imf and gas
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
electronegativity
tendency of an atom/group to attract electrons
0.4 < ∆e < 1.7 = polar
non polar if arrows pull equally in OPP directions
ion forces
higher charge
smaller atomic size
= stronger forces
ions are RAW charges
ion-ion
b/w IONIC bonds
charge
size
STRONGEST imf
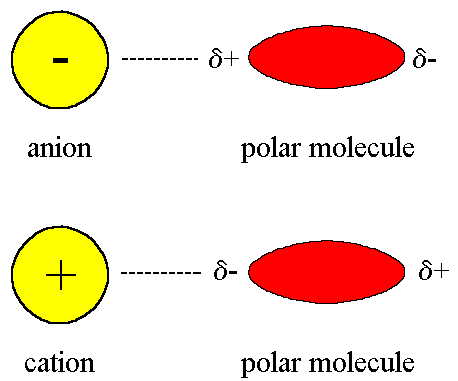
ion-dipole forces
b/w polar molec & ions
ion’s charge
polarity of molec
energy of solvation (energy to dissolve smt) INCREASES by stronger ion-dipole force
size decrease, charge increases
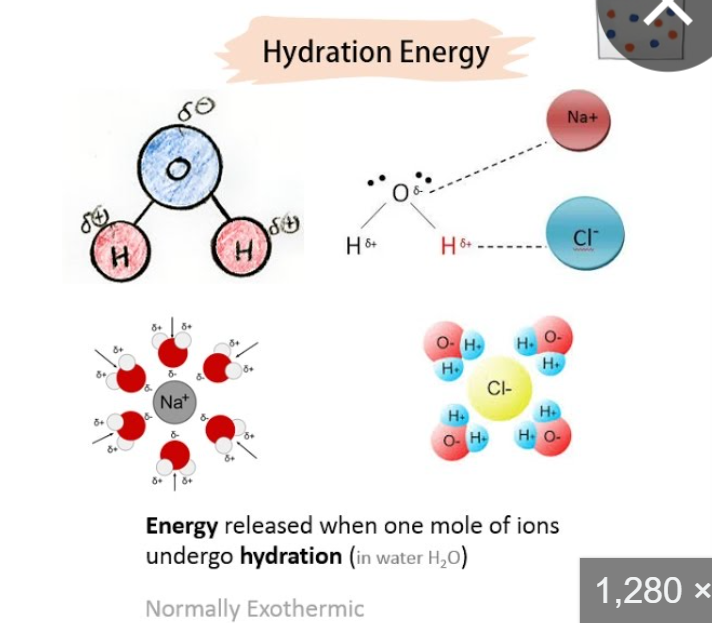
energy of solvation
energy to dissolve a solute in a solvent
INCREASES by stronger IMF
energy of hydration is one type
(ONLY ION-DIPOLE) charge > size
ion in water
soluble if
polar solvent
(water is polar) form H bonds - has OH, COOH, NH2
ionic/polar
NOT long alkanes
np solvents can dissolve np
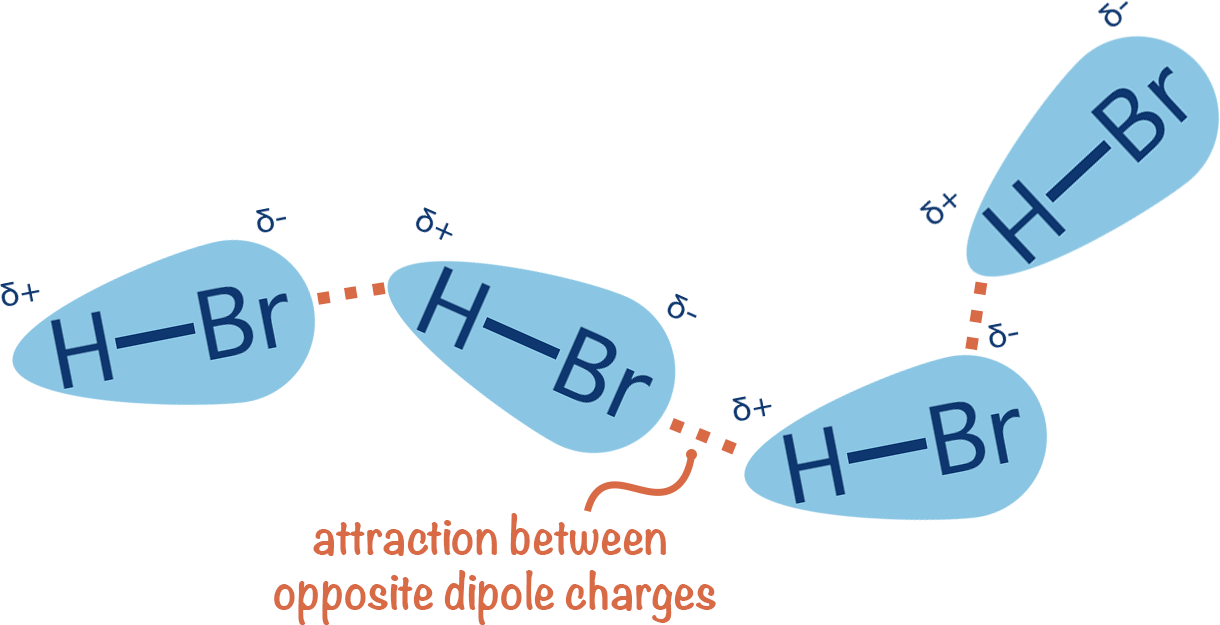
dipole-dipole forces
b/w polar molecules
polarity of molecule (EN)
∴ high dipole moment → high dipole-dipole
stronger the imf
harder to overcome bonds
higher boiling/melting points
polar > nonpolar
polars have permanent dipoles
np are temporary
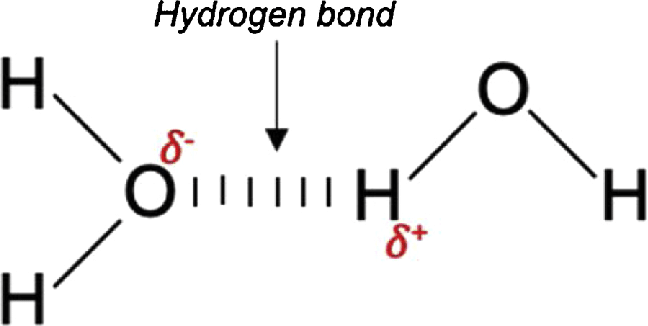
hydrogen bonding
STRONGEST form of dipole forces
part of dipole-dipole
hydrogen atoms like to have F.O.N
they prefer to bond to very EN atoms
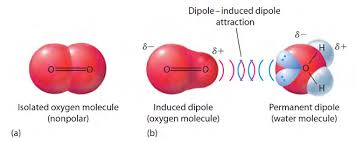
dipole-induced dipole
b/w polar and non polar
TEMPORARY attraction
the amount of inducibility → polarizability
“how easy to shift/shape the non polar”
dipole forces
polarizability
since its temporary, based on how many electron clouds
more e clouds, more electrons that can shift into a shape
think pixels
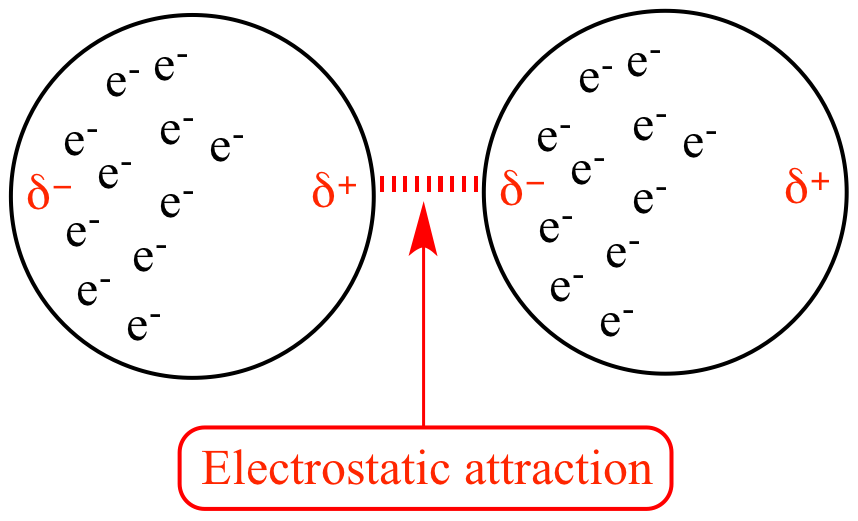
induced dipole induced dipole
(london dispersion forces)
affects all molecules, but VERY temporary and weak
occurs when electrons bunch up on one end causing a temporary dipole
np+np only has london force
isomers
straight chain will be bigger cuz bigger surface area
branches are itty bitty
vapour/gas pressure
weaker force = molecules escape easily = higher gas pressure
stronger force = molecules held tighter = lower gas pressure
gas molecules
gases exert pressure off its container
constant rapid motion ∴ low IMF
NO attraction
ALWAYS CONVERT CELCIUS TO KELVIN
phase changes
imf breaks when heats (endothermic)
cuz particles part away
imf forms when cools (exothermic)
particles need a force to squeeze them tgt
gases characteristics
invisible irl
very spaced out fills shape and vol
low density
elastic collisions (dont stick and flowy)
standard temp and pressure (STP)
measured in sea level
temp: 273 kelvin, 0°C
pressure: 1 atm, 760 mm Hg, 760 torr, 101.325 kPa
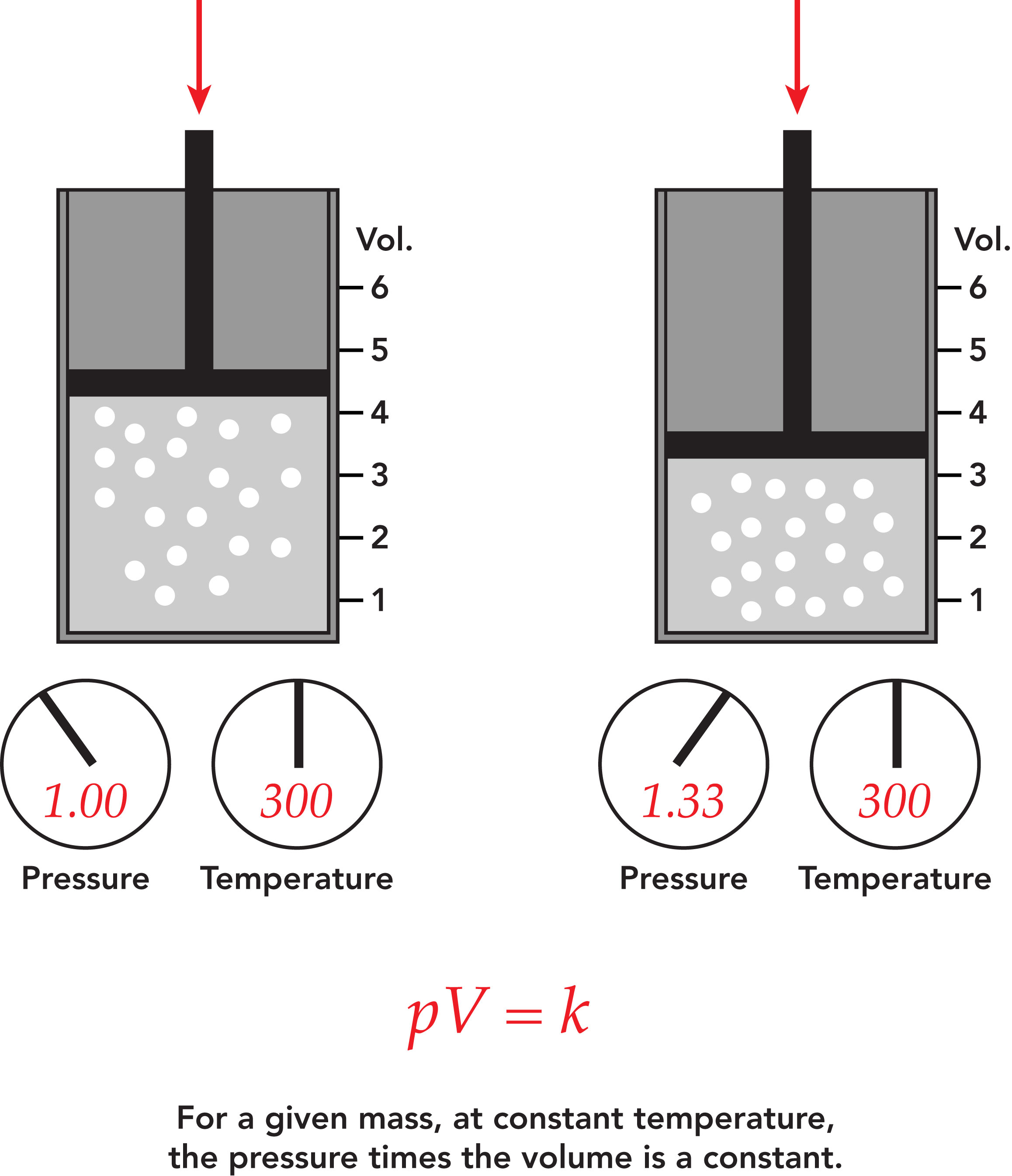
boyle’s law
pressure is inversely proportional to volume
pressure increase, volume decreases
P1 x V1 = P2 x V2
to boil on stove u “press(ure) the volume”
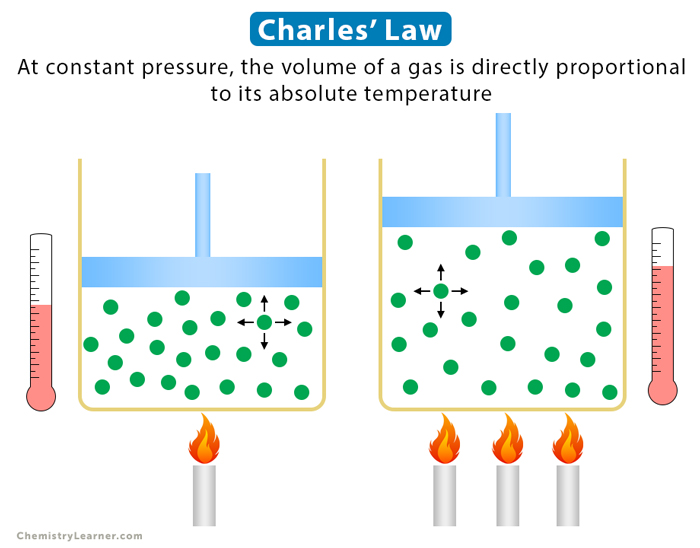
charles’ law
volume is proportional to temp
when temp increases, vol increases
TEMP IN KELVIN
V1/T1 = V2/T2
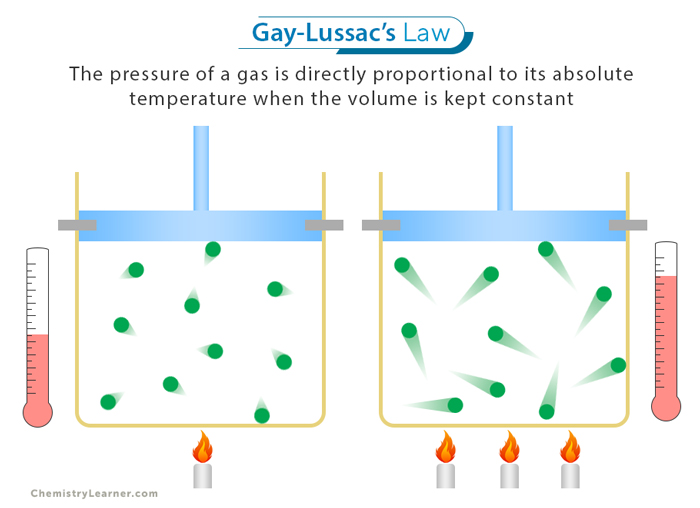
gay lussac’s law
pressure is proportional to temp
temp increases, pressure increases
P1/T1 = P2/T2
Avogadro’s law
volume is proportional to # of moles
vol increase, moles increase
V1/n1 = V2/n2
combined gas law
# of moles is constant
temp in kelvin
stp is 273, 1 atm, 760 mmHg
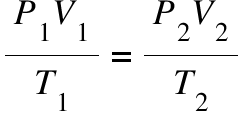
ideal gas law
used to calculate gases in ideal conditions
PV=nRT
R = GAS CONSTANT 8.314kPa(L/mol)(K)
dalton’s laws of partial pressure 1
law 1 - the sum of the partial pressures = total pressure
P1 + P2 = P total
daltons law 2
the sum of partial moles = total moles
n1 + n2 = n total
daltons law 3
partial pressure:total pressure = partial moles: total moles (mole fraction)
P1/P total = n1/n total

graham’s law
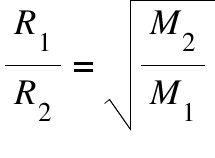
R1²/R2² = M2/M1
use to find unknown molar mass
the rate of flow of gases depend on the molar mass of the gas
lighter=faster, heavier=slower
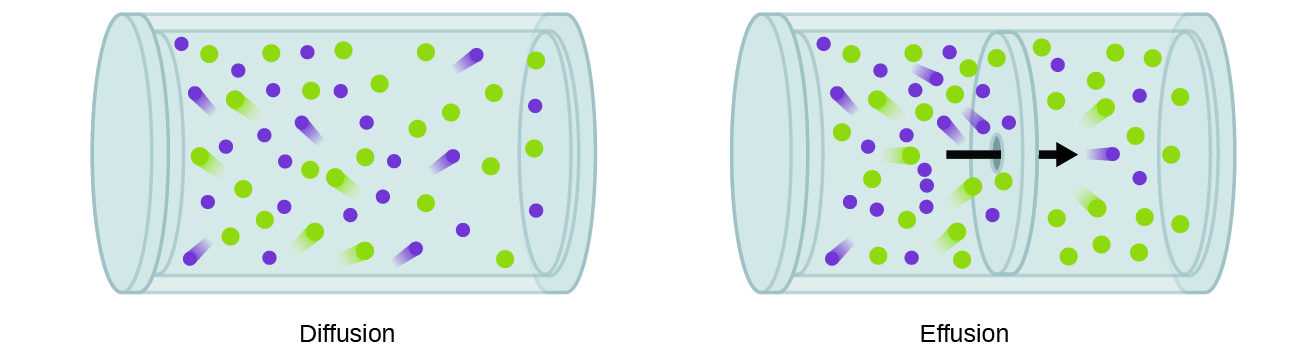
diffusion
mixing of different gases by random molecular collision and motion

effusion
gas molecules escape through a small hole of its container without any collision
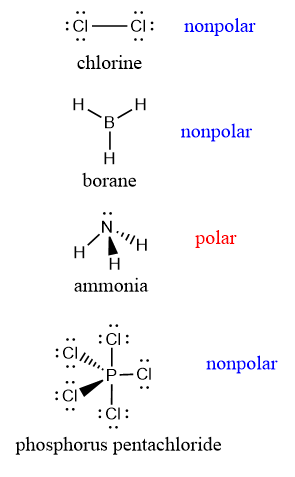
nonpolar vs polar molec
polar IF
asymmetrical lone pairs on central atom
diff terminal atoms
non polar if
2 lone pair on 6 groups, 3 lone pair on 5 groups
are all gases ideal
all gases become unideal in low temp (liquefaction/condensation begins) and high pressure (more crowded)