color vision
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
color
not a (single unique) physical property of things in the world, but a psychophysical phenomenon that depends of the complex relationships between a variety of disparate physical features
light detection, wavelength/spectrum discrimination, appearance
three steps to color vision
light detection
we must detect the light- our photoreceptors are only sensitive to a narrow bad of frequencies//wavelengths
wavelength/spectrum discrimination
must be able to differentiate between lights composed of different wavelengths or spectra (mixtures of wavelengths)
appearance
must be able to perceive the colors of objects and surfaces consistently under changing lighting conditions
spectral
referring to the wavelength of light
illuminant
the light source
power spectrum
description of the amount of energy (power) at each wavelength
absorption spectrum
describes photoreceptor response as a function of light wavelength/frequency
principle of univariance
the response of ant single photoreceptor is consistent with an infinite number of different wavelength-intensity combinations; a single type of photoreceptor cannot make spectral/color discriminations
scotopic
very dim
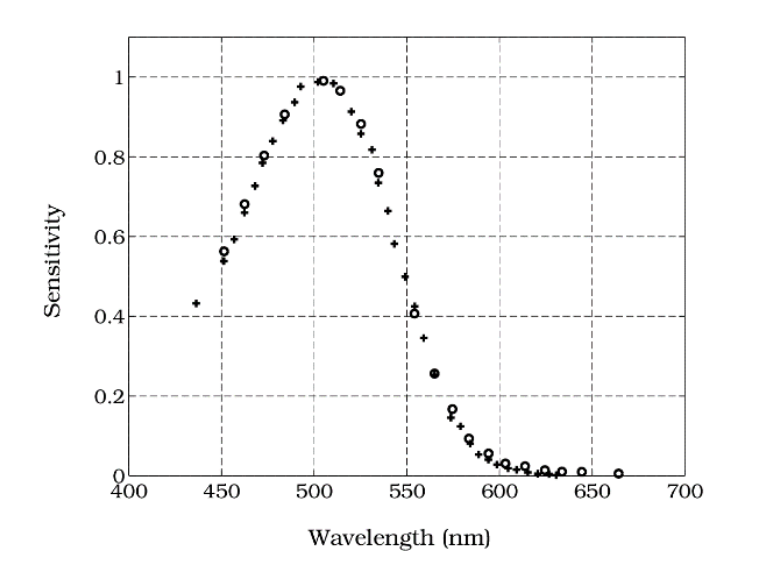
trichromacy
theory that the color of any light is defined in our visual system by the relationships of three numbers, the outputs of three receptors types now known to be the three cones; also known as the Young-Helmholtz theory- developed before scientists were able to measure the absorption spectra of photopigment or the response of the photoreceptors
non-spectral hues
percepts that cannot be produced by any single-wavelength
additive color mixing
a mixture of lights with different spectra; if A and light B are both reflected from a surface to eye, in the perception of color, the effects of those two lights add together
subtractive color mixing
a mixture of pigments; if pigment A and pigment B mix, some of the light shining on the surface will be subtracted by A and some by B. only the remainder contributes to the perception of color
color space
three-dimensional space that describes all colors
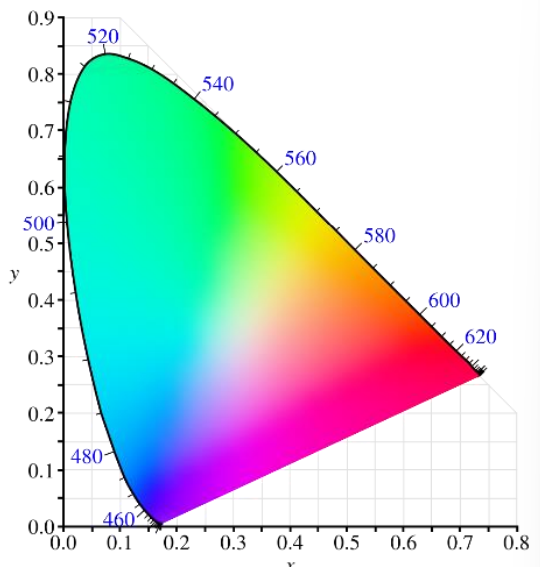
gamut
describes what colors any set of three lights can reproduce
opponent color theory
claims that perception of color is based on the output of three channels, each based on an opponency between two colors

illuminant
defined by power spectrum- amount of light energy at each wavelength
object
defined by reflectance function; percentage of light at each wavelength that is reflected
cones
defined by absorption spectrum; each cone class adds up light energy according to its absorption spectrum
rgc responses
defined by three spectral measurements; convey all color information to bran via opponent channels
anomalous trichromacy
one cone has abnormal cone pigment with absorption shifted closer to another (usually m shifted toward l)
protanopia
missing l cone/pigment
deuteranopia
missing m cone/pigment
tritanopia
missing s cone/pigment