Parts/functions of the cell and cell signaling/Structure of life
1/157
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
158 Terms
Eukaryotic cells
larger
contains DNA in nucleus
name means true nucleus
contains organelles
Prokaryotic cells
smaller
DNA is loose
name means before nucleus
no organelles
Similarities between eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells
cytoplasm
plasma membrane
Why would a cell want to have a higher surface area to volume ratio?
It’s faster to get things in and out of the plasma membrane
Which would have a higher surface area to volume ratio?
prokaryotic cell
eukaryotic
they are probably equal
prokaryotic cell
Cytoplasm
interior of the cell
filled with jelly-like cytosol
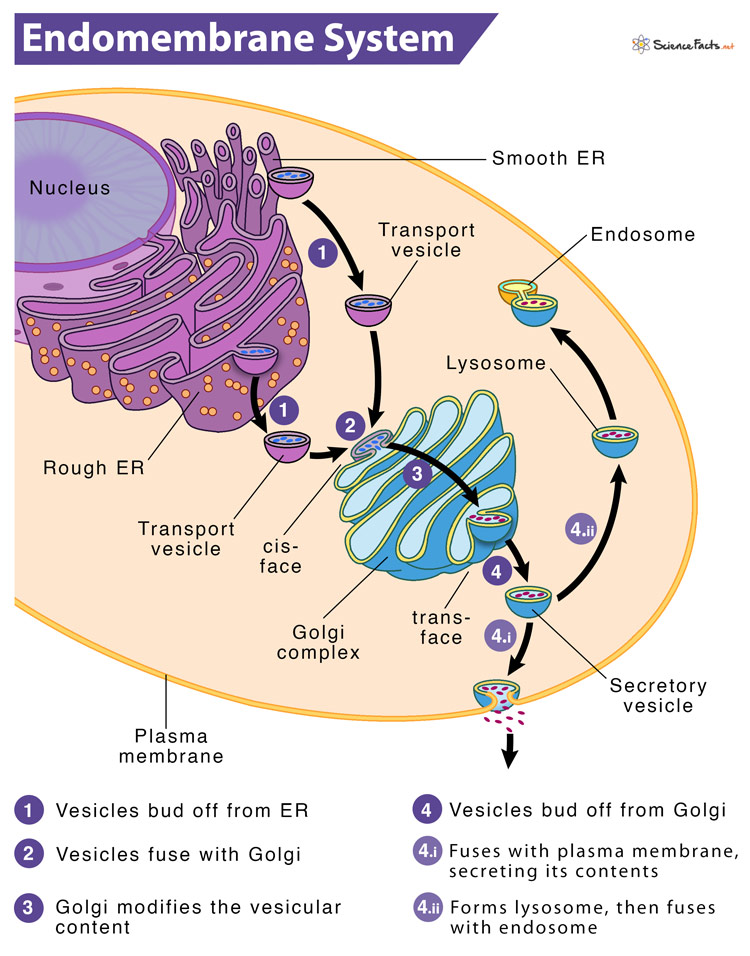
Endomembrane system
continuous with the nuclear envelope
intracellular network of membranes
What does the Endomembrane consist of?
nuclear envelope
endoplasmic reticulum
golgi apparatus
vesicles
Vesicles
little pouches of plasma membrane
functions
pinch off and float around to carry things
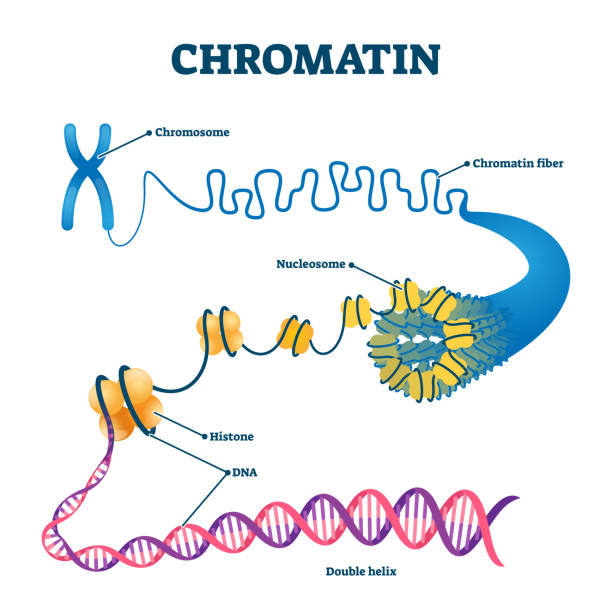
Chromatin
loosely wound DNA
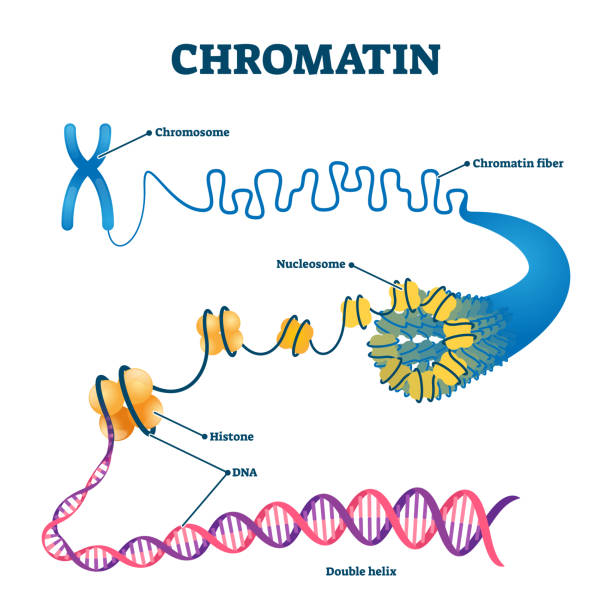
Chromosome
tightly wound DNA
Nuclear Envelope
barrier that separates the contents of the nucleus from the cytosol
Nucleolus
makes ribosomal subunits from proteins and rRNA (ribosomal RNA)
Nuclear Pore
very small opening for small molecules to pass in and out of the nucleus
Ribosome
made of rRNA and protein
facilitates turning mRNA into protein
not membrane bound so they are also found in prokaryotes
What is the main process that occurs in the nucleus?
houses the DNA
copies DNA
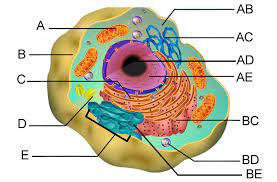
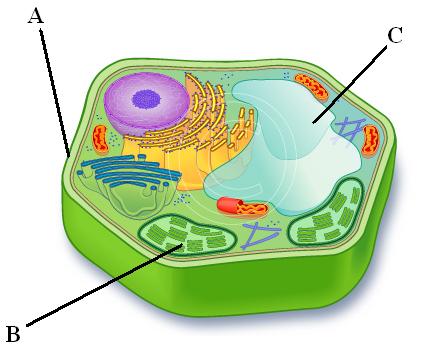
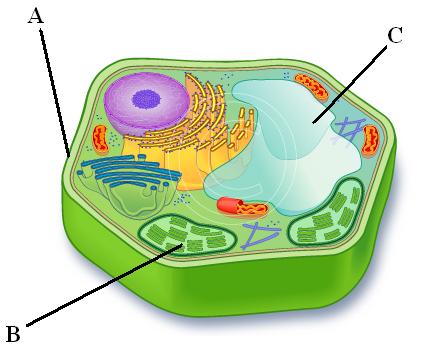
Endoplasmic Reticulum (C & BC)
Network of membranous sacs and tubules
cisternae
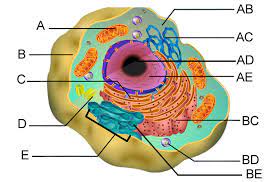
Smooth ER (C)
lipid synthesis
detox
calcium storage
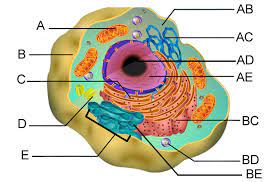
Rough ER (BC)
factory for protein creation (has lots of ribosomes)
manufactures membrane
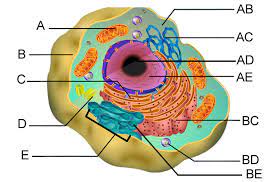
Golgi apparatus (E)
shipping and receiving
can also manufacture polysaccharides
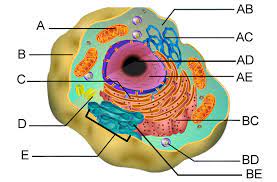
Lysosomes (BD)
Sacs of digestive enzymes
What is phagocytosis?
Cell eating
What is autophagy?
self eating
helps recycle cell components
Vacuoles (C)
large vesicle
big compartment
nucleus
endoplasmic reticulum
vesicles
golgi apparatus
vesicles
Which order of organelles would you expect a protein to be involved with during its production until it’s ready to do its job (from instruction to final product)?
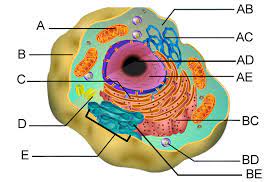
Mitochondria (A)
powerhouse of the cell
harness energy
cellular respiration
uses oxygen + fuel from food = ATP
Chloroplasts (B)
harness energy from the sun to synthesize carbohydrates
only found in plants
contains chlorophyll (green pigment)
What is the endosymbiont theory?
Theory that the mitochondria and chloroplasts were the primitive cells engulfed and developed into the cells we see today.
Evidence
double membraned unlike other organelles
they have their own DNA
main DNA in nucleus carries vast bulk of the cell info
Mitochondria and chloroplasts have their own DNA
Endosymbiont theory is supported by which of the following?
Mitochondria and chloroplasts have their own DNA
Mitochondria can consume other organelles
Thylakoids have smaller mitochondria inside them
The cell wall of plants had to arise to keep engulfed organisms inside
All of the above
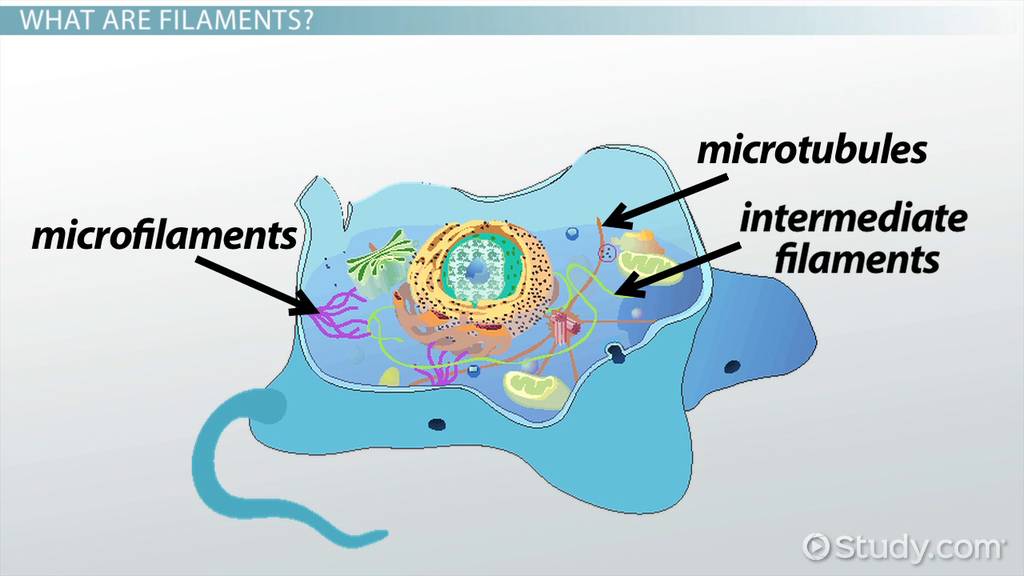
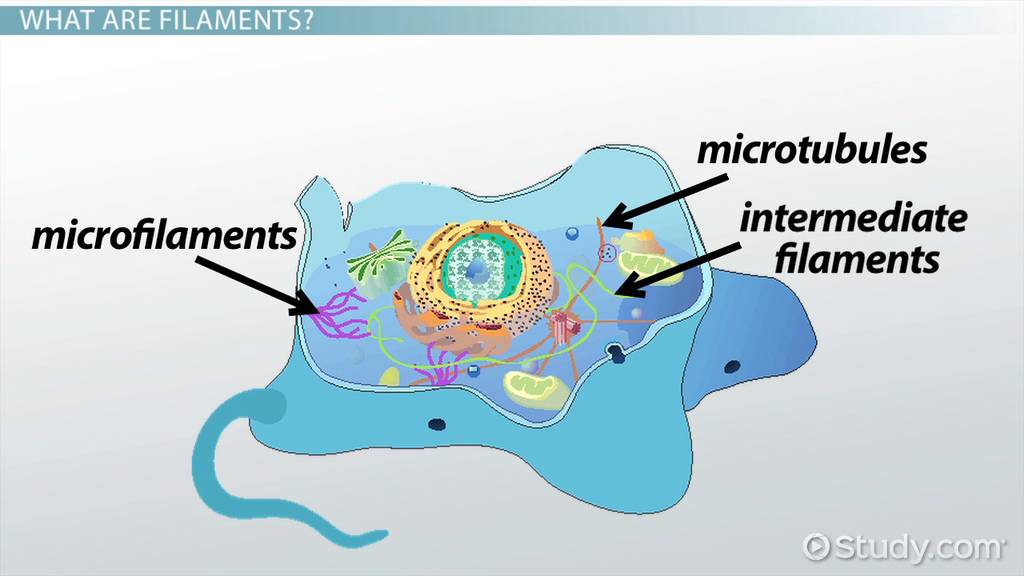
Cytoskeleton
internal scaffolding and movement
microtubules
intermediate filaments
microfilaments
What are the 3 types of components in the cytoskeleton?
Microtubules
hollow
made of tubulin (protein)
important in movement and structure
can be “tracks” for motor proteins
some originate from centrosome (not all … come from centrosomes)
separate the chromosomes during cell dividing
control the movement of cilia and flagella
What are the functions of microtubules?
Flagella: long undulating tail
Cilia: lots and lots of shorter mini-oars
What are flagella and cilia?
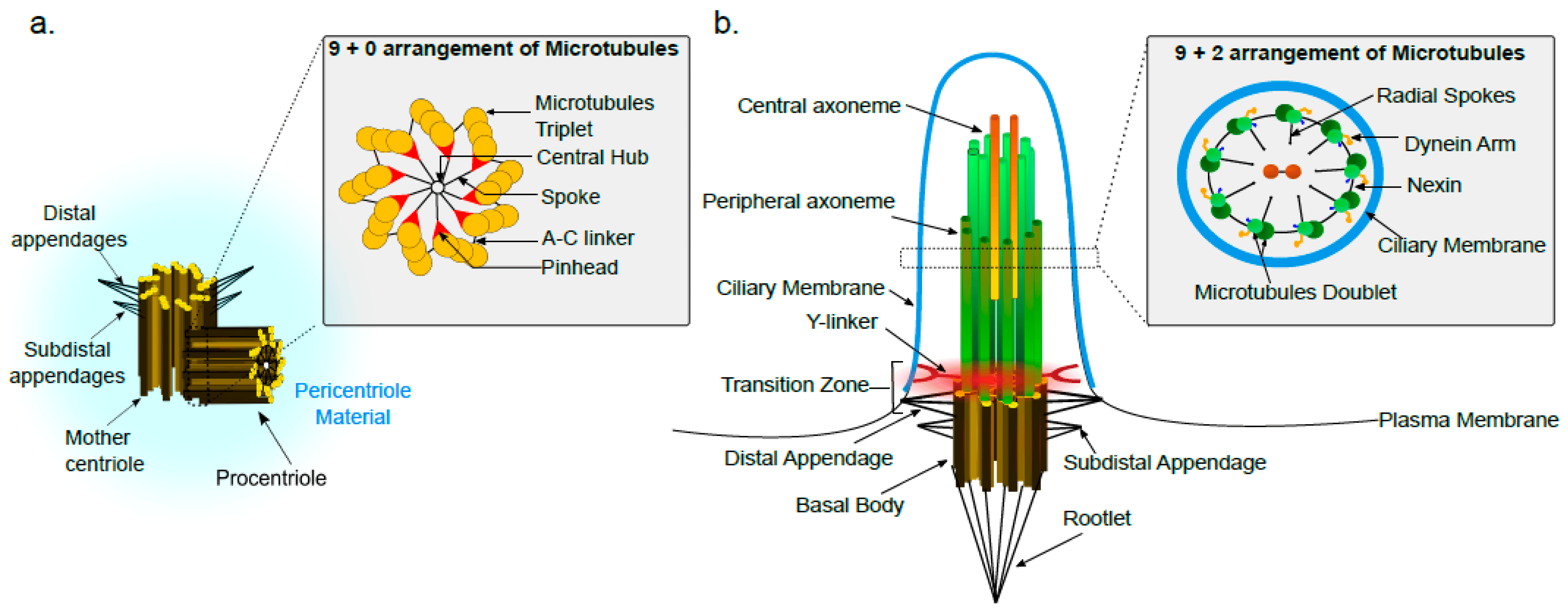
9+3 basal body
9+2 extended portion
How are microtubules arranged?
Intermediate filaments
twisted fibrous proteins (can be several types of proteins
function - anchor (holds things) and structure
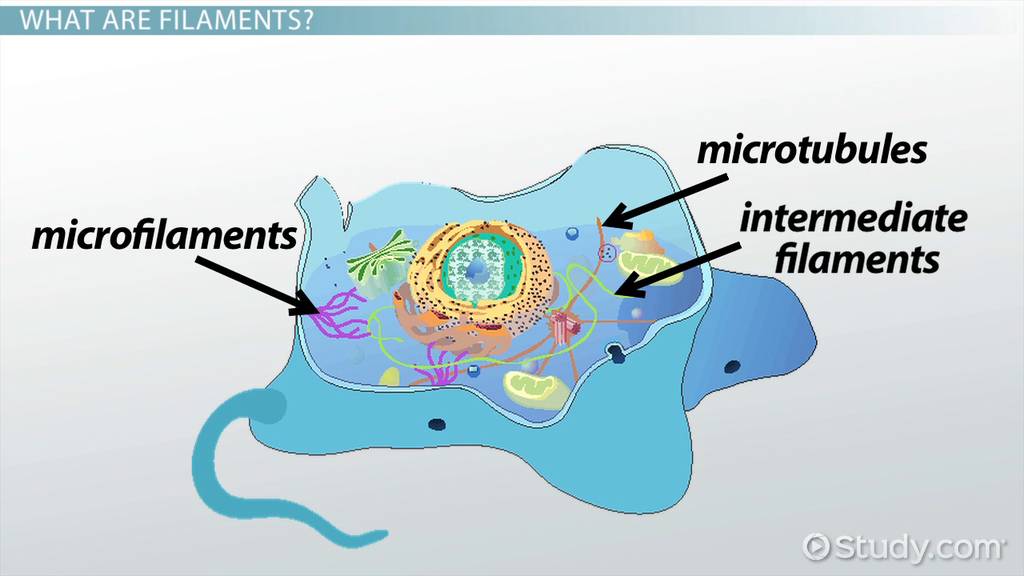
Microfilaments
made of actin (protein)
functions: muscle contraction, cytoplasmic streaming, cell shape
microtubules
If a drug disrupts the ability of the cell to move chromosomes during cell division, which structure would it likely be targeting?
What do plants and prokaryotes have that animal cells don’t?
cell wall
made out of cellulose
sturdy
standing upright because it has enough water
What is turgor?
bent over structure
happens because it lost too much water
What is wilting?
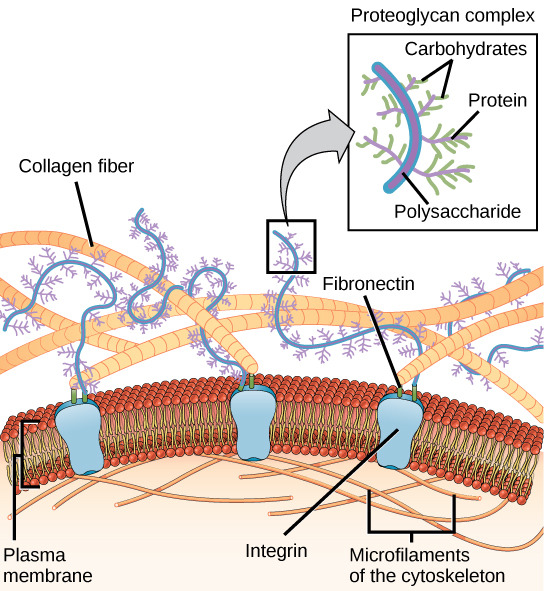
Extracellular matrix
in animal cells
complex protein and carbohydrates outside of the cell
tight junction
desmosome
gap
plasmodesmata (only in plants)
What are the 4 types of junctions?
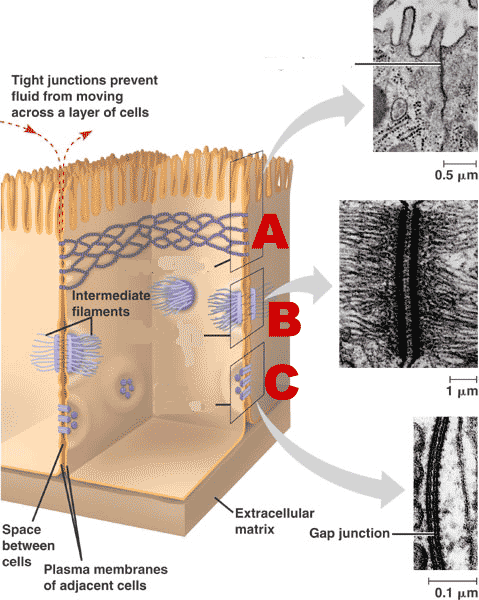
prevents cells from leaking (cell to cell)
A
What are tight junctions?
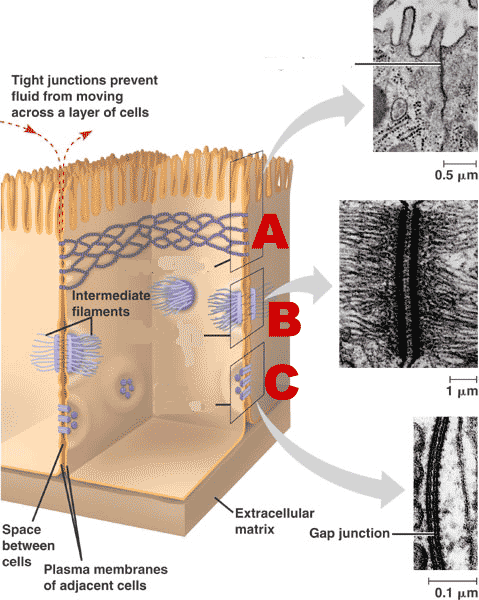
rivets
acts as molecular velcro
prevents cells from ripping apart
B
What is desmosome?
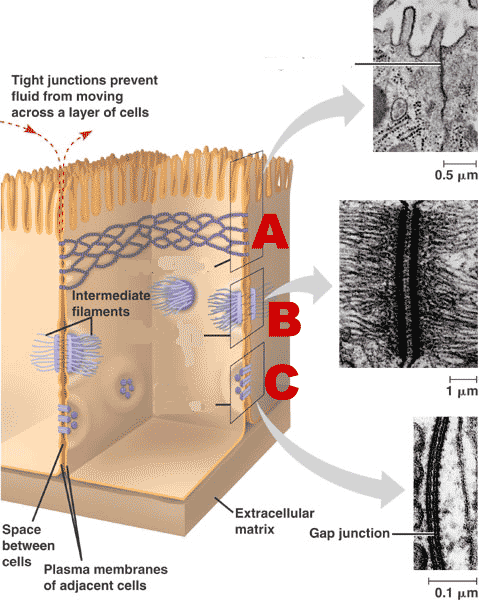
channel
facilitates fast communication
C
What are gap junctions?
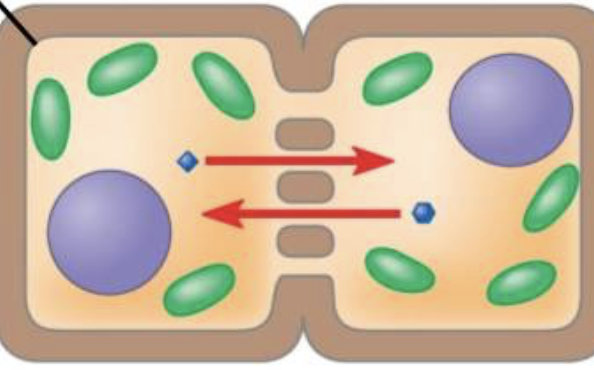
cell wall channels for plants
cytosol, water, and ions pass through
What is plasmodesmata?
gap junctions and desmosomes
Which types of cell junctions would you expect to find in a tissue that undergoes both high mechanical stress and needs to facilitate rapid, coordinated signaling?
Plasma membrane
separates intracellular from extracellular
selective permeable (blocks some movement and facilitates others with channels & receptors)
allows control
Membrane proteins
allows communication with extracellular environment
most specialized membrane functions
some tethered to intracellular structures
Integral: embedded
Peripheral: loosely bounded
What are the 2 types of membrane proteins?
transport channels
receptors for signal transduction
cytoskeleton attachment
enzymatic activity
intercellular attachment (cellular adhesion molecules)
cell-cell recognition
What are the 6 membrane protein functions?
Amphipathic
What is the word for something that is part hydrophilic and part hydrophobic (phospholipids)?
the polar heads face the interior and exterior of the cell with the tails forming the center of the membrane
Phospholipids orient themselves in aqueous solution such that _____.
it reduces fluidity at moderate temperatures
at cold temperatures it hinders solidification
What does cholesterol do when it’s in the membrane?
an ice dwelling fish
The plasma membrane shouldn’t be too rigid or too fluid. The cold would make the membrane solidify, but with more cholesterol it would make the membrane more fluid and offset the cold.
Which would have higher unsaturated fatty acids in its plasma membrane and why?
primary
secondary (co-transporters)
vesicular
exocytosis
endocytosis
phagocytosis (cell eating)
pinocytosis (drinking)
receptor-mediated endocytosis
What are types of active transport?
diffusion
simple
facilitated
carrier mediated
channel mediated
aquaporins - part of osmosis
What are types of passive transport?
substances will move until they are equally distributed with no energy required
What is diffusion?
From high to low concentration
How does the solute move in simple diffusion?
Osmolarity
concentration metric
# of molecules per volume fluid
Osmosis
movement of H2O to equalize the osmolarity
if a solute can’t pass, and water can, water will move across
Tonicity
ability of solution to alter cell’s water volume

Hypertonic
more solutes in a solution than cell
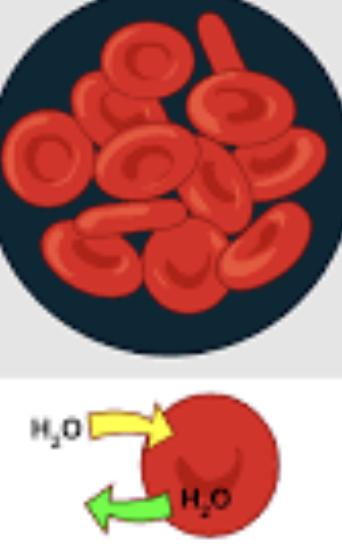
Isotonic
same solutes in solution as cell

Hypotonic
less solutes in solution than cell
Aquaporins
a channel specifically for H2O
speeds up the movement of H2O
Channel mediated diffusion
channel for molecules (specific to charge & size)
ion gated (ion has to be bounded for it to open)
voltage gated (closed until right electric voltage hits it)
Carrier mediated diffusion
physically moves large molecules
gain; osmosis
A red blood cell placed into a container of distilled water (that has, no solute molecules) will ____ water via _____
Primary transport only carry substances against the concentration gradient.
In secondary transport, primary transport goes against making the concentration change.
As a result, certain substances can diffuse down the concentration gradient.
What is the difference between primary and secondary transport?
Primary transport example
sodium-potassium pump
active transport
Is primary and secondary transport active or passive?
Secondary transport example
sodium-glucose cotransporter
They are signals that travel short distances to initiate a response.
gap junctions
cell-cell recognition
paracine: local regulator (synaptic)
What is local signaling?
Signals that travel through your entire body or more than half of your body to initiate a response.
endocrine
nervous tissue
What is long distance signaling?
nervous systems
Which of the following involves both electrical and chemical signals?
a. paracrine signals
b. local regulators
c. nervous systems
d. endocrine
reception
transduction
response
What are the 3 stages of cell signaling?
Reception
recognizing the signaling molecule
Transduction
covering the signal into a form that can trigger a cellular response
often involves relay molecules
Response
finally triggers the specific activity
Ex: breaks down glycogen or activates a specific gene
Plasma membrane receptors
Intracellular receptors
What are the 2 options for receptors?
a signaling molecule that binds specifically to another molecule
What is a ligand?
G-protein coupled receptor
ligand gated ion channel
What are examples of plasma membrane receptors?
utilizes a transmembrane receptor
binds GTP (energy shuttle molecule similar to ATP)
activates another enzyme
What does a G-protein coupled receptor do?
channel only opens when a specific ligand binds
allows movement of molecules that may trigger an intracellular response
What does a ligand gated ion channel do?
lipid soluble signals that can diffuse through the plasma membrane
steroids
What are intracellular receptors?
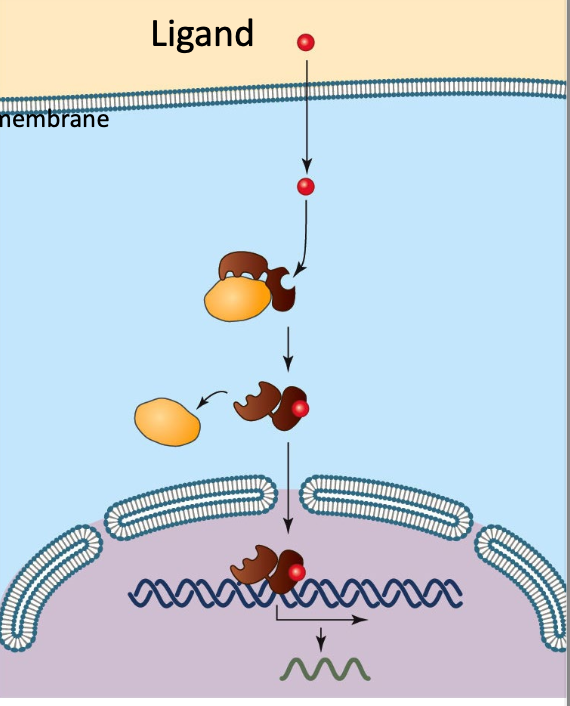
c. intracellular, because the receptor is located within the cell
The figure represents which of the following types of receptor and how do you know?
a. intracellular, because the signal is getting inside the cell
b. ligand gated ion channel because ligands are binding
c. intracellular, because the receptor is located within the cell
d. G-protein, because GTP is dropped off inside the cell
protein kinase
protein phosphatase
What are the two actions in the phosphorylation cascade?
It’s when a phosphate group is transferred, then it phosphorylates, and that activates a response.
What is protein kinase?
It’s when a phosphate group is removed and the response is deactivated
What is a protein phosphatase?
Amplification
What does transduction (phosphorylation cascade) result in?
e. both c and d
Where would you expect to find second messengers during signal transduction?
a. in the extracellular matrix
b. attached to DNA
c. in the transduction phase
d. activating protein kinases
e. both c and d
d. estrogen binds to specific receptors inside many kinds of cells, each of which has different response to its binding
At puberty, an adolescent female body changes in both structure and function of several organ systems, primarily under the influence of changing concentrations of estrogens and other steroid hormones. How can one hormone, such as estrogen, mediate so many effects?
a. estrogen is produced in high concentrations by a large number of different cell types
b. estrogen binds to common receptors inside several cell types, and each cell responds in the same way to its binding
c. estrogen does not affect cells that lack estrogen receptors in the cell membrane
d. estrogen binds to specific receptors inside many kinds of cells, each of which has different response to its binding
all chemical reactions in an organism
What is metabolism?
build up
ex: dehydration reaction
What is an anabolic reaction?
break down
ex: hydrolysis
What is a catabolic reaction?
motion energy
What is kinetic energy?
kinetic energy associated with random movement of atoms or molecules
ex: heat
What is thermal energy?
energy that matter possesses because of their location or structure
What is potential energy?