Module 2 - ID, Cancer, Hema, Fluids
1/396
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
397 Terms
infection
The process in which an organism has a parasitic relationship with a host
Prions
Corrupted proteins that are folded abnormally
What happens when prions and normal proteins come in contact?
Normal folded proteins (PrPc), prion causes a chain reaction of abnormally folded proteins (PrPsc).
Abnormal folded chain of proteins leads to dysfunction
What do Prions cause?
Transmissible Spongiform Encephalopathies
Transmissible Spongiform Encephalopathies
Uncurable, fatal chronic degenerative disease of brain
Examples of Transmissible Spongiform Encephalopathies
Cruetzfeldt-Jakob Disease and Kuru
How are prions transmitted
Coming into contact with infected tissue
What would be examples of infected tissue causing prions?
Ingesting animal brain, blood products, or contaminated surgical instruments
Are viruses living or non-living?
Non-living
Viruses characteristics
Subcellular, made of only nucleic acids and proteins, and they are obligate intracellular parasites (can only replicate in a host)
Viruses spread
Inject the contents through the tails. Causing infection and dysfunction.
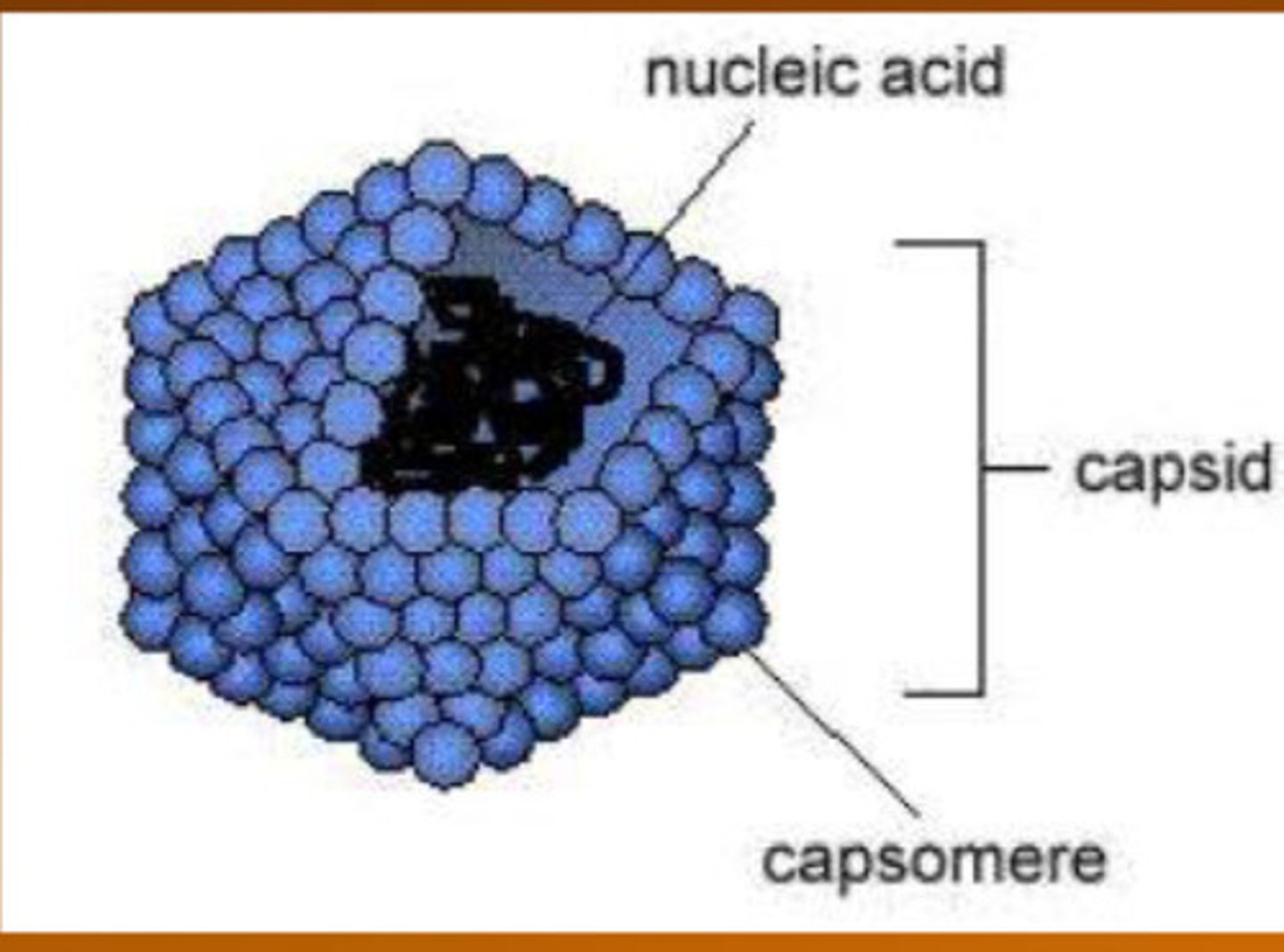
What is this a picture of?
Virus
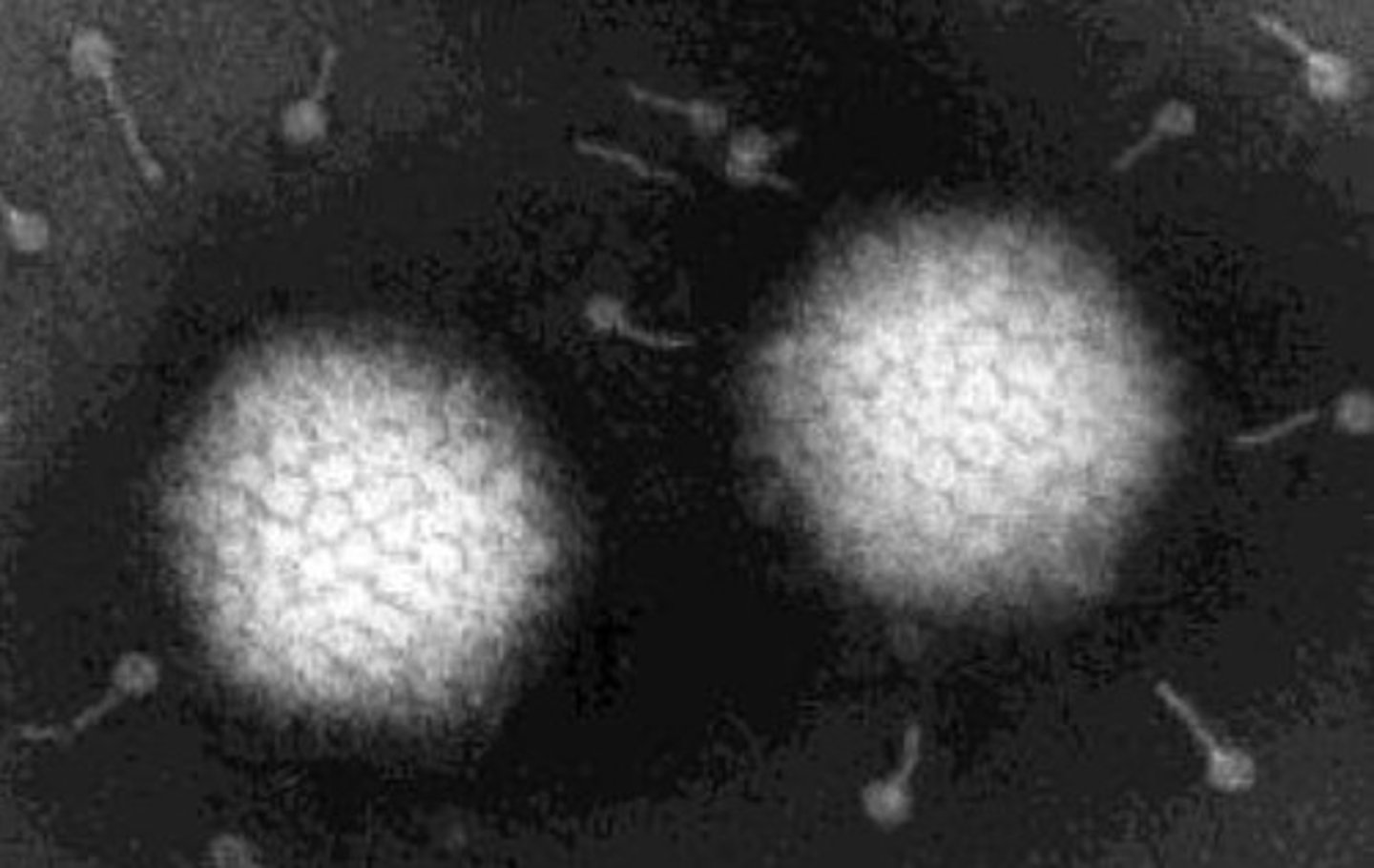
What is this a picture of?
Virus
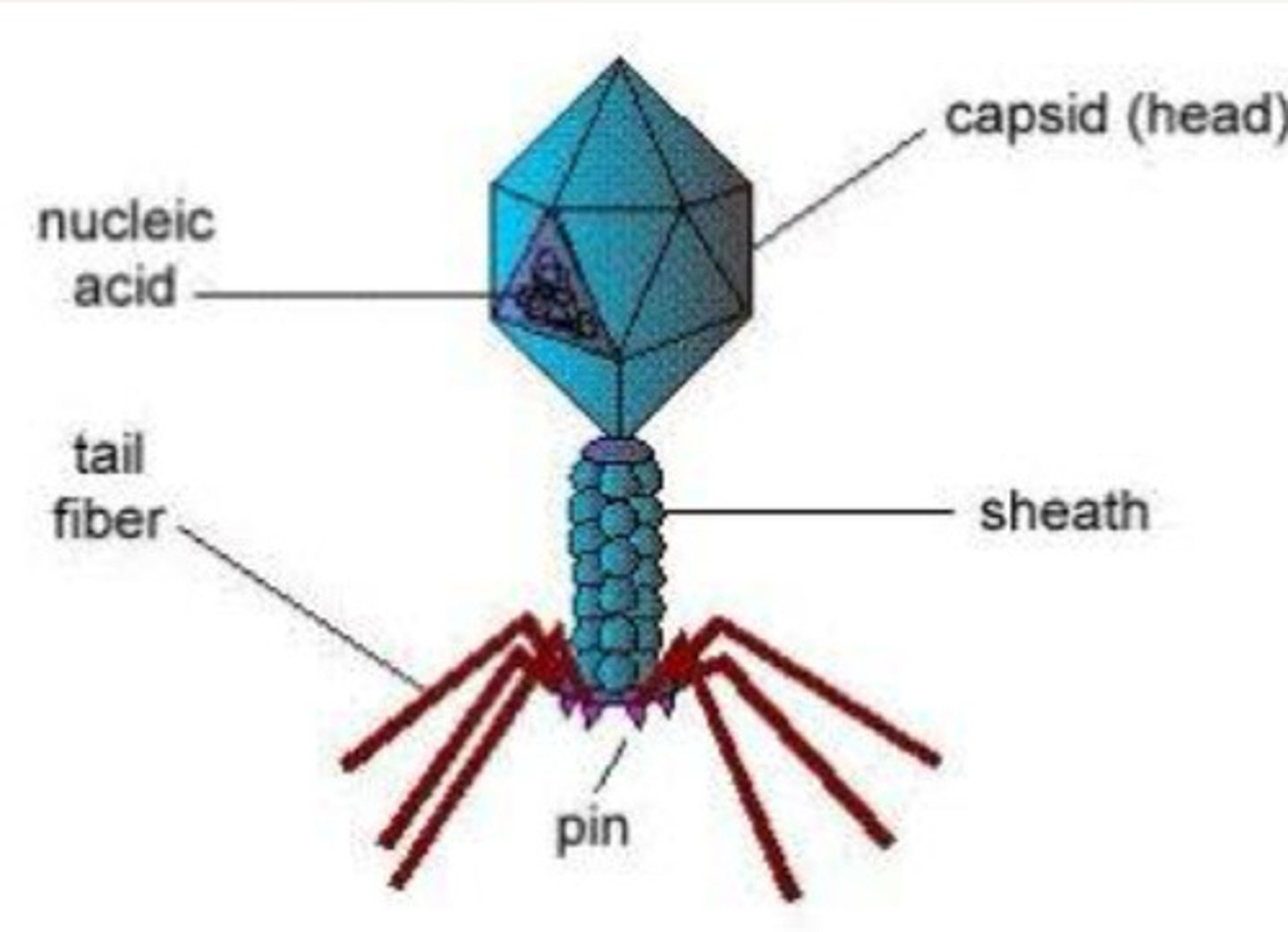
What is this a picture of?
Virus
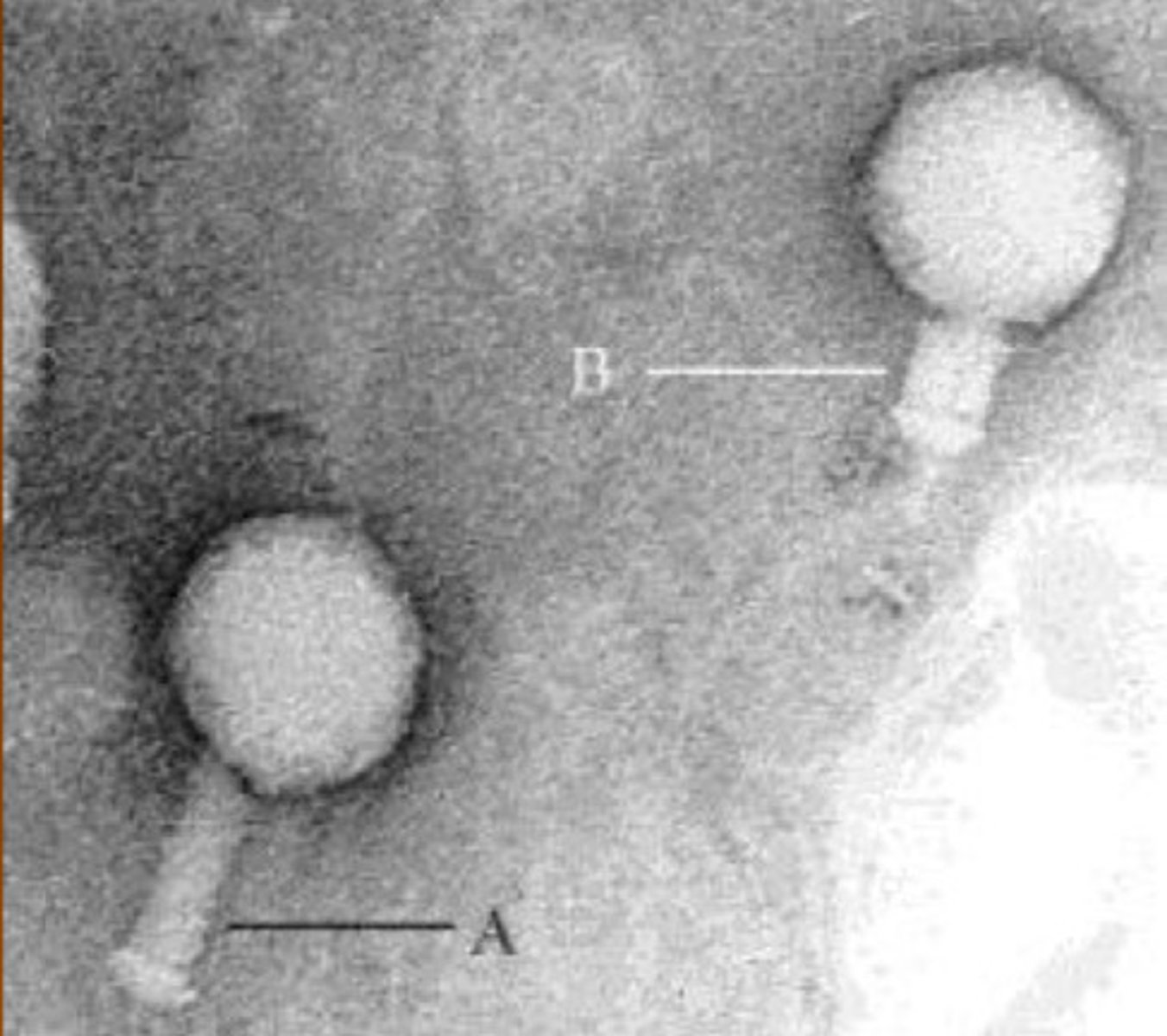
What is this a picture of?
Virus
Do we typically use traditional antibiotics for a virus? If not, what do we use?
No, we use anti-virals
Bacteria characteristics
Single celled, cell wall, grow independently (most of the time), grown on a culture medium (most), contain both RNA and DNA. They have no nucleus.
Bacteria is classified by
Morphology - shapes
Colony types
Gram staining (+/-) - be able to see with stain
Aerobic/anaerobic
Facultative - anaerobic without oxygen
Obligate - harmed by oxygen
Shape of bacilli
Long, oblong, look like Cheeto puffs
What is this a picture of?
Bacilli
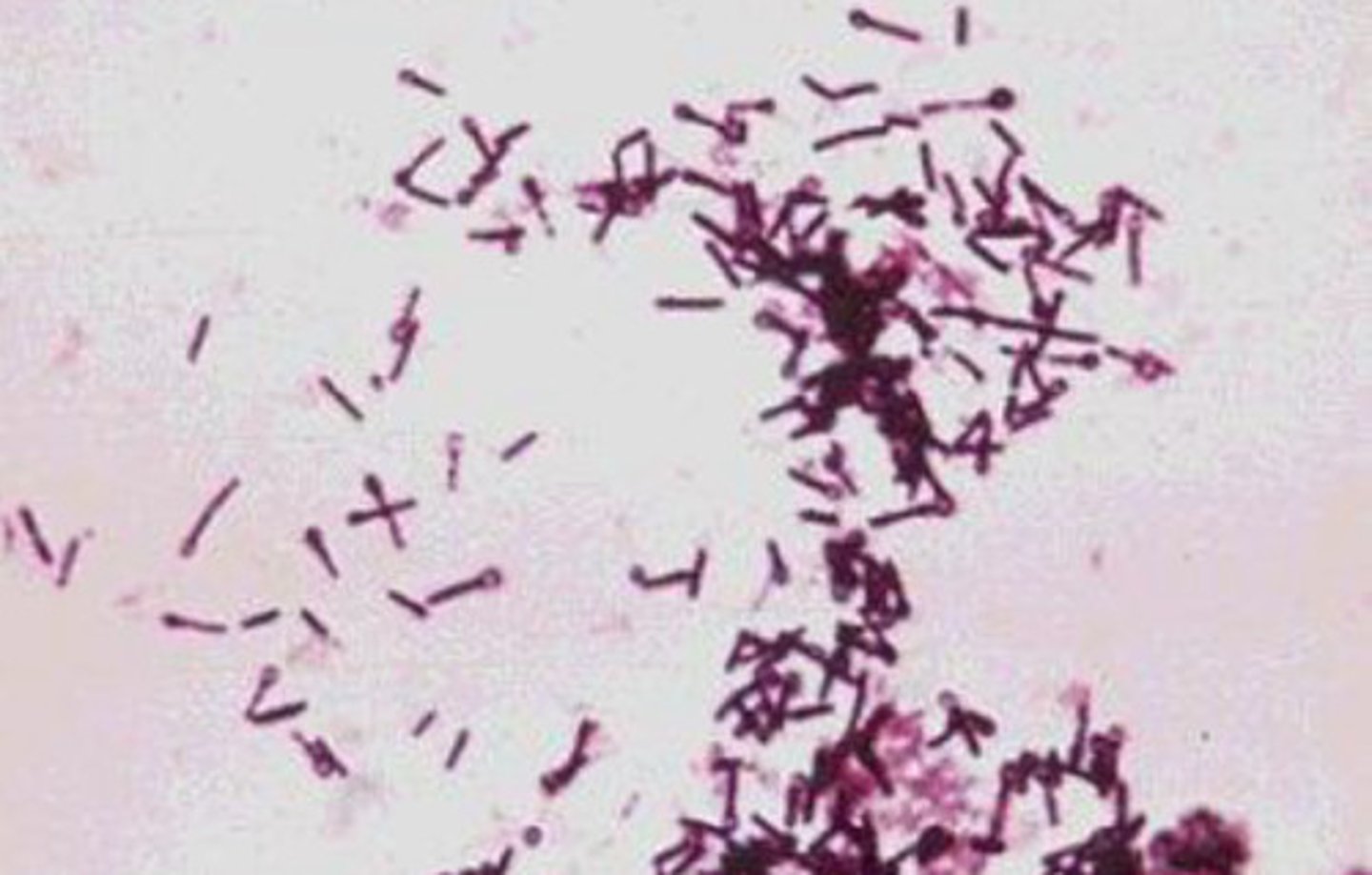
What is this an image of?
Bacilli
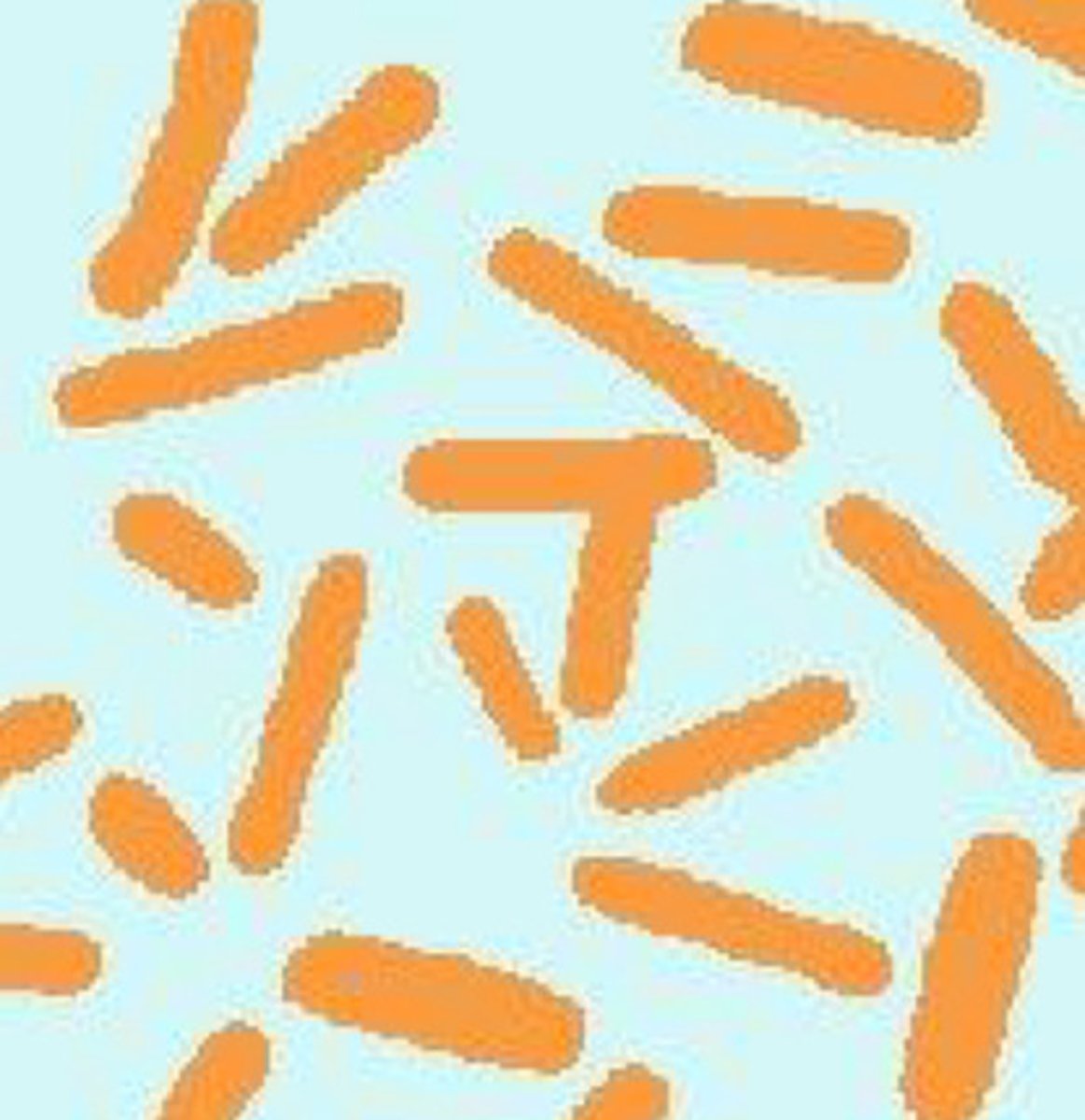
What is this an image of?
Bacilli
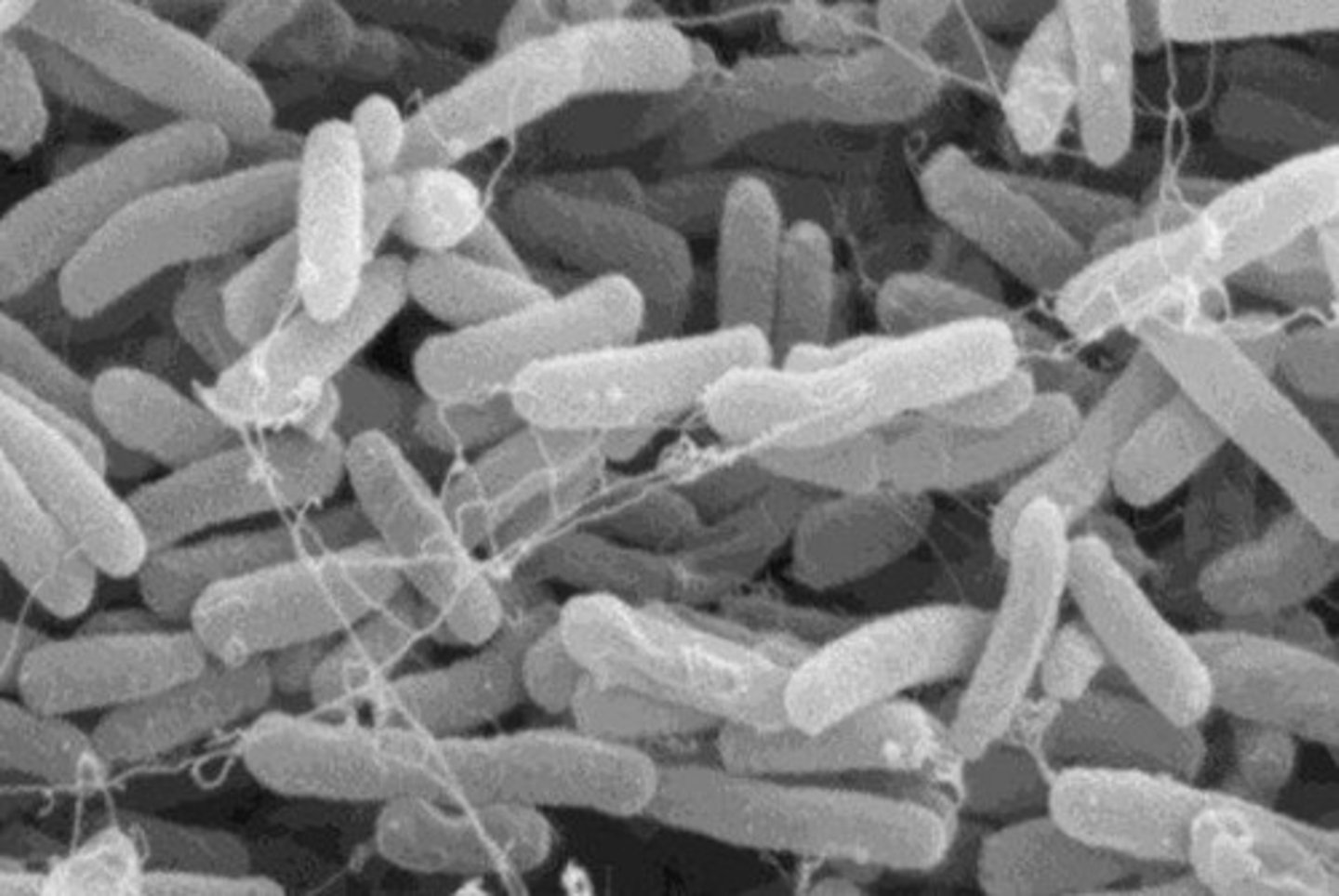

Shape of spirochetes
Spiral-like or worm
What is this an image of?
Spirochetes
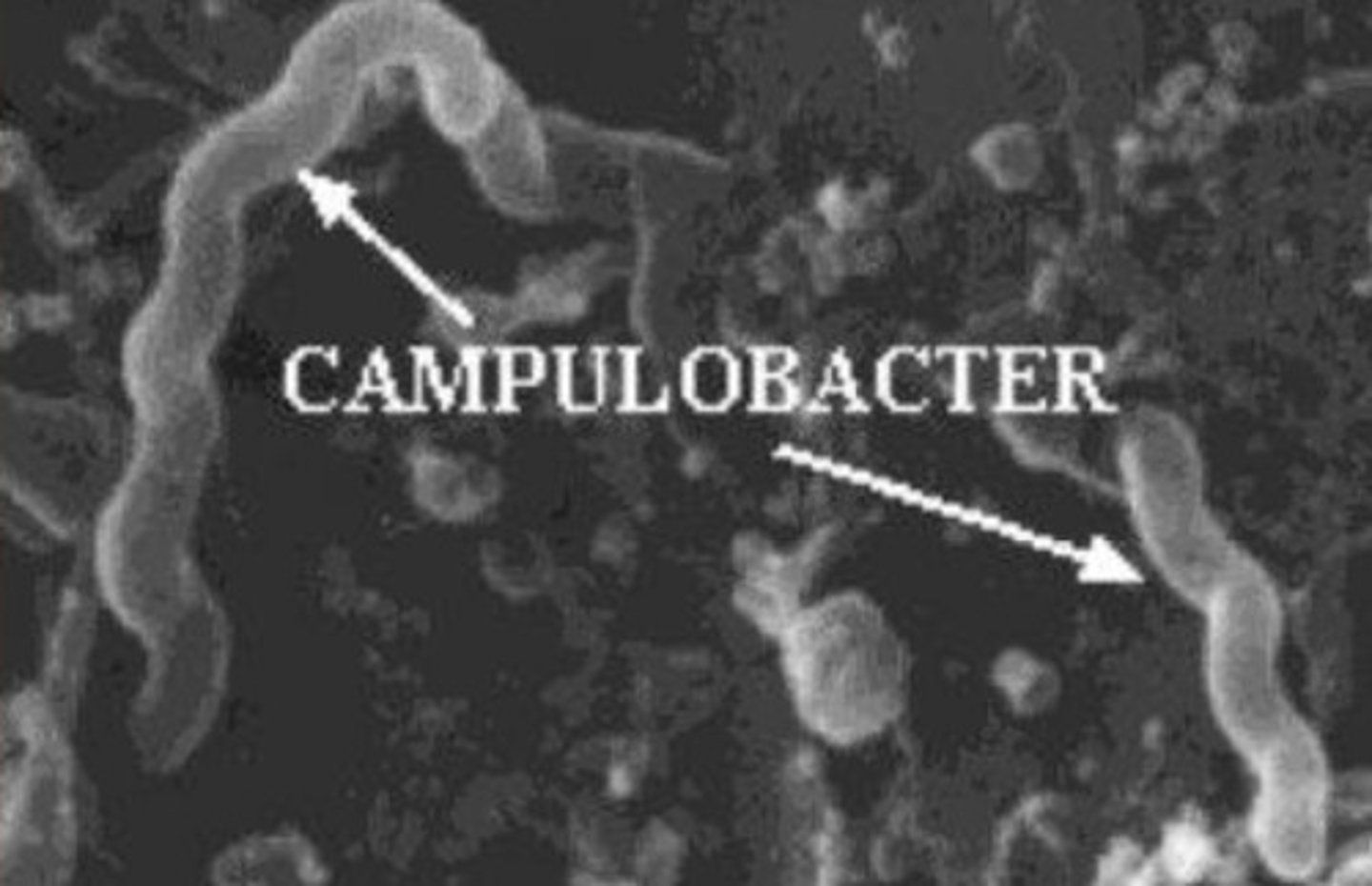
What is this an image of?
Spirochetes
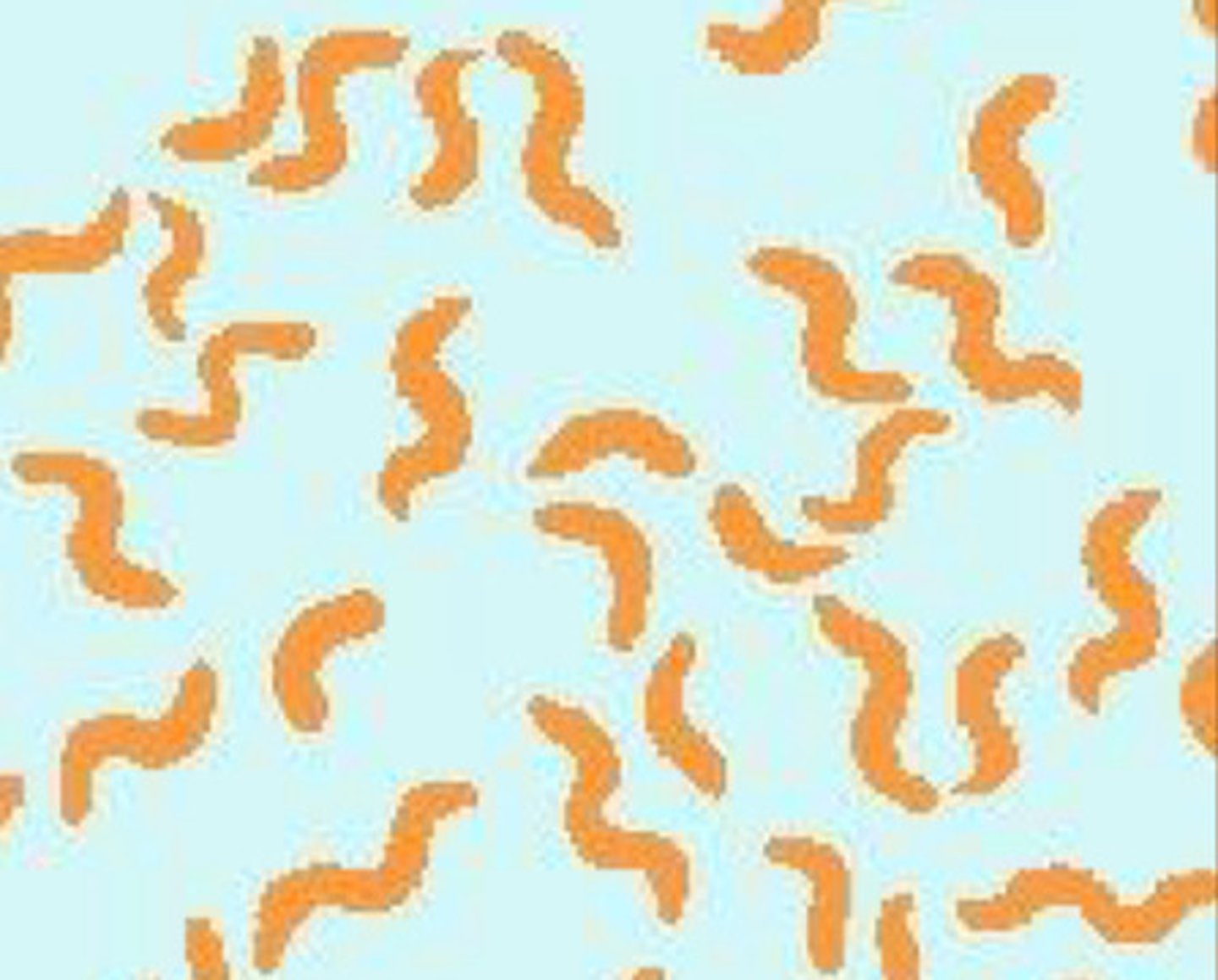
What is this an image of?
Spirochetes
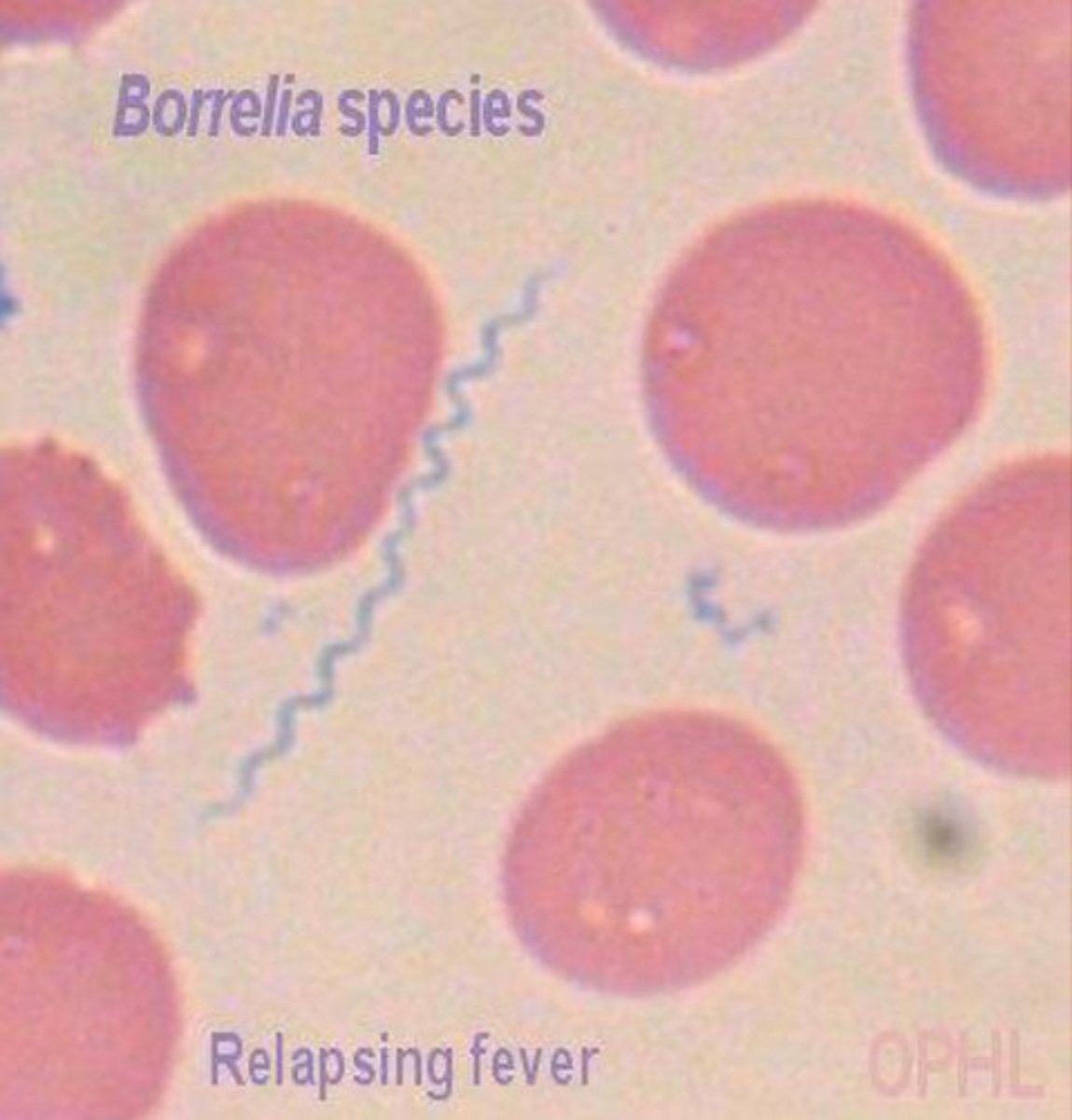
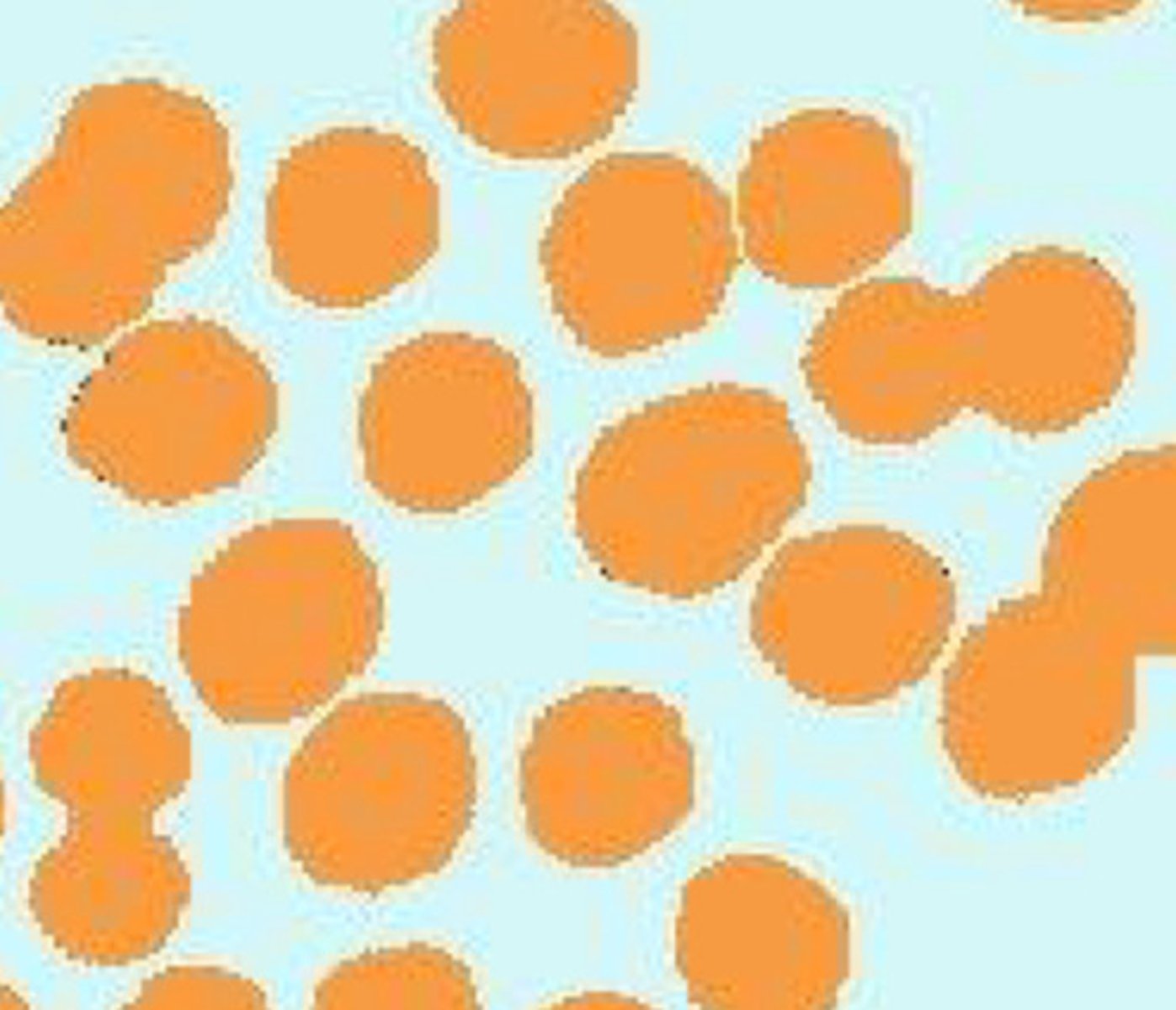
Shape of cocci
Sphere or circle
Colonization
The grouping together
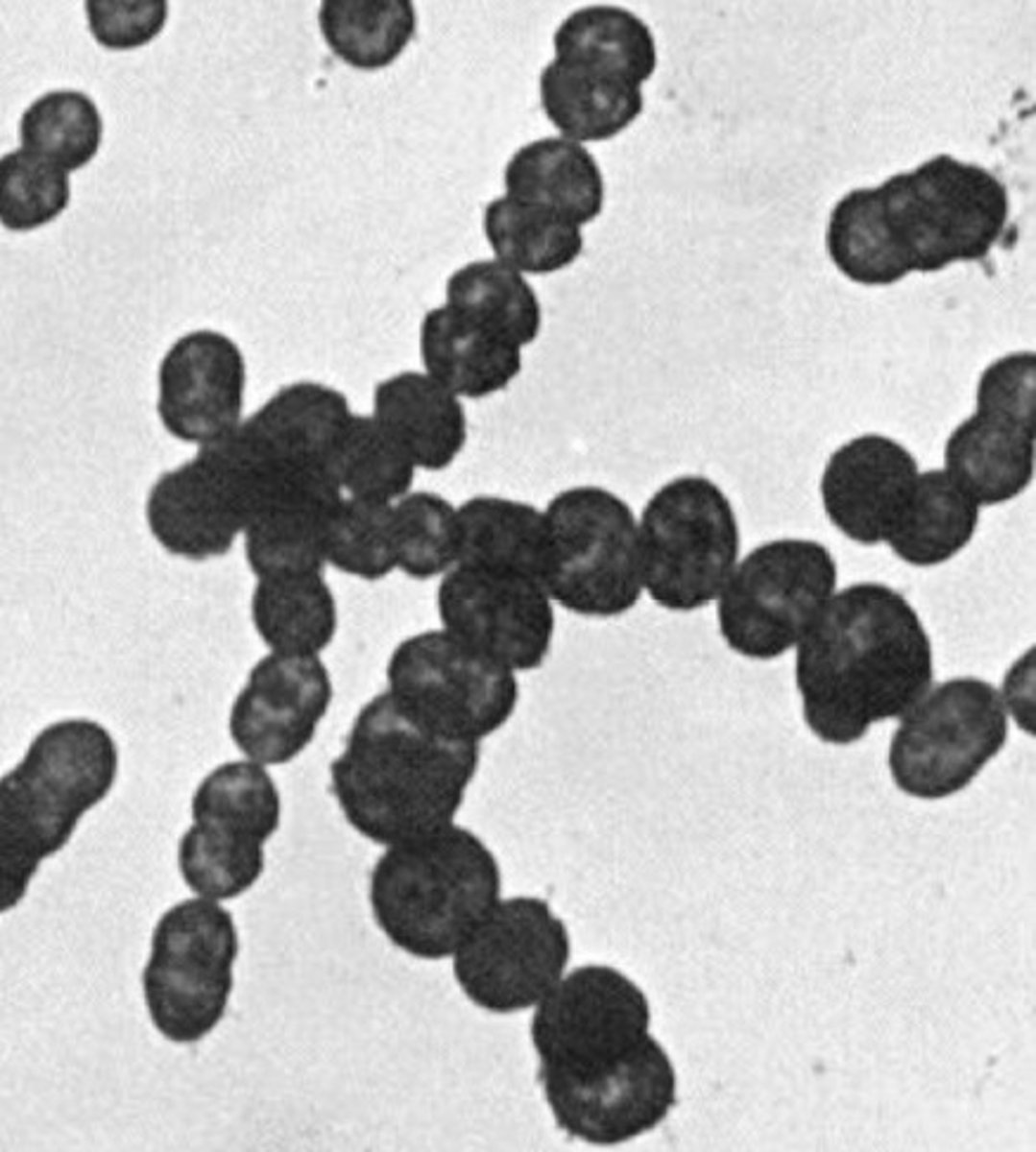
Streptococci
In strings/strands
Associated with strep
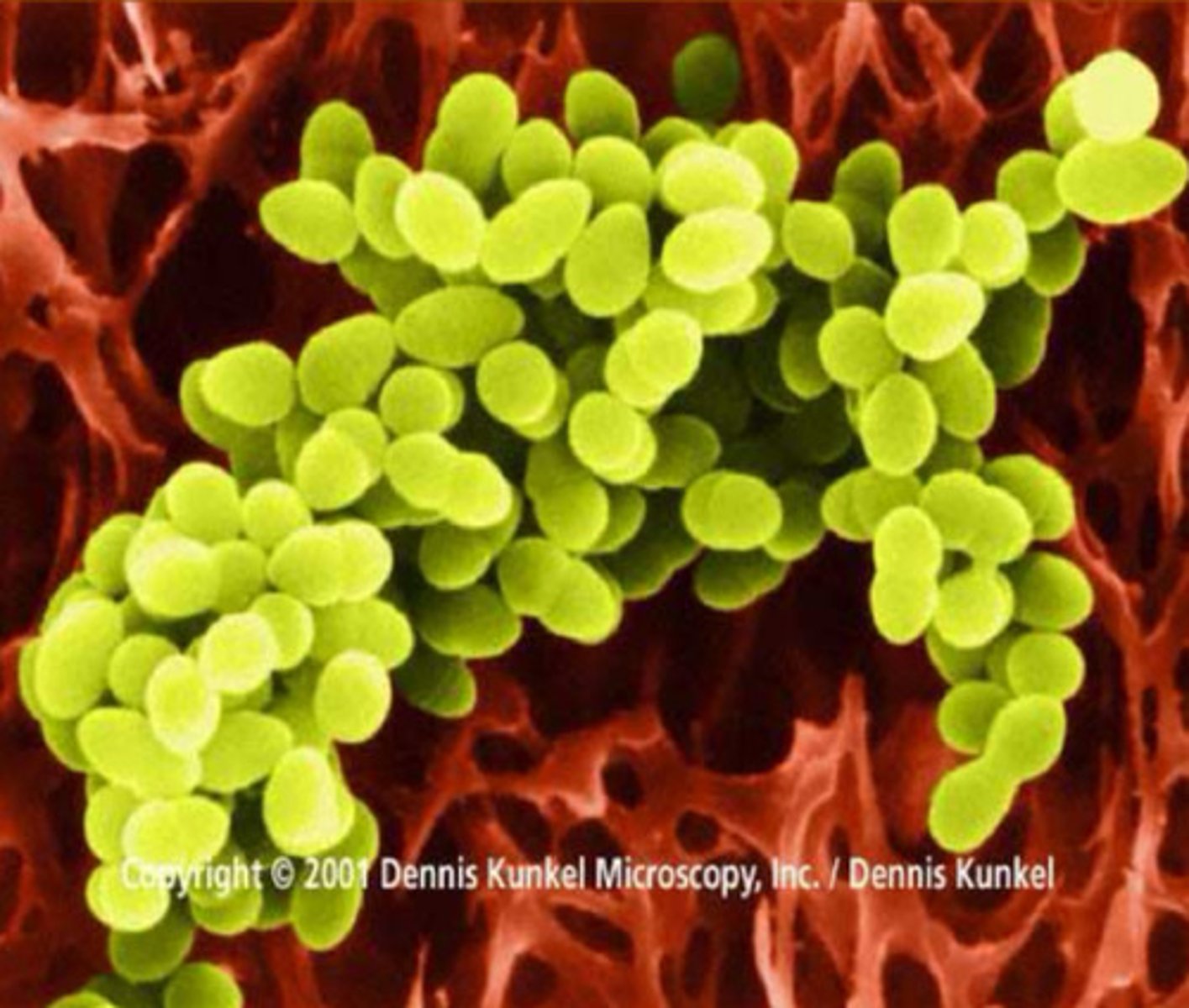
Staphylococci
clumps
Associated with staph infections
What is this an image on?
Cocci
What is this an image of?
Streptococci
What is this an image of?
Staphylococci
Mycoplasma Characteristics
No cell wall, Grow on culture medium, smaller, DNA and RNA, Creates ATP and proteins independently
What does mycoplasma cause?
Atypical pneumonia or STI
Rickettsiae Characteristics
Obligate intracellular parasites - unstable cell membrane, and cannot be grown on traditional culture media
Insect and animal vectors
Cell wall
DNA and RNA
Create ATP and Protein Independency
What does Rickettsiae cause?
Rocky Mountain spotted fever and typhus
Chlamydia Characteristics
Obligate intracellular parasites - can't make ATP by itself
Cell wall
Create Protein independency
Need Host for ATP
DNA and RNA
What does Chlamydia cause?
STI and pneumonia
Fungi Characteristics
Cell wall
Nuclear membranes
Yeast vs. molds
What does fungi cause?
infections in skin, GI, GU tracts
Protozoa Characteristics
Motile, Single celled organisms, Nucleus
What does protozoa cause in the US?
Giardia and trichomonas
What does protozoa cause in developing countries?
Malaria, sleeping sickness, amebiasis, leishmaniasis
Bacteria Pathophysiology
Invasion of tissue, Release Exotoxins and Endotoxins
Exotoxins
Poisonous substances secreted by bacteria
What do exotoxins do?
Cell lysis, degradation of extracellular matrix, cell dysfunction
Endotoxins?
Inflammatory/immune response, Cellular and tissue destruction
Viruses pathophysiology direct pathway
Produces a protein that damages the cell membrane
Virus pathophysiology indirect pathway
Produces a protein that is incorporated into the cell membrane, Immune system mounts a response to this protein
True or False: Sepsis is a syndrome associated with severe infection?
True
Is sepsis a systemic response to infection?
Yes, it enters the bloodstream
How is sepsis caused?
The release of bacterial endotoxins and/or exotoxins
Sepsis triggers the activation of what?
Inflammation cascade, coagulation cascade, complement system
Sepsis cycle
Infection, Bacteremia, Sepsis, Septic Shock, Multi-organ failure
What is the bacteremia stage?
Bacteria in the bloodstream
What is the sepsis stage?
2 or more of:
Temp>100 degrees, <96 degrees
HR>90
RR>20
WBC >12k, <4k
septic shock stage
Hypotension, Perfusion abnormalities, Altered mental status
multi-organ failure stage?
Failure of the kidneys, lungs, heart, liver, clotting, and CNS
What are the treatments for sepsis?
Treat primary infection, Fluid resuscitation, Medications to vasoconstrict, improve heart function, Treat organ failure, Immune modulators
Pathogen
The parasite or microorganism responsible for arousing a pathologic response
Infectivity
Pathogen's ability to invade and replicate in a host; how likely is the pathogen to infect someone
Pathogenicity
Ability of organism to cause disease; certain conditions or some disease can happen at any time.
Virulence
Potency of pathogen and producing severe disease; how bad it will be
Antigenicity?
The pathogen's ability to stimulate an immune response
What is are the sequences of infection?
Transmission, Contact, Airborne, Enteric, Vector-borne
contact transmission
Host is in direct/indirect contact with infection
Airborne transmission
Pathogen is inhaled in through contaminated droplets
Enteric transmission
Fecal/oral route
Vector-borne transmission
Indirect, intermediate, insects transmit the disease
Sequence of infection
Inoculation/portal of entry, Incubation, Prodromal period, Clinical disease, Convalescence, Recovery
Inoculation/portal of entry period
Pathogen fights past 1st line of defense
Incubation period
The period of time from when the pathogen enters until symptoms occur
Replication
Host may/not be contagious
Prodromal period
Mild non-specific symptoms
Clinical disease period
Body's response - immune, inflammation
true symptoms
Convalescence period
Resolution - body defeats pathogen
Recovery
No longer having the pathogen
Symptoms of infection
Fever, chills, sweating, malaise (general fatigue and feeling ill), nausea, vomiting
Symptoms in elderly for infection
Confusion, memory loss, difficulty concentrating
Signs of infection
Fever, rash, lymphadenopathy (swelling of lymph), and lymphangitis
What is this a picture of?
Lymphangitis
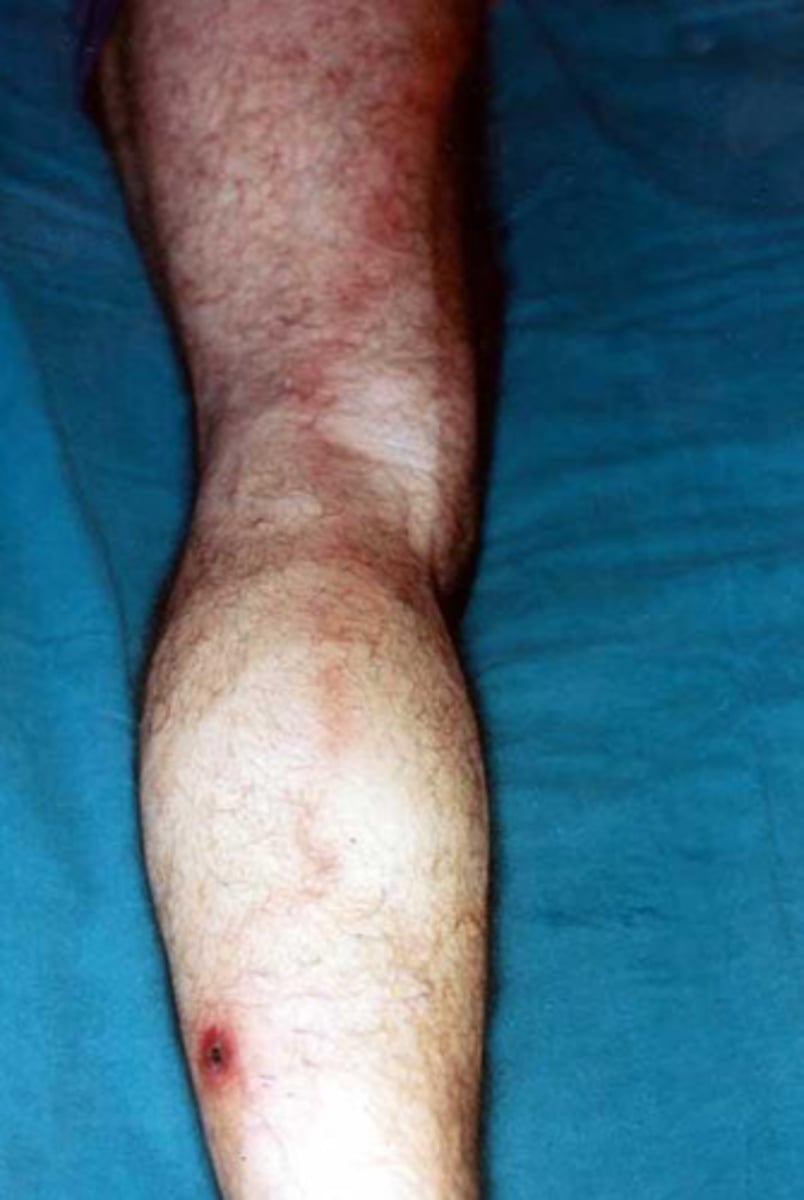
What is this picture of?
Lymphangitis
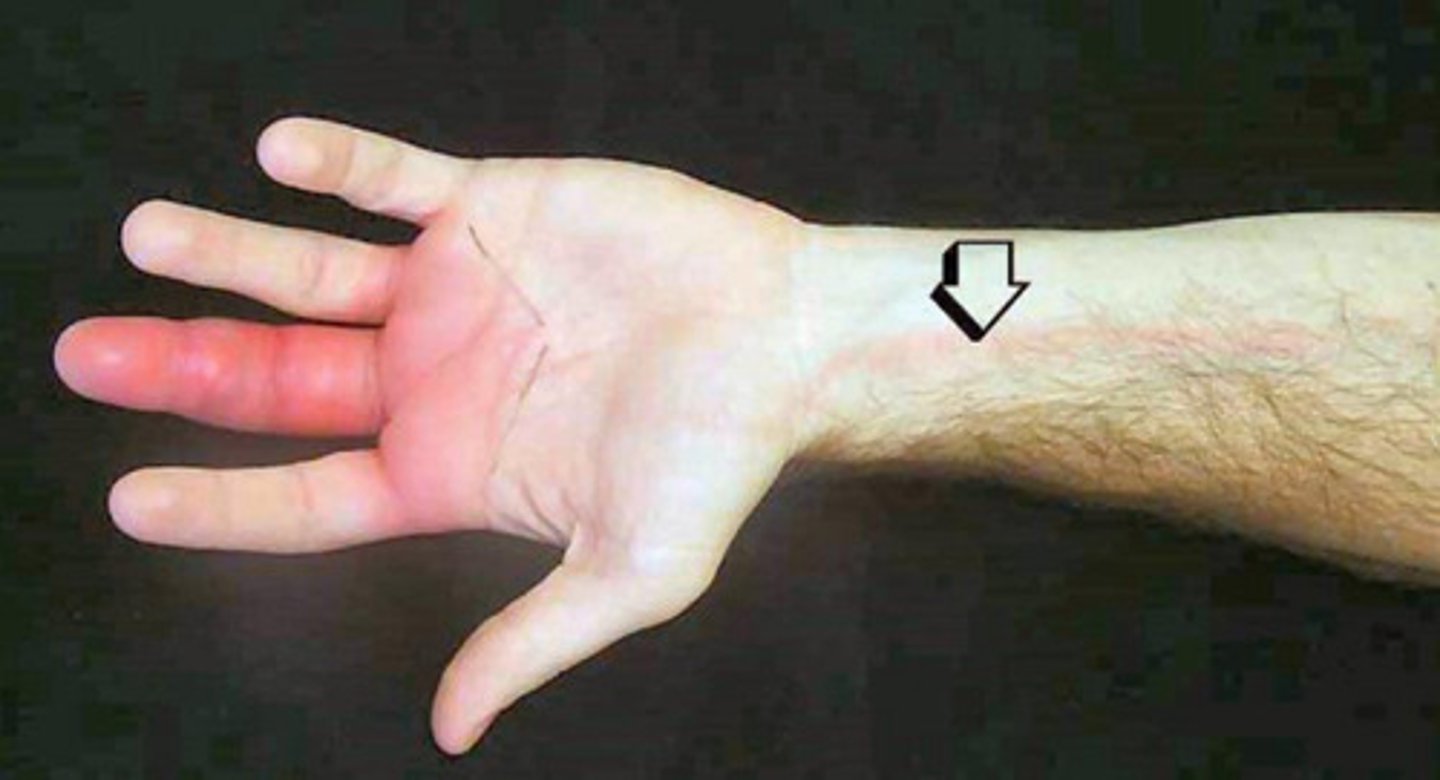
What is the ancillary testing for infection?
Direct visualization of the organism, Culture and sensitivity, Detection of microbial antigen or antibody, Clues that infection may be present, Detection of specific microbial nucleotide sequences
Direct visualization of the organism?
Gram staining - finding certain bacteria, Used by sputum or urinalysis
What is the difference between culture and sensitivity?
Culture is different because each bacteria grow differently. Cultures are 24 hours. Sensitivity is 48 hours. Sensitivity is different by seeing how long infected tissue grows, antibiotics are treatments.
What does the detection of microbial antigen or antibody help do?
Identify viral rapid strep test
What clues that infection may be present?
X-ray and WBC in urinalysis
What is the detection of specific microbial nucleotide sequences?
Viral and bacterial infections
How do we treat infection?
Local methods: Heat, incision and drain
Antibiotics - bacterial
Antivirals - viruses
Antifungals - fungals
What are the antibiotic mechanisms?
Destroy the cell wall
Inhibit protein synthesis
Inhibit DNA synthesis
Inhibit RNA synthesis
What does inhibiting the protein synthesis do?
Bacteria can't replicate
What does inhibiting DNA and RNA synthesis do?
Prevent function and replicate
Antiviral medications do what for the body?
Inhibit viral replication
Frequent resistance
Often use multiple medications
What are the preventions for infection?
Handwashing
Disinfecting tables/equipment
Personal protective equipment (PPE)
Vaccinate healthcare workers
Follow isolation procedures
If ill, avoid treating high-risk patients
Staphylococcus aureus
The most common staphylococcal infections
Normally on the skin, Break in skin or mucous membrane, Suppurative - form abscesses/ pus-filled
What can staphylococcus aureus cause?
Cellulitis, folliculitis, furuncles, carbuncles in skin
How does staphylococcus aureus spread?
Through hematogenous spreading (blood)
Bone, joint, and heart valves
How to control staphylococcus aureus?
Proper handwashing
What does MRSA stand for?
Methicillin-resistant staphylococcus aureus
How is hospital vs community acquired MRSA different?
Hospital MRSA is severe and hard to treat
Community acquired is mild and needs an antibiotic to treat