Adrenal Medulla
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
14 Terms
Adrenal medulla
Inner part of adrenal gland
Neuroendocrine organ → controlled by NS but release hormones into blood
Works alongside sympathetic nervous system (fight or flight response)
Structure of adrenal gland
Cortex - steroid hormones (cortisol and aldosterone)
Medulla - catecholamines (epinephrine, norepinephrine)
Adrenal medulla sympathetic
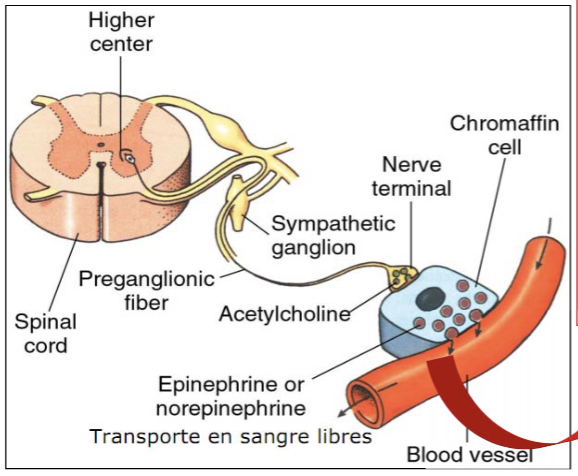
Giant sympathetic ganglion → instead of sending signals through nerves, releases hormones in blood
Preganglionic sympathetic neurons from spinal cord goes straight to medulla
These neurons release ACh → stimulates chromaffin cells (which act as postganglionic neurons)
Chromaffin cells release epinephrine and norepinephrine into bloodstream
Regulation of sympathetic adrenal medulla
Hypothalamus is the mean control center
Sends signals to activate SNS
This also stimulates the pituitary gland which releases ACh → stimulates cortisol from the adrenal cortex → prolonged the effects of epinephrine
Catecholamines
Play a key role in body’s stress response
Derived from amino acid tyrosine
Hydrophilic (hydro-soluble), circulate freely in blood
Like epinephrine, norepinephrine and dopamine
Catecholamine - epinephrine
Produced in adrenal medulla
Involved in fight or flight
Increases heart rate, blood pressure, blood sugar and dilates airways
Catecholamine - norepinephrine
Produced in renal medulla
Acts more like a neurotransmitter than a hormone
Causes vasoconstriction and increases blood pressure
Catecholamines - dopamine
Precursor to norepinephrine
Functions mainly as a neurotransmitter in brain
Also plays a role in motor control and hormone regulation
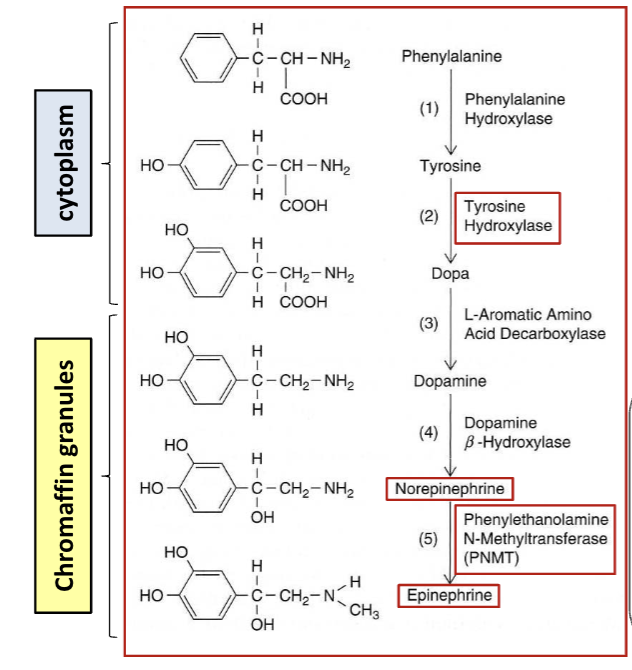
Catecholamine synthesis in chromaffin cells
Cytoplasm - Tyrosine hydroxylase adds a -OH (hydroxyl group) to tyrosine → L-DOPA
Cytoplasm - DOPA decarboxylase removes CO2 (carboxyl) group → dopamine
Secretory vesicles - Dopamine β-hydroxylase adds -OH group to carbon chain → norepinephrine
Adrenal medulla - PNMT adds methyl (CH3) group to norepinephrine → epinephrine
Trigger of catecholamine secretion
Stressor activates SNS
ACh from preganglionic fibers causes depolarization of chromaffin cells
Depolarization opens voltage-gated calcium channels, Ca2+ rushes in
This triggers exocytosis of hormone-containing granules
Alpha (α) receptors
Mostly cause constriction and help raise blood pressure
α1 - in blood vessels, causes vasoconstriction, sensitive to norepinephrine
α2 - nerve endings and pancreas, inhibits further release of norepinephrine (and insulin)
Beta (β) receptors
Mostly cause relaxation, stimulation or energy release
β1 - heart, increase heart rate and contractions, sensitive to epinephrine and NE
β2 - in lungs (bronchodilation), skeletal muscle (vasodilation) and liver (glycogenolysis - release of sugar), mostly epinephrine
β3 - adipose tissue, breaks down fat for energy, epinephrine
Carbohydrate metabolism
Liver - ↑ glycogenolysis (breakdown glycogen), ↑ gluconeogenesis (produce glucose)
Pancreas - ↑ glucagon (raise blood sugar), ↓ insulin (reduce glucose storage)
Muscles - ↑ glycogen breakdown for quick energy
OVERALL - ↑ glycemia (blood glucose for energy during stress)
Lipid metabolism
Adipose tissue - ↑ lipolysis (releases free fatty acids)
Liver - uses FFAs via β-oxidation to generate energy