Biology Lab exam #3
1/124
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
125 Terms
Cytokinesis
division of the cytoplasm to form two separate daughter cells
parent cell
original cell before cell division
daughter cells
the two new cells that result from mitosis and cytokinesis
cell cycle
the sequence of growth, DNA replication, growth, and cell division that all cells go through.
Interphase
the longest part of thr cell cycle. 90% of cell cycle. 3 sub-phases: G1, S, and G2.
G1 phase
cell increases in size and builds up energy reserves.
S phase
DNA replication
G2 phase
second phase of growth and energy acquisition.
M phase
active cell division. 10% of cell cycle
G0
mature non-dividing cells are in this phase. like nerve cells after maturity.
Mitosis
cell division, occurring in nucleotide cells that results in daughter cells with identical chromosomes and organelles to the parent cell. responsible for the growth abd maintenance of tissues associated with all life processes except sexual reproduction. 5 stages: prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase.
Prophase
the chromosomes condense and become more tightly coiled. they appear as teo sister chromatids bond together at the centromere. the cytoskeleton disassembles and the mitotic spindle begins to form. the nuclear envelope begins to break down.
Centromere
the central region where the two chromatids are bound together.
mitotic spindle
composed of the centrosomes and extending microtubules.
Prometaphase
the nuclear envelope fragments and the microtubules surrounding the spindle enter the nuclear area and interact with, and attach to the attached chromosomes. the chromosomes begin to move toward the cells equator.
Metaphase
all of the chromosomes become aligned at the metaphase plate and the centrosomes move to opposite poled of the cell, on either end of the mitotic spindle. longest of the mitotic phases.
Anaphase
cromatids are pulled apart creating daughter chromosomes. chromosomes move to opposite poles via spindle fibers, with the centromere leading the way. The spindles move apart from one another and the cell begins to elongate. as anaphase progresses, the chromosomes are pulled farther apart. it is the shortest stage.
Telophase
nuclear envelopes are formed around each around each of the newly separated sets of chromosomes. the chromosomes assembled at the poles of the cell become less condensed. nucleus is now divided into two identical nuclei.
Cytokinesis in animal cells
cleavage furrow forms and cell pinches in two
cytokinesis in plant cells
cell plate forms
Meiosis
A two-stage type of cell division in sexually reproducing organisms that results in 4 genetically distinct daughter cells with half the chromosome number of the original cell. Produces gametes (eggs and sperm).
Prophase I (Meiosis)
the chromosomes condense and the microtubule spindle forms. the homologous chromosomes pair up by size and theb become closely associated and entwined around one another during synapsis. crossing over then occurs. the chromosomes cross over one another exchanging genetic information and forming crisscrossed regions called chiasmata. the movement of centrosomes, the dispersal of nuclei, ans the breakdown of the nuclear envelope. requires 90% of time required for meiosis.
chiasmata
holds the two homologous chromosomes together through anaphase I.
Metaphase I (Meiosis)
Pairs of homologous chromosomes move to the equator of the cell. the chromatids in each chromosome attach to the kinetochore microtubules, directing one chromosome from each pair toward opposite poles.
Anaphase I (Meiosis)
Homologous chromosomes separate into sister chromatids. and each moves toward an opposite pole. Microtubules begin to shorten.
Telophase I (Meiosis)
the separated sister chromatids form a cluster at each pole of thr cells. forms 2 daughter cells with half the number of chromosomes as the parent cell.
Prophase II
a new spindlebapparatus is formed in each cell and the nuclear envelope breaks down.
Metaphase II
the chromosomes made of non-identical sister chromatids are positioned along the metaphase plate. the kinetochore microtubules attach to each of the chromatids.
Anaphase II
the sister chromatids separate from one another as the centromeres separate, and move to opposite poles of the cell.
Telophase II
the nuclei form and the chromosomes begin to decondense.
describe the process of the mitotic spindle and microtubules in mitosis.
In prophase, the mitotic spindle begins to form. It is composed of microtubules and is formed by centrosomes. In prometaphase. the microtubules enter the nuclear area and attach to the condensed chromosomes at the kinetichores. the chromosomes that are attached to the microtubules are theb moved toward the middle of the mitotic spindle. In metaphase, all of the chromosomes line up in the middle of the spindle and become aligned at the metaphse plate. Then in anaphase, the kinetochore microtubules shrink, and the daughter chromosomes are moved to opposite poles of the cell. the spindles also move apart from each other, elongation the cell.
Are the chromosomes in mitosis and meiosis a mixture of mother and father chromosomes?
the chromosomes in mitosis are a mixture of mother and father chromosomes. Half of the chromosomes come from you father and half come from your mother. in humans there are 23 pairs of chromosomes, one set from your mother and one from you father making 46 chromosomes total. During prophase I of meiosis there is an exchange of parts of chromosomes between parental and maternal homologs at the chiasmata (called crossing over), leading to chromatids that have both paternal and maternal segments.
G2 of interphase picture plant
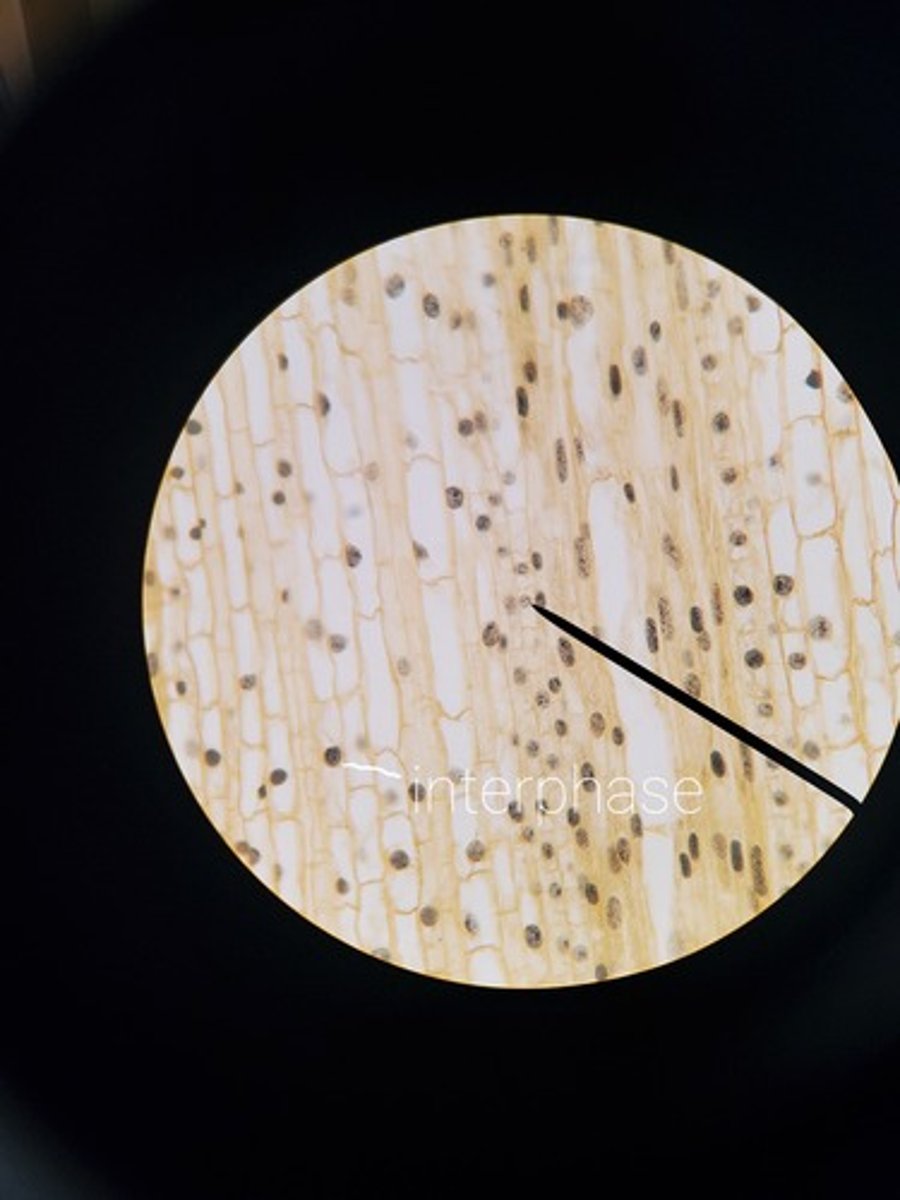
start codon
AUG (methionine) the first amino acid that signals the start of protein synthesis.
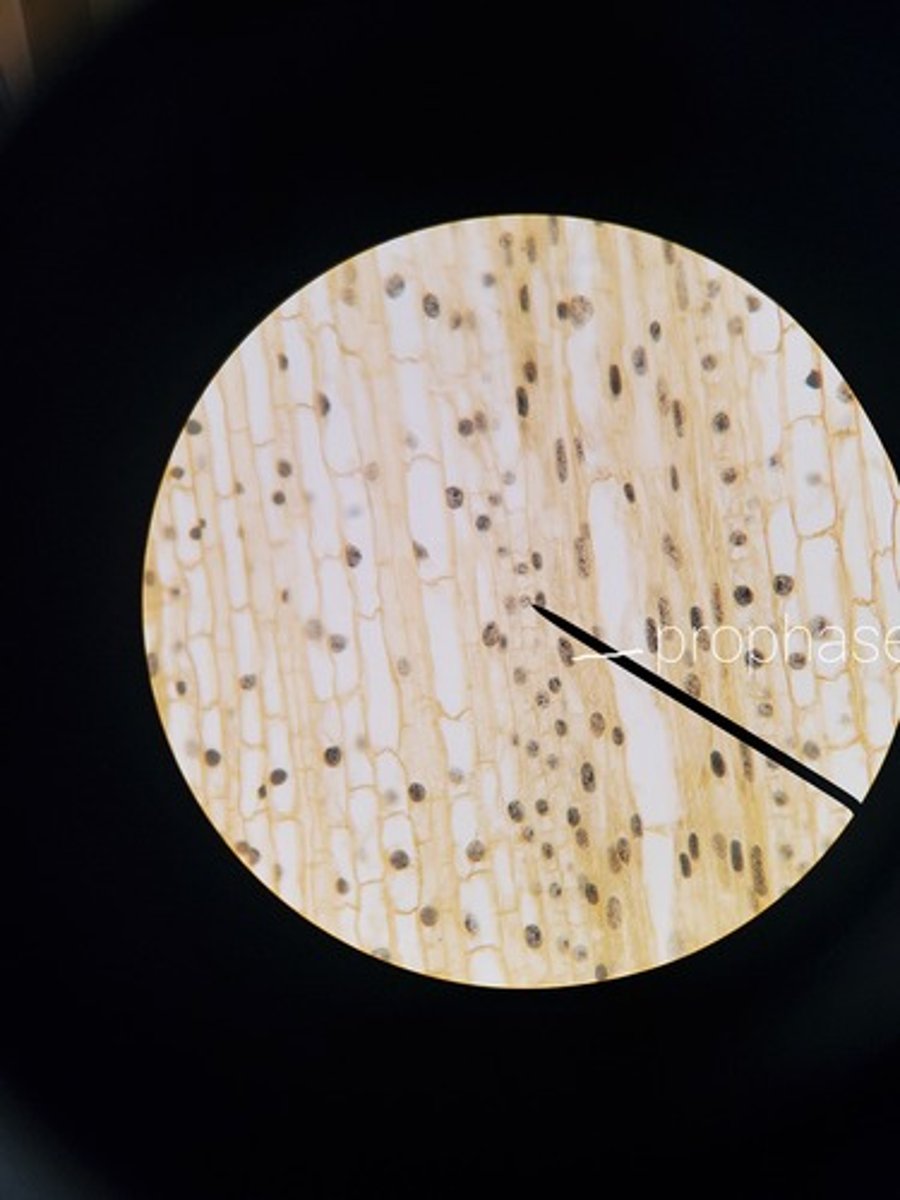
Prophase (picture) plant
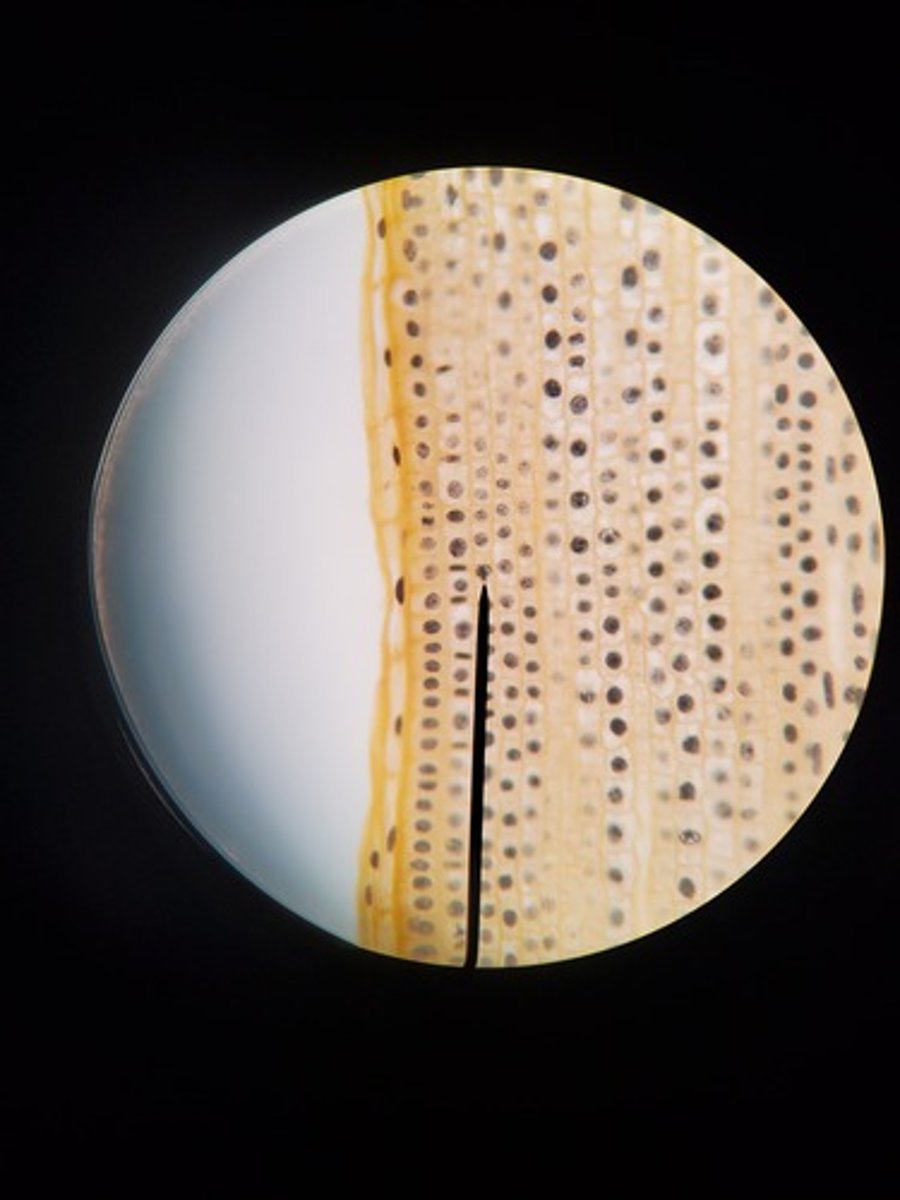
Prometaphase plant picture
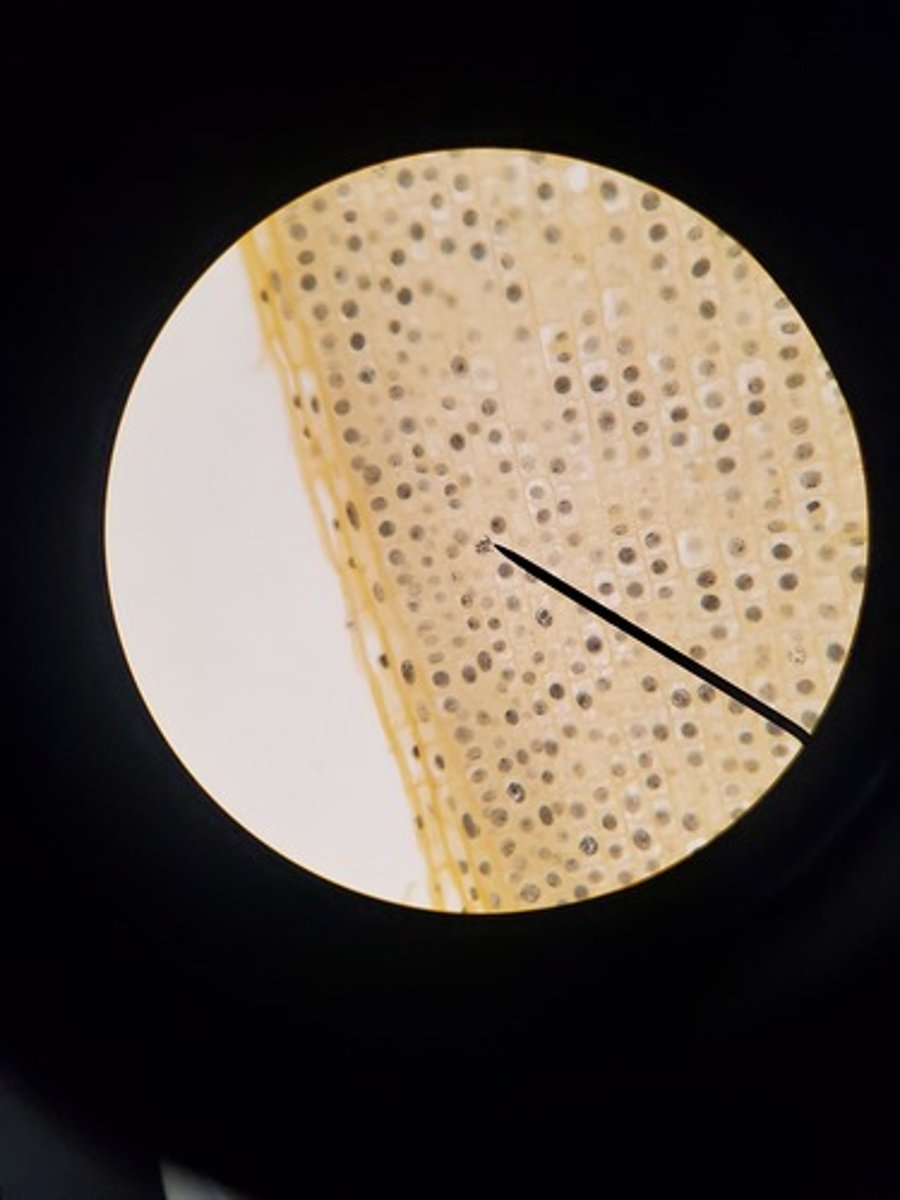
Metaphase plant picture
Anaphase plant picture
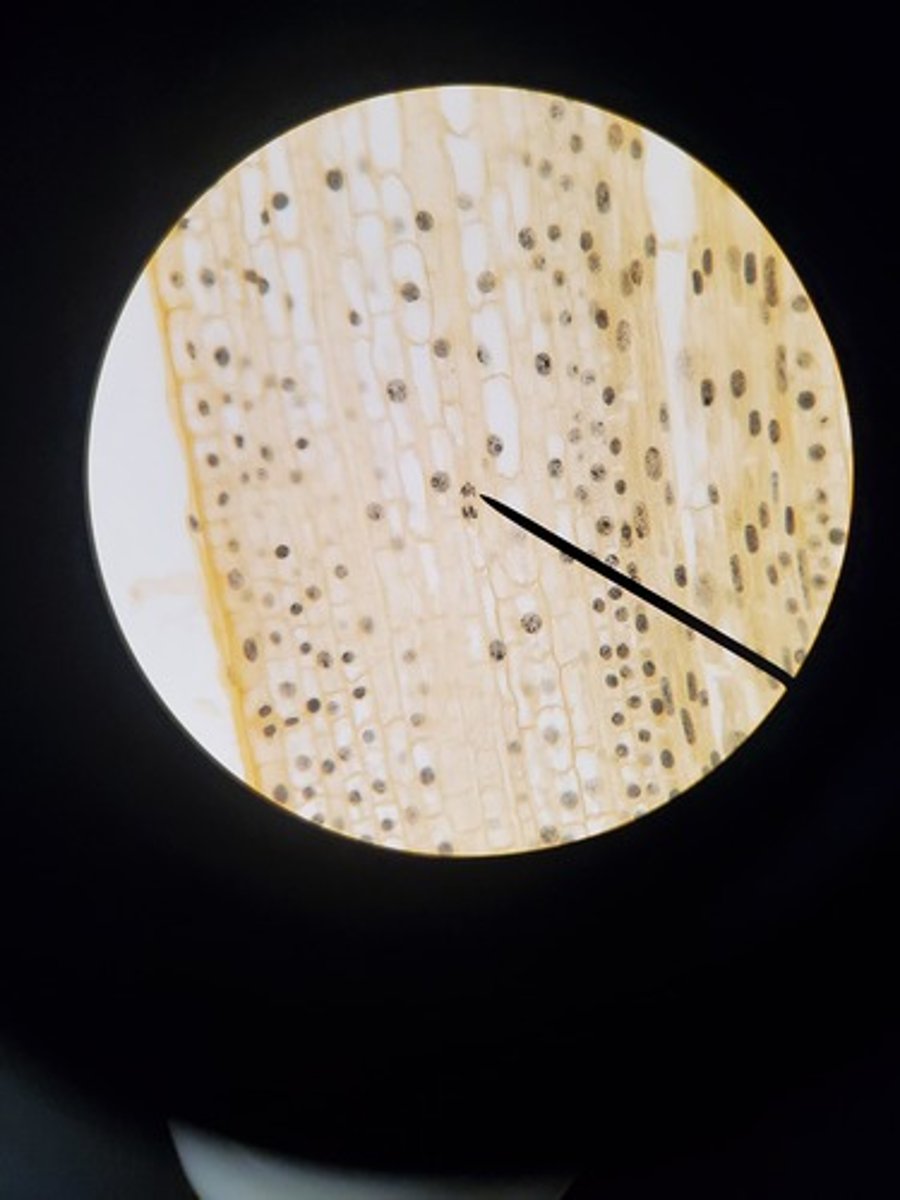
G2 of Interphase (Mitosis) animal picture
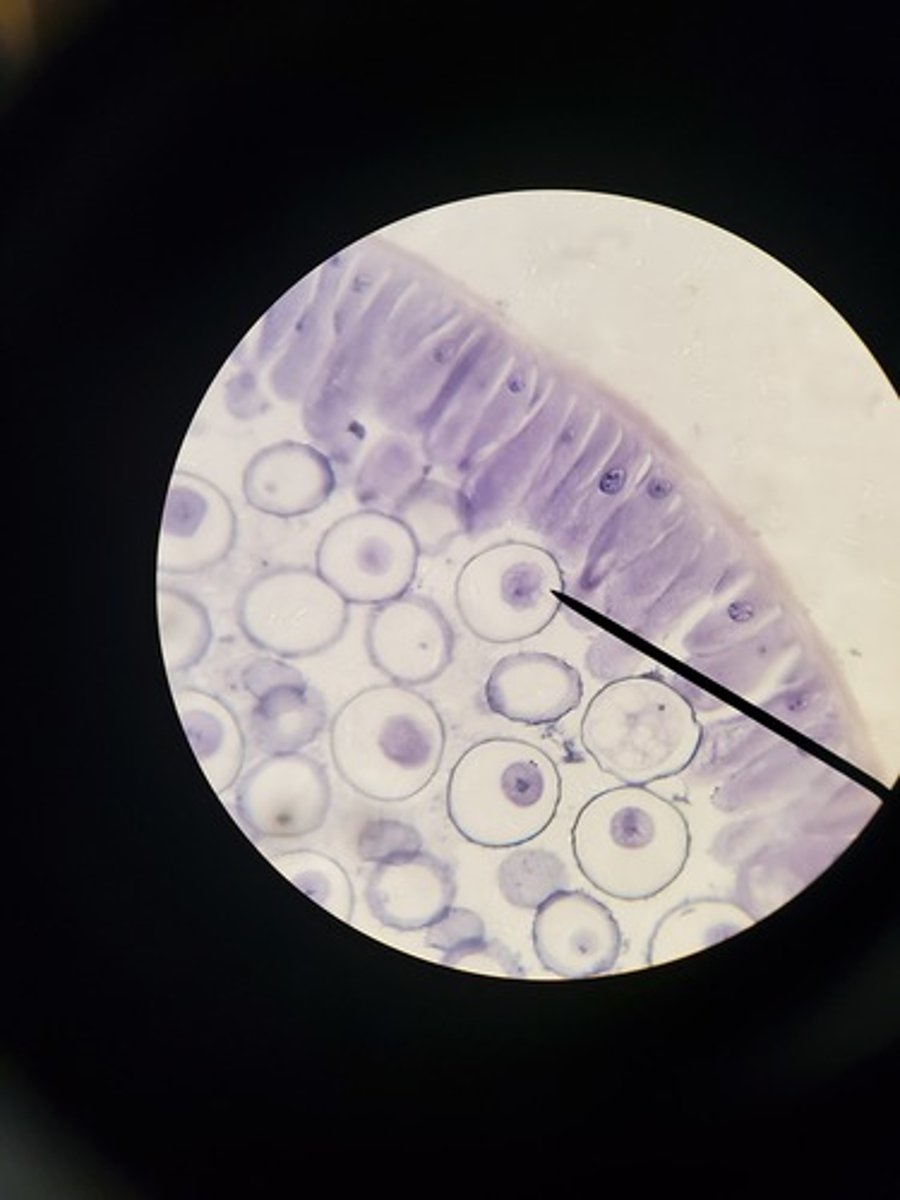
prophase in animal cell picture
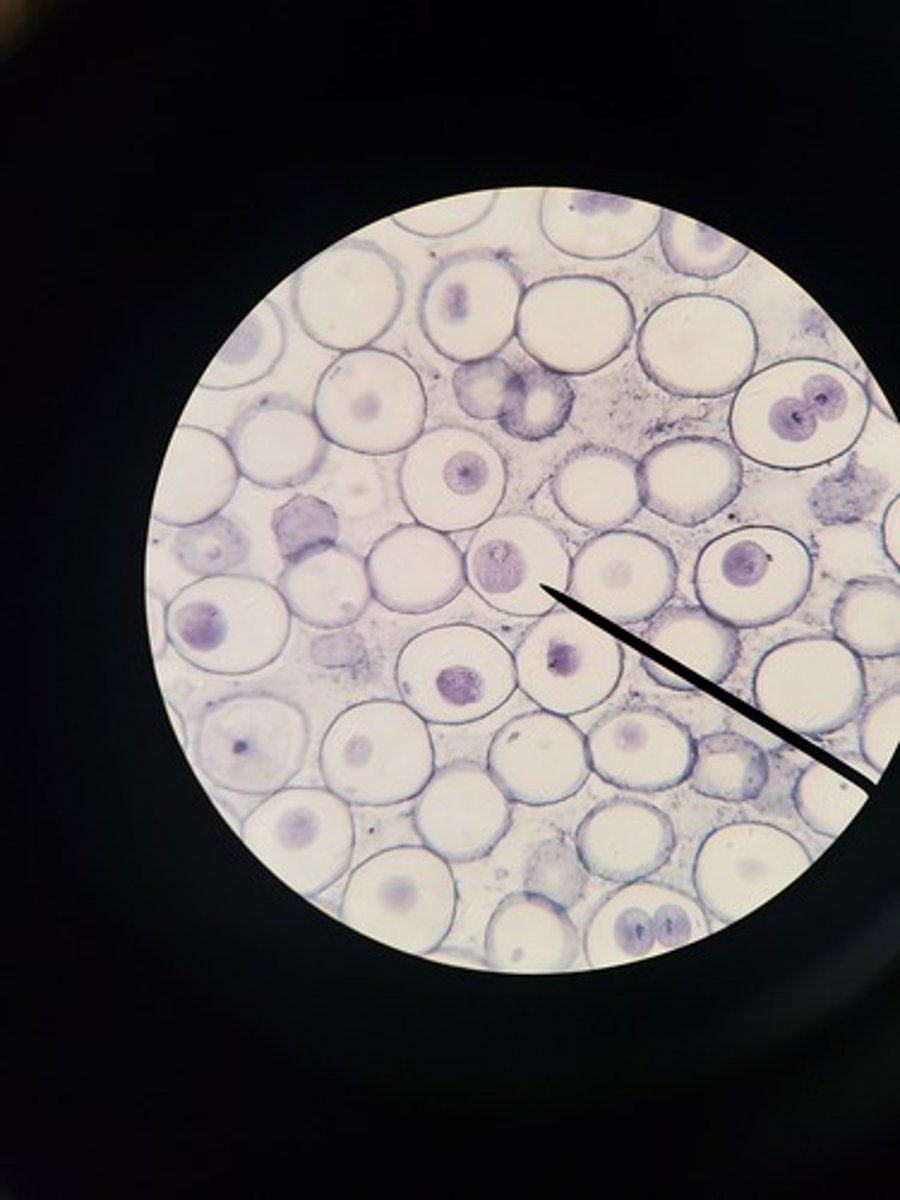
prometaphase in animal cell picture
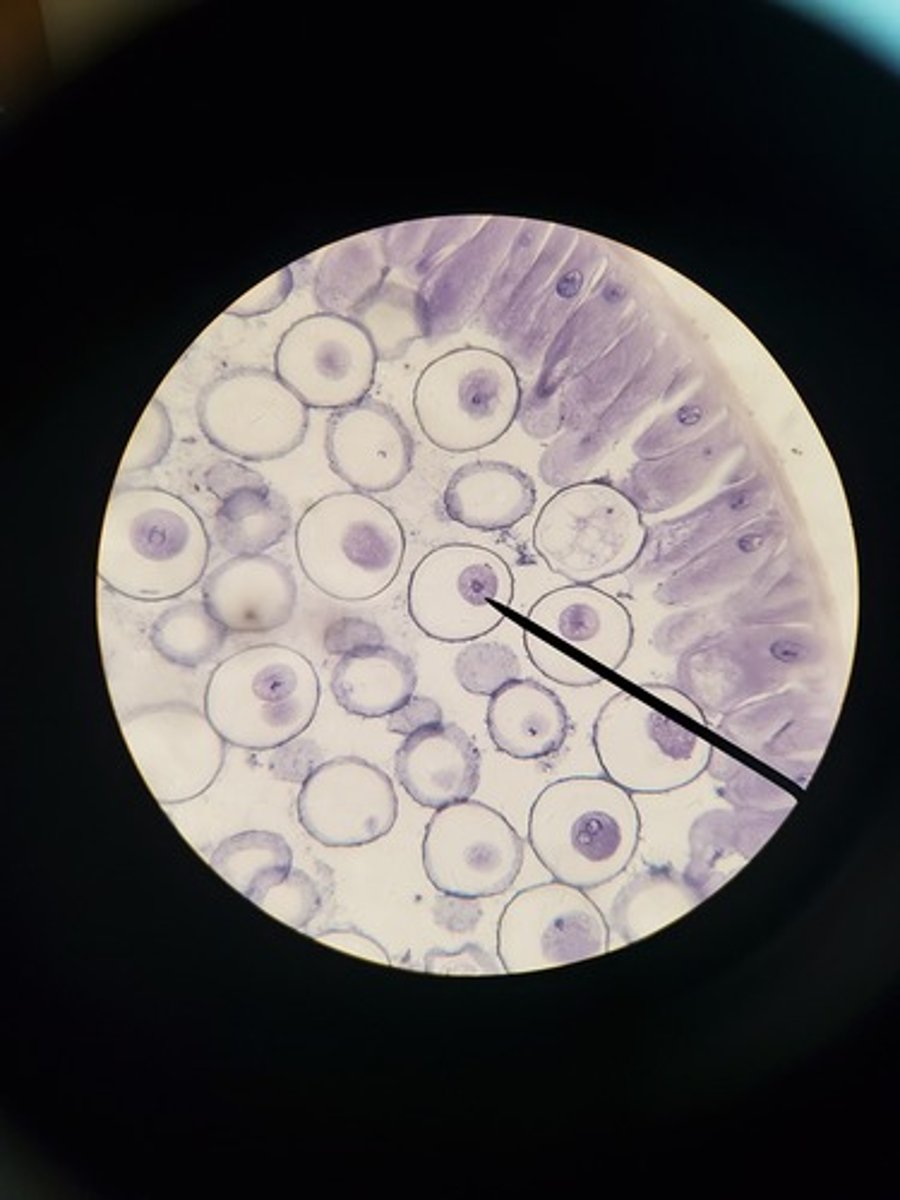
telophase plant picture
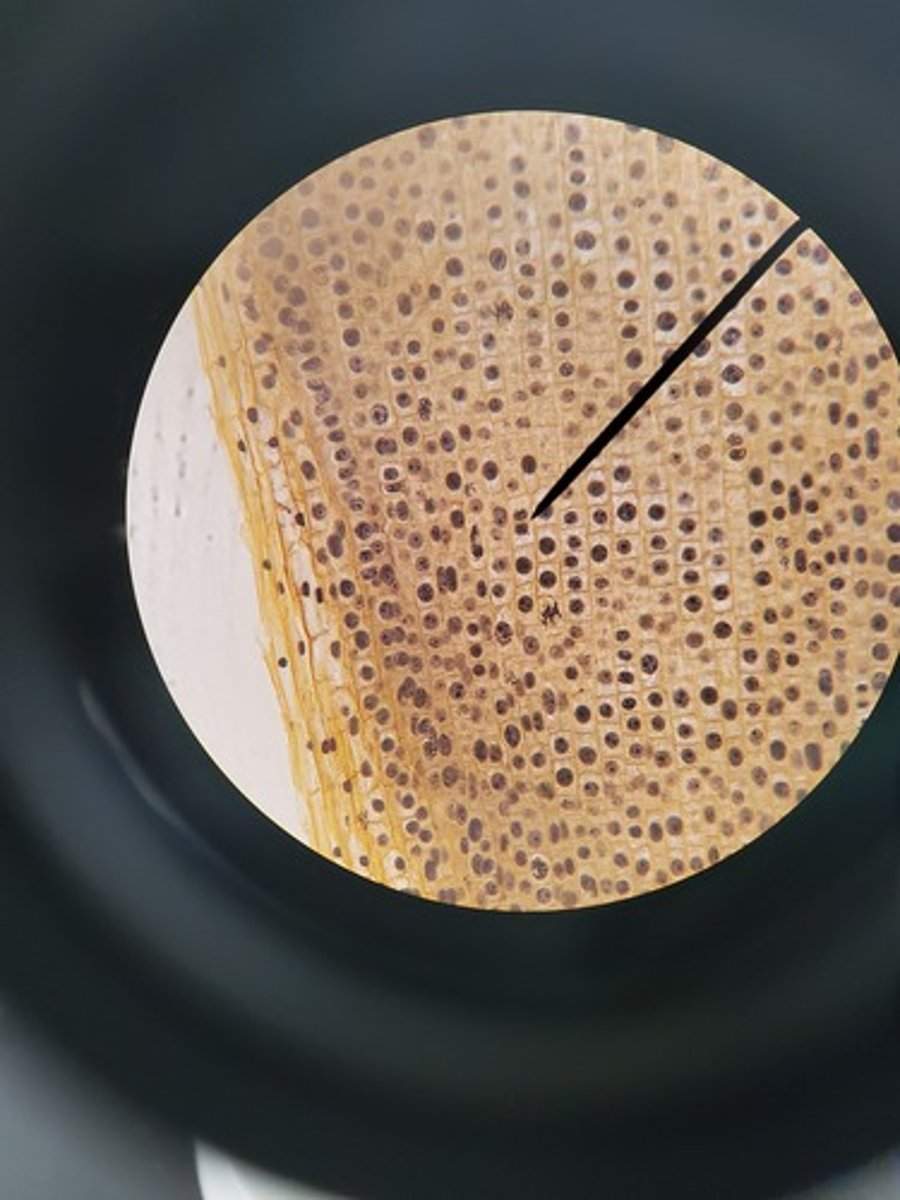
Recombinant DNA
DNA that has been manipulated by researchers so that one or more nucleotides have been inserted, changed, or deleted.
telophase animal cell picture
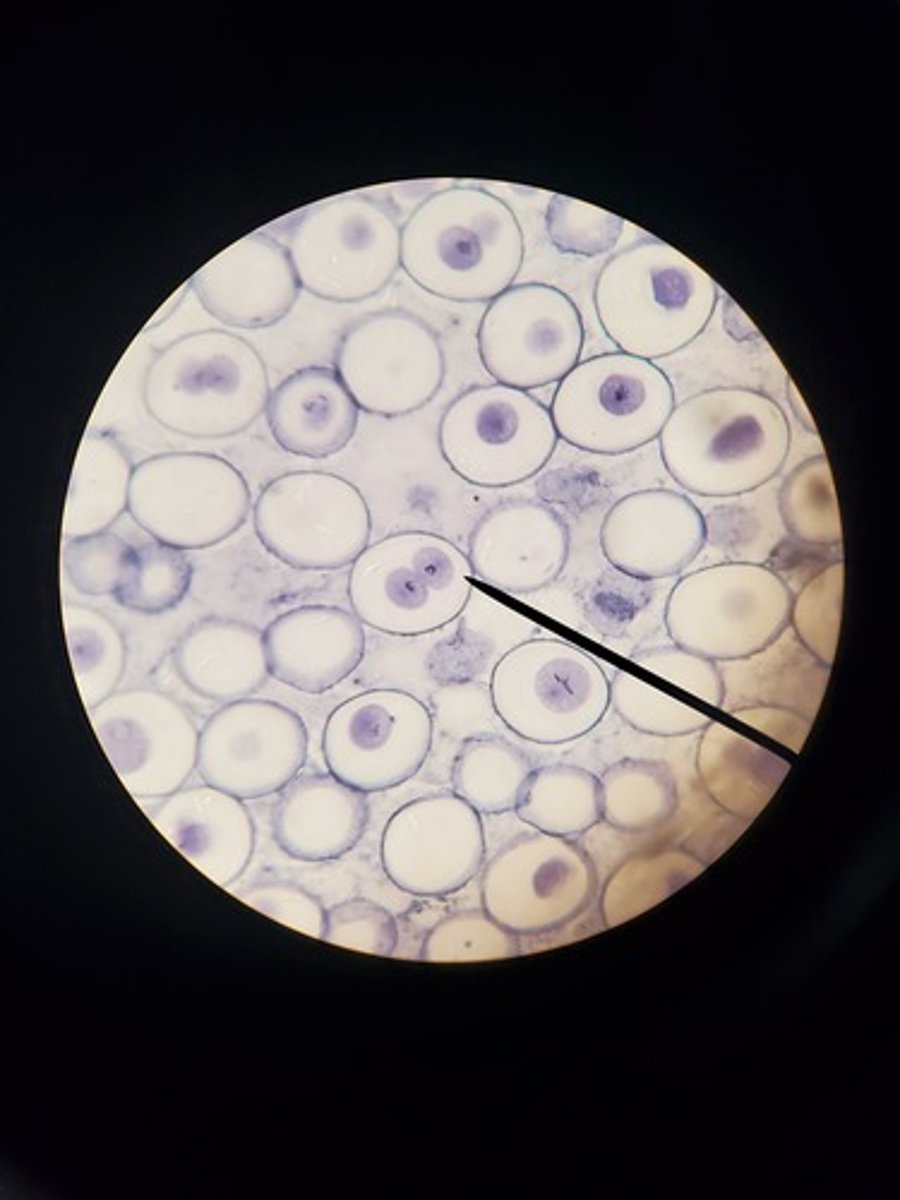
PCR (polymerase chain reaction)
A laboratory technique for amplifying and synthesizing DNA from an existing template.
Primers
short oligonucleotides (strands of nucleotides) ranging from 18 to 45 bases in length.
Metaphase picture animal cell
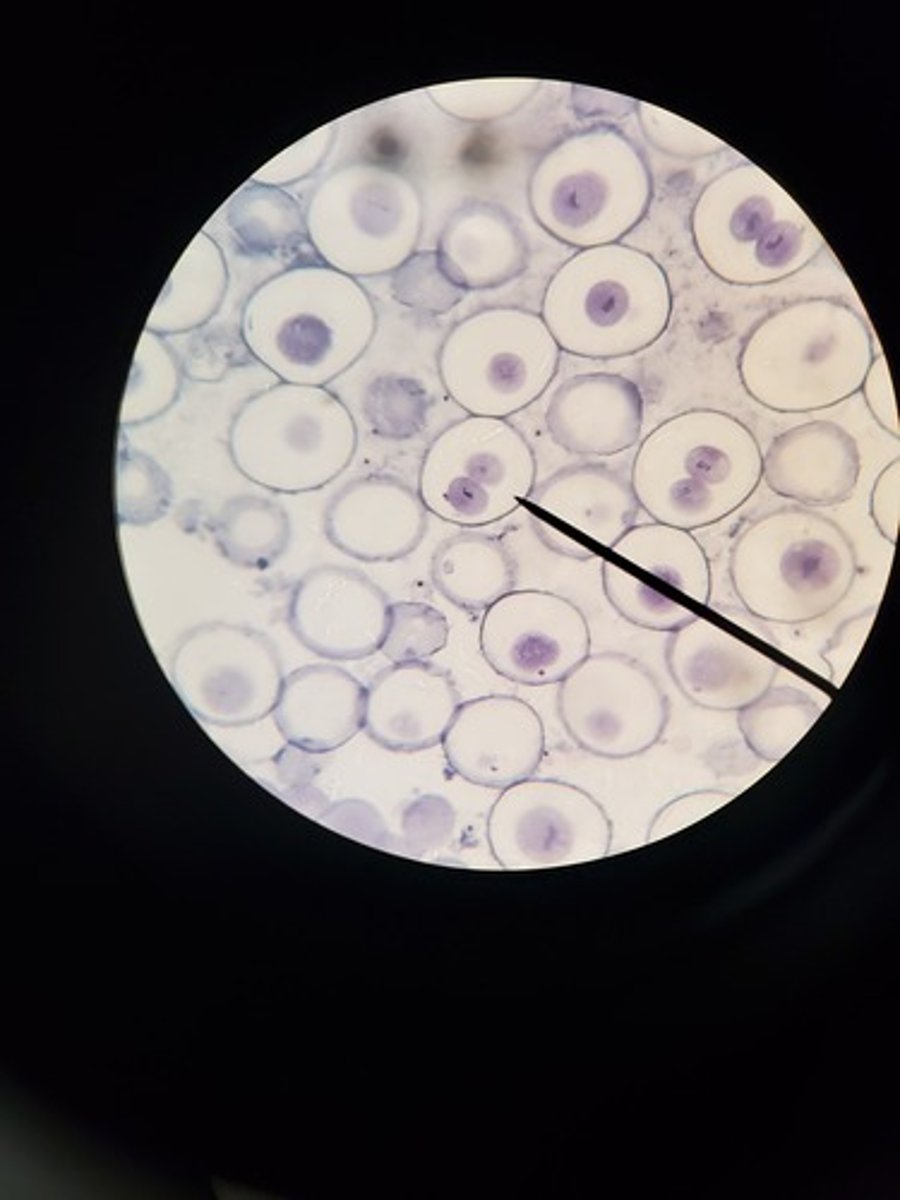
anaphase animal cell picture
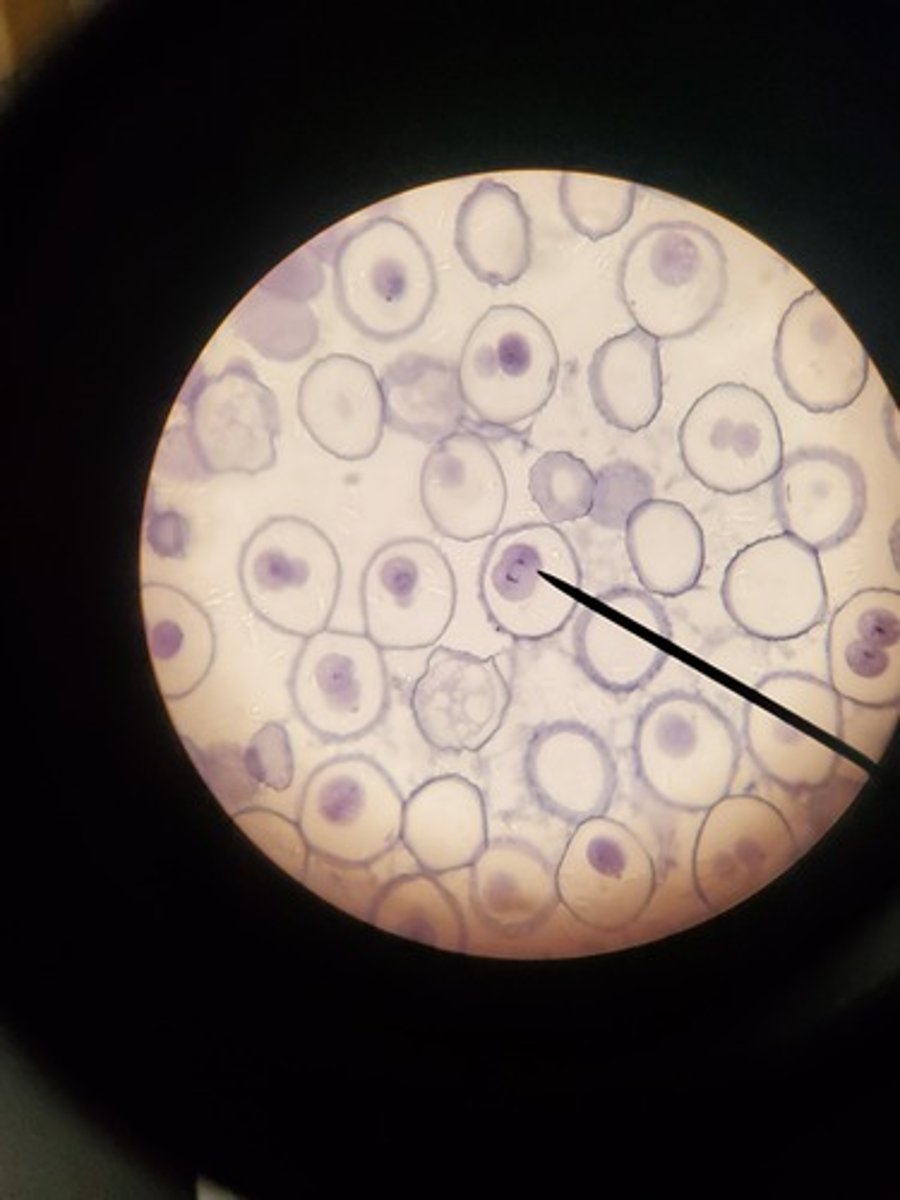
Denaturation
the DNA is heated to separate the two DNA strands from one another.
describe the similarities and differences between prophase I and prophase II.
In prophase I and Ii the spindle apparatus forms ans the nuclear envelope breaks down. in prophase I the homologous chromosomes pair up in synapsis and the cross over one another, exchanging genetic information and forming regions called chiasmata. this does not occur in prophase Ii. In prophase Ii. there are non-identical sister chromatids and no synapsis or crossing over occurs.
Genetics
the science of heredity, or how specific characteristics (genes) are passed from generation to generation.
Heredity
the distribution of features from one generation to the next. these features are called traits and are expressed in physical characteristics such as eye color, hair thickness. and height.
Chrimosomes
carry genes and are found in the nucleus. each chromosome contains one DNA molecule.
units of heredity
genes
human genetics
the scientific study of heredity as it relates to humans
Genotype
genetic makeup of an organism
Phenotype
An organism's physical appearance, or visible traits.
Alleles
Different forms of a gene
Diploid
2 sets of chromosomes, one from their mother and one from their father.
homologous pairs
pairs that contain the same types of genes
Annealing
the DNA is cooled which allows the primers to bind to the target DNA.
extension
the new DNA is synthesized with the help of DNA polymerase and deoxynucleotide triphosphates (dNTPs).
DNA polymerase
an enzyme that catalyzes the synthesis of the DNA along the template strand, starting at the 5x end and continuing to the 3' end. adds to 3' end.
Deoxynucleoside triphosphate (dNTP)
individual units of 4 nucleic bases (A, T, G, C) which help to build the new DNA.
Amplification
occurs in cycles. each cycle exponentially increases the number of newly synthesized DNA strands. a cycle consists of repeating the steps of denaturation, annealing. and extension.
the ___ step of PCR results in primers binding to the target DNA.
annealing
gel electrophoresis
a technique by which molecules are separated by size and electrical charge as a result of traveling through a block of agarode gel by means of an electric field.
what charge does DNA have?
negative. DNA travels from the cathode (negatively charged electrode) through the agarose gel to the anode (positively charged electrode)
the larger the molecule, the ___ it travels through the agarose gel.
slower
a catalyst enzyme that extends DNA strands
DNA polymerase
molecular biologists investigate the manipulation of ___ to understand the interactions between the various systems of a cell.
DNA, RNA, and protein synthesis
what creates the genetic code?
the order in which the four DNA nucleotides are arranged.
Recombant DNA has been manipulated so that one or more nucleotides have been ___.
changed, deleted , and inserted.
gel electrophoresis is used to separate DNA molecules by ___
size
true or false? both DNA and food dyes are negatively charged and move towards the positive pole during electrophoresis.
true
dominant allele
An allele whose trait always shows up in the organism when the allele is present.
recessive allele
An allele that is masked when a dominant allele is present
incomplete dominance
Situation in which one allele is not completely dominant over another allele. Example: red flower and white flower makes a pink flower.
sex-linked traits
Traits controlled by genes located on sex chromosomes. only present on the X or Y chromosome
hemizygous
A gene present on the X chromosome that is expressed in males whether it is recessive or dominant.
monohybrid cross
A cross between individuals that involves one pair of contrasting traits
dihybrid cross
Cross or mating between organisms involving two pairs of contrasting traits. punnet square in which 2 genes or traits of interest are examined at one time.
pedigree chart
family trees that show phenotypic patterns
Autosomal
all the other genes in the body that are not sex-linked.
cystic fibrosis
caused by a single recessive allele in the seventh chromosome. Thickened mucus in the lungs, liver, and digestive organs; death in early adulthood unless symptoms are treated
Tay-Sachs disease
recessive, lipids accumulate in brain cells, deterioration of nerve cells; mental and physical disabilities; death during childhood
sickle cell disease
recessive; red blood cells sickle (abnormal shaple with pointed ends); causes damage to organs
Achondroplasia
dominant; abnormal cartilage formation; dwarfism
Huntington's disease
Dominant; neurons degenerate; causes mental and physical deterioration; symptoms appear anytime from late childhood to middle age.
nondidjunction
an instance wen two pairs of homologous chromosomes or sister chromatids fail to separate during Anaphase I or II. Leads to abnormal gamets with too many or too few chromosomes.
Karyotype
the analysis of chromosomes. count the number and observing the size of the chromosomes. usually performed in utero (amniotic fluid tested) but can be performed on other tissues such as blood and bone marrow.
Down Syndrome
an extra copy of chromosome 21 (trisomy 21); delayed cognitive ability, oblique eye shape, flat nasal bridge.
Edwards syndrome
an extra copy of chromosome 18. structural heart defects, kidney defects, muscle dysfunction, widely spaced eyes, overlapping fingers (index with third and fifth with fourth)
Klinefelter syndrome
at least on extra copybof the X chromosome (XXY) male specific. reduced muscle strength, reduced testosterone production, increases height, broad hips, pronounced breasts, small testes, reduced fertility.
Patau Syndrome
Trisomy 13;cleft palate, as well as eye, brain, and circulatory defects.
Ring 18
ring shaped chromosome 18, resulting from deletion of chromosome tips. eye folds, increased distance between eyes, low set ears, heart defects
Triple X Syndrome
and extra copy of the X chromosome (XXX) female specific. mild or non phenotype manifestations; healthy with normal fertility. increased risk of delayed development.
Turner Syndrome
only one X chromosome (female specific) Only viable monosomy not resulting in death. reduced height, sterile, normal intelligence.
XYY syndrome
an extra copy of the Y chromosome (XYY) increased height, reduced cognitive ability, normal fertility
Genomics
the study of complete sets of genes in an individual and the interactions of these genes.