1.5 Atomic Structure and Electron Configuration
1/98
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
99 Terms
Atoms are made up from:
protons (positive), neutrons (neutral) and electrons (negative)
The nucleus contains:
protons and neutrons
the electrons move around the:
nucleus
Most of the mass of the atom comes from the:
protons and neutrons
most of the volume of an atom comes from the:
electrons
Electron Configurations are a way of describing the:
arrangement of electrons within an atom
Electron Configurations are predicted by the:
Quantum Mechanical Model of the atom
By solving the Schrödinger equation, we obtain:
4 quantum numbers (n, l, ml, ms)
The 4 quantum numbers describe:
probable location of the electrons around the nucleus of an atom
The inner electrons are called:
core electrons
The outer electrons are called:
valence electrons
Name of n quantum number:
Principle quantum number
Simple description of n orbital:
Distance from nucleus
Values of n orbital:
1, 2, ... n
The principle quantum number corresponds to ______ for s and p.
the row on the periodic table
The principle quantum number corresponds to ______ for d.
row - 1
The principle quantum number corresponds to ______ for f.
row - 2
Name of l quantum number:
Shape of orbital
l quantum number describes:
most likely place to find the electrons
Values for angular quantum number:
s=0, p=1, d=2, f=3
Shape of angular quantum number of 0:
o shape
Shape of angular quantum number of 1:
8 shape
ml quantum number name:
Magnetic quantum number
Magnetic quantum number describes the:
Orientation of orbital
Values for magnetic quantum number:
s=0, p=-1 0 1, d= -2 -1 0 1 2, f=-3 -2 -1 0 1 2 3
Name of ms quantum number:
Spin quantum number
Spin quantum number describes the:
Spin of electron (wave)
Values of spin quantum number:
-1/2, +1/2
How many electrons fit into each orbital?
2
The 2 electrons fit into each orbital are described as:
“up” and “down”
There are ______ different cloud-shapes that describe the space that the electrons are most likely to occupy
four
There are four different ______ that describe the space that the electrons are most likely to occupy
cloud-shapes
The four different cloud-shapes that describe the space that the electrons are most likely to occupy are called:
Orbitals
Orbitals are described using ______ letters
4
4 letters of orbitals:
s, p, d, f
The s shaped cloud is a:
sphere around the nucleus
The p shaped cloud looks like:
two balloons tied together
The p orbital can be arranged in ______ orientations around the nucleus.
three
Draw a picture showing the s orbital and the three different p orbitals apart and together.
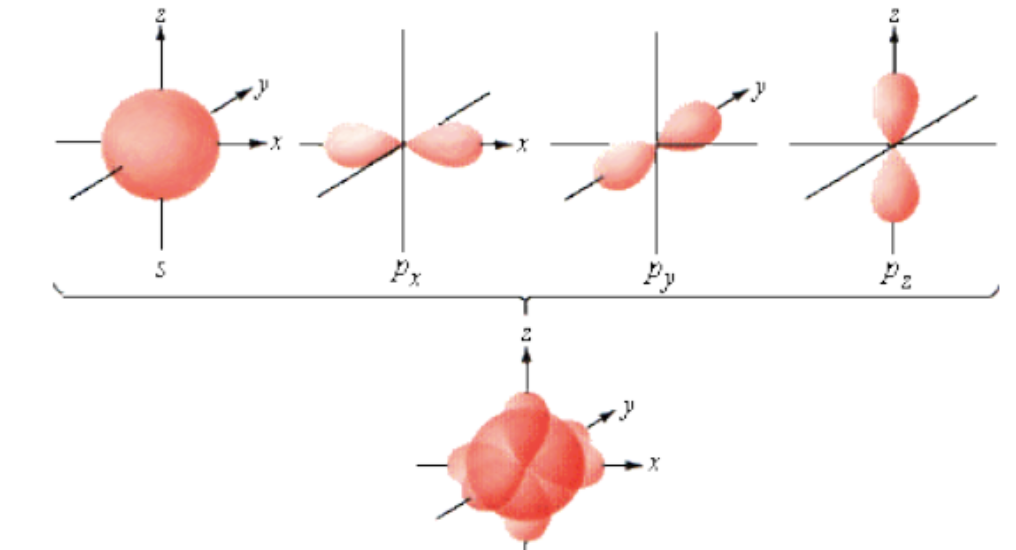
Can orbitals overlap?
Yes
Why can orbitals overlap?
They are electron clouds
Each orbital can fit ______ electrons
2
Each electron in a orbital has a same/different spin
different
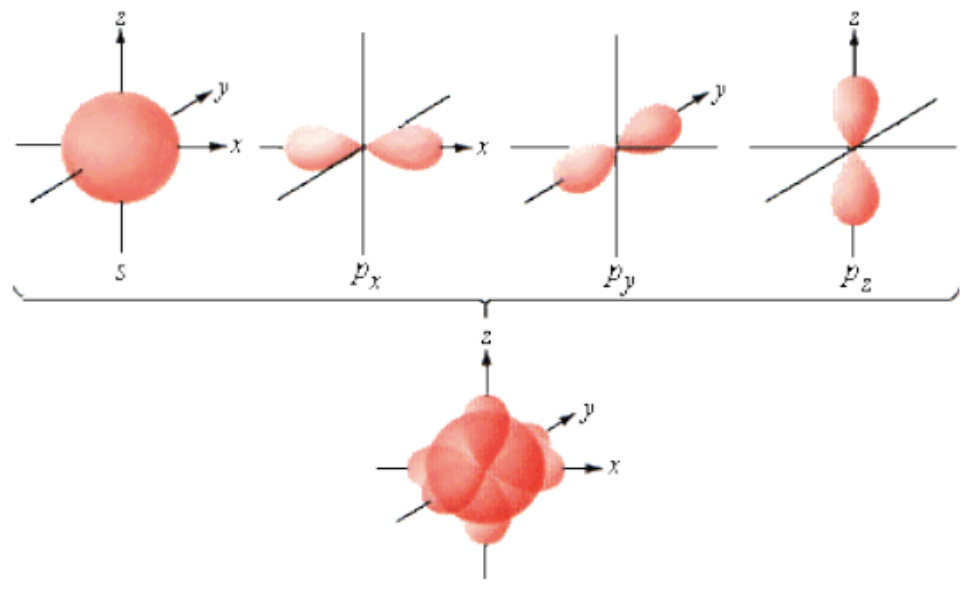
This picture shows the potential location for ______ total electrons.
8
Different distances from the nucleus are called:
energy levels
Each energy level has the same / different possible shapes
different
Possible shapes for energy level 1:
s
Number of electrons for principle quantum number 1:
2
Possible shapes for energy level 2:
s and p
Number of electrons for principle quantum number 2:
8
Possible shapes for energy level 3:
s, p, d
Number of electrons for principle quantum number 3:
18
Possible shapes for energy level 4:
s, p, d, f
Number of electrons for principle quantum number 4:
32
Electron configurations describe the ______ of the atom by showing ______
model, shells (energy levels) and orbitals
s subshell holds how many electrons?
2
p subshell holds how many electrons?
6
d subshell holds how many electrons?
10
f subshell holds how many electrons?
14
Electrons occupy the subshells starting with the:
lowest energy levels first
The “lowest” energy orbitals are the ______ to the nucleus.
closest
Lower energy orbitals would require the ______ energy to remove them.
greatest
Coulomb’s law tells us that:
the force between charged particles is proportional to the product of the two charges and the force is inversely proportional to the squared radius between them.
The force between charged particles will increase/decrease the further away the particles are.
decrease
Higher charges of charged particles and smaller distance between the charges result in a greater/lesser force of attraction.
greater
why does it take more energy to remove electrons that are closest to the nucleus?
smaller distances between charged particles result in a greater force of attraction.
the electrons that are on the valence shell, the outermost electrons, experience less of the:
nuclear pull
Why do the outermost electrons experience less of the nuclear pull?
the electrons that are in the core of the atom shield the attraction of the nucleus from the valence electrons.
Coulomb’s Law Formula:
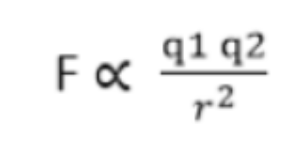
3 rules for electron configuration:
Aufbau principle, Hund’s rule, Pauli exclusion principle
electrons are added to the lowest subshells first and build up
Aufbau Principle
each subshell should have one electron before any are doubled up
Hund’s Rule
no two electrons can have the same set of 4 quantum numbers.
Pauli Exclusion Principle
Draw electron configurations in the periodic table
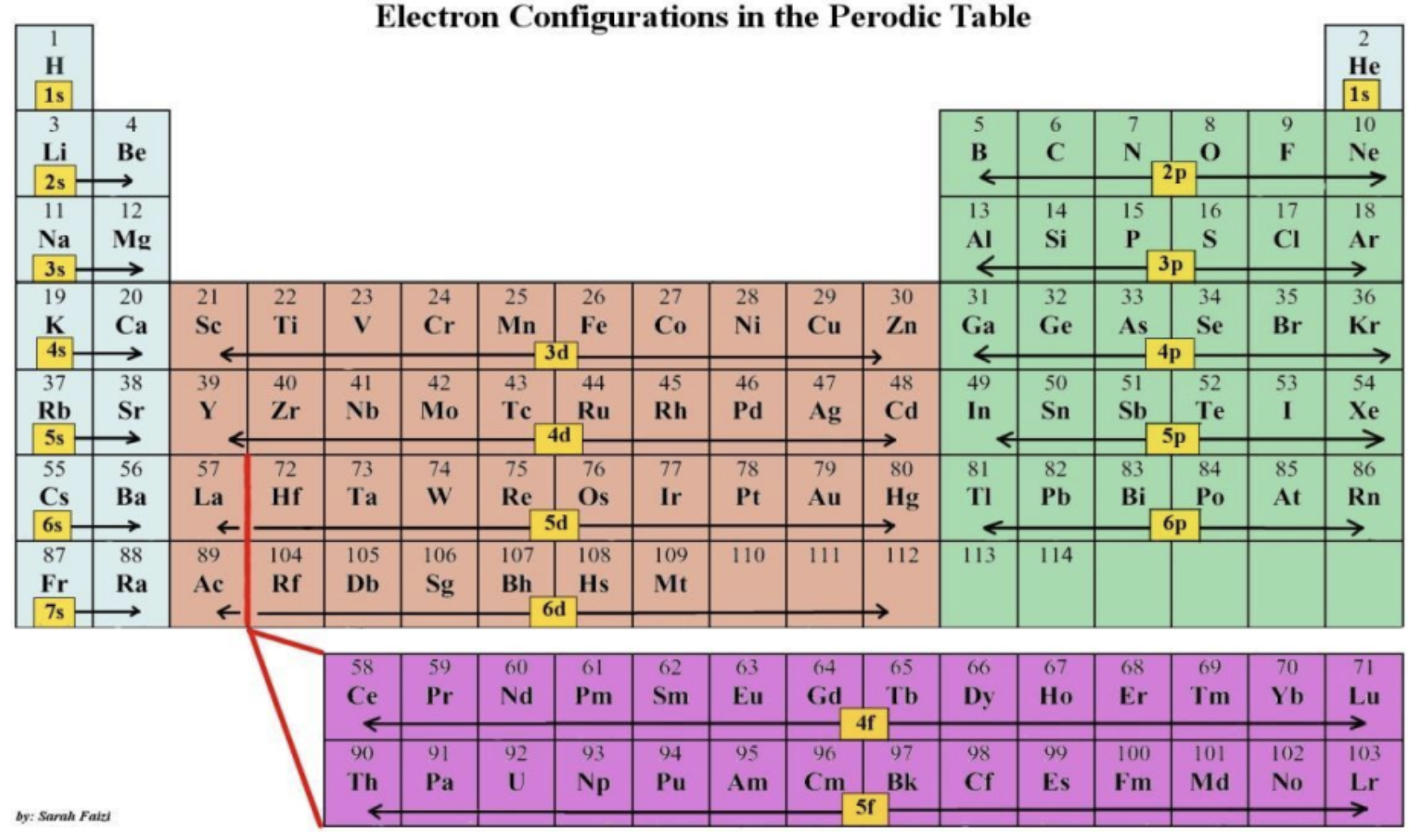
You can use the ______ to help you with the electron configuration.
Periodic Table
Draw Aufbau diagram in two ways:
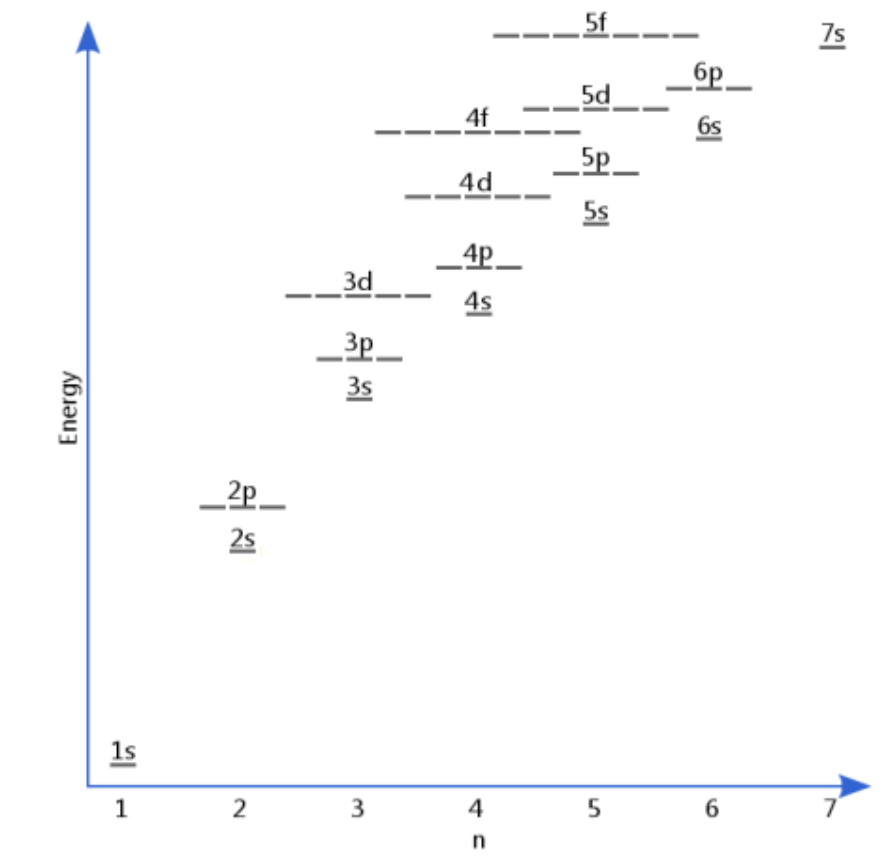
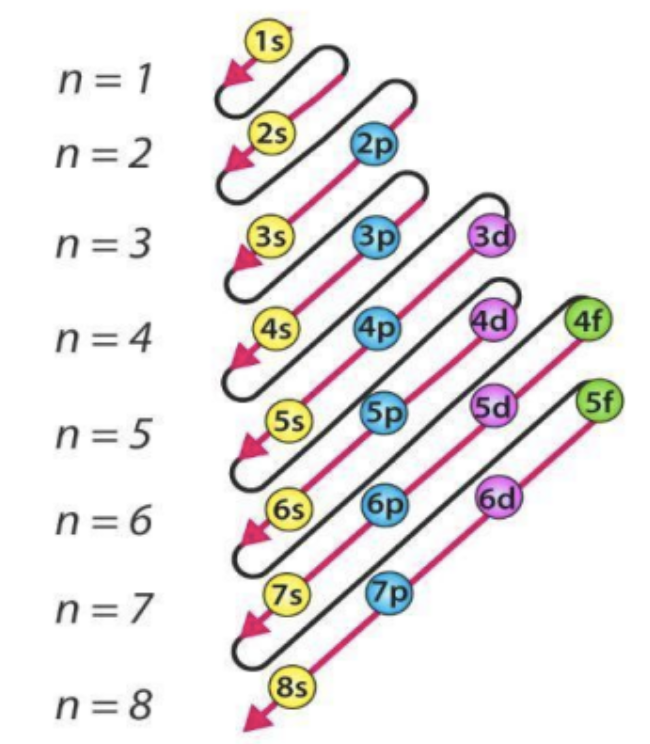
Electrons occupy the ____ energy orbitals (______ to the nucleus) first.
lowest, closest
The letter in electron configuration represents:
Subshells
The number on the top right hand corner of the letter in electron configuration represents:
Number of electrons in subshell
Numbers in front of the letter in electron configurations mean the:
energy level
s, p, d, f denote the ______ of the orbitals
shape
Orbital diagrams are very similar/different to/from electron configurations.
similar
Orbital diagrams show electrons as:
arrows
Compared the electron configuration, orbital diagrams provide additional insight into the:
interactions between the electrons in shared orbitals
Are orbitals vertical or horizontal?
Both
Orbitals are usually vertical or horizontal?
horizontal
When drawing electrons in orbital diagrams, always start with the up/down arrow
up
When drawing orbital diagrams, always start by filling the ______ energy level lines first.
lowest
In orbital diagrams, each box has how many electrons?
1/2
Two electrons in the same box in an orbital diagram must have:
opposite spins
Electrons in the same orbital having opposite spins is based on the:
Pauli Exclusion Principle
How to make sure you follow Hund’s Rule when drawing orbital diagrams?
When you have three (or more) lines in the same subshell, you put one arrow in each box before you make them share a line.
Hund’s Rule helps to:
minimize the electron-electron repulsions
To write an electron configuration using the short-cut method, start by:
locating the noble gas preceding your element
The noble gases are the elements in group ______ on the periodic table.
8A
Noble gases are known for being:
unreactive
Noble gases are unreactive because they have:
filled valence shells
Why are noble gases chosen for noble gas short-hand configurations?
They are unreactive
The noble gas shorthand takes the:
noble gas before the element and then continues on from there.