BIO 20A Midterm 2 Practice Problems
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
A biochemist mixes a double-stranded DNA molecule containing an origin of replication, nucleotides and all the enzymes required for replication in a test tube. When she she analyzes the products of this reaction, she discovers that they include the original DNA strands base paired with shorter strands of DNA with approximately 10 nucleotides of RNA at their 5' ends. What has she probably left out of the mixture?
DNA Polymerase I
During DNA replication, DNA polymerase adds nucleotides to the:
3ʼ end of the newly synthesized strand as it moves toward the 5ʼend of the template strand
Draw DNA replication fork. Include: primers, leading strand, lagging strand, Okazaki fragments, DNA helicase, DNA ligase, topoisomerase, DNA pol I, and DNA pol III
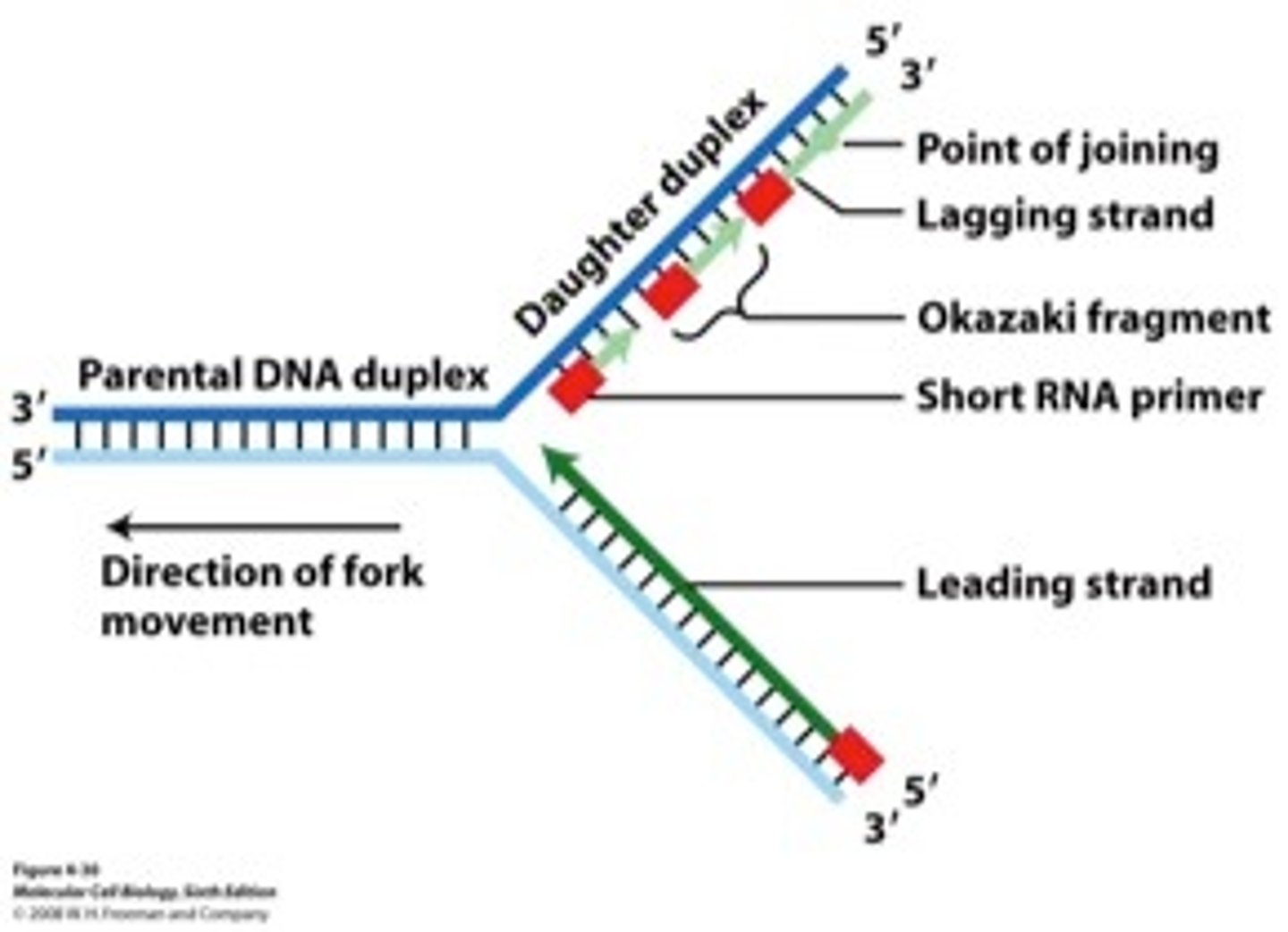
Which of the following helped show that DNA is the carrier of genetic information? Check all that apply
Bacteriophage inject DNA, not protein, into the bacteria they infect(CORRECT)
Heat-killed S bacteria can "transform" live R bacteria into a virulent strain.(CORRECT)
20 different amino acids are found in proteins, but only 4 different nucleotides are found in DNA
Mice injected with heat-killed R strains of bacteria die of pneumonia
You are studying the synthesis of DNA using a biochemical assay. The DNA molecule used for your assay has the following sequence: 3'-AAATTGGGCCATCATTTCGAGTATTCGACTCCCTAGATCCCCCCTATAGCGTT-5' You allow the primer 3'-TAGTAAA-5' to hybridize (hydrogen bond) with this DNA molecule and add DNA polymerase and nucleotides. The complete sequence of the newly synthesized strand of DNA (excluding the primer and template sequences) that will be synthesized in the above reaction is
5'-GGCCCAATTT-3', 5'GGCCCAATTT-3', 5' GGCCCAATTT-3'
The removal of introns and joining of exons is catalyzed by:
The spliceosome
Check all of the following statements about promoters that are true.
A promoter specifies where RNA polymerase initiates transcription(CORRECT)
A promoter specifies where DNA polymerase initiates replication
A promoter specifies which strand of DNA will be used as the template during transcription(CORRECT)
Which of the following statements about capping and polyadenylation in eukaryotic cells are true? (check all that apply)
They define the open reading frames of mRNAs
They influence the translation and stability of mRNAs(CORRECT)
They are modifications of the ends of mRNAs(CORRECT)
They are RNA processing events that occur in the nucleus(CORRECT)
Which of the following are major differences between DNA and RNA polymerases?
DNA polymerase, but not RNA polymerase, requires a primer to begin synthesizing the nucleic acid polymer(CORRECT)
RNA polymerase, but not DNA polymerase, requires a primer to begin synthesizing the nucleic acid polymer
RNA polymerase, but not DNA polymerase, is unique to eukaryotic cells
DNA polymerase, but not RNA polymerase, is unique to eukaryotic cells
DNA polymerase is involved in replication; RNA polymerase is involved in transcription(CORRECT)
A protein is synthesized from its _______ as the ribosome moves toward the ______ of the mRNA.
N to C terminus; 3ʼ
Which of the following statements is false?
a mutation in a promoter is unlikely to alter the sequence of the polypeptide encoded by a gene
a mutation in a 5ʼ or 3ʼ splice site must alter the sequence of the protein encoded by a gene(CORRECT)
a mutation in a transcriptional terminator is unlikely to alter the sequence of a protein encoded by a gene.
a frameshift mutation changes the sequence of a protein
a missense mutations replaces one amino acid with a different amino acid
Which of the following would be most likely to have a dramatic effect on the amino acid sequence of a protein?
a two base deletion in an intron
a three base insertion in an exon
a single base substitution in a promoter
a one base insertion just before the start codon
a one base insertion just after the start codon(CORRECT)
As a ribosome translocates along an mRNA molecule by one codon, which of the following occurs?
The tRNA that was in the A site moves into the P site.(CORRECT)
The tRNA that was in the P site moves into the A site.
The tRNA that was in the E site moves to the P site
The tRNA that was in the A site departs from the ribosome.
The tRNA that was in the A site moves to the E site
Which of the following polypeptides (written from their N terminal ends) is encoded by the followingmRNA? (hint: there is no left or write in a cell!)
3ʼ GG AUG AGU AUA CUU ACG GGU GAA GUA CAU UAA CCC C 5ʼ
Met Lys Trp Ala Phe Ile
The ribosome
catalyzes the formation of the peptide bond during translation(CORRECT)
has both DNA and protein components
removes introns from RNAs
is unique to eukaryotic cells
all of the above
Draw a complete, clearly labeled diagram of a ribosome translating the mRNA 5'-GCCGUGUUCAUGGCGCCGGAACUGUAACUUACGC-3' immediately before the second and third amino acids are joined by a peptide bond. Note that the sequence of polypeptide encoded by this mRNA is Met-Ala-Pro-Glu-Leu. Thus, the second amino acid is Ala and the third amino acid is Pro.
Something like the picture, but real answer is #7 on Self-Assessment Quiz 10
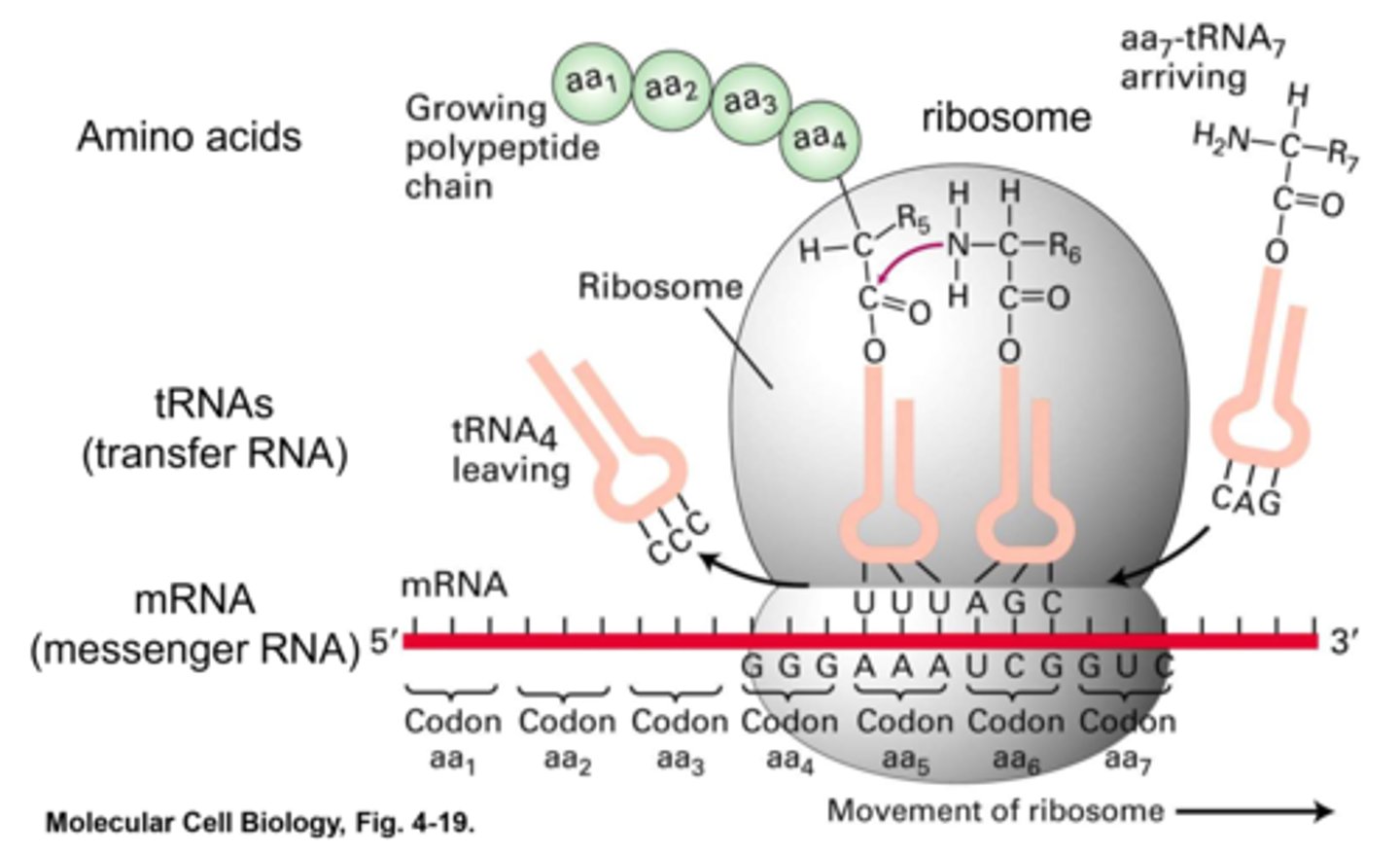
In general, which of the following modes of gene regulation is associated with long lasting changes in gene expression?
Translation
Alternative splicing
Transcriptional regulation(CORRECT)
Post-translational modifications (e.g. phosphorylation)
Which of the following occur when cellular iron levels drop? Check all that apply
Iron-regulatory proteins bind the operator
Iron-regulatory protein binds iron-response elements (CORRECT)
Ferritin levels decrease(CORRECT)
The translation of the ferritin mRNA decreases (CORRECT)
Check all of the following that apply to polycistronic RNAs
are often encoded by operons (CORRECT)
allow for the coordinated regulation of multiple proteins involved in the same biochemical pathway (CORRECT)
are components of the ribosome
are components of the spliceosome
encode two or more proteins (CORRECT)
In general, which of the following modes of gene regulation have the fastest, most readily reversible effects?
Translation
Transcriptional regulation
Alternative splicing
Post-translational modifications (e.g. phosphorylation) (CORRECT)
Match each of the following with the appropriate category
trp repressor->protein
iron-response element-> RNA sequence
trp operator->DNA sequence
ferritin->protein
A mutation in the gene encoding the trp repressor leads to the production of an altered protein that binds the operator in the absence of tryptophan. Which of the following best describes the biological consequences of this mutation?
The level of the enzymes involved in trp biosynthesis would increase as the level of trp increases
The level of the enzymes involved in trp biosynthesis would be low under all conditions (CORRECT)
The level of the enzymes involved in trp biosynthesis would only be expressed when trp levels are low
The level of the enzymes involved in trp biosynthesis would be high under all conditions
You are studying the synthesis of DNA using a biochemical assay. The DNA molecule used for your assay has the following sequence:
3'-AAATTGGGCCATCATTTCGAGTATTCGACTCCCTAGATCCCCCCTATAGCGTT-5'
You allow the DNA primer 3'-ATCTAGGGAG -5' to hybridize (hydrogen bond) with this DNA molecule and add DNA polymerase and nucleotides.
The complete sequence of the newly synthesized strand of DNA (excluding the primer and template sequences) that will be synthesized in the above reaction is...Write the sequence from its 5' end to its 3' end, but do not include anything but the sequence in your answer (e.g. GAAAT not 5'-GAAAT-3')
Correct answer:
GGGGGGATATCGCAA
A mutation that changes a codon into a termination codon is a:
nonsense mutation
The BLANK determines which strand of DNA will be used as the template for transcription
promoter
Which, if any, of the following statements are true? Check all that apply
The ribosome contains both RNAs and proteins (CORRECT)
Initiation and termination codons define the regions of DNA transcribed by RNA polymerase
Alternative splicing can allow some genes to encode more than one protein(CORRECT)
Which of the following specify the region of an mRNA that encodes a protein?
promoters and terminators
N and C termini
start and stop codons(CORRECT)
5' and 3' splice sites
exon and introns
Which of the following statements about capping and polyadenylation are true?
They can influence the stability and translation of mRNAs (CORRECT)
They define the boundaries of open-reading frames
They are found at the 5' and 3' ends of introns
Which of the following statements about DNA replication are true? (check all that apply)
During the synthesis of the lagging strand, DNA polymerase III moves along the template strand away from the replication fork (toward the origin)[CORRECT]
During the synthesis of the leading strand, DNA polymerase III moves along the template strand toward the replication fork (away from the origin)[CORRECT]
During the synthesis of the lagging strand, DNA polymerase III moves along the template strand toward the replication fork (away from the origin)
During the synthesis of the leading strand, DNA polymerase III moves along the template strand away from the replication fork (toward the origin)
Which of the following catalyzes the formation of the peptide bond during protein synthesis?
the peptidyl tRNA
the anticodon
the ribosome(CORRECT)
the spliceosome
aminoacyl tRNA synthetase
A mutation in which of the following regions would probably have the greatest effect on the amino acid sequence of a protein encoded by a gene?
promoter
coding region(CORRECT)
5' untranslated region
exon
3' untranslated region
Which of the following adds the correct amino acid to a tRNA?
a codon
an anticodon
the ribosome
peptidyl transferase
aminoacyl tRNA synthetase(CORRECT)
Humans have approximately 25,000 different genes that encode mRNAs but can produce a much larger number of different proteins. Which of the following help explain this observation?
alternative splicing allows some genes to encode more than one protein(CORRECT)
the 5' ends of human mRNAs are capped
human mRNAs are translated in three different reading frames
many human proteins are not encoded by genes
Which of the following happens after the formation of a peptide bond during translation? (check all that apply)
The tRNA in A site moves to the P site(CORRECT)
The tRNA in the P site moves to the E site and exits the ribosome(CORRECT)
The next codon to be "read" moves into the A site(CORRECT)
The tRNA in the P site moves to the A site
The next codon to be "read" moves to the P site.
True or false: The coding region of a eukaryotic mRNA always corresponds to a single exon.
False
Fill in the blanks
During translation, the ribosome moves from the BLANK ENDS of an mRNA as the protein is synthesized from its BLANK TERMINUS
5' to 3' end; N to C terminus
A mutation changes the termination codon of the mRNA encoding protein X from UAA to CCC. What will be the consequence of this mutation? You may refer to your codon table to help you answer this question.
One or more amino acids will be added to the N terminus of protein X
One or more amino acids will be added to the C terminus of the protein X(CORRECT)
Protein X will be shorter than normal
The length of protein X will be the same, but the last amino acid will be different
Which of the following occur when tryptophan levels are high in bacteria?
The transcription of the trp operon increases because the trp repressor no longer binds the operator.
The trp repressor binds the operator and blocks the transcription of the trp operon. (CORRECT)
The trp repressor directly blocks the translation of mRNAs encoding proteins that synthesize tryptophan
The trp repressor directly blocks the alternative splicing of the RNA encoded by the trp operon
Steps of translation in order in which they occur beginning with the initiation of translation
1. Binding of the small ribosomal subunit and initiator tRNA to the initiation codon
2. Binding of aminoacyl tRNA to the codon in the A site
3. Peptide bond formation
4. translocation of the peptidyl tRNA in the A site to the P site
5. Binding of the release factor the stop codon in the A site
Steps of gene expression
1. Binding of RNA polymerase to the promoter
2. Transcription elongation
3. Transcription termination
4. Export of mRNA from the nucleus to the cytoplasm
5. Initiation of translation
6. Termination of translation