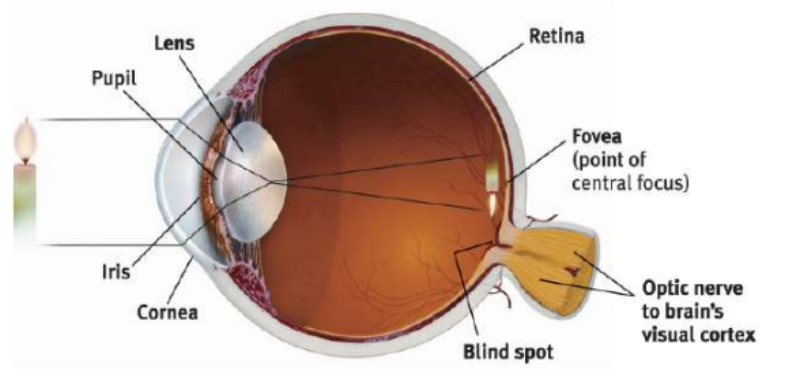
The Eye Anatomy
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
10 Terms
Cornea
Eye’s clear, protective OUTER LAYER covering pupil and iris → FRONT PART
Light enters the eye first through cornea
Pupil
Small ADJUSTABLE Opening in the center of the eye that light passes
CONTROLS LIGHT → iris opens and closes pupil
Iris
Ring of MUSCLE TISSUE that forms the coloured portion of eye → Controls the dilation of the pupil (expand and contract)
Controls size of pupil by opening and closing the pupil → DONT GET BLINDED
Responds to cognitive and emotional states
Lens
Transparent fluid-filled structure BEHIND PUPIL that changes shape to focus light on back of eye
Accomodation: Lens changes curvature and thickness to focus image on retina
Retina
Light Sensitive inner surface/ back of the eyeball, with RODS AND CONES and layers of NEURONS
Begin the processing of visual information
Fovea
Central FOCAL POINT in the retina → Area of greatest visual accuracy
Slightly above optic nerve → Eye’s cones cluster around fovea
Blindspot
Optic Disk is the point where the optic nerve leaves the eye → No rods/ cones
No rods and cones create a blind spot because no receptor rods/ cones
Optic Nerve
Comprised of the AXONS of the ganglion cells
Leaves through the back of the eye and carries neural impulses from the eye to the brain
Carries impulse to the thalamus and into the visual cortex of the occipital lobes
Track Light From Eye to Brain
Cornea → Pupil → Lens → Retine → Rods and Rods → Ganglion Cells → Optic Nerve → Thalamus → Occipital Lobe → Visual Cortex
Diagram for Eye