Peds Ex 2 Adolescence (2/5) Sandy
1/80
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
81 Terms
This is a period of physical and psychosocial growth that marks the transition from childhood to adulthood
Adolescence
When does Adolescence begin?
This begins with the onset of puberty and the psychological reaction to these developmental changes
When does adolescence end?
preparedness and
opportunity to assume an adult role in
society
Adolescence
A. Comprises nearly ____% the growing period of man
B. Only period of life after birth where ______ of growth increases
C. Period of significant _______ and _______ developmental changes
50
velocity
cognitive and
psychosocial
When one is able to produce children
Puberty
The beginning of the development of secondary sex characteristics
Pubescence
How do we stage physical development in adolescence?
Tanner staging
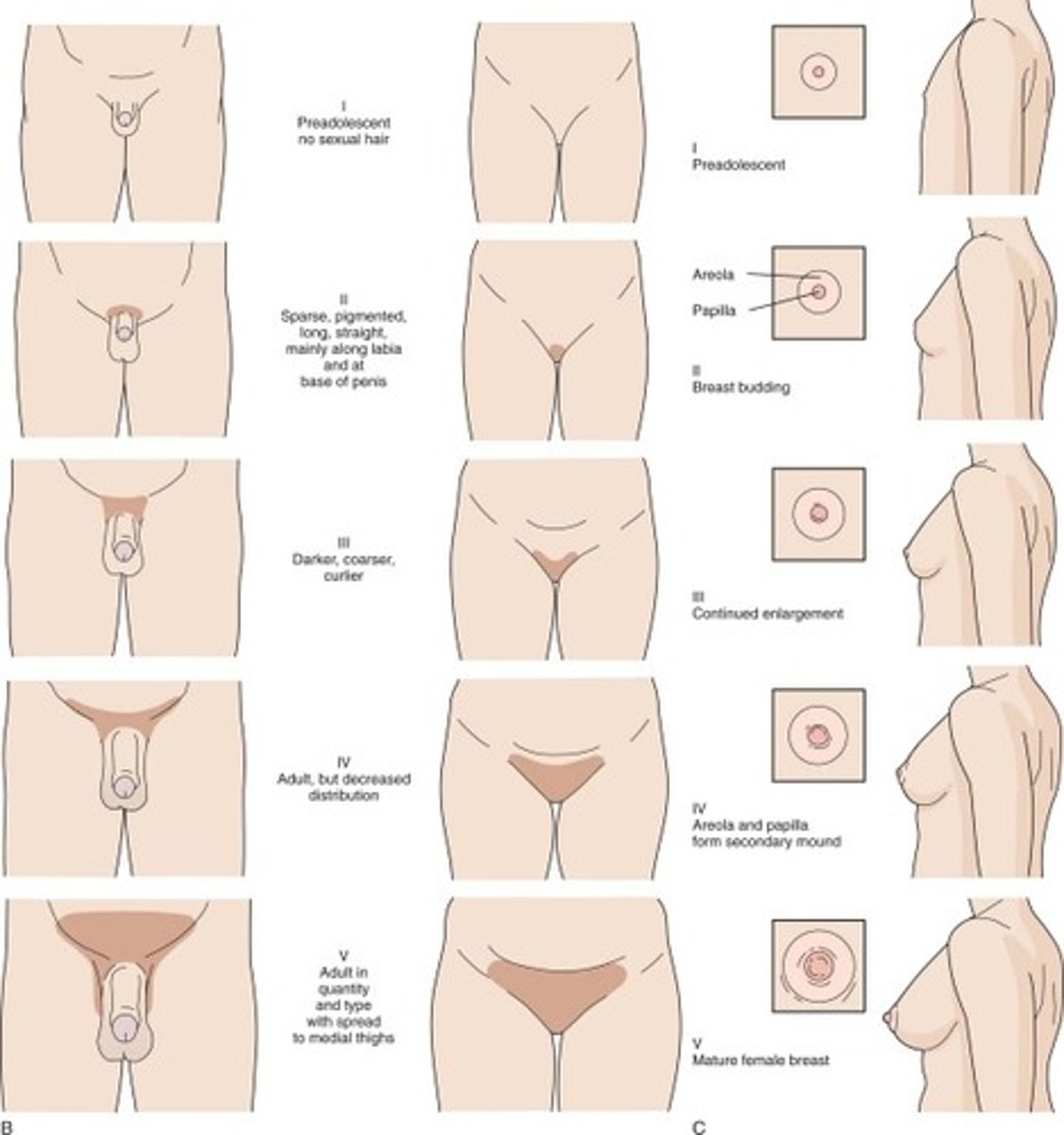
True/False
Males and females go through all the same tanner stages
True
The stages of development in adolescence occur in this period are always in the same sequence but differ in?
1. onset
2. velocity
3. time of completion
In males, rapid growth spurt does not occur until tanner stage _____ and ____
stage 3 and 4
In females, menses will not begin until somewhere around tanner stage ____, before this stage is when they get rapid growth spurt
Stage 4
During adolescence, all organs increase in size except?
Lymphoid tissue (Tonsils begin to shrink)
What are the 6 psychosocial tasks that all children must go through successfully?
1. Emancipation
2. Establish self-identity
3. Establish sexual-identity
4. Prep for future adult role in society (career, self support)
5. Develop a workable value system
6. Verbalize conceptually
Early adolescence (junior high school) begins with ________ and extends to ________
early pubescence at age 11-12
end of pubescence at 14-15
In the stage of adolescence, children....
A. Breakaway from childhood
B. Begin to emancipate from parent, but return for adult protection
C. Rapid swings in behavior/mood
D. Narcissistic and preoccupied with changes in appearance
E. Exaggerate physical complaints
F. Object relationships shifts from parent to other adults (hero worship and crushes, ie: teachers)
G. Sexual exploration in group/same sex activites
H. Feelings of omnipotence
I. Cognitive thinking: concrete → abstract (magical thinking persists)
Early adolescence (junior high school)
What is the first thing in early adolescence ya mother bitches to you about?
Clean ya room
1. When do allowances start?
2. When can you start negotiations with responsibilities and allowance?
1. 5 y.o
2. 9 y.o
How do you negotiate with a child and their allowance?
1. Write it down
2. Both parties sign it
3. Put is on the fridge
True/False
As a parent, you need to be able to negotiate and pick ur battles such as cleaning room
True (no food and give mom laundry)
In the stage of adolescence encompasses the high school years at age 14-18 y.o.
Middle adolescence
In the stage of adolescence, children...
A. Dependence- independence struggles prominent
B. Rebellion and rejections of adults
C. Attempts at autonomy
D. Newly mature physical body is tested- sports and flirting
E. Peer group important- demands allegiance and determines standards of language, dress, behavior
F. Antisocial behavior may be expressed
G. Experimentation is common: various substances, sexual and social behavior (smoking)
H. Omnipotence remains- risk taking is frequent
I. Idealistic thinking and devotion causes
Middle adolescence
In the stage of adolescence, adult status conferred by marriage, parenthood, or full-time employment soon after or even before HS graduation
Late adolescence
In the stage of adolescence, the decision of some to continue their education creates a prolonged transition period
Late adolescence
What are the goals of late adolescence?
1. Emancipation from parents
2. Capable of living away from home
3. Earning at least partial financial support ***
In this stage of adolescence, children...
A. Fairly clear and realistic sense of self as an adult in society. Has defined roles regarding career, family, and community
B. Firmly established a sexual identity and is capable of intimacy and mutuality in a sexual relationship.
Late adolescence
You have not made the transition from late adolescence to adult hood until?
Your family relates to you as an adult
The medical exam for adolescents consists of questions about PACES what is that?
P: Peer and parent related behaviors
A: Accidents, alcohol, abuse of drugs
C: Cigarettes
E: Emotions, eating patterns, exercise
S: School, STIs
1. What are the biggest concerns for adolescence? (in order of frequency)
2. What do they want more information about?
1. School, Drugs , Sex, Parents/family
2. Drugs, Sex education, venereal disease
What questions do you ask when parents comes in and request drug testing?
1. Have you talked to your child about drug use?
2. Why are you concerned about their using drugs? Have you found drugs or paraphernalia?
3. What will you do if the test is positive?
4. What will you do if the test is negative? A negative test does not indicate non-use
5. What do you think I can do?
What are the causes of delayed puberty?
A. Endocrine
B. Metabolic
C. Genetic
D. Psychosocial retardation
E. Constitutional and chronic illness
F. All of the above
F. All of the above
True/False
With delayed puberty, If hx and PE does not indicate there is a problem, you can wait without worrying too much
True
Prepubertal males DO NOT have testosterone production, but do have estrogen, which is why this can develop ______.
gynecomastia
Male gynecomastia is common and it may be UL or B/L. What causes it?
High estrogen (produced in liver)
When does gynecomastia regress?
1-2 years when androgen levels rises
Delayed menarche is aka ?
Primary amenorrhea
Primary amenorrhea:
1. No menses by age ____
2. No menstrual flow _____years after onset of pubescence (develop breast/hair but no period)
3. No menstrual flow ___ year after the age of mother’s age of onset
16
4-5
1
If PE is normal and patient present with primary amenorrhea, what should you r/o?
Anatomic abnormalities
What anatomic abnormalities can cause primary amenorrhea?
1. Imperforate hymen
2. Rokitansky syndrome
What is Rokitansky syndrome?
congenital absence of vagina/uterus
If patient presents with delayed puberty (pubescence) what do you want to r/o
1. Chromosomal
2. Congenital etiologies
What chromosomal abnormalities can cause delayed puberty?
A. Turners syndrome
B. Gonadal dysgenesis
C. Testicular feminization
D. True hermaphroditism (very rare)
A woman (phenotypically female) but genetically male due to the failure of testicular development. Have underdeveloped testes and no ovaries.
Testicular feminization
What is the most common cause for seocndary amenorrhea (start of menses then stop)?
Suppression of pituitary-hypothalamic axis
What is the first thing you want to r/o when patient has secondary amenorrhea?
Pregnancy **
Competitive athletes, weight loss, IBS, anemia, PCOS and malnutrition can cause _______ amenorrhea
secondary
What is the triad for PCOS?
1. Hirsutism
2. Obesity
3. Acne
(Dx should not be made during adolescence)
What is the most common cause for dysfunctional uterine bleeding?
anovulatory cycle
Irregular menses are normal during first 2 years because they are not _________
ovulating
What is the average range of menses after the onset in the first year?
18-83 days in the first year (every 2 weeks or every 3 months)
This type of dysmenorrhea is cause by absence of any specific pelvic pathology
Primary dysmenorrhea

This type of dysmenorrhea can be caused by structural abnormality, FB (ie. IUD), endometriosis or endometritis
Secondary dysmenorrhea

What is the tx for dysmenorrhea? why?
NSAIDs 2-3 days before onset of menses
- Cramps caused by prostaglandins,
What is the problem with eating disorders today?
its occurring in younger and younger children
What is main trigger for eating disorders?
Social media promoting being thin
An eating disorder in which there is a dietary restriction relative to thrive requirements because they have an irrational fear of weight gain and have a disturbed perception of body weight/shape
Anorexia Nervosa
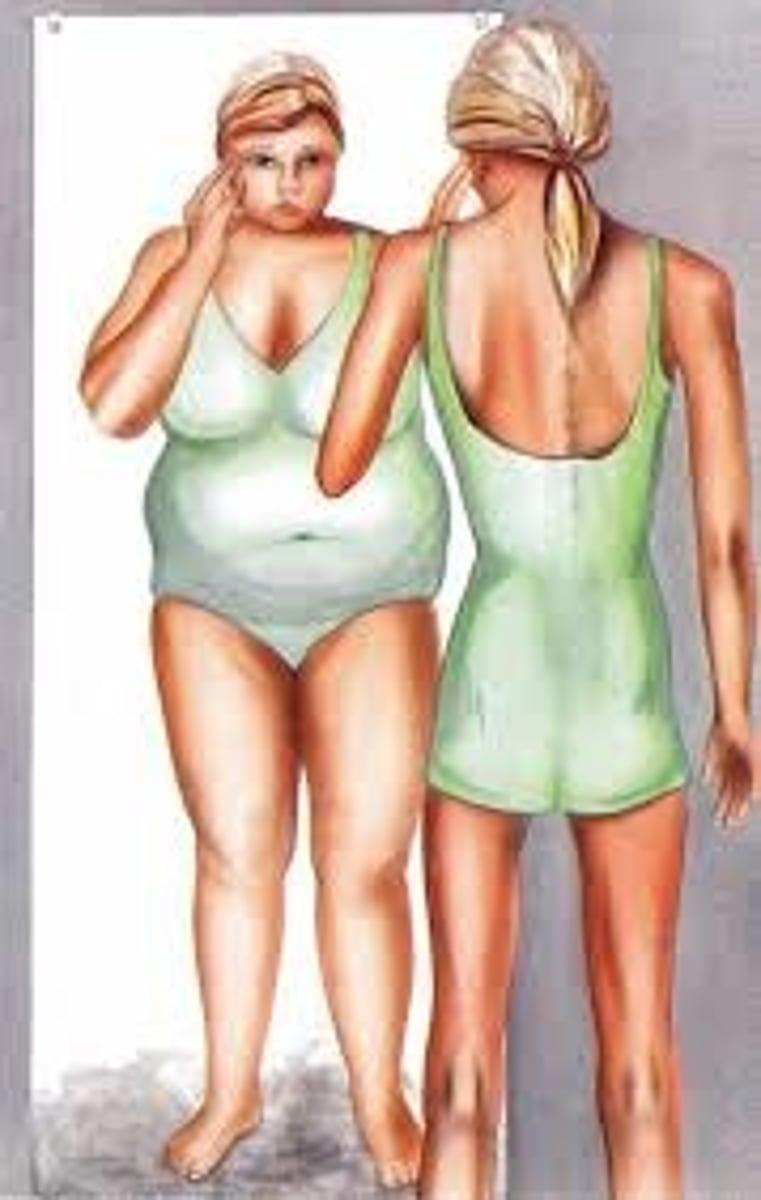

An eating disorder characterized by avoidance or restriction of certain foods because of color, smell and appearance. No distorted body image or fear of gaining weight. Tend to be younger children. This can be secondary to fear or episode of certain choking or vomiting
Avoidant/Restrictive Food Intake Disorder
(ARFID)
Bulimia is characterized by episodic binge eating followed by vomiting or purging. The recurrent episodes of binge eating in <___ hours and have a fear of not being able to stop eating during the binge. Minimum average of _____ binge eating episodes/week for at least ___2 months
2
2
3
What do all these eating disorders have in common?
Coexisting psychiatric disorders (depression, anxiety, OCD, trauma, substance abuse)
What are the psychological risk factors of eating disorders?
A. perfectionism
B. cognitive rigidity (refusal to follow rules)
C. childhood
D. anxiety disorders, or developmental immaturity
True/False
All eating disorders have disturbances in every organ system.
True
Compression of the superior mesenteric artery, 2/2 to the loss of the fat pad that separates the SMA from the duodenum. That can be a complication from eating disorders.
SMA syndrome
How do we dx anorexia nervosa?
loss of three menstrual cycles
- excessive physcial activity and denial of hunger
How do we diagnose bulimia?
tooth erosion with Russels sign
- 2 binge eating episodes per week for 3 months
Death rate of eating diorders is 10% due to?
CHF, cardiac arrythmias and electrolyte imbalances
What are the clinical sxs of eating disorders?
brady
postural hypotension
amenorrhea
sleep disturbacnes/impaired coginiton
Labs of eating disorders:
A. BUN
B. Na
C. K
D. Mg
E. Cl
F. Acidosis or alk?
G. LFTs
H. Z line
I. LH
J. T3
K. Bones
L. rate of suicide
M. EKG
A. high
B. low (mc)
C. low (mc)
D. low
E. HIGH!
F. alkolosis from Cl
G. high
H. barrets esophagus
I. low
J. low
K. osteoprosis
L. 18x increase
M. ST depression
What are the indications for hospitalization in patients with eating disorders?
(a) Evidence of dehydration/ electrolyte imbalances
(b) Severe malnutrition
(c) HR < 50 bpm during day or <45 at night
(d) Hypotensive
(e) Orthostatic hypotension (drops 20 mmHg)
(f) look at EKG possible prolonged QT
(g) Admitted outpatient treatment
What is the tx for eating disorders out-patient ?
1) Parents help to restore weight
2) Transfer control to adolescent for weight gain (must supervise)
3) Psychotherapy
4) NO MEDS
An aberration of normal breathing which leads to tachypnea and frequently syncope. Commonly seen in adolescents and preadolescents (females MC)
Hyperventilation syndrome
What is the cause of Hyperventilation syndrome?
What symptoms occur?
Stressful situation causes lightheadedness, dizziness, feels tingly weak and falls to the floor
What is the tx for Hyperventilation syndrome?
breathing in a paper bag to build up CO2
A lateral curvature of the spine, usually involving the dorsal or lumbar vertebrae or both and is accompanied by rotation of the involved vertebrae
Scoliosis
scoliosis is mc is idiopathic and should start looking for this as soon as
kid stands up - starts at age 2/3
What are the risk factors of progression of scoliosis?
1. sex
2. age
3. menarche or development of secondary sexual characteristics in males at the time of discovery
Premenarchal girls with 20 -30° curves are at higher risk of progression than girls do __ years after the onset of menses – as they grow their scoliosis gets worse
2
What degrees curve do we worry about for prepubescent and premenarchel due to an increase risk of progression ?
20-30
Patient has a curve when standing but when they bend down the spine straightens. This is due to one leg being shorter than the other
Nonstructural scoliosis
Rib hump on forward bending indicates axial rotation
Structural scoliosis
This patient presents with chest pain, can point/palpate where it hurts and states it gets worse on inspiration. Which pt will present like this , nonstructural or structural scoliosis?
nonstructural
1. What is the most common cause of costchondritis?
2. Tx?
1. nonstructural scoliosis because rib is pushed anteriorly and irritates sternum
2. Crack back and get insole
Tx for:
Curve >45
20-40 (immature)
20-40 (mature)
1. spinal fusion
2. brace
3. observe