EXAM 2 (4) Population growth part 2
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
Population growth rate dN/dt
change in the number of individuals in a population per unit time
intrinsic growth rate (b-d)=r
r is the per capita rate of increase(measures how fast a population would grow per individual)
The highest possible per capita growth rate for a population.
birth rate and death rate for each individual
rmax: occurs when birthrate is at its highest and deathrate is at its lowest
When B=D r=0
when deathrate is higher than birthrate=-r
exponential growth equation
(dN/dt)=rN
founding populations
when you have a new population in a habitat
recovering populations
population basically crashed (Ex. disease)
what are some assumptions of exponential growth
unlimited space
unlimited resources
small population (as populations become larger reosurces become more unlimited)
very little competition
includes birth and death rates
logistic growth equation
(dN/dt)-rrelN(k-N)/K)
rrel- relative growth rate, how an individual can reproduce relative to the influence population size has on that individual
carrying capacity (k)
max number of individuals a habitat can support
k is not constant
whats the population growth when N=K
zero
whats the poulation growth rate when N>K
negative. the population is larger than the environment can support, resources become limited and there are more deaths=negative growth
whats the population growth rate when N<K
positive, the population is less than the carrying capacity. resources arent limited so the population can grow
density independence
doesn’t depend on population size, affects the population no matter what
limits population size regardless of the populations density
alter birth and death rates
usually environmental changes
exponential model: population grows without being limited by its size
ex. storms drought, wildfires
if r is constant, the number of individuals added to the population changes, but the rate of increase in the same
Density dependence
Factors that affect population size in relation to the population’s density.
alters survivorship and fecundity based on density
affects the population more when there are lots of individuals
logistic growth curve
defines k
*examples with terns and the islands
logistic growth model graph
includes density dependence
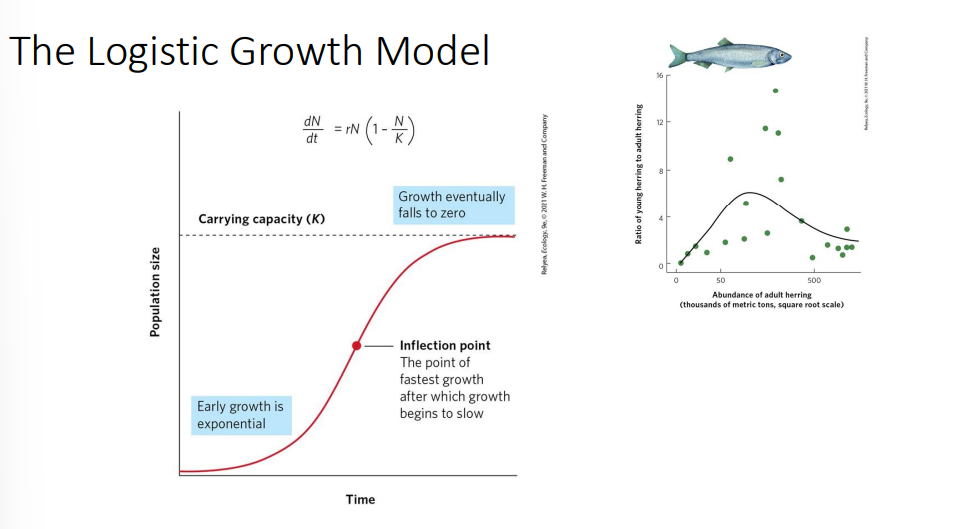
inflection growth
the population size where growth is fastest, halfway to the carrying capacity
tern population
example of negative density dependece
As the tern population expanded in Buzzards Bay, Massachusetts, it colonized Bird Island. Rapid growth of the population filled most of the available nesting sites, and the birds then colonized Ram Island. Once again, the population grew and occupied most of the available nesting sites. The terns then colonized Penikese Island.
Negative density dependence
When the rate of population growth decreases as population density increases