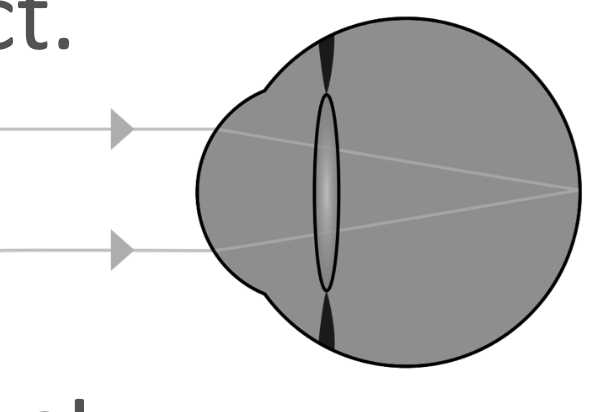
Wide angel rays
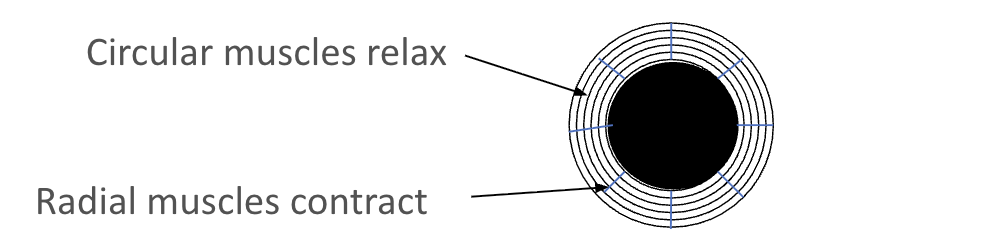
What happens to the ciliary muscles and suspensory ligaments when focusing on a distant object?
Ciliary muscles relax.
Suspensory ligaments tighten.
Lens is pulled thin.
This is to refract light weakly.
Almost parallel rays.