Lecture 27: Protein Sorting
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
What determines the fate of a protein during translation?
The site of translation, which can be co-translational or post-translational sorting.
What are the two types of transport through the nuclear pore complex?
Passive diffusion for molecules with a molecular weight (MW) <20 kDa and active transport for those with MW >60 kDa, which requires energy (GTP).
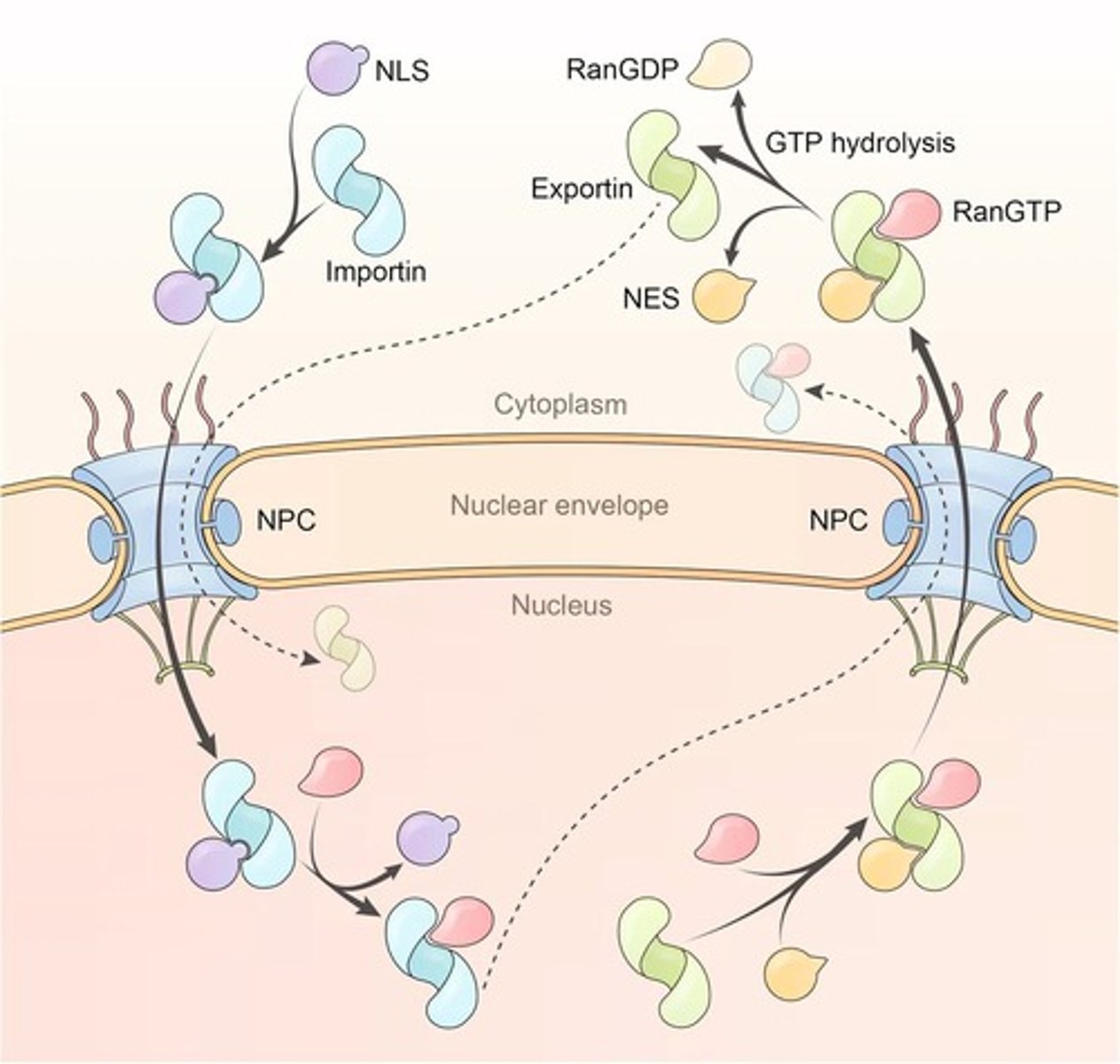
What is the role of the nuclear localization signal (NLS)?
The NLS is an amino acid sequence that is necessary and sufficient for proteins to enter the nucleus.
What is a bipartite nuclear localization signal (NLS)?
A type of NLS that consists of two separate parts, similar to other NLSs, and some NLSs are formed by proper protein folding.
What is the function of the nuclear export signal (NES)?
The NES is an amino acid sequence necessary and sufficient for proteins to leave the nucleus.
What amino acids are commonly found in a nuclear export signal (NES)?
Leucine (Leu), Glutamine (Gln), Proline (Pro), Glutamic Acid (Glu), Arginine (Arg), and Threonine (Thr).
What is the size of the human mitochondrial genome?
The human mitochondrial genome is 16.5 kb and includes 13 protein-coding genes, 22 tRNA genes, and 2 rRNA genes.
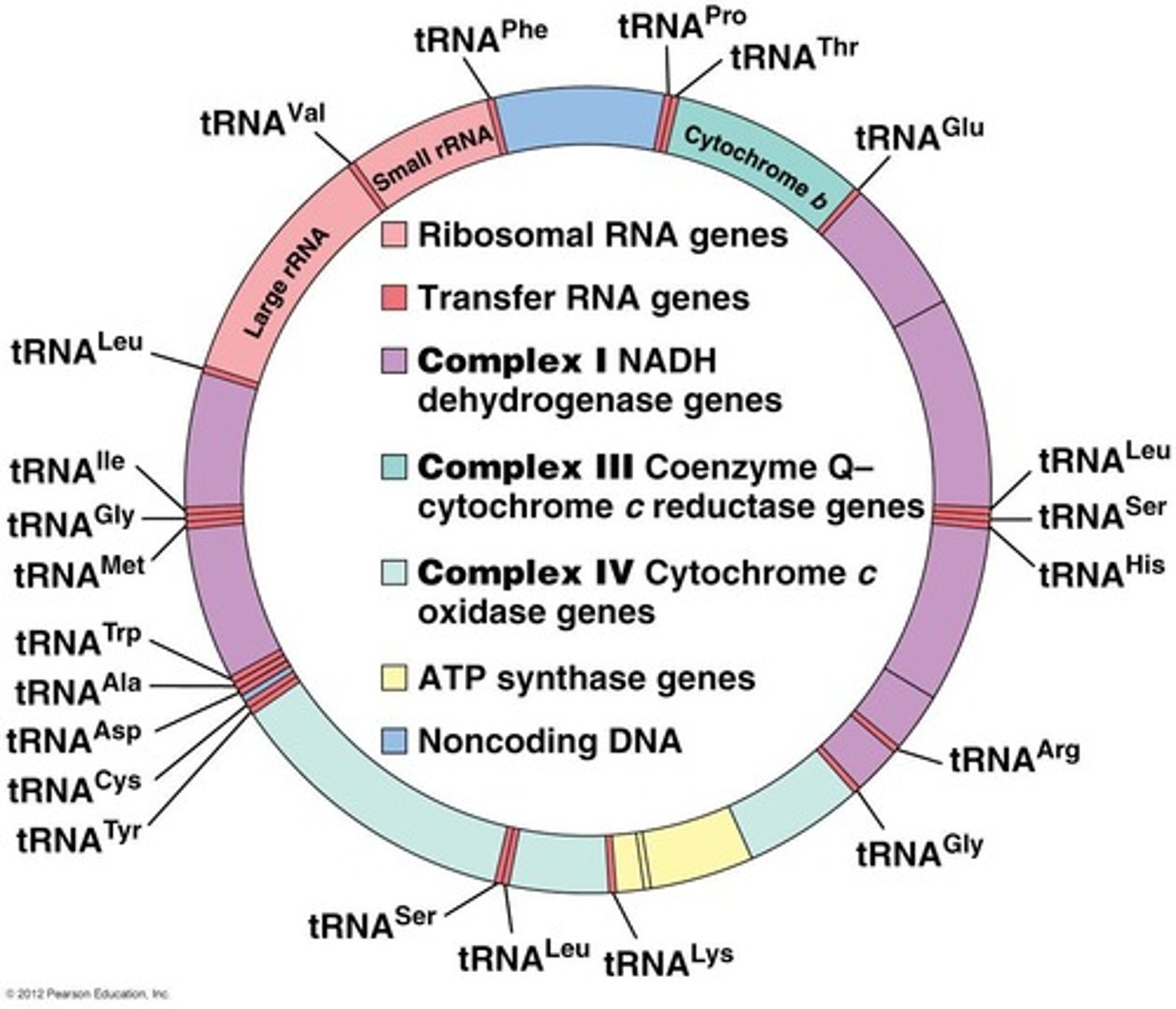
Where are most mitochondrial proteins transcribed and translated?
Most mitochondrial proteins are not coded for by mitochondrial genes; they are typically transcribed in the nucleus and translated in the cytosol.
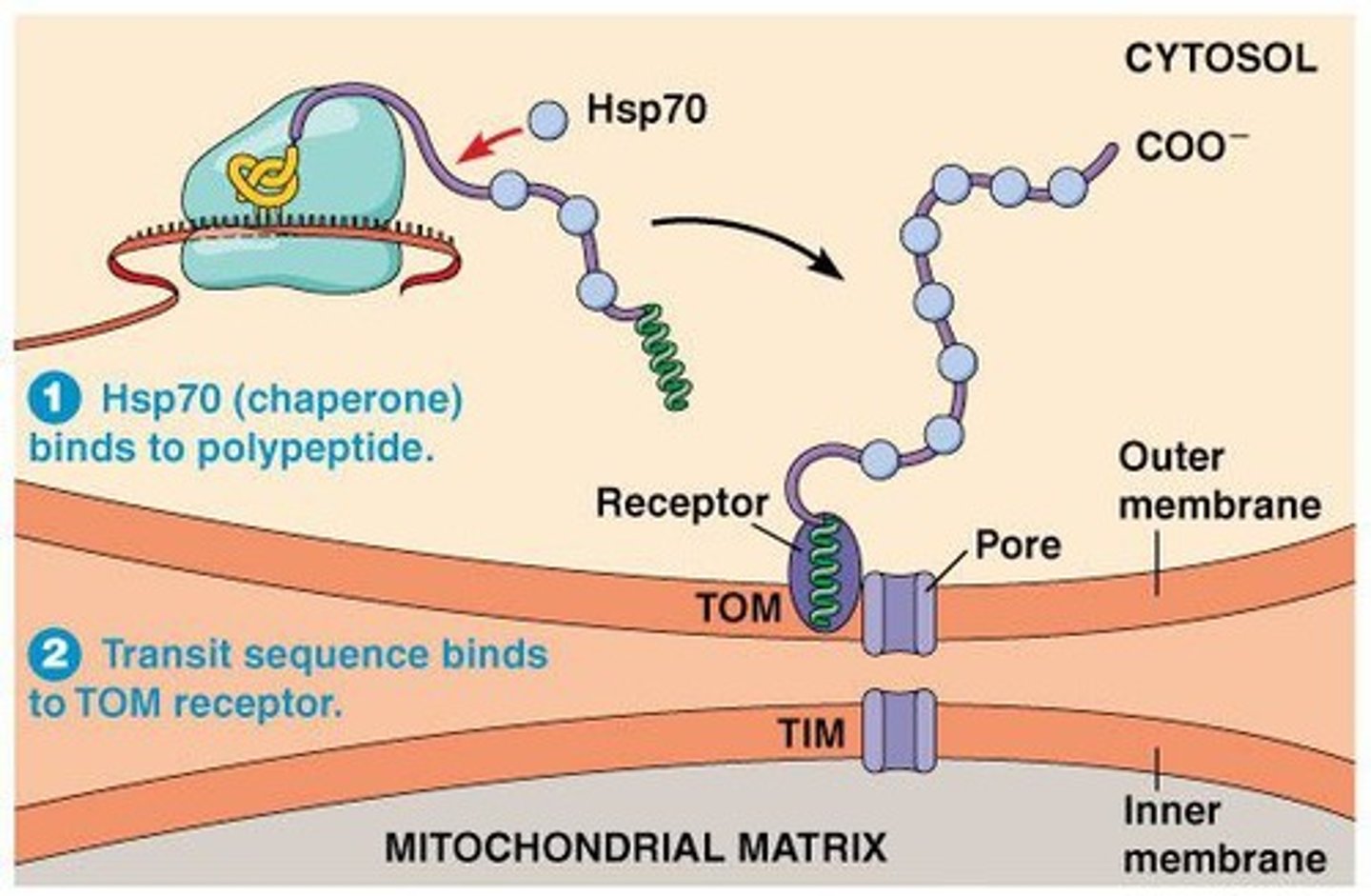
What type of gradient exists in mitochondria?
An electrochemical gradient exists, characterized by a concentration gradient and electrical potential across the mitochondrial membranes.
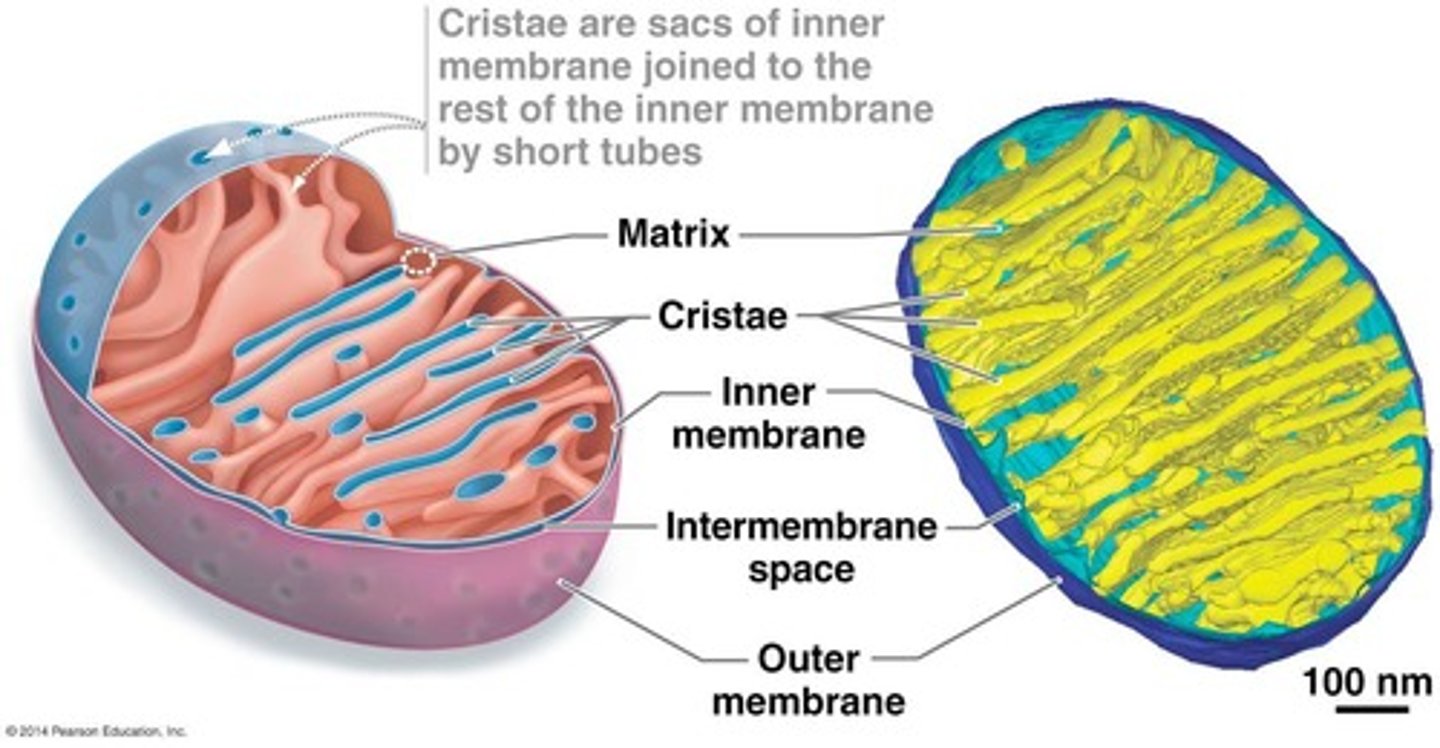
What is the pH difference between the mitochondrial matrix and the cytosol?
The mitochondrial matrix has a pH of 8, while the cytosol has a pH of 7.
What is the role of chaperonin complexes in mitochondrial protein import?
Chaperonin complexes assist in mitochondrial protein import, although they are not strictly required.
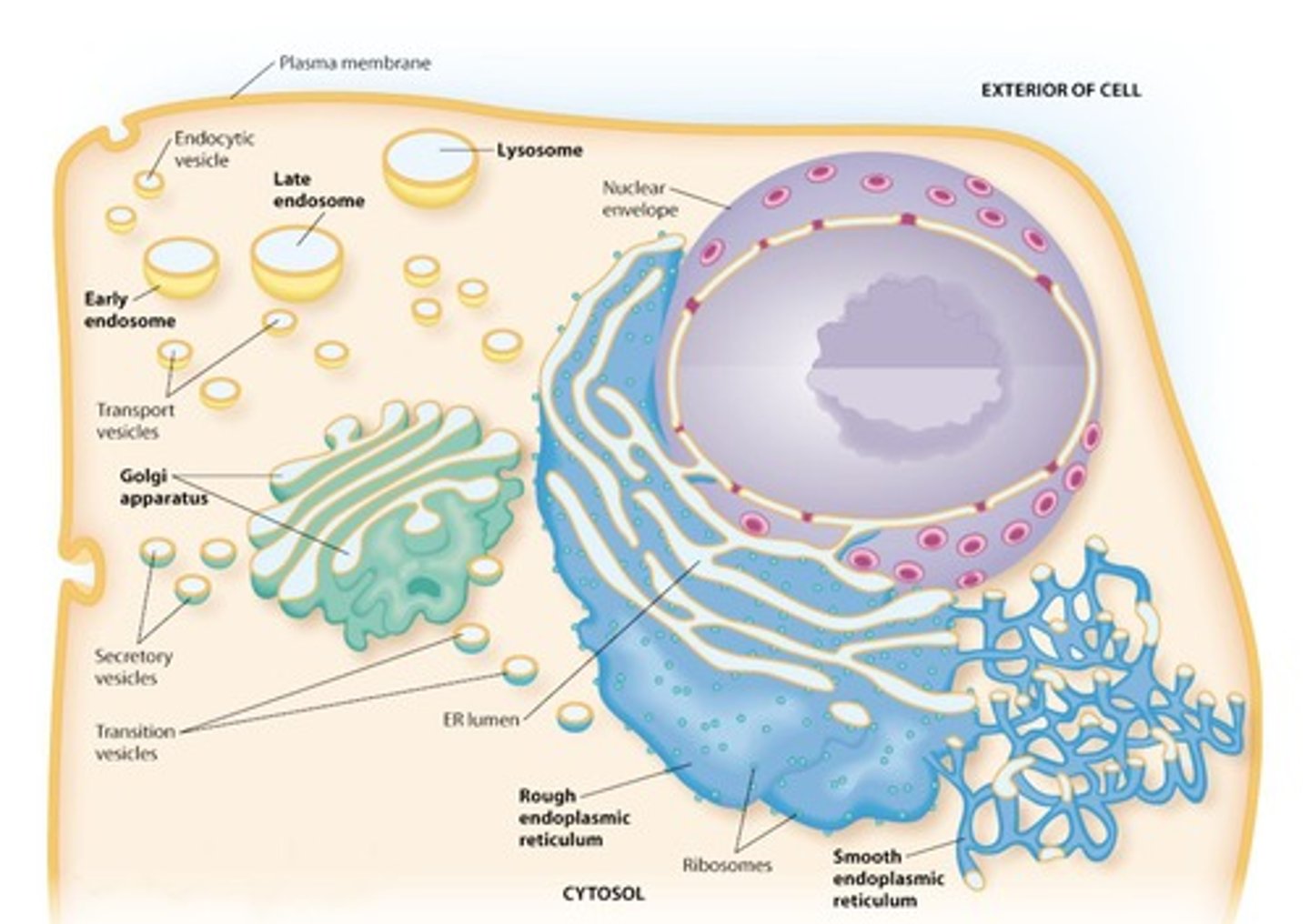
What is the Endomembrane System?
The Endomembrane System is a network of membranes within the cell that includes the nuclear envelope, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, lysosomes, and vesicles.