Unit 3 Flashcards
1/18
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
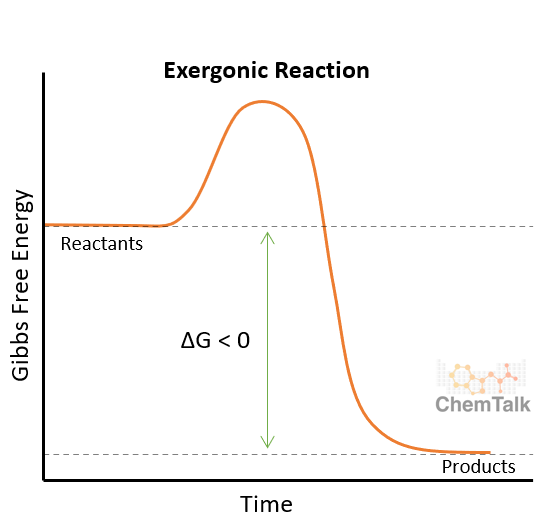
Catabolic
Hydrolysis reactions; exergonic
Anabolic
Dehydration synthesis reactions; endergonic
Competitive Inhibitors
Molecules that have similar structure to a enzymes substrate and bind to the active site in order to inhibit the substrate and thus enzyme activity. This inhibitor is dependant on substrate concentration
Non-competitive inhibitors
Inhibitors that bind somewhere outside the active site, causing the active site itself to change structure thus causing the substrate to be unable to bind to the enzyme at all.
Light Dependant Reactions
a catabolic process occuring in the thylakoid where light energy is converted into chemical energy in the form of ATP and NADPH, releasing oxygen as a byproduct
LDR Step 1
sunlight hits electrons exciting them, causing the the electrons to orbit photosystem II and spin faster
LDR Step 2
photolysis occurs, breaking H2O to oxidize it by using light energy
LDR Step 3
electrons from H2O are transported through electrons carrier in the thylakoid membrane to NAD+, causing it to reduce
The Calvin Cycle
an anabolic process where a series of chemical reactions occur in the stroma, using energy from the previous reaction (ATP and NADPH) to convert carbon dioxide into glucose and other organic molecules such as ADP and NAD+
TCC Step 1 - Carbon Fixation
An enzyme called RuBisCo captures carbon dioxide and attaches it to a molecule called RuBP
TCC Step 2 - Reduction
ATP and NADPH are used to convert the RuBP molecules into a three-carbon sugar called G3P
TCC Step 3 - Regeneration
Some of the G3P molecules are used to remake RuBP and the rest are used to build glucose and other sugars
Cellular Respiration
the process of converting chemical energy stored in glucose into ATP, the cell’s primary energy source, through three stages
Glycolysis
first stage of CR occuring in the cytosol, where glucose is converted into two molecules of pyruvate, ATP is produced, and NAD+ is converted into NADH
Pyruvate oxidation also occurs, where the two pyruvate produced in the process goes into the mitochondrial matrix and his converted into Acetyl CoA
Citric Acid Cycle
second stage of CR occuring in the mitochondrial matrix, where the Acetyl CoA made in pyruvate oxidation goes through a series of chemical reactions, oxidizing and producing ATP, NADH, FADH2
Electron Transport Chain
The final stage of CR occuring in the inner mitochondrial matrix, with the energy from NADH and FADH2 being used to generate ATP by passing electrons down a series of embedded proteins that then powers the pumping of protons from into the intermembrane space. Oxygen is final electron acceptor, combining with protons in the matrix to form H2O
Chemiosmosis occurs, a process where protons flow back into the mitochondrial matrix through ATP synthase. This powers powers the enzyme ATP Synthase to synthesize ATP from ADP + Pi ,known as oxidative phosphorylation
Oxidation
A process where molecules lose electrons
Reduction
a process where molecules gain electrons
Anaerobic respiration
a type of cellular respiration that occurs in the absence of oxygen, generating ATP by breaking down glucose with alternative electron acceptors instead of oxygen. Glycolysis is the only process to occur, as it can function both aerobically and anaerobically.
lactic acid forms in animals, and ethanol forms in plants