hominin evolution - comparison of species
1/24
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Ch 13.1 & 13.2
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
define bipedal / bipedalism
when an organism uses 2 legs/rear limbs
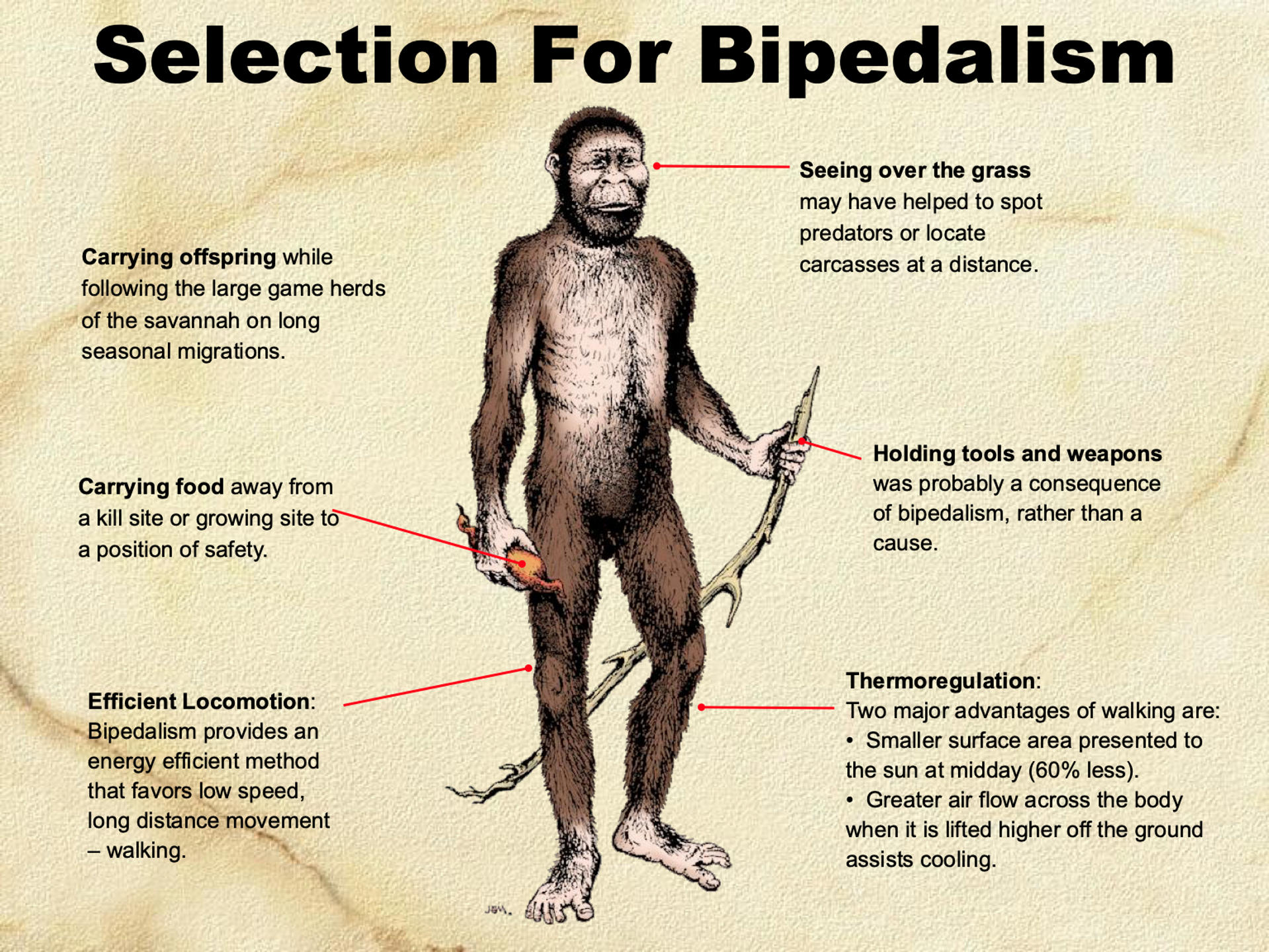
identify advantages of bipedalism
identify body features that have gradually increased during the evolution of hominins
cranial capacity
number of convolutions of the cerebral cortex
size of frontal lobe
identify body features that have gradually decreased during the evolution of hominins
reduction in prognathism & the development of a forehead
Early hominin had a lower jaw & similar face to the great apes, but during evolution their (hominin) faces became flatter, what caused this?
during evolutions the teeth become smaller, therefore took up less space, resulting in a flatter face
give examples of fossil evidence of Australopithecus afarensis and Australopithecus africanus
Taung skull, Laetoli footprints and ‘Lucy’.
describe the teeth & jaw of Australopithecines
they had short canines and a lack of diastema, with the teeth arranged in a parabolic shape and a projecting lower jaw.
state the avg cranial capacity & describe the forehead & foramen magnum of Australopithecines
low forehead
avg cranial capacity was 480cm3
Their foramen magnum was more central than in other apes, and the skull more rounded at the back.
describe the spine, feet & fingers of Australopithecines
Australopithecines were bipedal, with a non-opposable big toe and an ‘S’-shaped spine.
The fingers were heavily built and more suitable for a power grip than a precision grip.
when did Australopithecus afarensis & Australopithecus africanus exist?
Australopithecus afarensis existed 3.9–2.8 million years ago, earlier than Australopithecus africanus, who existed 3.2–2.0 million years ago.
Paranthropus robustus are thought to form a branch in hominin evolution, when were they living?
1.8–1.2 million years ago
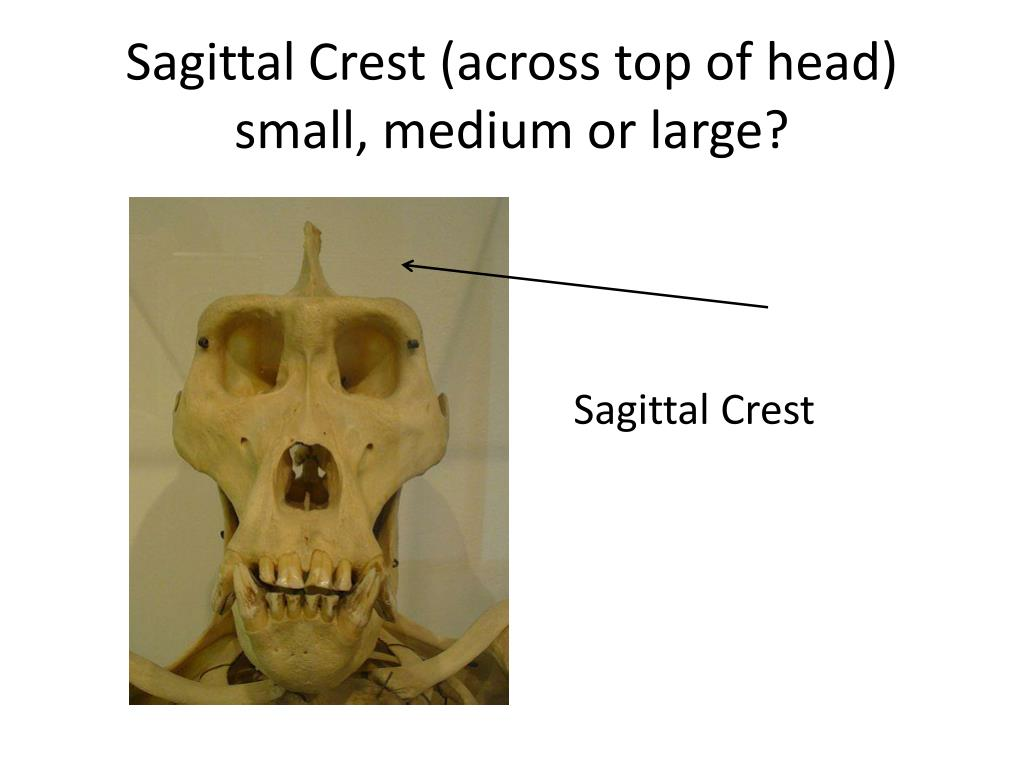
describe the sagittal crest, mouth, face & avg cranial capacity of Paranthropus robustus
They were robust with a large sagittal crest with strong chewing muscles and molars.
They had a larger cranial capacity, with an average of 520 cm3
they had a wide, dish shaped face with less prognathism.
describe the brain size of Homo Habilis & compare skull features & teeth to australopithecines
they had a larger brain (610 cm3 ) and smaller teeth than the australopithecines.
When compared to the australopithecines, their skulls were rounder, the foramen magnum central, the dental arcade rounder and with less prognathism.
describe the arms, legs & fingers of Homo habilis
The arms of Homo habilis were long and the legs short.
The fingers were slightly curved, indicating a power grip. However, they were also capable of a precision grip
describe the cranial capacity & forehead of Homo erectus
cranial capacity was 1050 cm3
their forehead low and sloping,
describe the jaw & size of molar teeth of Homo erectus - & what does the size of their molar teeth indicate?
their jaw large, thick and rounded, without a chin.
The molar teeth were smaller, indicating a diet similar to that of modern humans.
where & when did the Homo neanderthalensis exist?
they were an evolutionary branch who existed in Europe during the ice age.
describe the height & build of Homo neanderthalensis
They were short in stature with a heavier build than modern humans
describe the skull & face of Homo neanderthalensis
They had big faces, low but large skulls, heavy brow ridges and an occipital bun at the back of the skull
their face showed greater prognathism than modern humans due to the nasal bones projecting forward.
what is the cranial capacity of the Homo neanderthalensis?
Their cranial capacity was larger than that of modern humans at 1485 cm3
Cro-Magnon people were early Homo sapiens - compare their skull to neanderthal
Their skulls were shorter from front to back and higher than the skulls of Neanderthals.
describe the brow rides, prognathism & state the avg brain size of the Cro-Magnon people
They also showed reduced brow ridges and prognathism, and brains averaging 1350 cm3
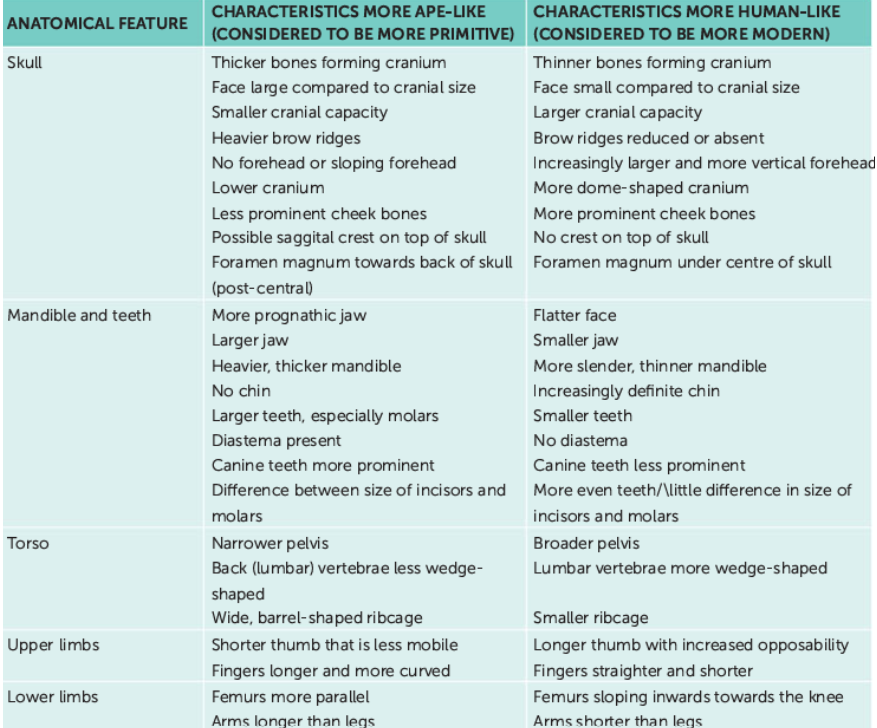
contrast anatomical features (skull, teeth, mandible, torso, upper & lower limbs) between characteristics that are more ape-like (primitive) & human-like (modern)
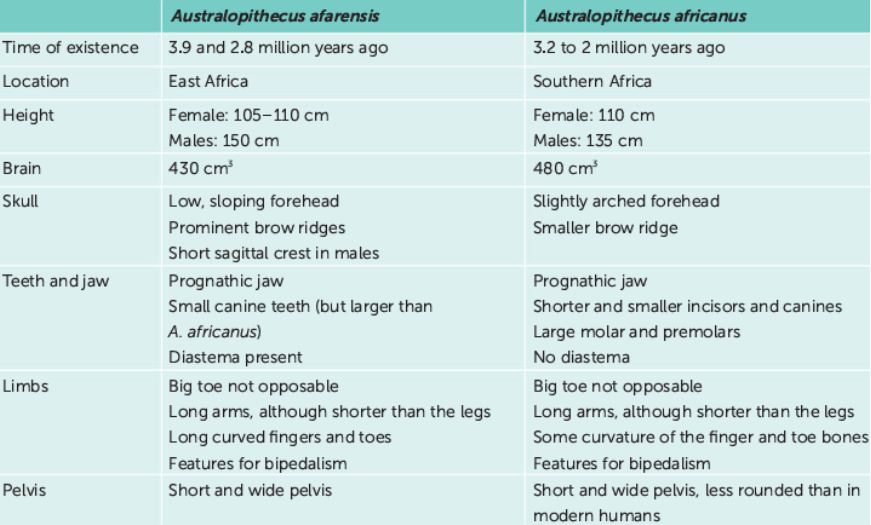
compare & contrast Australopithecus afarensis & Australopithecus africanus (time of existence, location, height, brain, skull, teeth, jaw, limbs & pelvis)
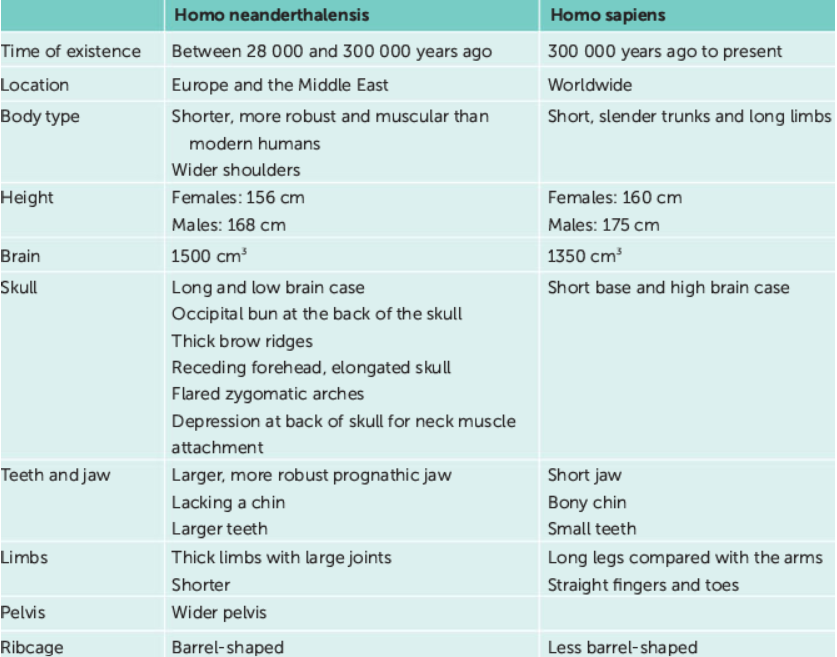
compare & contrast Homo neanderthalensis & Homo sapiens (time of existence, location, body type, height, brain, skull, teeth, jaw, limbs, pelvis & ribcage)