B - Naming conventions of compounds and ions
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
Define a binary ionic bond
Ionic bond formed from only two elements
Describe the procedure for naming Binary ionic compounds
Name of cation first
Anion second
-ide suffix is added to anion’s root name
Describe the procedure for naming binary ionic compounds where the metal can have multiple oxidation states in the compound
Name of cation first
Roman numerals are added to cation’s name
Anion second
-ide suffix is added to anion’s root name
Name the ion formulas, systematic and common names of Chromium

Name the ion formulas, systematic and common names of Cobalt
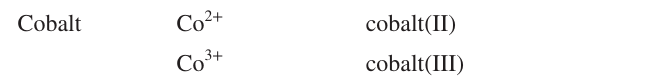
Name the ion formulas, systematic and common names of Copper
Name the ion formulas, systematic and common names of Iron
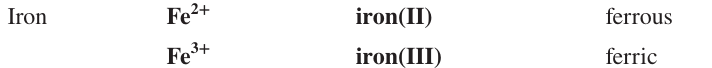
Name the ion formulas, systematic and common names of Lead

Name the ion formulas, systematic and common names of Mercury
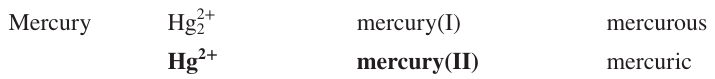
Name the ion formulas, systematic and common names of Tin
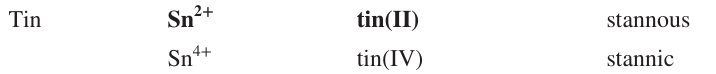
Describe the procedure for naming ionic compounds with polyatomic ions
Cation first
Polyatomic second with full name
e.g. Cr2(CO3)3 = Chromium(II) Carbonate
Describe the procedure for naming ionic compounds which are hydrates
The full name of the ionic compound first
Greek numerical prefix + ‘-hydrate’ is added to the end
e.g. CuSO4 • 5H2O = Copper(II) Sulphate pentahydrate
Define a binary acid
Acid only containing two elements
e.g. HCl
Describe the procedure for naming binary acids
hydro + anion root + -ic + acid
e.g. HCl = Hydrochloric acid
Define an oxoacid
An acid which contains a polyatomic ion with oxygen in it
e.g. HClO4
Describe the procedure for naming oxoacids
oxoacid name + -ous/-ic suffix + acid
-ous is used if the anion contains the -ite suffix
-ic is used if the anion contains the -ate
e.g. Nitrate (NO3-) becomes Nitric acid and Nitrite (NO2-) becomes nitrous acid
Describe the procedure for covalent compounds
Greek prefix + Element with lower group number/higher row +++ Greek prefix + second element + -ide
-a is dropped when naming oxides
e.g. N2F4 = Dinitrogen tetrafluoride