Year 9 Chemistry End Of Year Assessment (Purity, Formulations & Chromatography, Global Reserves & Potable Water 1-28, Life Cycle Analysis & Recycling and Using Materials 27-41)
1/87
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Imported From Save My Exams
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
88 Terms
What is a pure substance?
A pure substance is a single element or compound that contains no other substances.
What is the difference between a pure substance and a mixture?
A pure substance consists of only one substance (an element or a compound), while a mixture contains two or more different substances not chemically combined.
True or False? Salt dissolved in water is a pure substance.
False. A solution of salt dissolved in water is a mixture.
State what is meant by the term melting point.
The melting point is the temperature at which a solid turns into a liquid.
What is a boiling point?
The boiling point is the temperature at which a liquid turns into a gas.
What property can be used to distinguish a pure substance from a mixture?
Melting point and boiling point can be used to distinguish a pure substance from a mixture.
True or False? Pure substances have a range of melting and boiling points.
False. Pure substances have sharp, specific melting and boiling points, while mixtures have a range.
How can melting and boiling points distinguish between pure substances and mixtures?
Pure substances have specific and sharp melting and boiling points, while mixtures have a range.
Define a formulation.
A formulation is a mixture designed as a useful product.
Give an example of a formulation.
Examples include fuels, cleaning agents, paints, medicines, alloys, fertilisers, and foods.
True or False? Many products are complex mixtures in which each chemical has a particular purpose.
True. Many products are mixtures where each chemical serves a specific function.
How is a formulation made?
By mixing components in carefully measured quantities to ensure desired properties.
True or False? Formulations are compounds.
False. Formulations are mixtures.
What is paper chromatography used for?
To separate substances with different solubilities in a solvent and identify components of a mixture.
What does a single spot on a chromatogram indicate?
That the substance is pure.
What should the base line on a chromatogram be drawn with?
A pencil.
True or False? The solvent level should start above the pencil line on a chromatogram.
False. The solvent should not start above the line to avoid ruining the chromatogram.
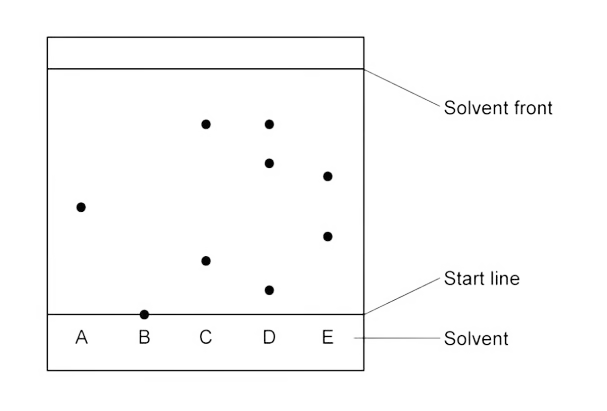
How many substances are in sample D?
There are 3 substances in D.
True or False? Multiple spots on a chromatogram indicate a pure substance.
False. Multiple spots indicate a mixture.
True or False? If two substances are the same, they will produce identical chromatograms.
True. Identical substances yield identical chromatograms.
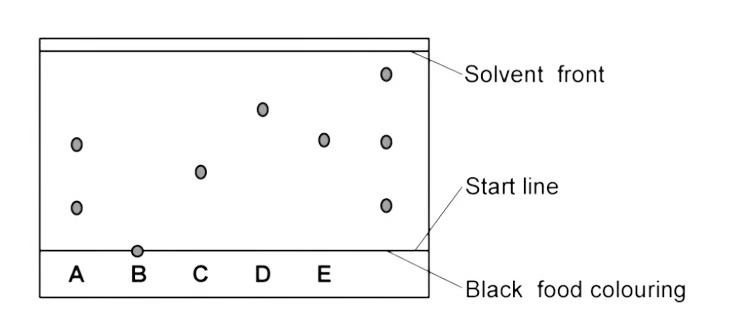
Which colours from A–E does black food colouring contain?
It contains A, E and an unknown.
Why should the baseline in chromatography be drawn in pencil?
Because pencil won't contaminate or run, unlike ink.
State the equation to calculate the retention factor (Rf value).
Rf = distance travelled by sample ÷ distance travelled by solvent front.
What does an Rf value closer to 1 indicate?
That the component is highly soluble in the solvent used.
True or False? The Rf value of a compound is always the same, regardless of the solvent used.
False. Rf value depends on the solvent used.
What is the purpose of calculating Rf values in paper chromatography?
To help chemists identify unknown substances.
Why does an Rf value have no units?
Because it is a ratio.
What does the Rf value range between?
Between 0 and 1.
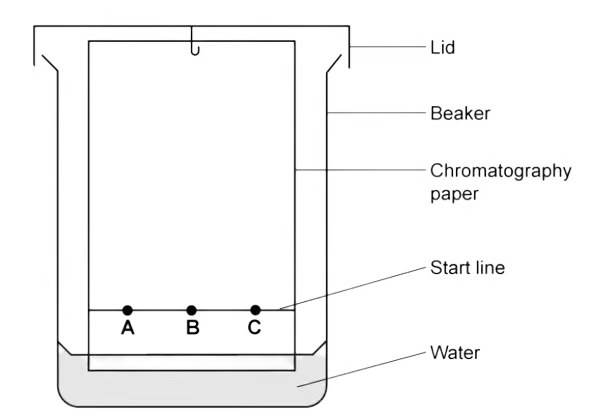
Identify the mobile and stationary phase in chromatography.
Mobile = water; Stationary = chromatography paper.
True or False? If two substances are the same, they will produce identical chromatograms.
True. Identical substances give identical chromatograms.