Protostomes
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/47
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
48 Terms
1
New cards
Protosomes
large group of bilaterally symmetrical animals
2
New cards
Protosome
initial invagination (blastopore) becomes mouth in formation of gut
3
New cards
Bilateria
bilaterally symmetrical triploblasts. Many appear in Cambrian explosion
4
New cards
Invertebrate bilaterates
95% of animal species
5
New cards
Ecdysozoans
synapomorphy: extracellular protective exoskeleton (hard) or cuticle (soft). Must molt for growth (Ecdysis)
6
New cards
Roundworms (Phylum Nematoda)
unsegmented. psuedocoelomates. complete digestive tract. hydrostatic skeleton. longitudinal muscles only. cuticle with collagen. gas exchange through body wall
7
New cards
Nematoda
mostly free living, some parasitic in humans (Ascaris).
8
New cards
Arthropoda
Features:
segmented bodies organized in regions called tagmata.
exoskeleton made of chitin. allows for muscle attachment.
segmented bodies organized in regions called tagmata.
exoskeleton made of chitin. allows for muscle attachment.
9
New cards
Exoskeleton allows for
muscle attachment. protect from predation and desiccation. in crustaceans strengthened by CaCo3
10
New cards
Paired, jointed appendages
enable movement of rigid body (“jointed foot”)
11
New cards
Physiology of Arthropoda
coelomates
open circulatory system
complete digestive tract
complex mouthparts for food
open circulatory system
complete digestive tract
complex mouthparts for food
12
New cards
Land adaptations of protostomes
Live in moist soils/habitats. Gills/lungs inside body. waxy layer on body surface (cuticle), (insects).
without skeleton limited in size
without skeleton limited in size
13
New cards
Challenges of living on land
Desiccation of body
Respiratory gas membranes must be moist
Supporting the body without water.
Respiratory gas membranes must be moist
Supporting the body without water.
14
New cards
Modular body plans
small set of elements used to create a body. can be rearranged in different ways to create a body. by changing expression of existing genes
15
New cards
Genetic toolkit
share common toolkit of genes, especially genes responsible for development. differential gene expression
16
New cards
Lophophore
ciliated feeding structure. ex. barnacle foot
17
New cards
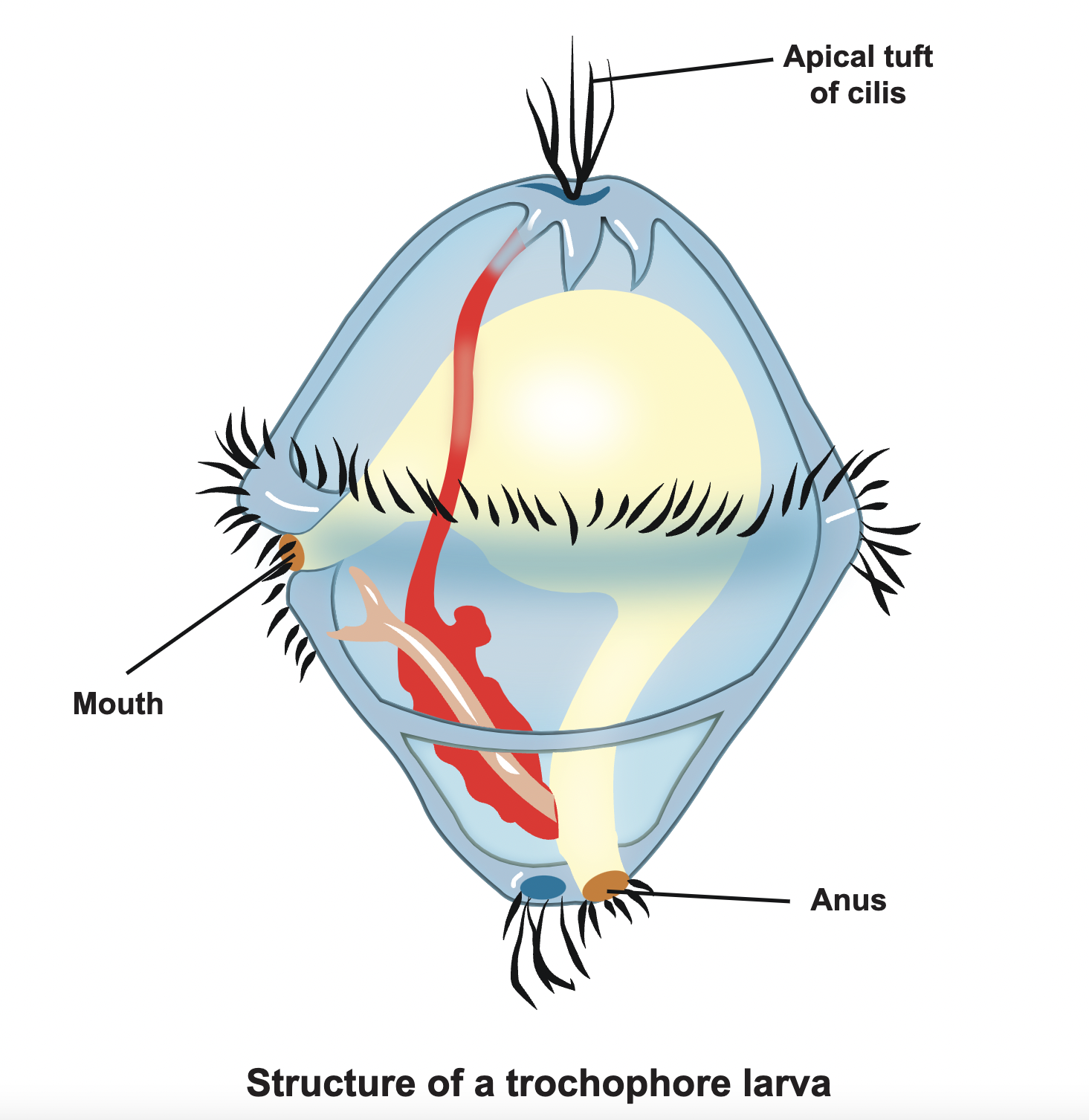
Trochophore
ciliated larval stage
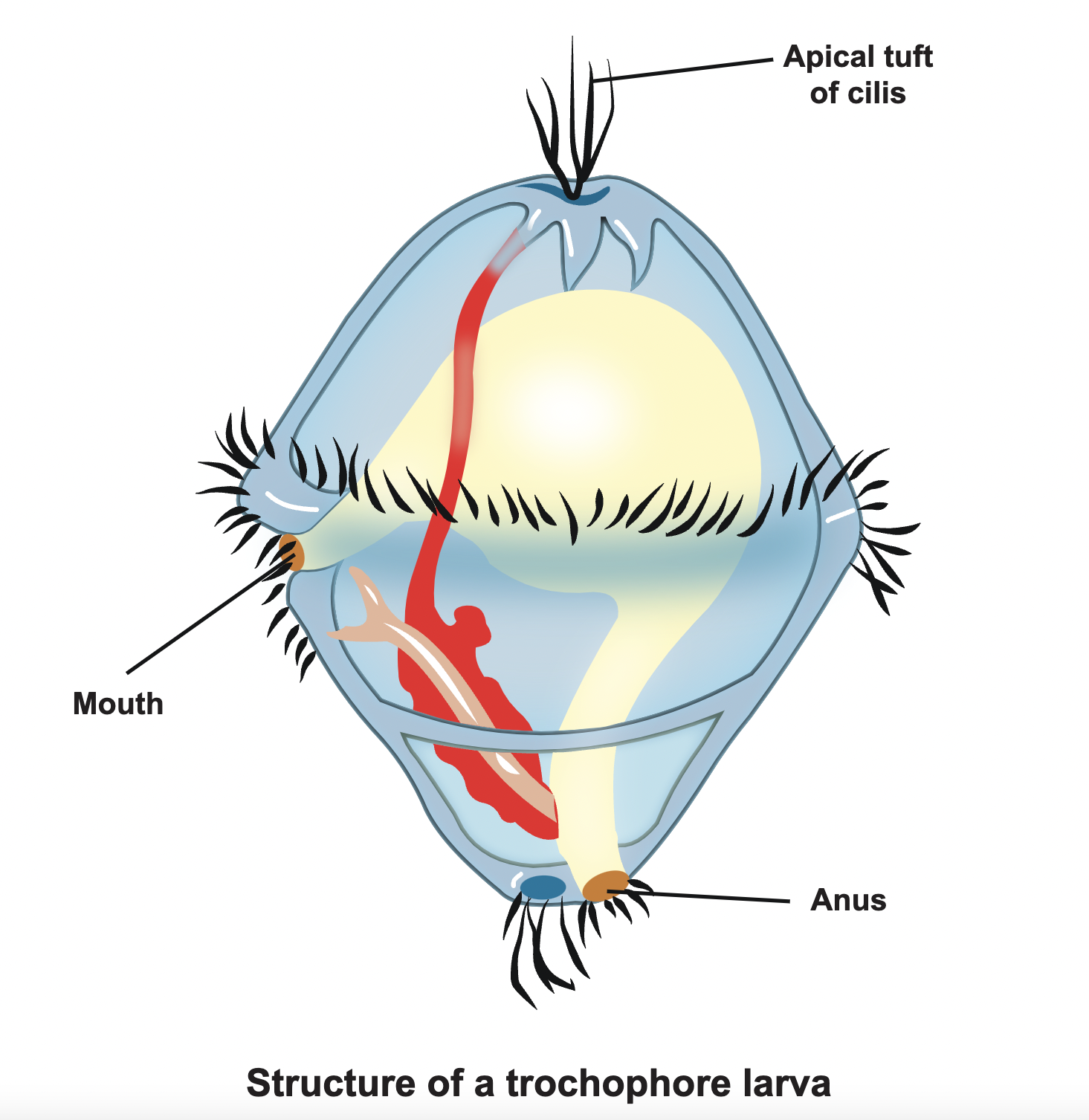
18
New cards
Lophotrochozoa
includes phylums Mollusca, Platyhelminthes, and Annelida. no molting and grow incrementally.
19
New cards
Phylum Platyhelminthes
flatworms (flukes, turbellarians, tapeworms)
flattened body plan to allow gas exchange
gastrovascular cavity
acoelomates (no body cavity)
flattened body plan to allow gas exchange
gastrovascular cavity
acoelomates (no body cavity)
20
New cards
Which phylum contains acoelomates?
Platyhelminthes
21
New cards
Which phylums have incomplete digestive tracts?
Platyhelminthes and Cnidarians
22
New cards
Phylum Annelida (Lophotrochozoa)
earthworms + relatives, marine annelids (free-living), and leeches (ectoparasites)
23
New cards
Phylum Mollusca (Lophotrochozoa)
coelomates (greatly reduced coelom)
Foot, visceral mass and mantle specialized modular body plan
Foot, visceral mass and mantle specialized modular body plan
24
New cards
Foot
large muscle at base of clam
25
New cards
Visceral mass
houses internal organs, digestive, reproductive and excretory organs in mollusks
26
New cards
Mantle
secrete shell.
27
New cards
Radula
rasp-like tongue
28
New cards
Mollusks have
open circulatory system and a complete digestive tract
29
New cards
Class Bivalvia
clams, mussels, scallops and oysters. 2 hinged valves form shell. foot is digging organ. and they are filter feeders
30
New cards
Class Gastropoda
snails slugs and relatives. most have one part shells or none
31
New cards
Class Cephalopoda
squids, octopuses, chambered nautilus, and cuttlefish
foot = tentacles
no or reduced shell
closed circulatory system
complex camera eyes.
foot = tentacles
no or reduced shell
closed circulatory system
complex camera eyes.
32
New cards
Tardigrada
tardigrades. segmented bodies and limbs. can withstand hot and cold, extreme pressure and low O2
33
New cards
Onychophorans
velvet worms sister taxa to arthropods.
34
New cards
Class Chilopoda (Arthropoda>Myriapoda)
carnivorous. one pair of legs per segment (two legs in a segment). has venomous claws/fangs
35
New cards
Class Diplopoda ( Arthropoda>Myriapoda)
detritivores. two pairs of legs per segment (four legs in a segment)
36
New cards
Subphylum Chelicerata
chelicerae (appendages) can be used in feeding, defense, sensory reception etc. four pairs walking legs, and one pair of pedipalps
37
New cards
Class Arachnida (Arthropoda>Chelicerata)
spiders, ticks, mites and scorpions. two major tagmata, Cephalothorax and abdomen. fang tipped chelicerae, some are predators and some ectoparasites
38
New cards
Which arthropod classes have a cephalothorax and abdomen?
Arachnida and Crustaceans
39
New cards
Subphylum Pancrustacea
insects + crustaceans
40
New cards
Crustaceans (Arthropoda>Pancrustacea)
mostly aquatic, land example pillbug. major component of zooplankton (ex. copepods and naupilus larva)
41
New cards
Crustacean body
2 pairs of antennae. biramous (branched) appendages, two tagmata: cephalothorax and abdomen. reinforced exoskeleton of CaCO3, like with barnacles
42
New cards
Insecta (Arthropoda>Pancrustacea)
most can fly. head, thorax and abdomen. 1 pair of antennae (head)
1 pair of mandibles (head)
3 pairs of walking legs (thorax)
1-2 pairs of wings. (thorax)
1 pair of mandibles (head)
3 pairs of walking legs (thorax)
1-2 pairs of wings. (thorax)
43
New cards
What class has a head, thorax and abdomen as its tagmata?
Insecta.
44
New cards
Metamorphosis
morphological transformation from larva to adult
45
New cards
Hemimetabolous insects
incomplete metamorphosis. egg>nymph>adult
46
New cards
Holometabolus insects
complete metamorphosis. egg>larva>pupa>adult
47
New cards
Lepidopterans
complete metamorphosis. moths and butterflies. larva resemble bird droppings
48
New cards
Hymenopterans
ants, bees and wasps. highly social insects. undergo complete metamorphosis