economies of scale
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
explain financial economies of scale
have more credibility as a large firm
able to negotiate lower interest rates and larger loans
explain technical economies of scale
by hiring more workers (TC rises)
make workers specialise in jobs
they can thus solely focus on them
boosting productivity and resulting in a higher output per worker (Q rises more than TC)
thus, AC falls (as TC is spread over a larger range of output? is this necessary)
explain marketing/purchasing economies of scale
they are able to bulk buy advertising/raw materials
have bargaining advantage
able to negotiate better unit rates of marketing/purchasing
spread costs over a larger volume of sales/output (TC rises slower than Q rises → AC falls)
explain co-ordination/communication diseconomies of scale
as the firm grows too large, it becomes more difficult for the firm to maintain an effective flow of information through the company
impacting productivity
TC rises much faster than Q → AC rises
explain morale diseconomies of scale
as the firm grows too large, workers feel a sense of alienation from the company (they are easily replaceable)
thus, morale becomes low and their productivity falls
TC rises faster than Q rises → AC rises
explain economies of information
R&D knowledge is shared among firms in the industry (e.g. cost-saving tech)
technology is improved
boosts productivity of individual firms
TC falls over the same range of output/while Q rises → AC falls
explain economies of concentration
many firms are concentrated in one area
transport infrastructure for that area is more invested in and developed
thus it becomes cheaper to access raw materials (TC falls)
TC falls over the same range of output → AC falls
explain strain on infrastructure (EDOS)
firms are too concentrated in one area
infrastructure is taxed to its limits → e.g. traffic congestion
TC rises due to increased fuel consumption
productivity falls due to loss of time (Q falls)
AC rises
explain shortage of resources (EDOS)
industry grows larger → shortage of certain raw materials/labour
competition for said resources pushes up price (TC rises)
TC rises much faster than Q → AC rises
define EEOS
the savings in costs that occur to all firms as a result of the expansion of the industry/concentration of firms in a certain location
define IEOS
cost savings that occur as a result of the firm’s expansion/increasing the scale of production and have been created by the firm’s own policies and actions
define IDOS
increases in long run average costs that occur to the firm as a result of the expansion of the firm, which is the result of the firm’s own policies and actions
define EDOS
increases in costs that occur to all firms in an industry as a result of the expansion of the industry/concentration of firms in a certain location
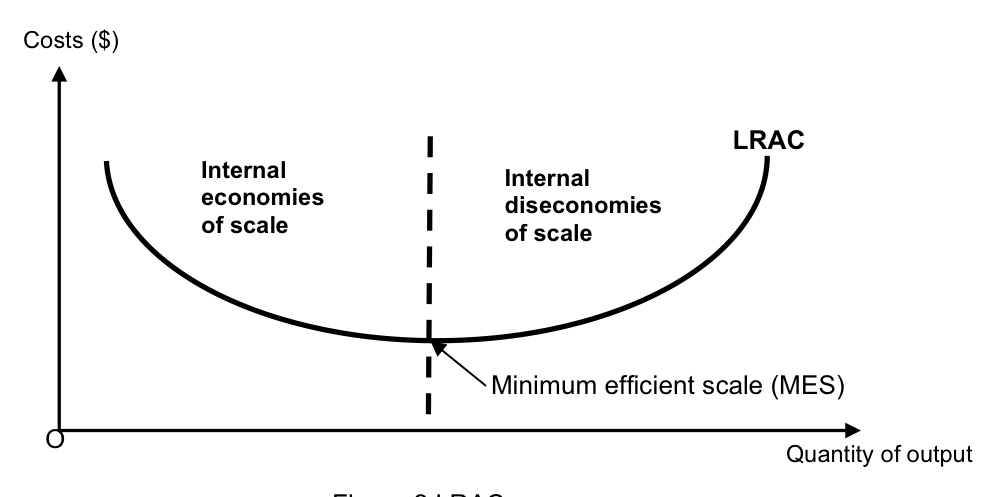
how is IEOS/IDOS represented diagrammatically?
IEOS: the falling part of the LRAC curve
IDOS: the upward sloping part of the LRAC curve
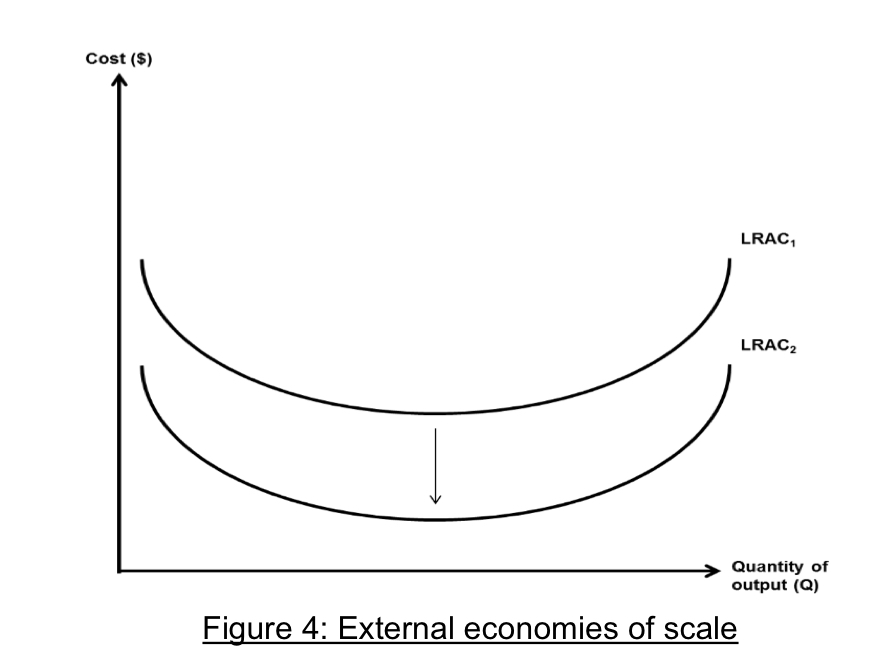
how is EEOS/EDOS represented diagrammatically?
EEOS: downward shift of the LRAC curve
EDOS: upward shift of the LRAC curve