Lecture One: Anotomical terms And Homeostasis
1/123
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
124 Terms
Words Origins and Combinations
English Greek And Latin comparisons
Under=hypo= sub all have the sam meaning
Hypogastric= Subgastric
Substances and Colors
Coll=glue (collagen)
Cyano=Blue (Cyano-tic)
Descriptions and directions
Brady= slow (Brady-cardia) ex Brady was slow at baseball practice
Ab= away (ab-duct)
Tacky
Fast
common suffixes :itis
Inflammation ex bronchitis
Common suffixes
ic,ac,ary,ous, pertaining to (apne-ic,cardi-ac,cutane-ous)
Pertaining to
Being relevant or related to something
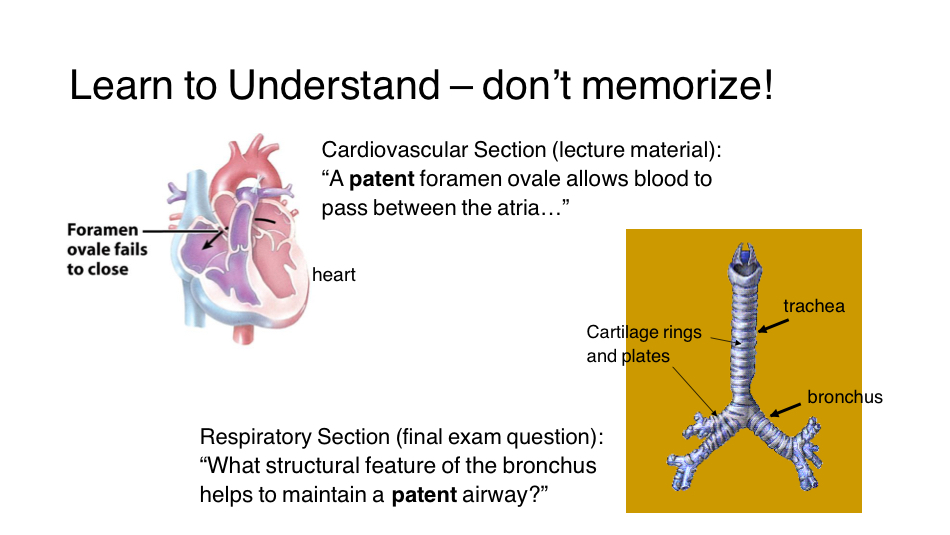
Patent= open hole
The structure that helps maintain a patent airway is the cartilage rings and plates
Body Positions
Anatomical Position
Standing up straight, arms are facing out to make bones parallel
Adducted: arms are added back to body
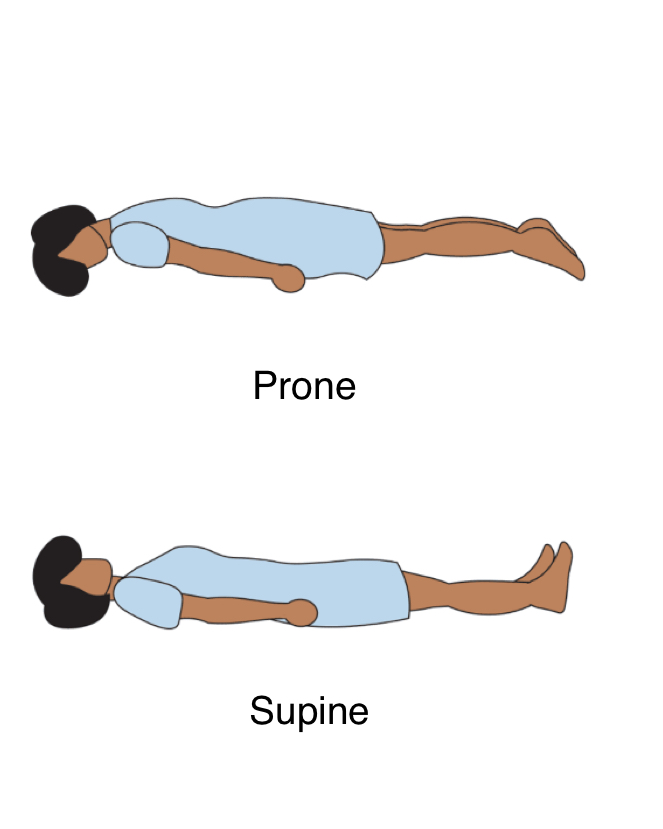
Prone Position
face Palming to bed = Prone position
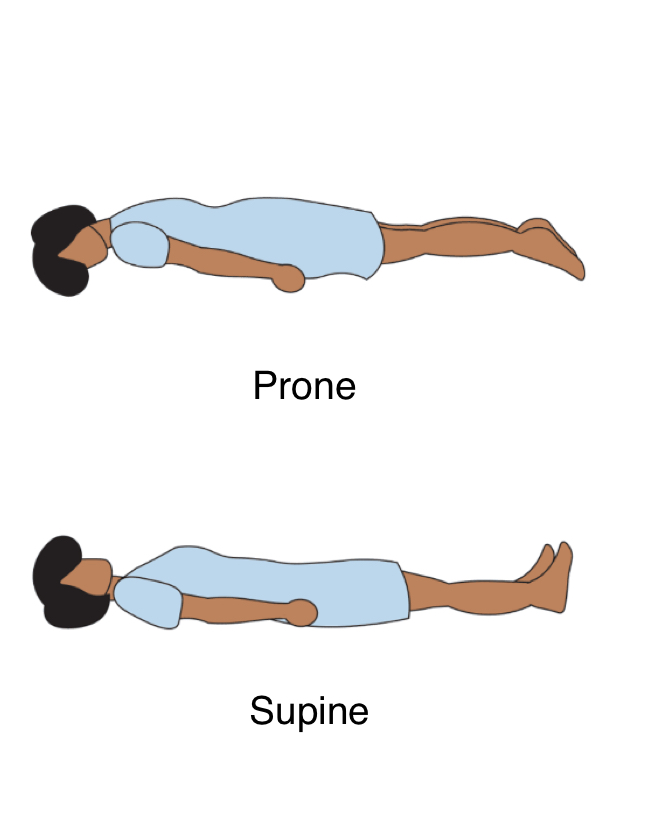
Supine position
Will most likely see in nursing, patient laying on their bad on their back
Semi Fowler position
Kinda like a dentist position 15-45 degree angle
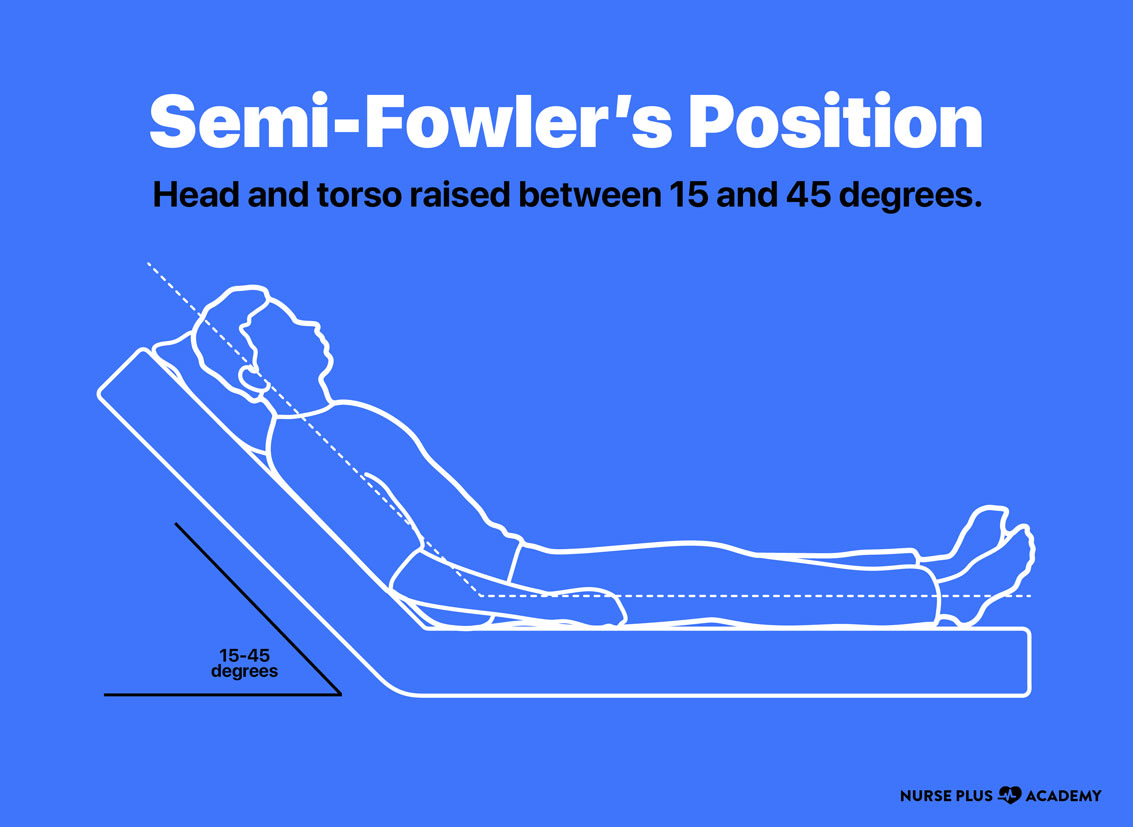
Fowler position
Low Fowler position
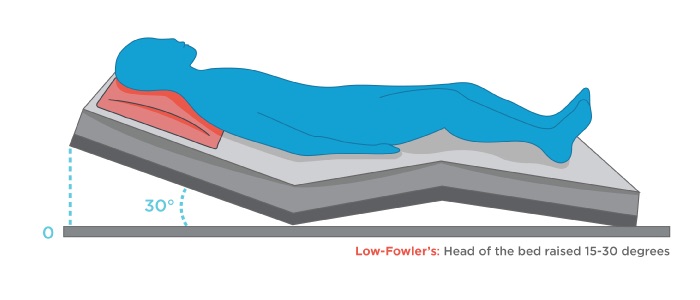
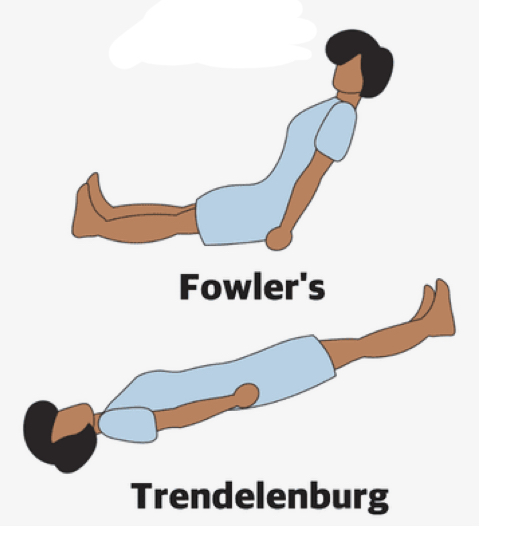
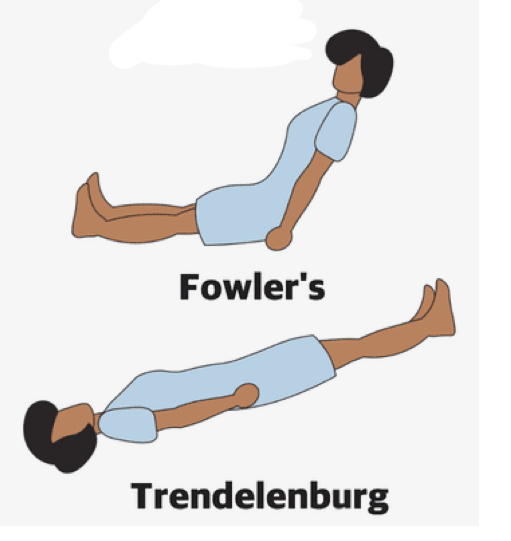
What is this position
Fowlers
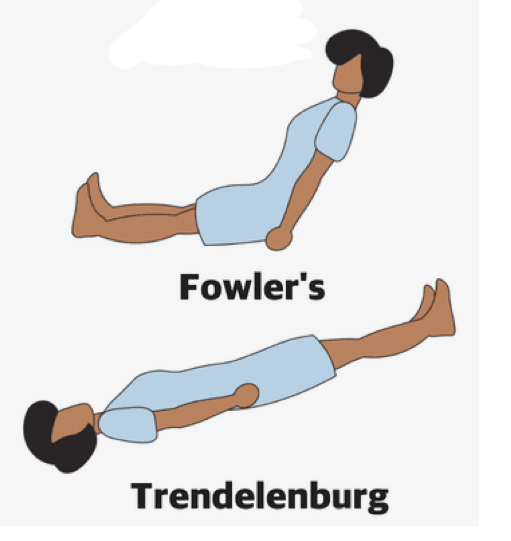
What is this position: Trendelenberg
trendelenburg
Regional names
Dorsal surface is back= ie dorothy turned her back on Steve
Ventral Surface is the front of the body = ie veins get blood taken away from the front of our bodies
The human body is divided up into several major regios that can be identified externally (5 regions)
The regions consist of
Head
Neck
Trunk
Upper limb
Lower Limb
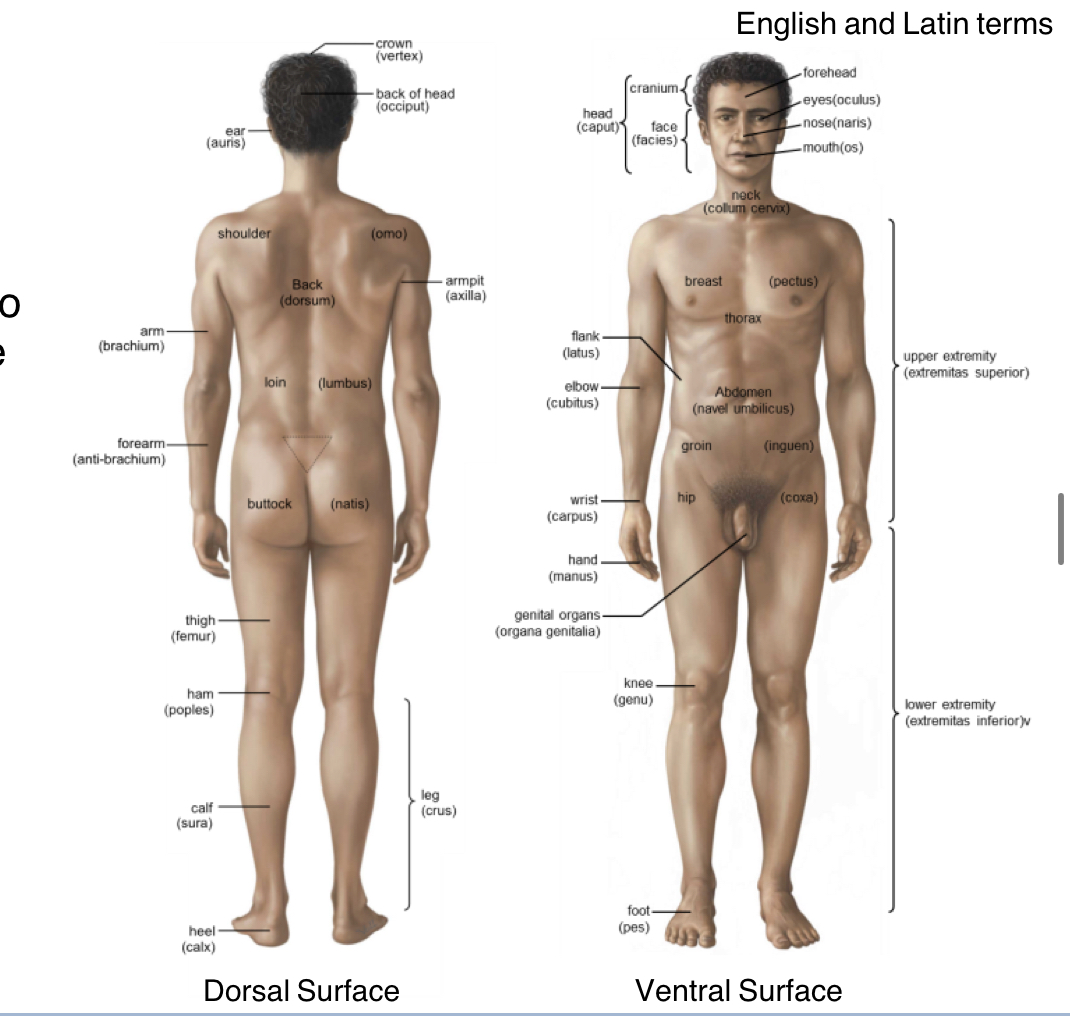
D→ Vertex
crown of head at the very top where a crown would be placed
D→ Occiput
Back of head
D→ Auris
Ears
D→ Omo
Shoulder
D→ Brachuim
Arm ie often broken brachuims
D→ Axilla
Armpit rmbr doc
D→ Lumbrus
Loin→ Kidney area back
D→ Anti-Brachuim
Forearm under elbow
D→ femur
Thigh
D→ Poples
Hamstring or Ham which is behind knee
D→ Crus
Leg ie Jesus legs crossed while crucified
D→ Calx
Heel ie calluses forming behind heel after wearing new shoes
V. Caput
Head
Cranium
Forehead
Oculus
eyes
Naris
Nose
Os
Mouth
Facies
Face
Collumn Cervix
Neck
Pectus
Chest ie pecs
Thorax
Where sternum lays
Latus
Flank, right by floating ribs
cubitus
Elbow
Carpus
wrist ie carpal tunnel
Organa Genitalia
Genital Organs
Genu
Knee
Pes
Foot
Navel Umbilicus
Abdomen
Ingueen
Groin
Coxa
Hip ie cóccix
extremistas Superior
upper extremity
Extermitas inferior (V)
Lower Extermity
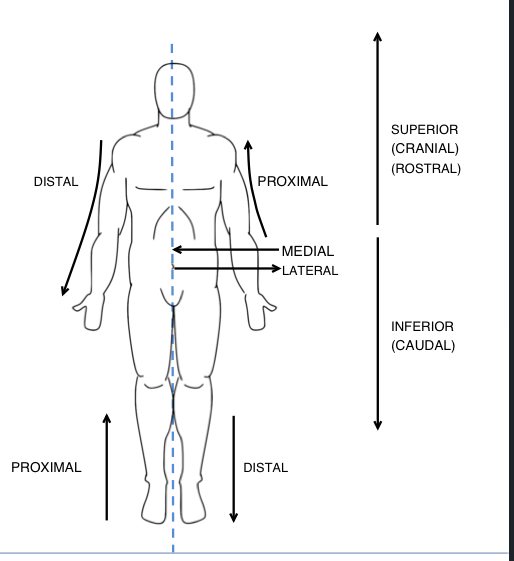
Describe the of one body part relative to another and often grouped in pairs with opposite meanings
Superior/inferior
Anterior/ postérgala
Medial/lateral
Proximal /distal
Superficial / deep
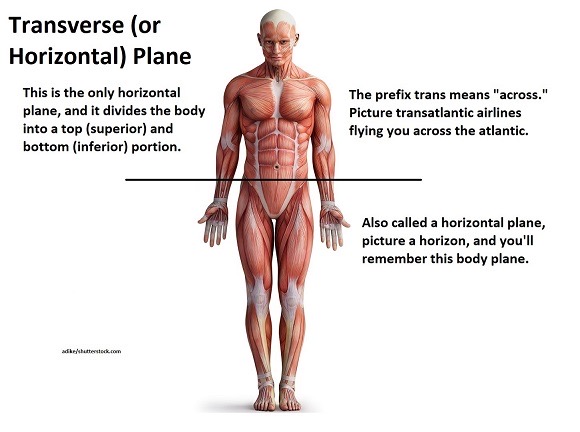
Planes and sections
Parts of the body can be studied in relation to planes imaginary flat surfaces that pass through body parts
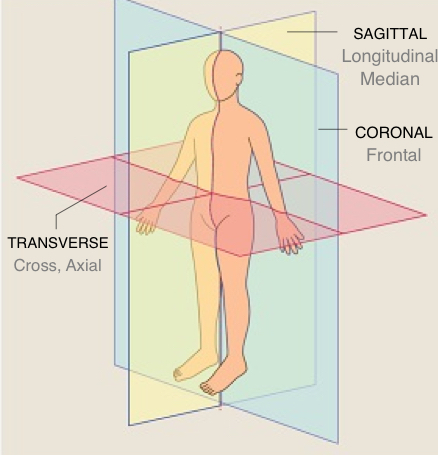
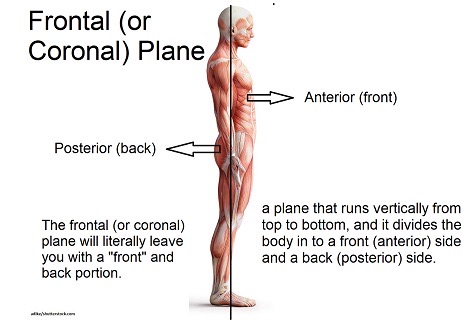
Frontal/Coronal Plane
Body Split into Two halves (front and Back)
Sagital/Longitudinal Median Plane
2 halves but this time Right and Left
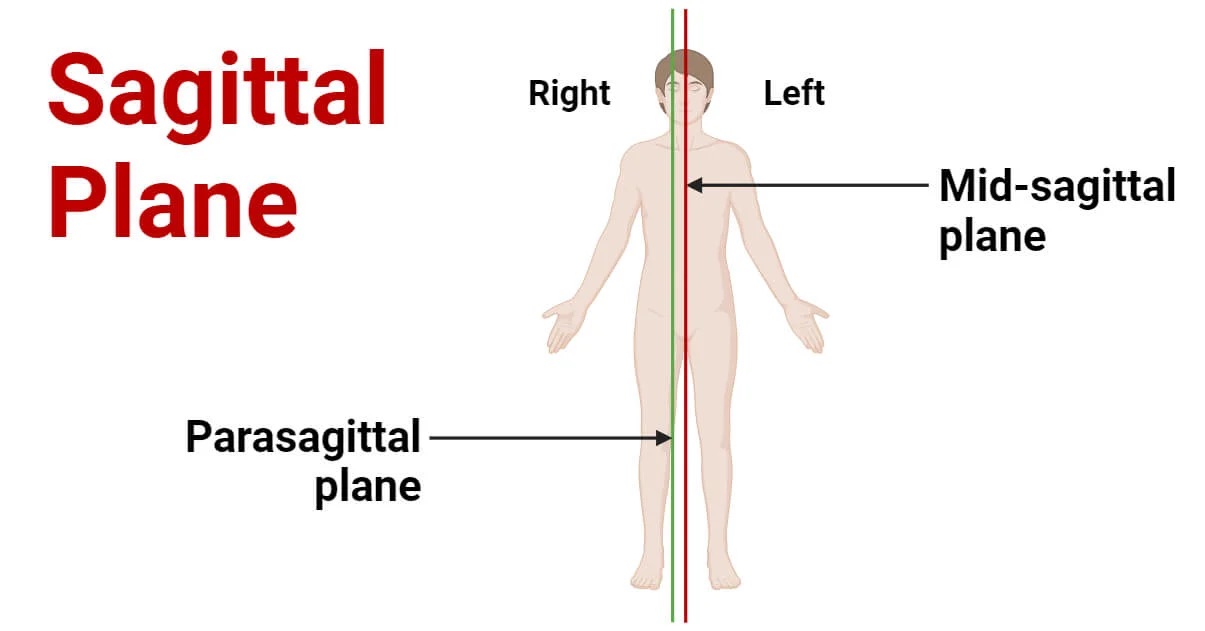
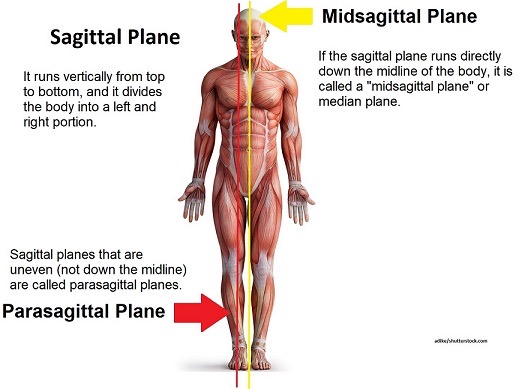
Midsagittal Plane
If the saggital plane is split perfectly in half
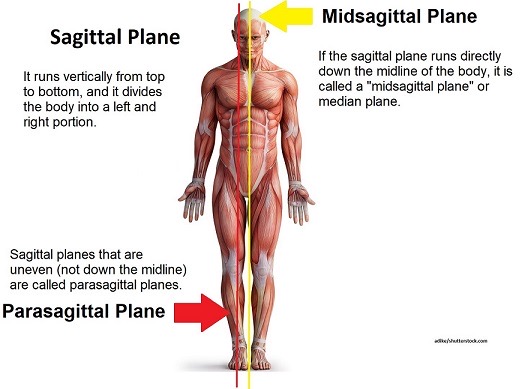
Parasagital Plane
para means near so a plane that is near the half but not exactly midsaggital
Axial,Cross,Trasnsverse Plane
Top half, and bottom half
How are Chest x rays taken
Chest x rays are obtained in PA view (post anterior) viewed as if facing the patient
MRI And CT Scans
Are viewed as f pt were in supine position, and you are looking at them from feet towards the head Caudal to Cranial View is transverse, cross and axial plane
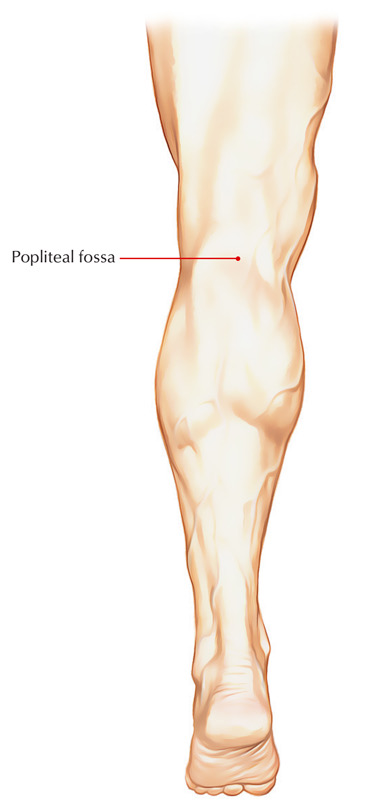
Fassa
A depression on body ie back of knee, skin is pushed in due to depression this si called the Popliteal fassa
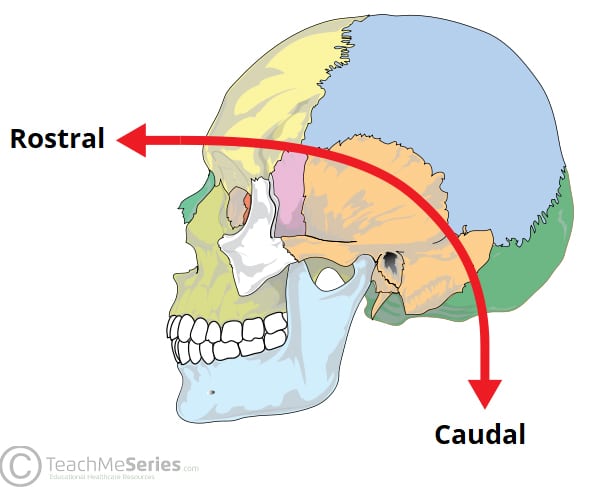
Rostral (think of nostril) And Caudal
Rostral means toward the nose or head, while caudal means toward the tail or tailbone these terms are often used in embryology and neurology
Body Cavities
Organs that move are pushed into body cavities
What are body cavities lined with
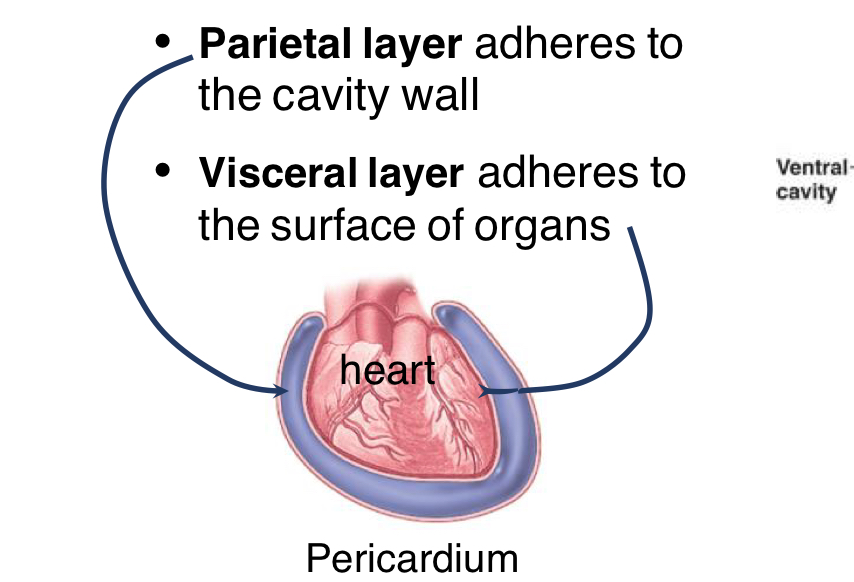
Body cavities are lined by a serous membrane (watery eg white consistency) this secretes serous fluid and consists of two layers
Parietal Layer
outermost layer that Adheres to the cavity wall
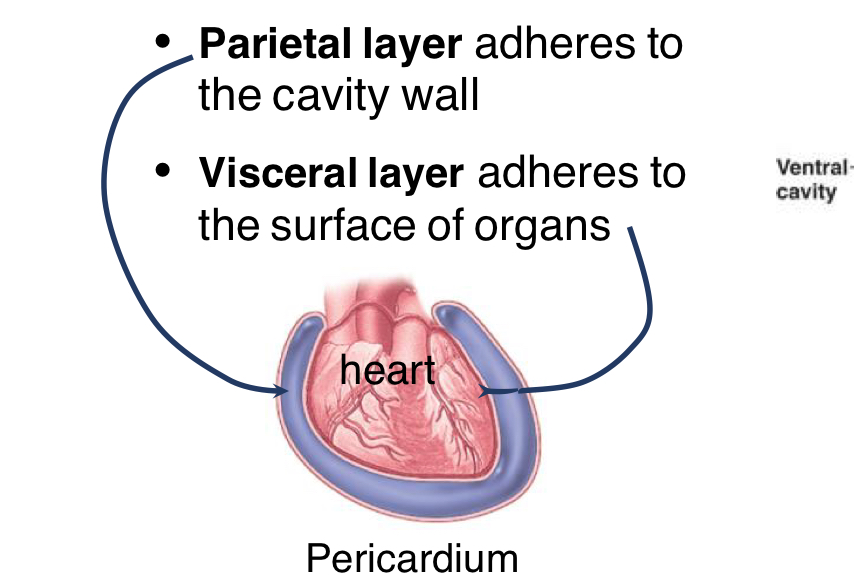
Visceral Layer
innermost layer directly touching organ (adheres to the surface of the organ)
1) the Cranial cavity consists of
Brain and spinal cord
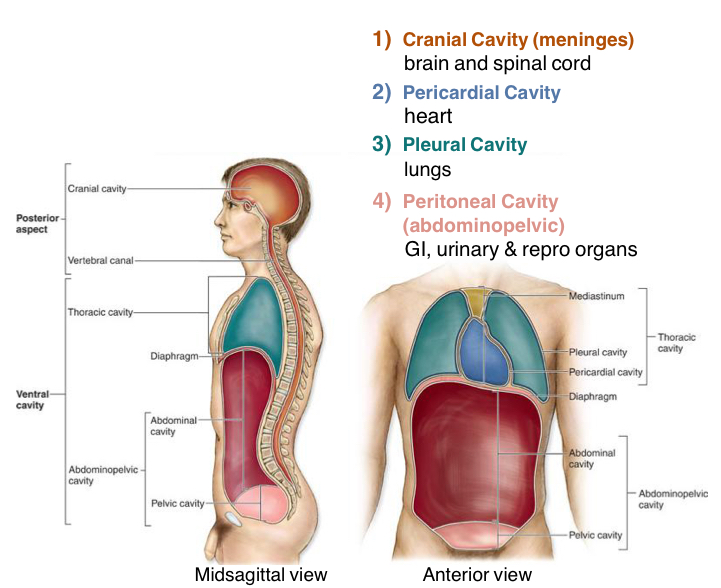
2) The Pericardial cavity consist of
The Heart only
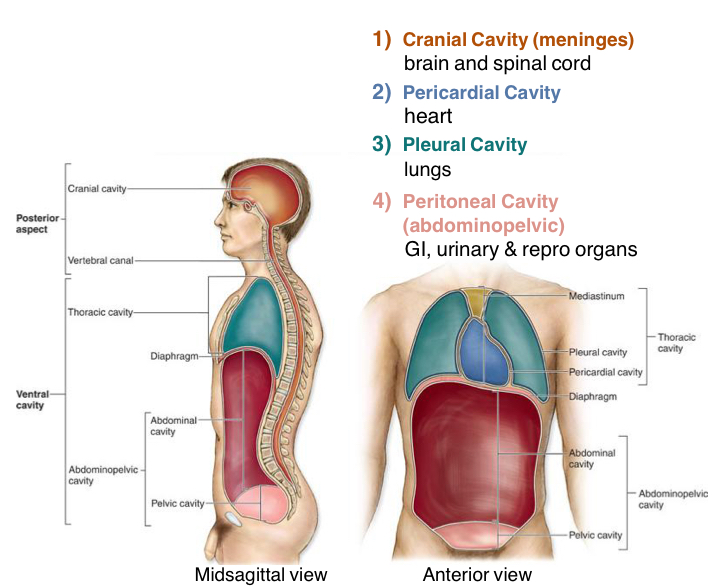
3) Pleural Cavity Consists of
Lungs Only
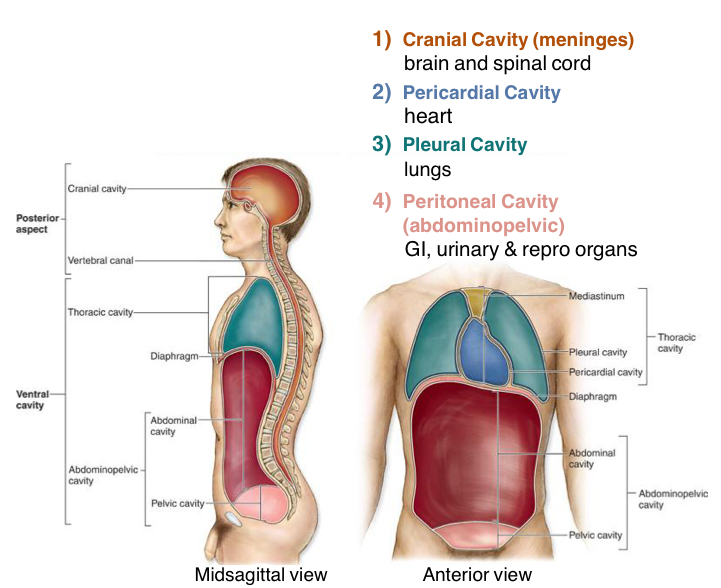
4) What does the Peritoneal Cavity (Abdominopelvic)Cavity consist of
1)GI (digestive organs under diaphragm)
2)Urinary organs
3)Reproductive Organs
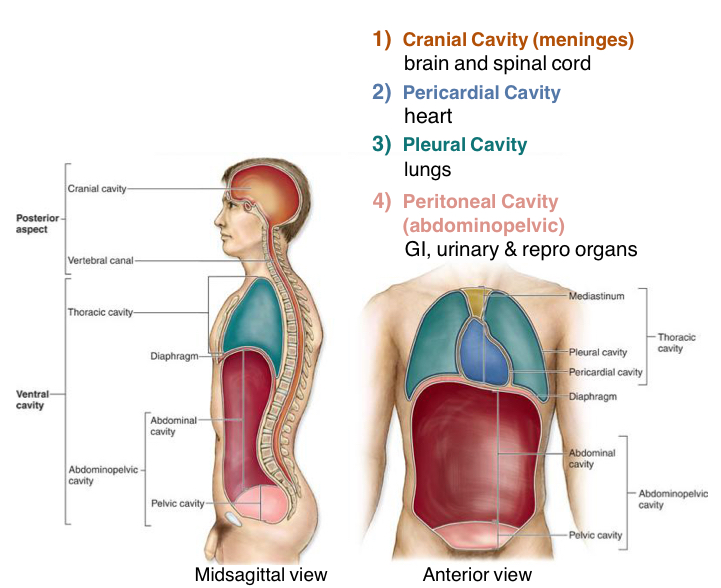
Body Cavities Concept
Must understand

Concept of potencial spaces
The concept of "potential space" refers to two main ideas: in anatomy, it's a physical space between tissues that can expand to hold fluid or air, such as the pleural cavity around the lungs,
are potencial spaces that Have potencial to be filed with fluid, blood or air, resulting in death or disease
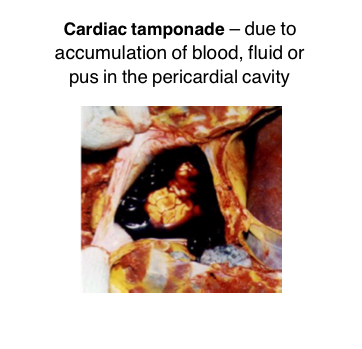
Body Cavities
Due to accumulation of blood, fluid or pus in pericardial cavity
Cardiac Tamponade
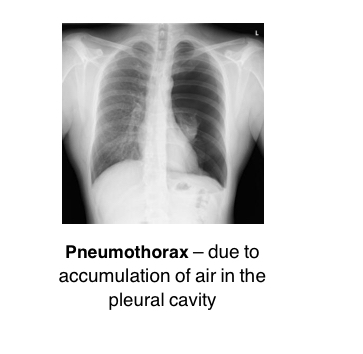
Due to accumulation of air in the pleural cavity, may be caused due to punctures in cavity
Pneumothorax
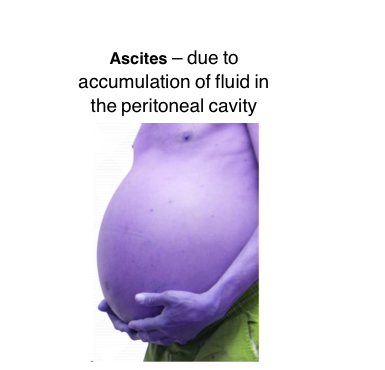
due to accumulation of fluid in the peritoneal cavity also known as abdominopelvic
Ascites
Can be used to locate deep organs. It is the basis for physical assessment
Surface Anatomy
Ribs and intercostal spaces
Thoracic Landmarks
Fun fact 1-5 Thoracic Landmarks are key for breath sounds
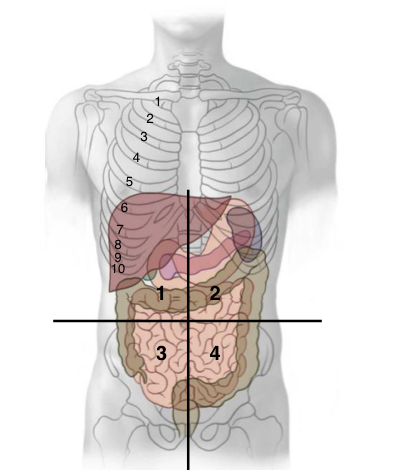
Abdominal quadrants (4)
1) right upper quadrant
2) Left upper quadrant
3) Right lower quadrant
4)Left lower quadrant
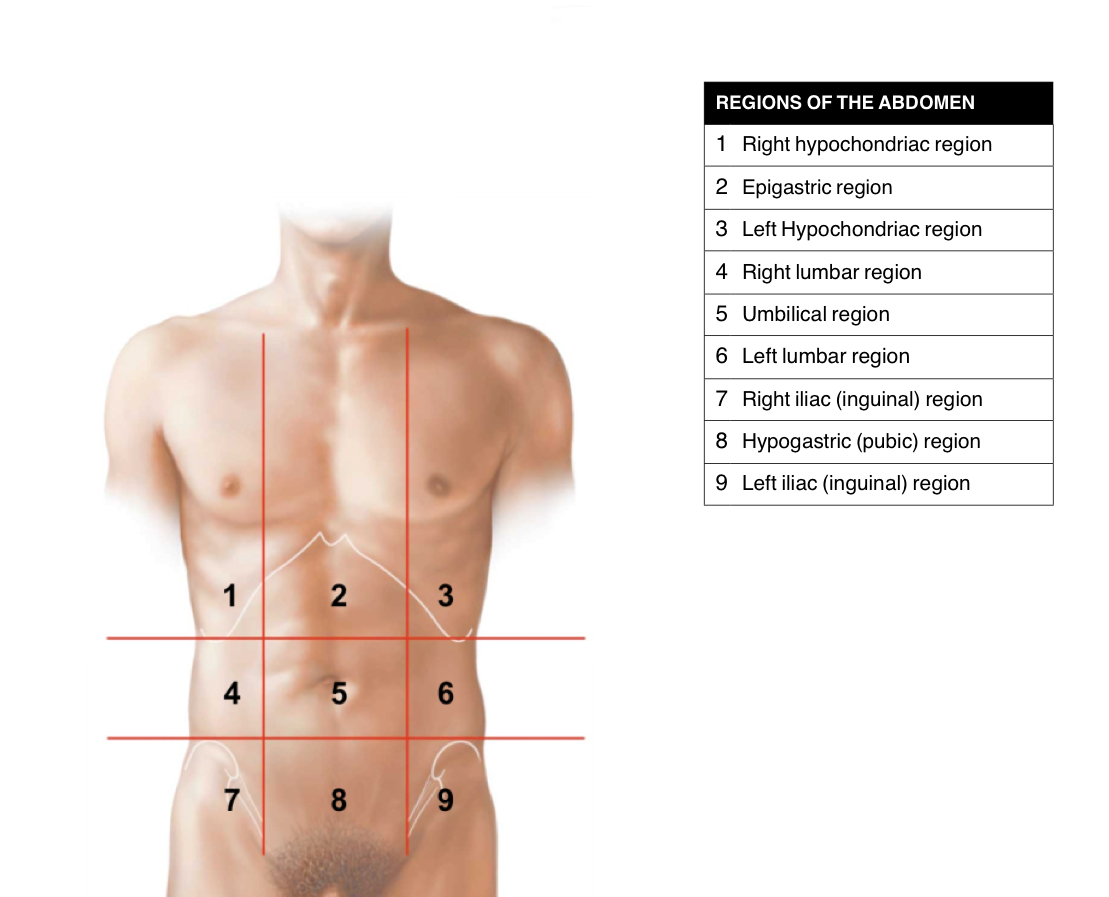
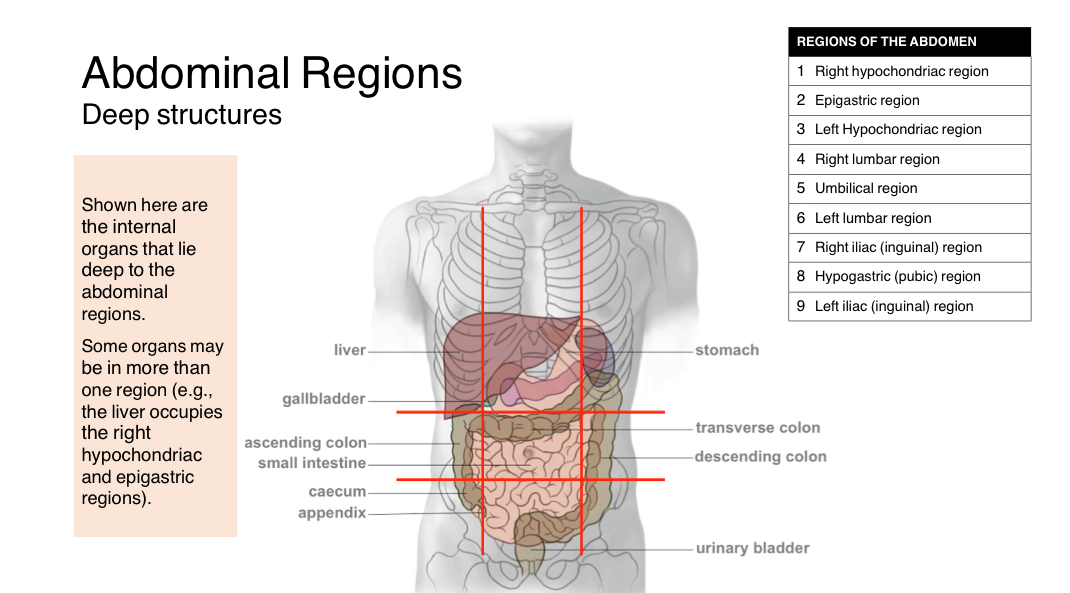
Abdominal regions
Surface anatomy
Practice on whiteboard
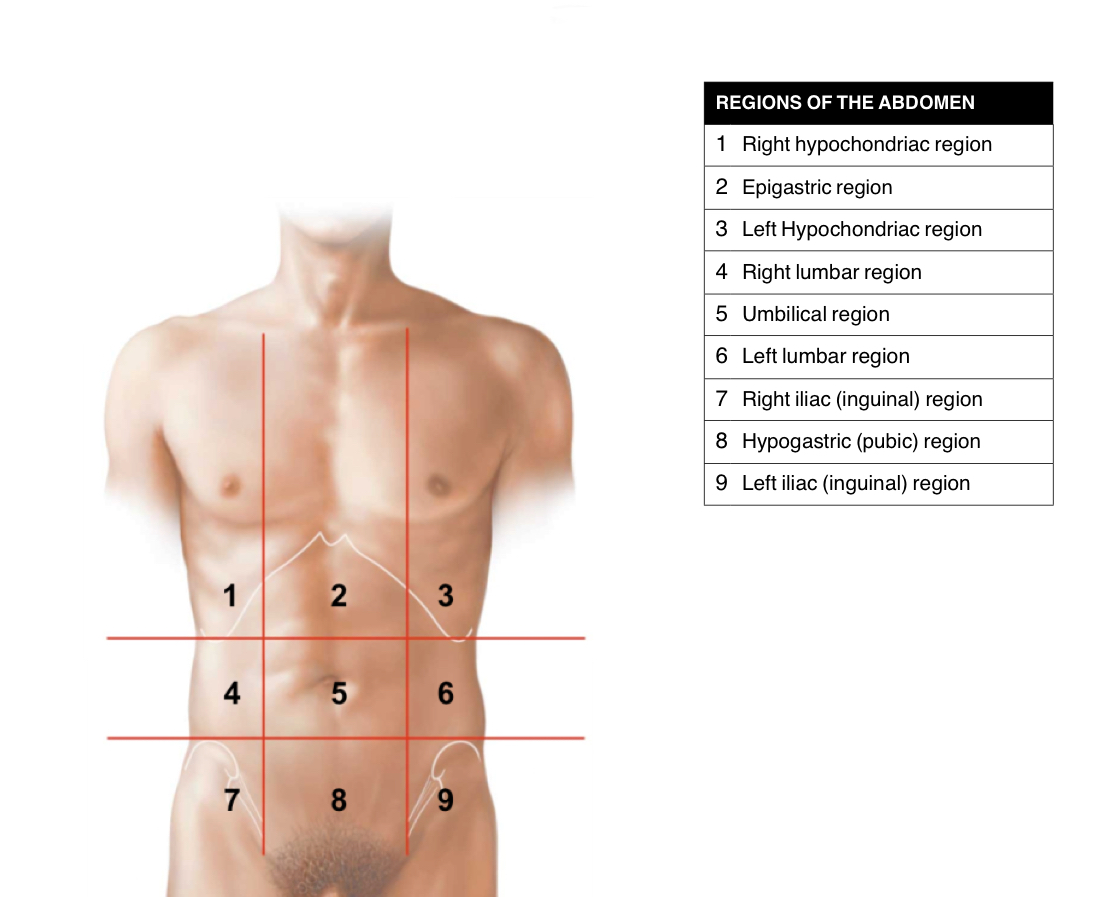
Abdominal Regins
Deep structures
Practice on whiteboard
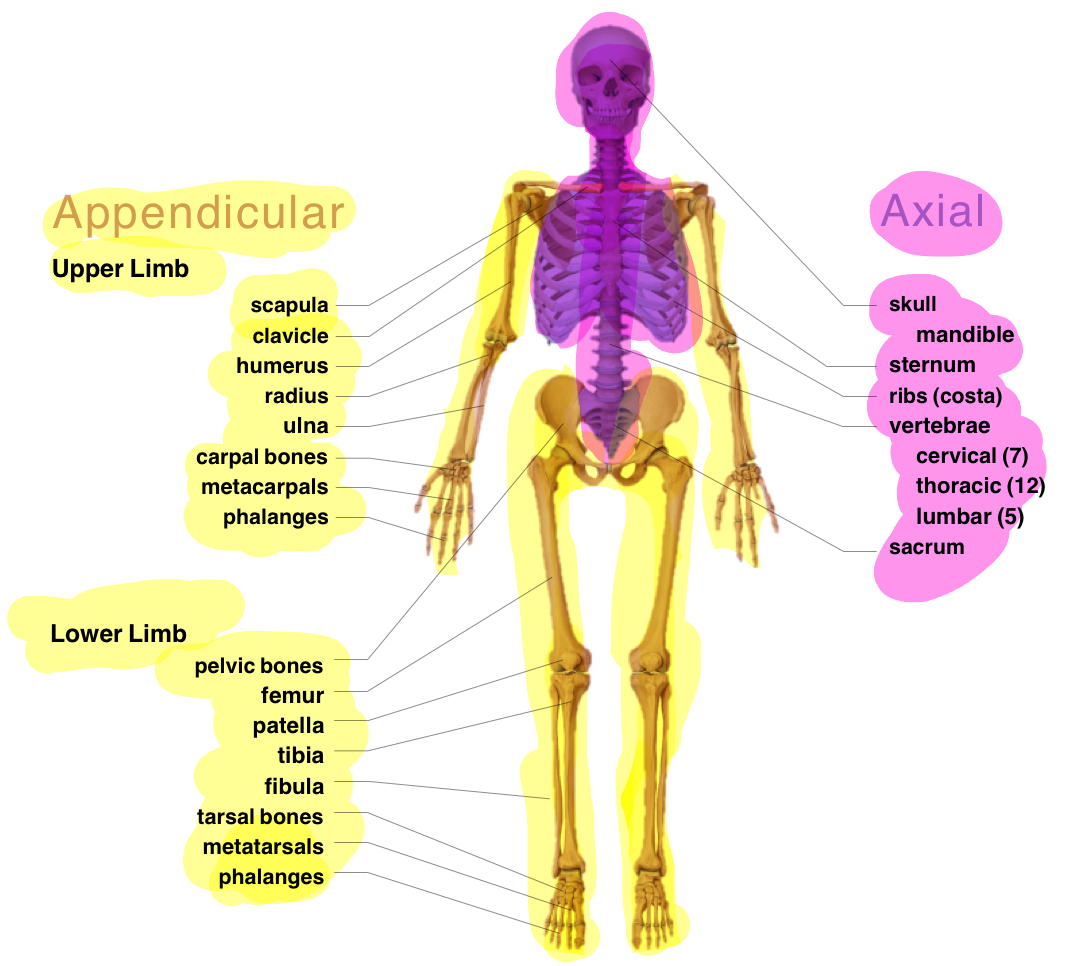
Appendicular VS AXIAL
BONESSS
Practice on whiteboard
Homeostasis
Homeostasis comes from homeo= sameness and statis= means standing still
Hyperglycemia
Too much glucose
“A self-regulating process by which biological systems maintain stability while adjusting to changing external conditions.”
Homeostasis
Homeostasis is an envelope (range) of internal conditions that support life
Virtually every parameter in the body (e.g., temperature, pH, ion concentration, blood pressure, serum glucose levels, etc.) must remain within a narrow range (envelope) that is compatible with life
Departures from the homeostatic envelope can lead to disease or even death!
External pertubations
External perturbations that disrupt homeostasis may include extremes in environmental temperature or oxygen levels in the atmosphere
internal Pertubations
that disrupt homeostasis may include the sugar in the food we eat or the waste products of metabolism
Homeostasis is Dynamic
Homeostasis is considered dynamic because
the internal body environment is not static but requires continuous monitoring and adjustment to maintain a stable, although fluctuating, balance within a narrow range of conditions, like temperature or blood sugar levels
Dynamic
Constantly changing within limits
Ex: body temperature, blood glucose, and pH fluctuate but are kept within a normal range
what participates in homeostasis
Cells
Tissues
Organs
Systems
What are the two key systems that maintain homeostasis
Nervous system
Endocrine system
Nervous system
How it works: Uses electrical impulses (nerve signals) to send messages quickly.
Effect: Produces rapid responses to restore balance
Example: If your body temperature rises, the nervous system signals sweat glands to cool you down.
Endocrine system
How it works: Uses hormones (chemical messengers carried in the blood) to communicate with target organs.
Effect: Produces slower but longer-lasting responses.
Example: If blood sugar is high, the pancreas releases insulin (a hormone) to lower it over time
Nervous Vs Endocrine
Nervous system = fast, short-term corrections (electrical signals).
Endocrine system = slower, longer-term corrections (hormones).
Feedback systems (Feedback Loops)
cycle of events in which body conditions are
Monitored
Evaluated
Changed
Re-monitored
two types of feedback Systems
Positive
Negative ( most feedback loops are neg)
variable ( Controlled condition)
Variable( controlled condition)
Ex: Body temp, Blood sugar lvls, BP
Effector
Effector receives signals from control center aka variable effector directly alters that variable ex: direct effect
In NEG: Brings variable right back to its desired range (set point) to where we want it in homeostasis; this usually deprives the the system of the stimulus
In POS: it exaggerates the deviation Variable) in that set point so we are actually exaggerating the stimulus until a unique event occurs and resets the whole system