Kinesiology - Final Exam
1/334
Earn XP
Description and Tags
EVERYTHING
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
335 Terms
atlantooccipital joint
C1 + occiput
flexion/extension (“yes”) + light lateral bending
synovial joint
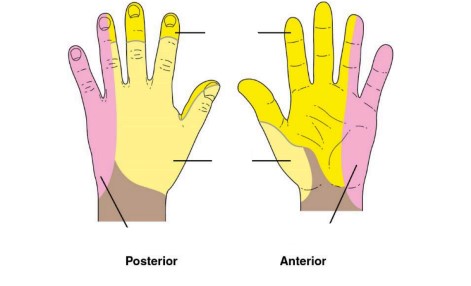
what nerve innervates the top yellow
median nerve
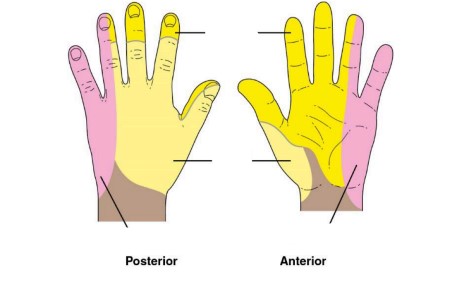
what nerve innervates the bottom yellow
radial nerve
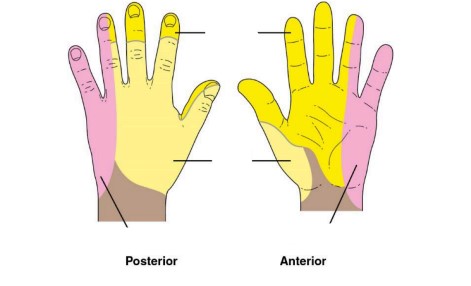
what nerve innervates the pink
ulnar nerve
atlantoaxial joint
C1 + C2
rotation (“No”)
atlas rotates on dens of axis
synovial joint
cervical spine…
more mobile, less stable → triaxial
thoracic spine…
more stiff (limited by ribs) → lateral flexion
lumbar spine
strongest → flexion/extension + minimal lateral flexion
ribs…
minimal motion → elevation/depression
true ribs
pairs 1 - 7
false ribs…
pairs 8 - 10
floating ribs…
pairs 11 - 12
intervertebral discs (23)
function: shock absorption + flexibility
adjacent vertebral bodies: cartilaginous discs
weight-bearing
facet joints: synovial joint
cervical ligaments (and thoracic & lumbar lol)
anterior longitudinal ligament
posterior longitudinal ligament
ligamentum flavum
nuchal ligament
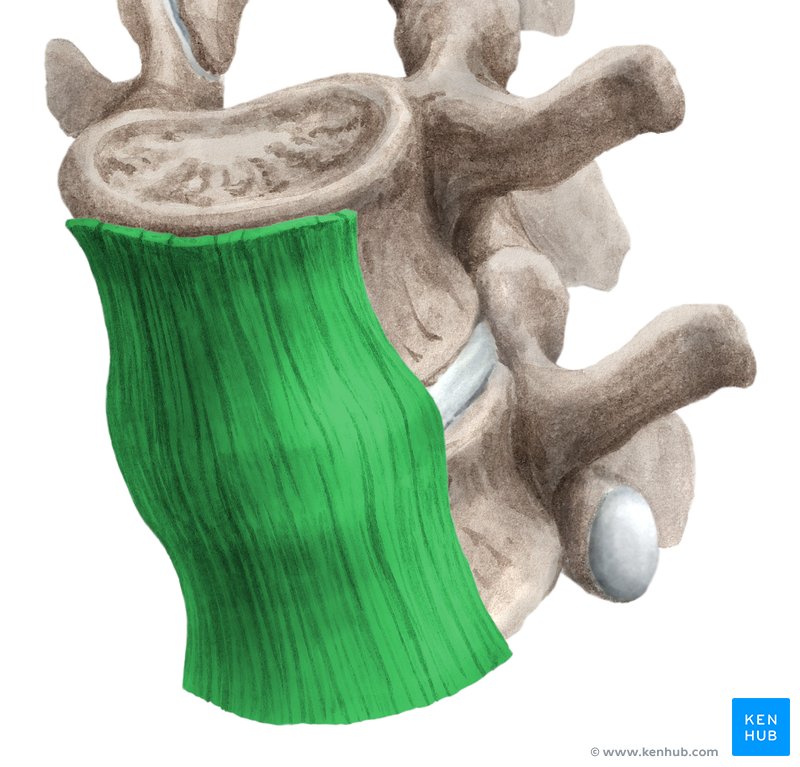
what is this
anterior longitudinal ligament
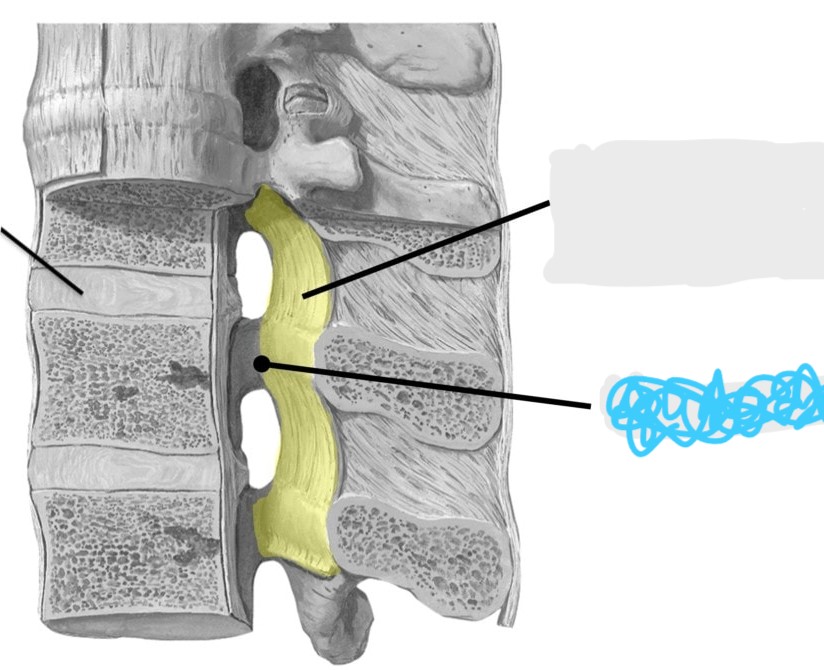
what is this
ligamentum flavum
what is this
nuchal ligament
what is this
posterior longitudinal ligament
anterior longitudinal ligament
anterior vertebral ligament
prevents excessive extension
posterior longitudinal ligament
posterior vertebral bodies
precents excessive flexion
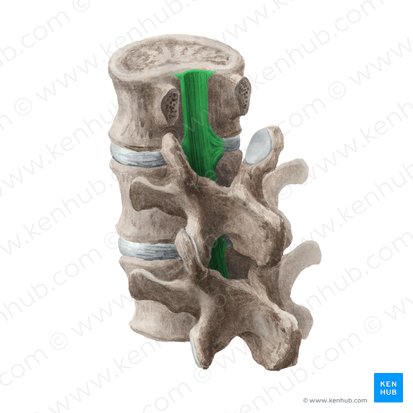
ligamentum flavum
forms posterior border of vertebral canal
prevents excessive flexion
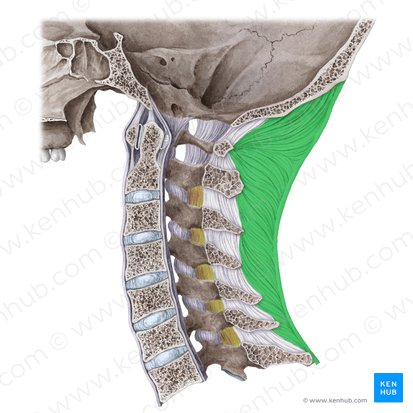
nuchal ligament
from nuchal line of occiput to tips of spinous processes
supraspinal ligament + interspinal ligaments
prevents excessive flexion
sternal
sternocostal ligaments
costoxiphoid ligaments
costovertebral + costotransverse
many small ligaments support joint capsules
prevent excessive flexion
torticollis
head laterally flexed to one side, rotated to opposite side
sciatica
pain descending posterior thigh/leg along path of sciatic nerve
cause: disc herniation/disruption
spinal stenosis
narrowing of vertebral canal + compression of spinal cord/nerve roots
ankylosis spondylitis
chronic inflammation + fusion of vertebral column joints
spondylosis
bony spurs, thickening of ligaments, decreased disc height
pressure on spinal nerve roots
spondylolysis
defect in vertebral lamina
spondylolisthesis
anterior slippage of vertebrae
fractures
caused by: compression, trauma, osteoporosis
fracture with dislocation
caused by: trauma
effects: compression of spinal cord, avulsion of nerve roots
SS: loss of motor/sensory function
cervical strain
caused by: whiplash
functions of respiratory system
supply oxygen to body + eliminate carbon dioxide from body
respiration
gas exchange
ventilation
moving air in/out of lungs → airflow
thoracic cage =
sternum + ribs/costal cartilages + T1 - T12
costovertebral joint
rib + vertebral body
costotransverse joint
rib + transverse facet of transverse process
chondrosternal joint
ribs + sternum
elevation/depression movements
gliding of costovertebral/chondrosternal joints
how does the thoracic cage move during: Inhalation
cage moves up + out
how does the thoracic cage move during: Exhalation
cage moves down + in
intrathoracic volume: inhalation
diaphragm descends with contraction
intrathoracic volume increases, pressure decreases
volume increases, pressure drops, air flows in
intrathoracic volume: exhalation
diaphragm descends with relaxation
intrathoracic volume decreases, pressure increases
volume decreases, pressure rises, air flows out
quiet inhalation (muscles)
diaphragm + external intercostals
quiet exhalation
relaxation of diaphragm / external intercostals
deep inhalation (muscles)
diaphragm + external intercostals + SCM + scalene + pec minor + levator costarum + serratus posterior superior
forced inhalation
contraction of diaphragm/external intercostals + levator scap + upper trap + rhomboids + pec minor
forced exhalation
internal intercostals + internal/external oblique + TVA + rectus abdominis + QL + serratus posterior inferior
paradoxical breathing
diaphragm functions, intercostals dont
pursed lip breathing
exhaling with closed lips to decrease airflow and increase time for gas exchange
pleurisy
inflammation of pleura
pneumothorax
collapsed lung
flail chest
loss of ability to expand lungs (rib fracture)
bronchitis
inflammation of bronchi
emphysema
distention, destruction of alveolar walls + loss of lung tissue elasticity
asthma
spasm of bronchial walls restricting airflow
hyperventilation
rapid breathing removes more CO2
stitch
cramp from diaphragm during exertion
tasks accomplished with gait
weight acceptance
single-leg support
single-leg advancement
gait cycle
one complete sequence of one LE
stride
1 foots cycle (heel strike → heel strike)
from one foot touching ground to it touching the ground again
stride length
horizontal distance traveled during a stride
stride width
side to side distance
step
from 1 foot to the other
from one foot touching the ground to the other foot touching the ground
step length
horizontal distance between initial contact of one foot and initial contact of the other foot
cadence
number of steps per minute
stance leg
closed chain
swing leg
open chain
vertical displacement
usually 2 inches (highest at midstance, lowest heel strike)
horizontal displacement
usually 2 inches (highest at midstance)
lateral pelvic tilt
movement of hips up/down as pelvis drops
mnemonic for: Stance Phase
I Like My Tea Perfect
mnemonic for: Swing Phase
I Make Tea
stance phase
weight acceptance + SL support, 60% of cycle
initial contact →
heel strike
loading response →
foot flat
midstance →
midstance
terminal stance →
heel off
preswing →
toe off
initial swing →
acceleration
midswing →
midswing
terminal swing →
deceleration
initial contact / heel strike
first double stance, initial weight shift
joint angles:
hip = 20 degrees flexion
knee = 5 degrees of flexion
ankle = 0 degrees
loading response / foot flat
body weight continues to shift over stance leg
joint angles
hip = 20 degrees of flexion
knee = 15 degrees of flexion
ankle = 5 degrees of plantar flexion
midstance / midstance
end of double stance
joint angles
hip = 0 degrees
knee = 5 degrees of flexion
ankle = 5 degrees of dorsiflexion
MTP = 0 degrees
terminal stance / heel off
initiation of forward propulsion, lateral tilt decreasing w/opposite weight shift
joint angles
hip = 20 degrees of extension
knee = 5 degrees of flexion
ankle = 10 degrees of dorsiflexion
MTP = 30 degrees of extension
preswing / toe off
forward propulsion ends
joint angles
hip = 10 degrees of extension
knee = 40 degrees of flexion
ankle = 15 degrees of plantar flexion
MTP = 60 degrees of extension
double stance
both LEs on ground, 20% of gait cycle
initial swing / acceleration
swing advancement begins
joint angles:
hip = 25 degrees of flexion
knee= 60 degrees of flexion
ankle = 5 degrees of plantar flexion
midswing / midswing
no acceleration/deceleration
joint angles:
hip = 25 degrees of flexion
knee = 25 degrees of flexion
ankle = 0 degrees
terminal swing / deceleration
second double stance
joint angles
hip = 20 degrees of flexion
knee = 5 degrees of flexion
ankle = 0 degrees
joints in the pelvis
lumbosacral
sacroiliac joint
pubic symphysis
lumbosacral (angle/degrees)
normal angle: 30 - 40 degrees
higher/increases = increased lumbar lordosis
lower/decrease = decreased lumbar lordosis
lumbosacral (joint motions)
flexion + extension
rotation
lateral flexion
sacroiliac joint motions
nutation
counternutation
nutation
sacral flexion; superior portion of sacrum rotates anteriorly + inferior portion rotates superiorly
trunk flexion or hip extension
anterior pelvic tilt