Chapter 25
1/68
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
69 Terms
For long term memory what must be done
permanent synaptic modification
What is memory acquisition
initial stage of memory where information is encoded in the brain
How does memory acquisition happen
we alter neural firing patterns, this is for temporary memory
What is memory consildation
temporary synaptic modifications that are made permanenet
What must be done for memory consolidation
New gene expression and protein synthesis
How do we keep a facial memory
neurons in area IT become more selective over more exposure
How do neurons become more selective in area IT
They are stimulus selective and they make different firing pattern for each face
Does one neuron in area IT tells us a face
no
How do multiple neurons tell us a face in area IT
We have a distributed pattern of activity that there is a ratio of neuron firing, rate
if neuron 1,2,3 fire at medium, large, and small it mark
if neuron 1,2,3 fire at small, medium, and large, it is Mohab
Why is distributed patterns important in firing cells
that if one neuron dies that the other neurons can still create that memory
but memory does degrade not loss
What is the neural network model
memory is encoded in the pattern of activity across many neurons
What invertebrate was used to study memory
Aplysia
How does sensitization of withdrawal reflex work in aplysia
a shock is given to the tail, it activates the sertonin modulatory neuron, it synapse on sensory neuron
Sensory neuron stimulating cAMP and activates PKA in axon terminal
What does PKA do in the sensory neuron
makes the sensory neuron release more glutmate onto the motor neuron
How does long term sensization happen in the Aplysia
more PKA activation results in gene expression and protein synthesis, this happens in the presynaptic neuron
How is short-term memory altered
different patterns of synaptic transmission
Hippocampus receives input from what
Entorhinal cortex
What is the pathway from entorhinal cortex to the hippocampus
Perforent Path→Mossy fiber synapse→ Schaffer collateral synapse
What is the perforent path
Entorhinal cortex→dentate gyrus
What is mossy fiber synapse
Dentate gyrus→CA3
What is Schaffer collateral synapse
CA3→CA1
Does LTP and LTD happen in the hippocampus
yes
What did Bliss and Lomo figure out
high frequency electricau stimulation of excitatory pathway produces LTP in awake rats
this was the Perforent Path
LTP + LTD Schaffer Collateral
How long does LTP lasts
1 year
Is LTP input specific
yes, it gives LTP to the neurons that was fired
What is the key to LTP
activation of NMDA receptors
How are NMDA receptors stimulated
via glutamate which binds to AMPA also and then depolarizes the membrane to release the Mg+2 block and allow for NMDA receptors to open which allows Ca+2 to come in
What is spike timing dependent plasticity
the strength of synaptic connections between neurons is modified based on the timing of their action potentials
What does Ca+2 do when it enters via NMDA receptor
Activates Protein Kinase C and CamKII
What does a Kinase do in general
phosphorylates things
How is AMPA receptor affected by PKC and CaMKII
AMPA gets phosphorylated on the cell membrane
What does CaMKII do
it increases the amount of AMPA receptor on the cell surface
Why do postsynaptic neuron extend to presynaptic neuron
due to presence of new AMPA receptor
If LTP happens what else must happen
LTD
How does the brain determine whether we have a LTD or LTP in the HIPPOCAMPUS
LTD is due to weak depolarizes due to an input
LTP is due to strong depolarizes due to an input
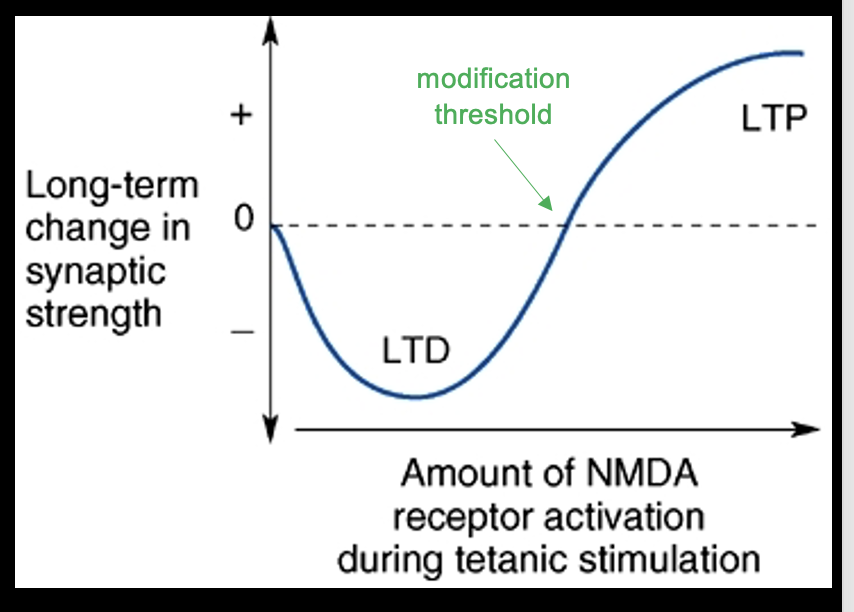
(this is called the sliding modification threshold)
What happens if the depolarization is neither weak or strong
We don’t get an LTD or LTP
is LTD calcium dependent
yes
How does LOW Ca+2 cause LTD
Low Ca+2 activates protein phosphatase which de-phosphorlaytes AMPA receptor and other postsynaptic protein
Fun fact about AMPA receptors
½ of AMPA receptors turn over every 15 minutes
What is the steady state of AMPA receptors
each AMPA removed is replaced by a new one
What is the steady state after LTP/LTD
Non-GluR1 AMPA receptor is replaced with a new non-GluR1 Ampa receptor
LTP starts with GluR1 receptor which is converted to non-GluR1
What is the side effect of GluR1 knocked out mice
Imparied Hippocampal LTP and cerebellar LTD
What are the 3 types of fibers in the cerebellum
Climbing fiber, parallel fiber, and purkinje cells
What does the Climbing fibers do
They receive excitatory input from medulla and uses it to coordinate planned movement with sensory input
this helps with a wrong movement that u did
What do parallel fibers do
they receive input from cerebellar granule cells, they relay motor commands from the motor cortex to the cerebellum
What do the purkinkje cells do
they are the main cerebellar output
How does LTD take place at the cerebellum
it involved pairing climbing fibers with parallel fibers, such pairing alters the Purkinje cells
LTD in the Cerebellum vs LTP in the hippocampus
they have the same mechanism
It LTP and LTD frequency dependent
yes
What was the mouse box shock expierement
scientists recorded the schaffer collateral synapse of CA1 neuron, before and after the shock, the outcome was that there was highended EPSP of neuron
meaning they learned
What blocks LTP learning in hippocampus
NMDA antagonists
What is the composition of NMDA receptor
two NR1 and two NR2
from the NR2 (we have NR2A and NR2B)
What affects the function of the NMDA receptor
ratio of NR2A and NR2B subunits
Why is sliding modification threshold important
it maintains neuronal stimulus selectivity and memory
because too much LTP would impair learning
How do we get LTP in NMDA receptors
increasing NR2B subunits (which allows more Ca+2)
How do we get LTD in NMDA receptors
increasing NR2A subunits (which allows less Ca+2)
Is phosphorylation and regulation of receptor sub units permanent
No
How does CaMKII work
It’s like a clothpin, one section of regulatory and other region is catalytic, it’s typically seen closed, but it opens when Ca+2 bound calmodulin binds to it, it ecposes the catalytic region,
a large elevation of Ca+2 can result in autophosporylation which makes catalytic region stay on FOREVER!
What is the molecular switch hypothesis
How CamKII work, and how it keeps postsynaptic AMPA receptors phosphorylated which helps in long term memory
What protein is seen in Long term memory Consolidation
Protein Kinase M Zeta
What does Protein Kinase M Zeta do
It’s mRNA form is translated when strongs amount of LTP-induced Ca+2 comes in
The protein phosphorylates other proteins that regulate AMPA receptor insertion
phosprylates it’s own proteins involved in it’s own translation
this happens even in the absence of Ca+2
Why is do people think Protein Kinase M Zeta is seen in memory consoldiation
A PKMZ inhibitor can erase LTP and memories
What does CREB do
help in protein synthesis for long term memory
How does CREB work
CREB-2 binding blocks transcription and new protein synthesis
CREB 1 moves CREB 2 and allows for transcription and new protein synthesis
What is presistence of LTP depended on
whether presynaptic stimulation is stron enough to trigger a new protein syntehsis
How do we get protein synthesis from LTP
an epsp can lasts hours creates protein
What does the new proteins do
it helps with synaptic remodeling, via increasing dendrites
How is LTP kind of not input specfic
When having a weak LTP on one input followed with a strong Input from anohter neuron, it can make proteins to help both synapses out
this has a time frame of 2 hours