Anatomy #3.5- Pancreas+Spleen/Stomach+Urinary
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
Transverse section at pancreas level
Pancreas
The pancreas is a long narrow retroperitoneal organ that lies posterior to the stomach
Extending from the concavity of the duodenum to the hilum of the spleen
Found in a horizontal-oblique line
Lies in epigastric and left hypochondriac
It is approximately 12cm long and 2cm thick
Five parts of pancreas
Ucinate process
Head
Neck
Body
Tail
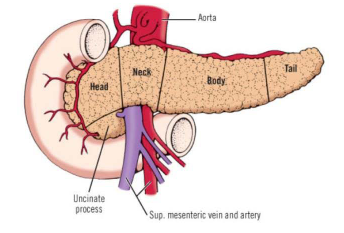
Head
Thickest part of the gland
Two vessels can be commonly seen running through the head
Common bile duct in the right posterior aspect
Gastroduodenal artery in the anterior aspect
Lies approximately level L2-L3
Head is anterior to the IVC and renal veins
A transverse section through the head of the pancreas typically intersects the second part of the duodenum that is at the left margin of the head
Uncinate Process
Medial and posterior extension of the head of the pancreas that hooks towards the back of the abdomen
It may hook around two very important blood vessels
Superior mesenteric artery
Superior mesenteric vein
Lying between the superior mesenteric vein and IVC
The uncinate process is posterior to the superior mesenteric vessels
Neck
The neck, the constricted portion of the gland is located between the pancreatic head and body
Located just posterior to the neck is the portal splenic confluence where the portal vein is formed by the merging of the superior mesenteric and splenic veins
Body
The body is the largest and most anterior portion of the pancreas, extending transversly to the left, anterior to the aorta, and superior mesenteric atery
The splenic vein runs along the posterior surface of the body on its route to the portal splenic confluence
The body tapers superiorly and posteriorly into the pancreatic tail
The body lies posterior to the stomach
Tail
The tail extends into the left anterior to the left kidney to end at the splenic hilum
Splenic artery forms the superior border
Splenic vein forms the posterior border
The stomach forms the superoanterior border
The most superior portion of the pancreas is the tail near the spleen
anterior view of pancreas
Transverse view of pancreas with important vessels
Vascular landmarks
Fucntions of the pancreas
Exocrine function- acini cells produce digestive enzymes for digestion secreted via the pancreatic duct
Endocrine function- islets of langerhands cells produce insulin and glucagon, the control blood levels of nutrients
It delivers its endocrine hormones into the draining venous syste and its enzymes into the small intestines
The endocrine hormones help control plasma glucose concentration
Pancreatic digestive enzymes include amylase for the digestion of starch, lipase for the digestion of lipids, peptidases for protein digestion, and sodium bicarbonate to neutralize gastric acid
Pancreatic duct
Wirsung’s duct- the main pancreatic duct, extending the entire length of the gland
Santorini’s duct- secondary duct, enters duodenum at minor papilla
Wirsung’s duct
the main pancreatic duct, extending the entire length of the gland
Enters the medial second part of the duodenum with the common bile duct at vater’s ampulla (major duodenal papilla)
Santorini’s duct
secondary duct
Enters the duodenum at the minor papilla approximately 2cm proximal to Vater’s ampulla